Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 29, 2015 8:21 AM
|
The TOP 10% information you need!
The scoops deal with published (classical or OPEN) and grey literature (blogs, websites, social networks, press releases) allowing rapid access to recently published relevant information May 29, 2015 you were 26796 visitors, viewing this topic 34.5K times., 4900 scoops May 2025: >8.2K scoops, >98.2 visitors, >177,8 views

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 4, 10:56 AM
|
Researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo (Unifesp - Universidade Federal de São Paulo) in Brazil have uncovered a previously unrecognized immune-evasion mechanism used by #SARSCoV2, revealing how the #virus directly manipulates host cell #RNA to suppress #antiviral defenses.
▪️ Published in NAR Molecular Medicine, the study shows that beyond conventional immune evasion, SARS-CoV-2 interacts with host RNA in infected #lung cells in a uniquely sophisticated way, disrupting #interferon signaling, a cornerstone of innate #immunity.
▪️ Led by Prof. Marcelo R. S. Briones, the research demonstrates that viral RNA rapidly engages long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) - including UCA1, GAS5, and NORAD - immediately after cell entry. Through N⁶-methyladenosine (m⁶A) methylation, the virus alters RNA structure, destabilizing classical base pairing and promoting alternative interactions that weaken RNA-RNA regulation and blunt interferon responses.
▪️ Notably, UCA1 emerged as a central regulatory node, showing altered expression and increased methylation while directly interacting with both the viral #genome and interferon pathway components.
▪️ The work, with key contributions from Cristina Mendes Peter and Caio De Oliveira Cyrino, leveraged Oxford Nanopore Technologies sequencing and #machinelearning analyses to map RNA interactions and methylation patterns in real time, with mathematical support from Fernando Antoneli and Nilmar Moretti.
💡 While fundamentally mechanistic, these findings reshape our understanding of RNA virus #biology and point toward potential therapeutic strategies, including targeting RNA methylation enzymes to restore antiviral immunity.
🗃️ See comments section for reference. | 16 comments on LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 4, 3:52 AM
|
Un « supermicroscope » révèle en direct l’infiltration des virus de la grippe dans nos cellules
👉👉 L’article dans sa totalité: https://lnkd.in/epE5XRAv
👉👉 Vidéo Youtube: Comment les virus de la grippe pénètrent-ils dans nos cellules ?: https://lnkd.in/e-9Pr88Q
Vers de nouvelles thérapies antivirales plus efficaces et plus ciblées.
Une nouvelle technique de microscopie permet pour la première fois d’observer en direct et en haute résolution le processus par lequel les virus de la grippe pénètrent les cellules. Combinant deux puissants outils d’imagerie, la technique a mis en lumière la manière dont les cellules tentent activement de se défendre avant d’être infectées. La technologie pourrait contribuer au développement de thérapies antivirales plus efficaces et plus ciblées.
Les virus de la grippe utilisent leurs protéines de surface, dites hémagglutinines, pour pénétrer et infecter les cellules. Plus précisément, elles interagissent avec les molécules d’acides sialiques présentes au niveau des glycolipides et des glycoprotéines structurant la surface des cellules. La fixation stable à la surface de la cellule s’effectue par le biais de liaisons multivalentes entre plusieurs hémagglutinines et acides sialiques.
Une enzyme appelée neuraminidase induit ensuite la rupture des acides sialiques, permettant au virus de pénétrer à l’intérieur de la cellule. L’interaction compétitive entre les hémagglutinines et l’enzyme permet au virus de se diffuser latéralement le long de la membrane cellulaire. Il s’agit notamment d’un processus cellulaire dynamique essentiel au fonctionnement des cellules (pour l’absorption de substances vitales telles que les hormones) que les virus détournent afin de les infecter.
La diffusion latérale à la surface de la cellule permet au virus d’identifier le point d’entrée idéal pour la pénétrer, c’est-à-dire la région de la membrane où de nombreuses molécules réceptrices sont regroupées. Une cavité stabilisée par une protéine spécifique appelée clathrine se forme ensuite à cet endroit pour englober le virus à l’intérieur d’une vésicule. Cette vésicule migre vers l’intérieur de la cellule pour se dissoudre, libérant ainsi les protéines virales.
L’observation de ce processus membranaire dynamique est essentielle à la compréhension du potentiel des virus grippaux à infecter les cellules. Cependant, les techniques de microscopie conventionnelles ne disposent pas de la résolution suffisante pour détecter les mouvements de ces virus au niveau des membranes cellulaires, dont l’épaisseur de la bicouche lipidique est d’environ 5 à 10 nanomètres....
Sources :
-How influenza viruses enter our cells: https://lnkd.in/eJ7QErs3
-PNAS - Enhanced visualization of influenza A virus entry into living cells using virus-view atomic force microscopy: https://lnkd.in/exQayP-J

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 30, 2025 3:58 AM
|
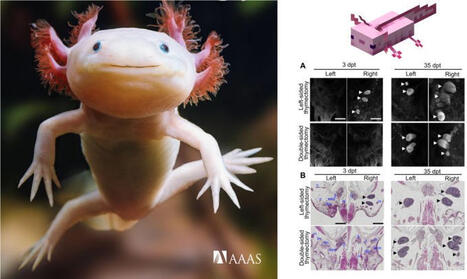
𝗔𝘅𝗼𝗹𝗼𝘁𝗹𝘀 𝗿𝗲𝗴𝗿𝗼𝘄 𝗮 𝘁𝗵𝘆𝗺𝘂𝘀 𝗳𝗿𝗼𝗺 𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗰𝗵
🧠 𝗔 𝗽𝗮𝗽𝗲𝗿 𝗮 𝗱𝗮𝘆 𝗸𝗲𝗲𝗽𝘀 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗶𝗻 𝗱𝗲𝗰𝗮𝘆 𝗮𝘄𝗮𝘆 🧠
Tuesday 30 December 2025
𝘛𝘩𝘪𝘴 𝘴𝘵𝘶𝘥𝘺 𝘴𝘩𝘰𝘸𝘴 𝘵𝘩𝘢𝘵 𝘢𝘹𝘰𝘭𝘰𝘵𝘭𝘴 𝘤𝘢𝘯 𝘧𝘶𝘭𝘭𝘺 𝘳𝘦𝘨𝘦𝘯𝘦𝘳𝘢𝘵𝘦 𝘢 𝘧𝘶𝘯𝘤𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯𝘢𝘭 𝘵𝘩𝘺𝘮𝘶𝘴 𝘢𝘧𝘵𝘦𝘳 𝘤𝘰𝘮𝘱𝘭𝘦𝘵𝘦 𝘳𝘦𝘮𝘰𝘷𝘢𝘭, 𝘳𝘦𝘷𝘦𝘢𝘭𝘪𝘯𝘨 𝘢 𝘮𝘪𝘥𝘬𝘪𝘯𝘦-𝘥𝘳𝘪𝘷𝘦𝘯 𝘱𝘳𝘰𝘨𝘳𝘢𝘮 𝘵𝘩𝘢𝘵 𝘳𝘦𝘣𝘶𝘪𝘭𝘥𝘴 𝘵𝘩𝘺𝘮𝘪𝘤 𝘴𝘵𝘳𝘰𝘮𝘢 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘱𝘰𝘪𝘯𝘵𝘴 𝘵𝘰 𝘯𝘦𝘸 𝘸𝘢𝘺𝘴 𝘵𝘰 𝘳𝘦𝘴𝘵𝘰𝘳𝘦 𝘵𝘩𝘺𝘮𝘪𝘤 𝘧𝘶𝘯𝘤𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯 𝘢𝘧𝘵𝘦𝘳 𝘥𝘢𝘮𝘢𝘨𝘦 𝘰𝘳 𝘢𝘨𝘪𝘯𝘨.
💡𝗧𝗮𝗸𝗲 𝗵𝗼𝗺𝗲 𝗺𝗲𝘀𝘀𝗮𝗴𝗲
• Juvenile axolotl regenerates thymus de novo after complete thymectomy, restoring nodule morphology by 35 days post-thymectomy.
• Single-cell RNA sequencing shows regenerated thymus reconstitutes thymic epithelial cells, T cells, and stromal niches; transplantation proves renewed hematopoietic progenitor cell homing and thymopoiesis.
• FOXN1 is essential for thymus size and T cell output, yet dispensable for rudiment initiation; MDK (midkine–protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type Z1) signaling is an early regeneration trigger.
🔥𝗜𝗺𝗽𝗮𝗰𝘁
• Defines a regeneration-specific midkine axis that could be harnessed to rebuild thymic epithelial niches after thymectomy or involution.
❓𝗢𝗽𝗲𝗻 𝗾𝘂𝗲𝘀𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀
• What is the lineage source of de novo thymic epithelial cells?
• Can midkine activation restore mammalian thymus after complete ablation?
• How is self-tolerance enforced without clear corticomedullary architecture?
𝗠𝗼𝗹𝗲𝗰𝘂𝗹𝗮𝗿 𝗯𝗮𝘀𝗶𝘀 𝗳𝗼𝗿 𝗱𝗲 𝗻𝗼𝘃𝗼 𝘁𝗵𝘆𝗺𝘂𝘀 𝗿𝗲𝗴𝗲𝗻𝗲𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗶𝗻 𝗮 𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘁𝗲𝗯𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗲, 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗮𝘅𝗼𝗹𝗼𝘁𝗹
Anna Czarkwiani, Macrina Lobo, Lizbeth Bolaños-Castro, Ph.D. et al.
Science Immunology, December 2025
Corresponding author(s): Rene Maehr, Max H Yun
🔗 𝘓𝘪𝘯𝘬 𝘵𝘰 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘱𝘢𝘱𝘦𝘳 𝘪𝘯 𝘤𝘰𝘮𝘮𝘦𝘯𝘵𝘴
🧩 𝘐𝘭𝘭𝘶𝘴𝘵𝘳𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯 𝘢𝘥𝘢𝘱𝘵𝘦𝘥 𝘧𝘳𝘰𝘮 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘱𝘢𝘱𝘦𝘳 + 𝘚𝘤𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘤𝘦 𝘐𝘮𝘮𝘶𝘯𝘰𝘭𝘰𝘨𝘺 𝘤𝘰𝘷𝘦𝘳 + 𝘮𝘺 𝘤𝘩𝘪𝘭𝘥𝘳𝘦𝘯'𝘴 𝘧𝘢𝘷𝘰𝘶𝘳𝘪𝘵𝘦 #𝘮𝘪𝘯𝘦𝘤𝘳𝘢𝘧𝘵 𝘤𝘩𝘢𝘳𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳!

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 21, 2025 4:11 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 12, 2025 8:34 AM
|
One of the most clinically useful aging markers is hiding in plain sight.
And it isn’t found in your genome.
At the Geneva Longevity Summit, I sat beside two pioneers Steve Horvath and Gordan Lauc, whose work has reshaped how we think about biological time.
The discussion made something very clear:
We are entering the era of immune-aging clocks, and IgG glycans are leading the way.
For decades, we assumed the genome held the answers to lifespan and disease risk.
But the data tells a different story.
Genetics explains only 10-30% of the variance in chronic disease and longevity. The rest comes from the biological systems that change in response to life: epigenetics, metabolism, immune signaling, and inflammation.
That’s where glycans come in.
Glycans are complex sugar structures attached to proteins. They regulate immunity, inflammation, and communication between cells. And because most plasma proteins (including IgG) are glycosylated, the IgG glycome becomes a real-time map of immune aging.
Here is why this matters clinically:
• IgG glycans shift predictably with age.
• This remodeling contributes directly to inflammaging.
• Pro-inflammatory patterns rise. Anti-inflammatory patterns fall.
• Women experience an accelerated shift during perimenopause due to estrogen loss.
• GlycanAge correlates strongly with frailty, metabolic dysfunction, and cardiovascular risk.
And unlike genetics, glycan profiles are reversible.
Lifestyle, sleep, exercise, nutrition, stress load, and hormone therapy, especially estradiol in menopausal women, can all modify glycan age.
Glycans reflect immune balance over weeks to months, are stable enough for clinical decisions, and responsive enough for intervention tracking.
Multiple clinics are piloting GlycanAge alongside lipid panels and HbA1c.
What would you do with a clearer window into your own immune age?
References:
Glycosylation: mechanisms, biological functions and clinical implications. (2024)
Recent advances in N-glycan biomarker discovery among human diseases. (2024).
| 25 comments on LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 8, 2025 4:26 AM
|
Architecture of the neutrophil compartment
- Millions of neutrophils are produced every day by the bone marrow through a well-defined series of differentiation steps before their release into the circulation as terminally differentiated, non-proliferative cells that eventually infiltrate most tissues.
- Neutrophils exhibit remarkable phenotypic and functional diversity across tissues and disease, yet the lack of understanding of how this immune compartment is globally organized challenges translation to the clinic.
- Here the authors performed single-cell transcriptional profiling of neutrophils spanning 47 anatomical, physiological and pathological scenarios to generate an integrated map of the global neutrophil compartment in mice which was named NeuMap.
- NeuMap reveals that neutrophils organize in a finite number of functional hubs that distribute sequentially during maturation to then branch out into interferon-responsive and immunosuppressive states, as well as a functionally silent state that dominates in the healthy circulation.
- TGFβ, IFNβ and GM-CSF push neutrophils along the different trajectories, while transcription factor JUNB controls angiogenic and immunosuppressive states and promotes tissue revascularization.
- The architecture of NeuMap appears to be conserved across sex, environmental and genetic backgrounds, as well as in humans.
- Limitation of the study: relatively small number of pathophysiological conditions analysed. Perturbations associated with allergy, autoimmunity, mucosal inflammation or diseases associated with old age as well as developmental processes remain uncharted in NeuMap.
- This study delineates the global architecture of the neutrophil compartment and establishes a framework for exploration and exploitation of neutrophil biology.
https://lnkd.in/eh-hw66V
#immunology #science #singlecell #omics

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 5, 2025 7:38 AM
|
Stanford scientists have discovered that cancer cells don’t just use one trick to hide from the immune system—they use two separate “don’t-eat-me” signals to stop macrophages from killing them.
The first signal, CD47, was already famous for acting like an invisibility cloak that tells macrophages to back off, and blocking it with an anti-CD47 antibody is already in human trials.
In the Nature Immunology paper, the same Stanford team also found that tumors use MHC class I as a second stop signal by binding to a macrophage receptor called LILRB1, which suppresses the macrophage’s ability to engulf and destroy the cancer.
When researchers blocked both CD47 and LILRB1 in mice, tumors rapidly filled with immune cells, shrank significantly, and became far easier for the body to clear.
This shows that many cancers survive by running two overlapping escape systems, and turning off both “don’t-eat-me” pathways at once may dramatically boost the immune system’s ability to attack and eliminate tumors. | 17 comments on LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 30, 2025 4:52 AM
|
Immunity to solid tumors is associated with the hallmarks of cancer-associated inflammation and the ability of immune mechanisms to limit tumor progression. Application of expanded tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte adoptive T cell therapy (TIL ACT) in clinical trials is now practiced at many sites around the world. Prior to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), an approximate 50% objective response rate was consistently observed across multiple institutions for patients with melanoma. This now-approved strategy approaches 35% in recent studies from the USA and 49% with more highly selected patients in Europe. Here, we focus on early TIL studies in non-melanoma epithelial neoplasms. Increased understanding of cancer immunology has allowed changes in the TIL expansion process to include: (1) initial generation of TIL from fragments, (2) use of specialized large-scale culture vessels, (3) use of the rapid expansion protocol to enable ‘young’ TIL prosecution, and (4) treatment regimens employing non-myeloablative (NMA) chemotherapy followed by brief interleukin-2 administration. NMA leads to homeostatic proliferation of the transferred T cells, engraftment, profound neutropenia and lymphopenia, and improved clinical outcome. A key success of TIL ACT relies on the quality, specificity, and number of pre-existing TIL. This, in turn, is highly influenced by the suppressive tumor microenvironment. Thus, any means to alter ‘cold tumor (non-T cell inflamed)’ to ‘hot tumor (T cell inflamed)’ is theoretically desirable to improve both the quality and quantity of TIL obtained before harvest. Combinations of other immunotherapies such as application of ICB, co-stimulatory molecule agonist antibodies, autophagy inhibition, and dendritic cell support strategies could provide additional improvements in TIL therapy and enable harnessing of the adaptive immune response to enhance the clinical outcome of TIL-ACT patients.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 20, 2025 5:05 AM
|
Epigenetic and metabolic programming of innate immune cells shapes host defense and disease susceptibility.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 17, 2025 4:09 AM
|
Venez découvrir en avant première notre Livret d'Immunologie sur notre stand, ouvrage à destination des élèves en primaire. Il sera bientôt disponible sur notre site internet et sera distribué gratuitement aux enfants par les ambassadeurs de l'immunologie, qui présentent notre belle discipline, à l'occasion de la journée de l'immuno (qui est le 29 avril).
SFI Société Française d'Immunologie
#Immunologie
#vulgarisation
#science
#livre
#systèmeimmunitaire
TIMC Lab
Université Grenoble Alpes | 18 comments on LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 16, 2025 4:51 AM
|
Sign in or join now to see posts like this one and more.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
October 15, 2025 4:43 AM
|
Immunometabolism, the intersection of cellular metabolism and immune function, has revolutionized our understanding of T cell biology. Changes in cellular metabolism help guide the development of thymocytes and the transition of T cells from naive to effector, memory and tissue-resident states. Innate-like T cells are a unique group of T cells with special characteristics. They respond rapidly, reside mainly in tissues and express T cell receptors with limited diversity that recognize non-peptide antigens. This group includes invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells, mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells and some populations of γδ T cells. Different subsets of innate-like T cells rely on specific metabolic pathways that influence their differentiation and function and distinguish them from conventional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Although there are differences between innate-like T cell types, they share metabolic and functional features. In this Review, we highlight recent research in this emerging field. Understanding how metabolic programmes differ between innate-like T cells and other T cells may open opportunities for tailoring innate-like T cell responses and adoptive T cell therapies for use in cancer, metabolic and autoimmune diseases. Functional and metabolic properties of innate-like T cells — namely, iNKT cells, MAIT cells and some γδ T cells — differ from those of conventional T cells. This Review describes how metabolic pathways support innate-like T cell properties such as acquisition of effector capability in the thymus, rapid responsiveness, tissue persistence, antigen adaptation and functional flexibility.
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 6, 1:02 PM
|
Long COVID (LC) involves a spectrum of chronic symptoms after acute severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. Current hypotheses for the pathogenesis of LC include persistent virus, tissue damage, autoimmunity, endocrine insufficiency, immune dysfunction and complement activation. We performed immunological, virological, transcriptomic and proteomic analyses from a cohort of 142 individuals between 2020 and 2021, including uninfected controls (n = 35), acutely infected individuals (n = 54), convalescent controls (n = 24) and patients with LC (n = 28). The LC group was characterized by persistent immune activation and proinflammatory responses for more than 180 days after initial infection compared with convalescent controls, including upregulation of JAK-STAT, interleukin-6, complement, metabolism and T cell exhaustion pathways. Similar findings were observed in a second cohort enrolled between 2023 and 2024, including convalescent controls (n = 20) and patients with LC (n = 18). These data suggest that LC is characterized by persistent activation of chronic inflammatory pathways, suggesting new therapeutic targets and potential biomarkers of disease. Long COVID (LC) involves a spectrum of chronic symptoms after resolution of acute severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. Barouch and colleagues show that LC is characterized by persistent activation of chronic inflammatory pathways and T cell exhaustion.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 4, 5:23 AM
|
Every leukocyte class shall have its day in atherosclerosis. With an international team we summarize the current evidence supporting mechanisms by which mast cells can participate in this disease. Inflammation has many faces, and reaginic antibody (IgEs) can link adaptive to innate immunity unleashing a multitude of mast cell mediators that can modulate arterial and microvascular biology. #atherosclerosis #angiogenesis #inflammation #allergy #cardiology #cardiovascularmedicine #heartattack #myocardialinfarction #immunology #microvasculature

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 1, 4:38 AM
|
Since the discovery of the segmented shape of the neutrophil nucleus, scientists have pondered its physiological relevance. Yet, to this day, neither the functional relevance nor the molecular mechanisms underlying the segmentation of the neutrophil nucleus are fully understood. Some experimental evidence supports a role of nuclear segmentation in efficient neutrophil migration but its impact on key neutrophil functions, such as phagocytosis, degranulation or production of reactive oxygen species, remains unclear. Nonetheless, the role of nuclear shape in remodelling chromatin and regulating gene expression has high potential for biological and translational relevance. This Review aims to compile and connect the current studies on the neutrophil nucleus, while also discussing studies in other cell types that could inform us about the relevance or mechanisms of nuclear segmentation. In this Review, the authors consider a long-standing immunological conundrum — why do neutrophils have a segmented nucleus? They discuss the mechanisms that may underlie segmentation of the neutrophil nucleus and explain how nuclear segmentation may affect neutrophil functions, including migration and phagocytosis.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 23, 2025 7:03 AM
|
The process of phagocytosis creates intracellular compartments (organelles known as phagosomes) that are central hubs for innate immune sensing of potentially dangerous microorganisms, cells, cellular debris and foreign objects. Receptors, enzymes and signalling molecules are specifically enriched in these compartments, wherein they learn everything they can about the phagocytosed material and signal for the cell to mount appropriate responses. The phagosome organelle is also a compartment that facilitates nutrient and metabolite harvesting from internalized materials. This Review explores recent developments in our understanding of phagocytosis as a specific mechanism of innate immune sensing. We discuss efforts to identify the catalogue of proteins that are enriched in different types of phagosomes to learn how these molecules work together to tailor inflammatory and antimicrobial immune responses. In this Review, Li and Underhill discuss recent advances in understanding the process of phagocytosis. The authors highlight how phagocytosis is integral for innate immune sensing and explain how the phagocytosed material itself shapes the phagocytosis process.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 16, 2025 10:57 AM
|
🚀 New preprint: A single-cell cytokine dictionary of human peripheral blood
Excited to share our new preprint, “A single-cell cytokine dictionary of human peripheral blood”.
In this work, we generated the Human Cytokine Dictionary:
👉 9.7 million single-cell transcriptomes across
👉 12 human PBMC donors and
👉 90 individual cytokine stimulations,
👉 by far the largest single-cell perturbation dataset from primary human immune cells to date.
This dataset lets us systematically map how human immune cell types respond to cytokines, uncover cell type–specific activities, donor-specific vs consensus responses, cytokine similarity groups, and higher-order cytokine-cytokine and cell-cell communication networks. A particularly interesting story is the IL-32-β–initiated cascade that rewires myeloid programs from antiviral/Th1-type responses towards a neutrophil-driven, IL-10–modulated inflammatory state.
To make this resource broadly usable, we also introduce huCIRA (Human Cytokine Immune Response Analysis), a Python package that
• exposes cytokine-induced gene and program signatures, and
• allows researchers to decode cytokine activity in their own single-cell and spatial transcriptomic datasets.
We showcase this on datasets from systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and NSCLC.
Huge congratulations and thanks to our four co–first authors Lukas Oesinghaus, Sören Becker, Larsen Vornholz and Efi Papalexi,👏 for driving this enormous effort.
This project was only possible thanks to a fantastic collaboration with Parse Biosciences, leveraging their GigaLab platform to reach this unprecedented data scale, and to the Seelig lab for a truly inspiring and fun partnership across engineering, computation, and immunology.
I also want to thank Nir Hacohen and colleagues for their pioneering mouse Immune Dictionary (Cui et al., Nature 2024), which provided a key conceptual and analytical reference point for our human cytokine dictionary.
You can read the preprint here:
🔗 https://lnkd.in/gFB3NAdC
Looking ahead, I hope this work can serve as a blueprint for analyzing the many large-scale perturbation datasets to come - as both a biological reference and a testbed for virtual cell models of cytokine biology.
🔧 Code & huCIRA package: https://lnkd.in/g7cMPic3
🧰 For broader single-cell perturbation analysis, also check out pertpy in the scverse ecosystem: https://lnkd.in/g_7cpUfH
Looking forward to feedback, reuse of the Human Cytokine Dictionary and huCIRA by the community. | 13 comments on LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 11, 2025 6:21 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 5, 2025 9:59 AM
|
Immunology is the most human—and the most beautiful—of disciplines. Thanks to B Andrade and M Araujo-Pereira for this very pertinent parallel.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 2, 2025 1:11 PM
|
This recent PNAS paper is making headlines. Why? Because it focuses on something extremely familiar - Tattoos!
Researchers explored how tattoo ink interacts with the immune and lymphatic systems and clearly demonstrated that its effects do not occur only at the tattoo's site. Instead, it can have a significant, long-term impact on the draining lymph nodes, which affect immune responses to events like vaccines and potentially many other situations as well.
Particularly relevant in a world where nearly 1 in 3 people is likely to have at least a tattoo. And a great example of how science can talk so directly to the general public when it feels familiar.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 21, 2025 10:45 AM
|
If you want to even begin to really understand how cells work, you need to watch this video first; and then reread all the static imagery text books of biochemistry & molecular biology again with fresh eyes. Excellent video Simon Reid.
#highereducation

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 18, 2025 1:17 PM
|
This Consensus Statement clarifies the existing subset-based nomenclature for T cells. Furthermore, it proposes an alternative modular nomenclature that is designed to be brief and flexible and to avoid ambiguity and unwanted implications.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 16, 2025 5:34 AM
|
A roadmap for defining “extrafollicular” B cell responses

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
October 31, 2025 8:28 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
October 11, 2025 2:52 AM
|
Mast cells, traditionally known for their roles in allergic reactions and pathogen defense, have been revealed to possess significant functional diversity within the tumor microenvironment (TME). Through single-cell RNA sequencing analysis across 15 solid tumors (385 samples from 264 patients), 10...
|






 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...