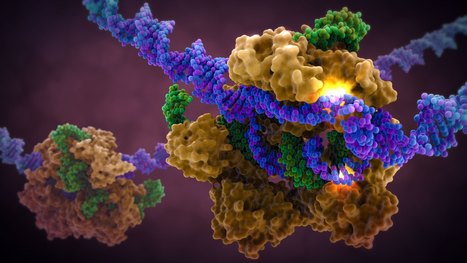
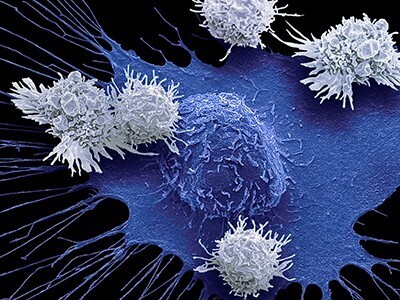
A landmark study published in Cell has shown that prime editing, a cutting-edge form of gene editing, can correct mutations causing Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood (AHC) with a single in-brain injection. The research team fixed the most prevalent ATP1A3 gene mutations in mouse models, reducing symptoms and more than doubling survival, a first-of-its-kind success in treating a neurological disease directly in the brain. CRISPR-based gene editing was delivered through an harmless adeno-associated virus called AAV9. In parallel, patient-derived cells (iPSCs) responded similarly, reinforcing the method’s promise for human translation. Importantly, this success opens the door to targeting other genetic brain disorders previously deemed untreatable. Although results are preliminary, this study provides robust proof‑of‑concept for personalized gene editing in the brain and opens doors toward potential treatments for other intractable genetic neurological disorders.






 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...

















This review offers a summary of the advanced methods recently developed to derive muscle progenitors from pluripotent stem cells, as well as gene therapy by gene addition and gene editing methods using ZFNs, TALENs or CRISPR/Cas9. The authors also discuss the main issues that need to be addressed for successful clinical translation of genetically corrected patient-specific pluripotent stem cells in autologous transplantation trials for skeletal muscle disorders.
www.geg-tech.com/Vectors