Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 8, 6:25 AM
|
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of arterial atherosclerosis and venous neointimal hyperplasia. We examined the effects of PDGF isoforms on smooth muscle cells (SMCs) from arterial and venous origins in order to further understand the differential responsiveness of these vasculatures to proliferative stimuli. Serum-starved human arterial and venous SMCs exhibited very different proliferative responses to PDGF isoforms. Whereas, proliferation of arterial SMCs was strongly stimulated by PDGF-AA, venous SMCs showed no proliferative response to PDGF-AA, but instead demonstrated a significantly greater proliferative response to PDGF-BB than arterial SMCs. Part of this difference could be attributed to differences in PDGF receptors expression.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 8, 6:09 AM
|
Platelets play an important role in the restenosis process after balloon angioplasty. Early experimental studies highlighted this role. Thrombocytopenia inhibits the intimal hyperplasia after arterial injury, provided it is established well before the time of injury and is sustained. Previous experimental studies and clinical trials testing antiplatelet drugs have been disappointing, suggesting that new and more powerful agents, such as the GP IIb/IIIa antagonists, may be required. These agents represent new hope to reduce restenosis after coronary angioplasty, as suggested by 6 months of follow-up in the EPIC study.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 8, 6:07 AM
|
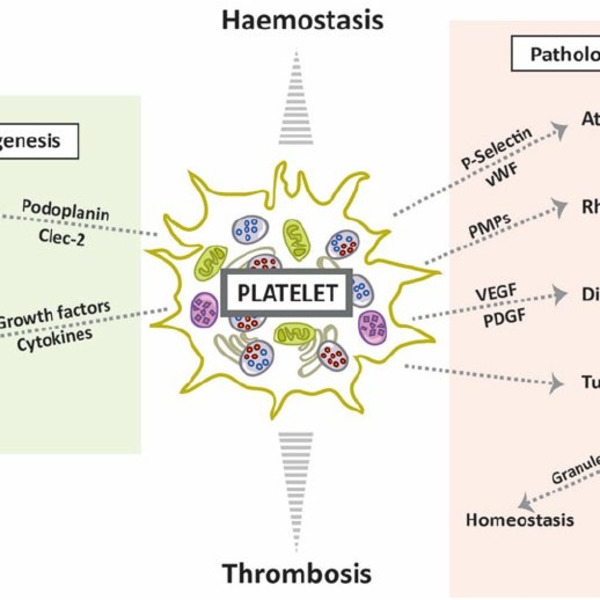
Platelets possess an armory of pro- and anti-angiogenic proteins, which are actively sequestered and highly organized in α-granule populations. Platelet activation facilitates their release, eliciting potent angiogenic responses through mechanisms that appear to be tightly regulated. In conjunction, the release of platelet-derived phospholipids and microparticles has also earned merit as synergistic regulators of angiogenesis. Consequently, platelets have been functionally implicated in a range of angiogenesis-dependent processes, including physiological roles in wound healing, vascular development and blood/lymphatic vessel separation, whilst facilitating aberrant angiogenesis in a range of diseases including cancer, atherosclerosis and diabetic retinopathy.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 8, 6:04 AM
|
With their exceptional structural and functional features, platelets play critical roles in hemostasis, vasomotor function, and immunity. In hemostasis, their contribution far exceeds their simple participation in the formation of the ‘platelet plug’. The multiple interactions that exist between platelets, the vessel wall, and the coagulation system complicate the fundamental process of hemostasis and particularly that of thrombosis. Antithrombotic drugs that interfere with platelet functions are under continuous development. The next frontier in this area will probably be reached when antithrombotic drugs that manage to differentiate thrombosis from hemostasis make their way into clinical practice, offering the prospect of safer antiplatelet therapy. Given the rapidly expanding use of the direct oral anticoagulants, establishing their exact impact on platelet functions is another open area for research.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 8, 6:02 AM
|
Deep learning applications may assist in automatically detecting coronary arteries on invasive coronary angiography (ICA).

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 8, 5:59 AM
|
Smooth muscle proliferation and migration after percutaneous intervention represent the end result of natural healing processes triggered by vascular injury. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, especially after stent implantation, plays a critical role in neointimal hyperplasia through cellular expansion and extracellular matrix deposition. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms responsible for smooth muscle cell proliferation has led to the development of novel therapeutic approaches, including rapamycin- and paclitaxel-eluting stents that have significantly improved the care of patients with coronary artery disease. To address the concerns about the potentially increased incidence of stent thrombosis in patients treated with drug-eluting stents, newer stents and coronary devices have been developed such as drug-eluting stents with biodegradable polymers, drug-eluting stents that are polymer-free, stents with novel coatings, completely biodegradable stents, bifurcation stents, and drug-eluting balloons.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 8, 5:57 AM
|
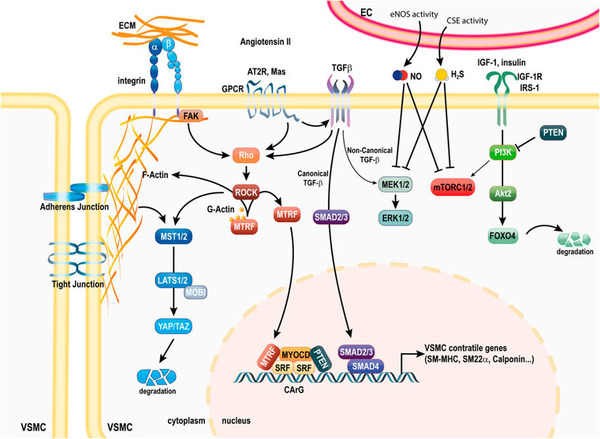
Arterial occlusive disease is the leading cause of death in Western countries. Core contemporary therapies for this disease include angioplasties, stents, endarterectomies and bypass surgery. However, these treatments suffer from high failure rates due to re-occlusive vascular wall adaptations and restenosis. Restenosis following vascular surgery is largely due to intimal hyperplasia. Intimal hyperplasia develops in response to vessel injury, leading to inflammation, vascular smooth muscle cells dedifferentiation, migration, proliferation and secretion of extra-cellular matrix into the vessel’s innermost layer or intima. In this review, we describe the current state of knowledge on the origin and mechanisms underlying the dysregulated proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells in intimal hyperplasia, and we present the new avenues of research targeting VSMC phenotype and proliferation.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 7, 3:22 PM
|
These result demonstrate that in vivo endothelial cells replication stops long before the aorta is repopulated and suggest that some mechanism other than contact between endothelial cells can prevent endothelial cell replication.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 7, 3:20 PM
|
Although animal models provide detailed knowledge about restenosis, large variability in the neointimal hyperplasia response impairs clinical translatability. The sequence and weighting of the different factors, such as mechanical stressors, endothelial permeability, monocyte influx, VSMC proliferation, and migration, as well as synthesis of extracellular matrix, need to be further investigated. For this purpose, it is necessary to be aware of the specific characteristics and distinct differences among the corresponding animal models.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 7, 3:18 PM
|
Under physiological shear conditions, a 50-fold higher number of recirculating biotinylated cells attached to the avidin-modified metal surfaces compared to bare metal counterparts. Delivery of biotinylated endothelial cells to the carotid arterial segment containing the implanted avidin-modified stent in rats results in immediate cell binding to the stent struts and is associated with a 30% reduction of in-stent restenosis in comparison with BMS.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 7, 3:17 PM
|
Restenosis at the site of an endoluminal procedure remains a significant problem in the practice of interventional cardiology. We present current data on intimal hyperplasia, which identify the major role of endothelial cells (ECs) in the development of restenosis. Considering endothelial denudation as one of the most important mechanisms contributing to restenosis, we focus more attention on methods of accelerating restoration of endothelial continuity. Prevention of restenosis may be achieved by promoting endothelial regeneration through the use of growth factors, EC seeding, vessel reconstruction with autologous EC/fibrin matrix, and the use of estrogen-loaded stents and stents designed to capture progenitor ECs.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 7, 3:13 PM
|
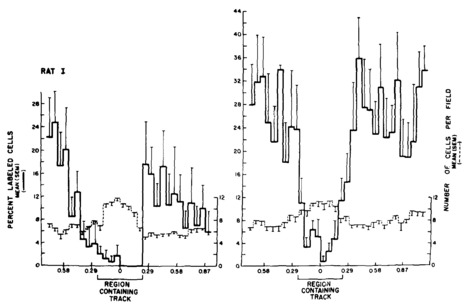
Reendothelialization was completed in < 66 h. During reendothelialization, cell migration and replication proceeded simultaneously until confluence was reached. Following confluence, as migration ceased, cell density returned toward control levels. It continued to rise, associated with continued, though attenuated, nuclear incorporation of [3H]thymidine, until it reached 112–212 times that of adjacent uninjured control endothelium.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 7, 3:00 PM
|
After 48 hours, this wound was covered by replicating endothelial cells which were densely packed together. This increased density remained over the site of injury for at least 4 weeks. A circular injury denuded a zone one to two endothelial cells wide. This wound was repopulated by endothelial cells within 8 hours without cell replication. No intimal thickening occurred in the vessels after either injury.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 7, 2:59 PM
|
Regeneration of the endothelial lining is mediated by cells flanking the injury. Endothelial repair does not require circulation of tip/stalk specification. Cells driving regeneration express a cohort of stress response genes. Atf3 is required for regeneration of the endothelial lining of large arteries

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
January 2, 11:56 AM
|
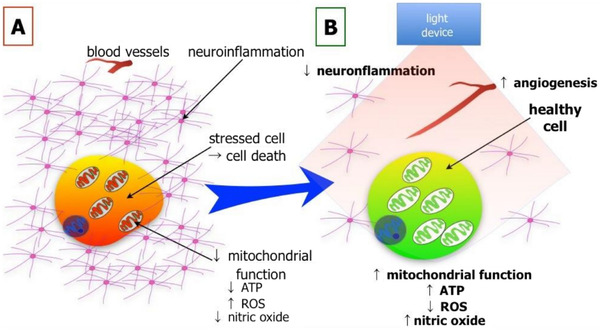
Two of the most common, often fatal, forms of cardiovascular disease are acute myocardial infarction and stroke. Both conditions involve compromised blood flow to target organs, resulting in dysfunction and subsequent death of cardiac and brain cells. Unfortunately, treatment options aiding the recovery phase have not been readily forthcoming over the years. In this narrative review, we explore the effectiveness of red and near infrared light treatment—known also as photobiomodulation (known henceforth as "light")—in improving the recovery process after either acute myocardial infarction or stroke in both preclinical and clinical studies. For preclinical studies, we consider the key findings gleaned from a large number of studies using a wide range of animal models that mimic the human conditions, showing that light treatment addresses the hallmarks of pathology associated with both these conditions; it stimulates mitochondrial activity, limits the infarct size, reduces inflammation and improves reperfusion.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
December 31, 2025 9:38 AM
|
Recently, angiography-derived index of microvascular resistance (angio-IMR) has emerged as a less invasive alternative to estimate CMD during cardiac catheterization. Whether CMD differs across vessel territories and populations remains disputed.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
December 28, 2025 7:52 AM
|
In a Corelab setting, the inter- and intra- observer reproducibility for strut count, strut apposition and strut tissue coverage measurements with OCT is excellent, ca. 1%. This emphasises the value of OCT as a tool for the clinical long-term assessment of stents.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
December 24, 2025 12:43 PM
|
The American Heart Association is backing an AI startup aimed at improving detection of hard-to-diagnose conditions like cardiac amyloidosis and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). The company, named Ultromics, offers a platform that analyzes routine echocardiograms to help clinicians catch disease earlier, particularly for women who are more likely to be missed.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
December 22, 2025 6:33 AM
|
Giacoppo and colleagues provide one of the strongest long term evidence that P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy offers better protection against major heart and brain events than aspirin after DAPT is completed following PCI, without causing more major bleeding. More importantly, the study raises an important question: why is aspirin still used as the standard antiplatelet drug when patient risk profiles have changed so much?

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
December 20, 2025 12:53 PM
|
The development of cardiovascular interventional devices, from drug-eluting stents to drug-coated balloons (DCBs), is hindered by a crucial bottleneck in the preclinical development pathway. The arteries of small animal models do not reflect the size and physiology of human arteries, thus often requiring device miniaturization that limits device performance. Large animal models, which are more anatomically relevant to humans, are costly and logistically demanding, making them suboptimal for the rapid, iterative prototyping required in early-stage device development. As a result, the transition of promising devices from benchtop characterization to in vivo testing remains inefficient owing to a long-standing gap in physiologically relevant, predictive preclinical testbeds. A system that mimics key features of coronary physiology outside the living system could help to overcome this gap.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
December 5, 2025 1:39 PM
|
By exploring new biomass sources and improving the preparation process or surface modification, B-CDs can be made to have anti-inflammatory, endothelialization-promoting, anticoagulation, and fluorescence imaging properties, which will play an important role in the application of vascular stents. Although B-CDs show extraordinary potential in the coating of vascular stents, there may be some challenges in practical applications, such as ensuring coating uniformity, long-term stability, and the feasibility of large-scale production. Future research may focus on improving B-CDs synthesis methods, synergies with drugs, optimizing coating processes, and exploring more functionalization strategies to fully realize the potential of B-CDs in vascular stents. At the same time, the long-term biosafety and biodegradability of B-CDs coating in vivo is also one of the future improvement directions. In addition, the study of B-CDs coatings also involves the combination of composites with other materials, such as metals or other nanoparticles, to create scaffolders with additional functions, such as promoting endothelialization or anti-inflammatory properties.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
December 2, 2025 7:06 AM
|
New research suggests that it disrupts biological clock. Exposure to light at night raises cardiovascular disease risk by up to 50 percent over sleeping in the dark, new research shows. But scientists say the effect isn’t from lack of sleep, but from disruption of the body’s master biological clock, the circadian rhythm.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
November 30, 2025 10:33 AM
|
At the American Heart Association Scientific Sessions, South Korean investigators reported the ADAPT AF-DES trial of anticoagulant monotherapy or combination therapy with a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) plus clopidogrel in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) who had a drug-eluting stent at least 1 year earlier.
This is very much a repeat of the AQUATIC trial, which showed clear superiority of anticoagulation monotherapy over anticoagulation plus low-dose aspirin in similar patients.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
November 30, 2025 10:32 AM
|
The TUXEDO-2 study is a randomized clinical trial evaluating percutaneous coronary intervention strategies, including stent choice, revascularization approach, and antiplatelet therapy, in 1,800 adults in India with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes and multivessel disease. All of the patients enrolled in the study had one of two specific drug-eluting stents implanted after a percutaneous coronary intervention to clear a blockage. Stents are implanted to increase blood flow in a narrowed or blocked vessel, and drug-eluting stents are coated with a medication to help reduce the risk of re-narrowing of the stents.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
November 30, 2025 10:31 AM
|
Nordanstig, who joined the session remotely, reiterated that drug-coated balloons and stents were not associated with reduced risk of amputation or improved quality of life compared with uncoated devices in the SWEDEPAD 1 and 2 trials of patients with chronic limb-threatening ischaemia (CLTI) and intermittent claudication, respectively. He added that higher five-year mortality with drug-coated devices in patients with intermittent claudication was noted.
|

Curated by Beeyond
BEEYOND is a consulting company in the field of disruptive innovation, accompanying established companies on out-of-the-core growth strategy, from creation of new concepts to product launch. Reach us at: contact@beeyond.fr.
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...