 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 29, 2015 8:21 AM
|
The TOP 10% information you need!
The scoops deal with published (classical or OPEN) and grey literature (blogs, websites, social networks, press releases) allowing rapid access to recently published relevant information May 29, 2015 you were 26796 visitors, viewing this topic 34.5K times., 4900 scoops June 2020 : >7.3K scoops, >94.5K visitors, #121K views December 2023: >8K scoops, >97,7K vis, >171,3K views May 2025: >8.2K scoops, >98.2 visitors, >177,8 views

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
October 15, 4:43 AM
|
Immunometabolism, the intersection of cellular metabolism and immune function, has revolutionized our understanding of T cell biology. Changes in cellular metabolism help guide the development of thymocytes and the transition of T cells from naive to effector, memory and tissue-resident states. Innate-like T cells are a unique group of T cells with special characteristics. They respond rapidly, reside mainly in tissues and express T cell receptors with limited diversity that recognize non-peptide antigens. This group includes invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells, mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells and some populations of γδ T cells. Different subsets of innate-like T cells rely on specific metabolic pathways that influence their differentiation and function and distinguish them from conventional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Although there are differences between innate-like T cell types, they share metabolic and functional features. In this Review, we highlight recent research in this emerging field. Understanding how metabolic programmes differ between innate-like T cells and other T cells may open opportunities for tailoring innate-like T cell responses and adoptive T cell therapies for use in cancer, metabolic and autoimmune diseases. Functional and metabolic properties of innate-like T cells — namely, iNKT cells, MAIT cells and some γδ T cells — differ from those of conventional T cells. This Review describes how metabolic pathways support innate-like T cell properties such as acquisition of effector capability in the thymus, rapid responsiveness, tissue persistence, antigen adaptation and functional flexibility.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
October 6, 7:13 AM
|
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2025 was awarded to Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell and Shimon Sakaguchi “for their discoveries concerning peripheral immune tolerance.”

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 25, 3:37 AM
|
Click here to edit the content

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 23, 8:43 AM
|
Human tumour cells express mutated and non-mutated proteins that can be processed and presented by these cells as peptides bound to human leukocyte antigen (HLA). Some of these peptides are recognized by cognate T cell receptors as ‘non-self’, leading to specific killing of tumour cells by T cells. This process is fundamental to the success of cancer immunotherapy, which exploits the ability of the immune system to eliminate transformed cells. Mutated antigens (neoantigens) have been implicated in the remarkable therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), which boost endogenous antitumour immune responses. In recent years, the combination of ICIs with personalized cancer vaccines that target neoantigens and other tumour-specific antigens has emerged as a new therapeutic strategy. However, the robust immune pressure that ICIs exert on cancer cells inevitably amplifies the phenomenon of immune editing, which can allow cancer cells to develop resistance mechanisms that subvert surveillance by the immune system. Diminished antigenicity can be due to defects in the antigen processing and presentation machinery, such as HLA-I/II loss of heterozygosity and loss of functional β2-microglobulin. This poses a considerable challenge for combination therapies that include ICIs and for the design of cancer-specific vaccines. Effective tumour-specific T cell immunity — and the success of cancer immunotherapies — relies on the presentation of antigens via human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecules. In this Review, Bassani-Sternberg and Huber explore recent advances in understanding the repertoire of tumour-specific antigens, as well as how disruptions in antigen processing and presentation contribute to immune evasion and resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. The authors also highlight how these insights can inform the design of personalized neoantigen-based vaccines and combination therapies aimed at outpacing tumour immunoediting.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 7, 8:07 AM
|
Pathogen-consuming cells found in fat tissue also play a part in lipid balance.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 4, 11:59 AM
|
The distribution of ~ 2 trillion immune cells in the human body.
Lymphocytes: ~ 40% of the number, and 15% of the mass
Neutrophils: ~ 40% of the number, and 15% of the mass
Macrophages: ~ 10% of the number, and 50% of the mass

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 26, 8:37 AM
|
🦠 La liste OMS 2024 des bactéries les plus préoccupantes vient d'être publiée dans le Lancet infectious disease https://lnkd.in/eYmnPyAm
💬 Elle est établie par la consultation d'expert du secteur chargée de scorer chaque bactérie selon 8 critères (mortalité, contagiosité, incidence, traitements disponibles etc voir les items en haut de la figure)
Quelques commentaires par rapport au classement 2017 :
- Les bactéries à gram négatif continuent de dominer largement le classement
- Les entérobactéries ont pris les 2 premières places (occupées en 2017 par Acinetobacter et Pseudomonas) ce n'est pas un détail, les entérobactéries sont des bactéries "communautaires" alors que Acineto et Pseudomonas sont essentiellement retrouvées dans les infections hospitalière
- Ainsi les Klebsielles résistantes aux carbapénèmes est maintenant l'espèce bactérienne qui préoccupe le plus, souvent resistante à tous les antibiotiques et très virulentes (on voit son score de mortalité et sa difficulté de traitement élevé sur la figure)
- La tuberculose résistante a été rajoutée et apparait au rang n°4
💡 Ce classement est un bon outil
pour les décideurs pour cibler la recherche anti-bactérienne sur les problèmes les plus importants
et pour le public/les journalistes pour savoir comment interpréter certaines annonces "spectaculaires" de découverte de nouveaux traitements en fonction de la bactérie concernée

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 23, 8:04 AM
|
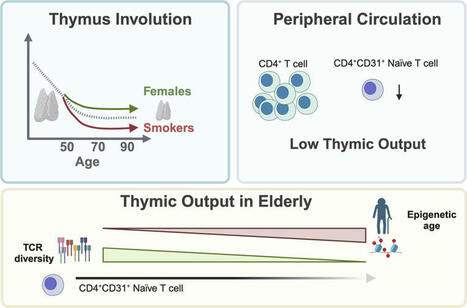
Functional thymic structures are embedded in the mediastinal AT. To effectively evaluate thymic output in aged individuals, we first sought to characterized functional thymic tissue obtained from patients (≥50 years) undergoing common cardiac surgical procedures, where these tissues could be...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 14, 4:07 AM
|
A new #ScienceReview offers an overview of recent research that reveals the immune system not only defends the body but also actively shapes and supports various life-sustaining processes through dynamic, reciprocal interactions with other physiological systems.
Learn more: https://scim.ag/40ZxtQw

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 8, 3:23 AM
|
A new special issue of Science explores the immune system at the molecular and cellular level and how it has evolved to govern multiple facets of human health.
Learn more: https://scim.ag/4m6vHWp

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 29, 1:55 AM
|
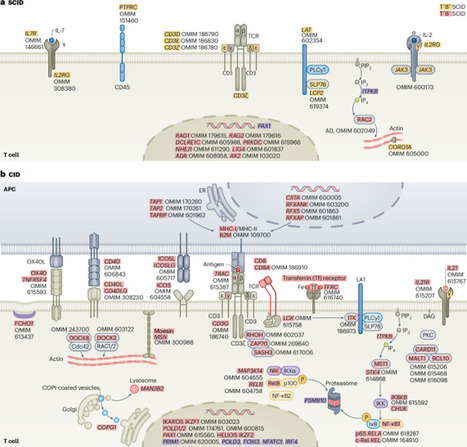
Cui et al. discuss new molecular and cellular insights underlying the pathogenesis of rare human diseases that arise from genetic inborn errors of immunity.
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
October 31, 8:28 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
October 11, 2:52 AM
|
Mast cells, traditionally known for their roles in allergic reactions and pathogen defense, have been revealed to possess significant functional diversity within the tumor microenvironment (TME). Through single-cell RNA sequencing analysis across 15 solid tumors (385 samples from 264 patients), 10...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
October 1, 3:44 AM
|
Long-lived plasma cells (LLPCs), which continuously secrete antibodies, play a central role in humoral immunity and form the foundation of effective vaccin

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 23, 12:01 PM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 15, 10:49 AM
|
The College’s Clinical Immunology Workforce Report finds critical staff shortages across services that diagnose and treat allergies, autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiencies.
Three quarters of UK immunology services report that they do not have enough staff to meet current clinical demand.
Dr Patrick Yong, Chair of the College Specialty Advisory Committee for Immunology, quotes:
"This is a sobering report. Many services rely on goodwill and unpaid overtime to keep running. We urgently need to establish more training posts and focus on retaining experienced consultants to ensure safe, effective patient care.”
Patients are facing delays to diagnosis and treatment, while consultants are at risk of burnout. The College is calling for more training posts, better support, and improved workforce planning.
Read the full report and recommendations on our website. https://lnkd.in/eyavzHsp

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 6, 6:17 AM
|
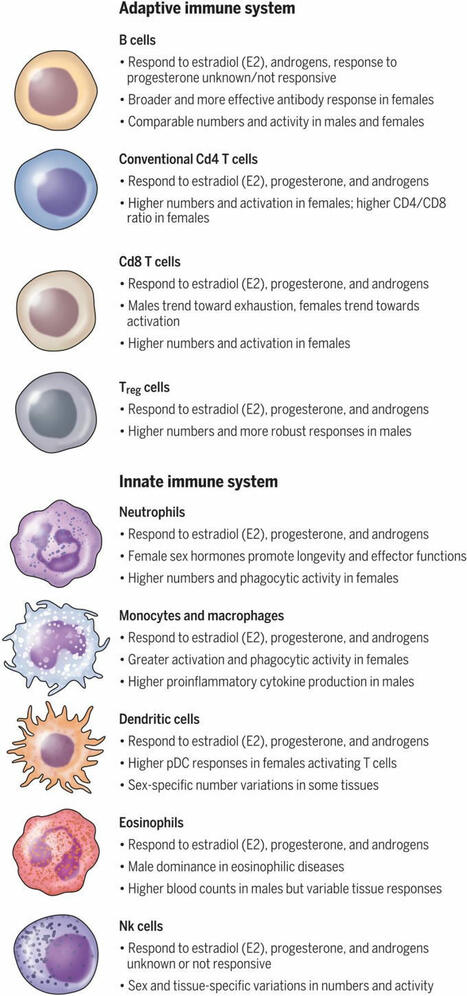
Researchers in a new #ScienceReview examine the influence that biological sex exerts on the immune system and immune-related diseases.
Learn more: https://scim.ag/4fCsDyA | 19 commentaires sur LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 4, 8:34 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 24, 8:13 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 16, 1:56 PM
|
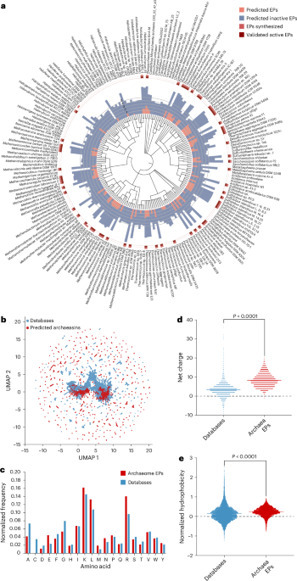
Antimicrobial resistance is one of the greatest threats facing humanity, making the need for new antibiotics more critical than ever. While most antibiotics originate from bacteria and fungi, archaea offer a largely untapped reservoir for antibiotic discovery. In this study, we leveraged deep learning to systematically explore the archaeome, uncovering promising candidates for combating antimicrobial resistance. By mining 233 archaeal proteomes, we identified 12,623 molecules with potential antimicrobial activity. These peptide compounds, termed archaeasins, have unique compositional features that differentiate them from traditional antimicrobial peptides, including a distinct amino acid profile. We synthesized 80 archaeasins, 93% of which showed antimicrobial activity in vitro against Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus spp. Notably, in vivo validation identified archaeasin-73 as a lead candidate, significantly reducing A. baumannii loads in mouse infection models, with effectiveness comparable to that of established antibiotics such as polymyxin B. Our findings highlight the potential of archaea as a resource for developing next-generation antibiotics. Use of artificial intelligence to mine proteomes of archaea led to the discovery of archaeasins, antimicrobials that kill drug-resistant bacteria in laboratory and animal models, offering a promising source of future antibiotics.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 16, 2:21 AM
|
The immune system permeates and regulates organs and tissues across the body, and has diverse roles beyond pathogen control, including in development, tissue homeostasis and repair. The reshaping of the immune system that occurs during aging is therefore highly consequential. In this Focus issue, Nature Aging presents a collection of reviews of and opinions on recent advances in research into immune aging.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 13, 3:47 AM
|
Tolerance requires diversity (of antigen presenting cells)

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 29, 2:54 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 28, 1:19 PM
|
Stromal cells are found in all tissues of the body. Among them, lymphoid stromal cells (LSCs) correspond to the cell subsets found in secondary and tertiar
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
























This topic is focusing mainly on fundamental systemic immunology.
Some subjects are particularly adressed, according to my personal interests in research or teaching, for instance
Lymph node
https://www.scoop.it/topic/immunology?q=lymph+node
Feel free to browse other related topics!
Mucosal Immunity:
http://www.scoop.it/t/mucosal-immunity
Immunology and Biotherapies
http://www.scoop.it/t/immunology-and-biotherapies
Autoimmunity
http://www.scoop.it/t/autoimmunity
Allergy and clinical immunology:
http://www.scoop.it/t/allergy-and-clinical-immunology
History of Immunology
http://www.scoop.it/t/history-of-immunology
and more recently
Fake News and Vaccinations
https://www.scoop.it/topic/assim-actualites