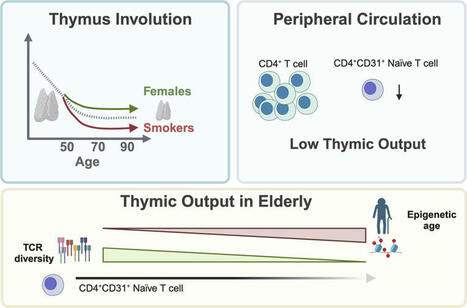
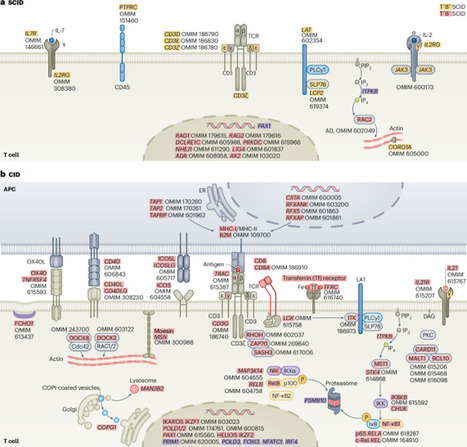
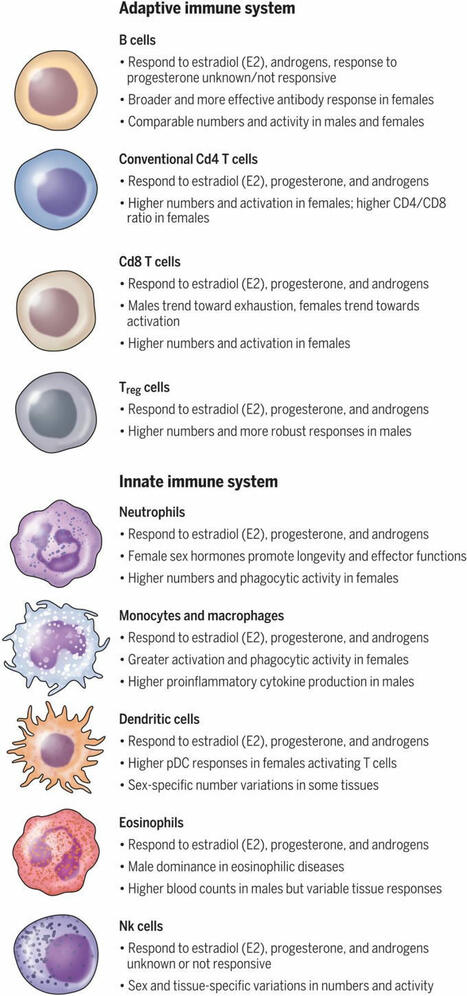
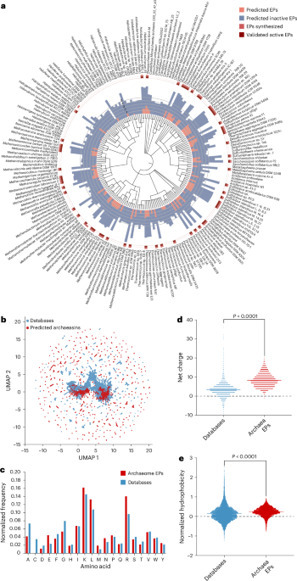
Th2 Cell Th2 cells stimulate B cell and eosinophil proliferation and reduce IFN-γ production by Th1 cells, thereby promoting humoral and allergic responses. From: Neurobiology of Disease, 2007 Related terms: View all Topics Effector CD4+ T Cells in the Intestines Craig L. Maynard, Casey T. Weaver, in Mucosal Immunology (Fourth Edition), 2015 Th2 Cells Th2 cells augment the eradication of parasitic helminthes that induce expression of IL-4 by innate immune cells, such as basophils and tissue-resident mast cells. IL-4 signaling to antigen-activated, previously naïve CD4 T cells results in activation of STAT6 and subsequent induction of the transcription factor GATA-3 (Bonecchi et al., 1998). Via secretion of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, Th2 cells orchestrate B cell class switching to IgE (Bonecchi et al., 1998), thereby priming basophils and mast cells for granule release, recruit eosinophils, and enhance mucus production, respectively. Human Th2 cells can be distinguished by surface expression of CCR4 and CRTH2 (Bonecchi et al., 1998; Abe et al., 1999; Nagata et al., 1999). Host Defenses in Skin Hui Xu, ... Craig A. Elmets, in Clinical Immunology (Fifth Edition), 2019 Th2 responses. Th2 cells are involved in type 2 immune responses, which are important for eradication of extracellular parasites and bacterial infection. They produce IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, and IL-13, which are important for the induction and development of humoral immune responses. IL-4 and IL-13 activate B-cell proliferation, Ig class-switching, and antibody production. Th2 cell-mediated inflammation is characterized by the presence of eosinophils and basophils, as well as extensive mast cell degranulation—a process dependent on cross-linking surface-bound IgE.24 IL-5 is a potent hematopoietic cytokine, which stimulates bone marrow production of eosinophils as well as activation and chemotaxis of eosinophils and basophils to affected tissue. In mice, Th2-cell deficiency profoundly increases susceptibility to Leishmania infection in skin. In humans, Th2 cells appear to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis (Chapter 44). A recent clinical trial with dupilumab, a fully human mAb that targets the IL-4 receptor-αα and blocks IL-4 and IL-13 signaling, improved atopic symptoms . Role of CD4+ T Cells in the Pathophysiology of Multiple Sclerosis Fumitaka Sato, ... Ikuo Tsunoda, in Multiple Sclerosis, 2016 Role of Th2 cells Th2 cells may play a protective role in MS, as Th2 immune responses have been shown to increase during remission in RRMS (Araki et al., 2003; Clerici et al., 2001). Decreased disease progression and exacerbation of MS during pregnancy have been associated with Th2-biased immune responses (Al-Shammri et al., 2004), although the exact mechanism remains unclear. Suppression of MS disease activities by immunomodulatory drugs, such as glatiramer acetate, has also been associated with enhanced Th2 immune responses (Weber et al., 2007). Experimentally, Th2 cells have been shown to regulate EAE and TMEV-IDD. In EAE induced with mouse spinal cord homogenate, injection of anti-IL-4 neutralizing mAb during the induction phase rendered resistant BALB/c mice susceptible to EAE (Constantinescu et al., 2001). The adoptive transfer of PLP-specific Th2 cell clones at the time of sensitization or disease onset prevented EAE in mice sensitized with PLP (Kuchroo et al., 1995). While T cell immunoglobulin mucindomain containing (TIM)2 has been shown to be preferentially expressed on the surface of Th2 cells and to negatively regulate Th2 immune responses, blockade of TIM-2/TIM-2 ligand interaction by administration of soluble TIM-2 fusion protein delayed the onset and decreased the severity of PLP-induced EAE by enhancing Th2 immune responses (Chakravarti et al., 2005). In TMEV-IDD, Th2 immune responses have also been demonstrated to suppress inflammatory demyelination in the CNS. Hill et al. (1998) demonstrated that during the early chronic phase of TMEV infection, infected mice treated with IL-4 developed less severe inflammatory demyelination compared with controls. Thus, the findings in EAE and TMEV-IDD suggest that Th1 cells could contribute to the pathogenesis of MS, while Th2 cells may play a protective role (Table 3). Cell-Mediated Defense against Infection Tobias M. Hohl, in Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases (Eighth Edition), 2015 Th2 Cells Th2 cells express a range of cytokines that influence B-cell differentiation and antibody production, eosinophil recruitment, and mucus production. The signature cytokines produced by Th2 cells are IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, but Th2 cells can also produce IL-9, IL-10, IL-25, and amphiregulin.20 Th2 responses are generated when naïve T cells are exposed to IL-4 at the time of T-cell priming. In the setting of low antigen concentrations, IL-4 can be produced by responding T cells.21 After antigenic challenge, IL-4 can also be produced by mast cells and basophils in the vicinity of T-cell priming.22,23 IL-4 signals naïve T cells via the STAT6 pathway to express GATA3, the master regulator of Th2 differentiation,24 a process that can be enhanced by IL-4– and STAT6-independent GATA3 activation,25 all of which drives the expression of additional downstream activators. Although Th2 cells are best known for causing or contributing to allergic diseases such as atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, and asthma, Th2 cells also contribute to defense against infections, particularly helminth infections of the gastrointestinal tract.26 In this setting, eosinophil recruitment, IgE production, and mucus hypersecretion can enhance parasite expulsion in an IL-4 and IL-13 signaling–dependent manner, a notion that is supported by murine studies of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection.27,28 The secretion of amphiregulin by Th2 cells can stimulate intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and expulsion of Trichuris muris, a nematode that infects mice.29 Besides Th2 cells, tissue-resident and Th2 cytokine-secreting innate lymphoid cells represent a significant source of IL-13 during the early stages of parasitic infection and promote expulsion.30-32 Aberrant Th2 responses to pathogens that require IFN-γ and Th1 responses for control can result in progressive infections and lethality. For example, Leishmania major infection of certain mouse strains induces Th2 responses that result in progressive in vivo replication and host death.33,34 In contrast, mouse strains that respond to L. major with Th1 responses clear and survive experimental infections. The mechanisms that determine whether an L. major–specific T-cell response will be predominately Th1 or Th2 are complex.35 In some mouse strains, Th2 responses occur because of T-cell responses to one dominant antigen called LACK (Leishmania analogue of the receptors of activated C kinase).36 In the absence of a T-cell response to this specific antigen, the responding CD4+ T cells differentiate into Th1 cells. In humans, the type of disease associated with Mycobacterium leprae infection is also tied to CD4+ T-cell differentiation. Th1 differentiation is associated with tuberculoid leprosy, a paucibacillary infection in which IFN-γ–producing T cells enhance microbial killing. The induction of type I interferon and IL-10 signaling in innate immune cells during leprosy can antagonize IFN-γ–dependent protection.37 Th2 differentiation is associated with high tissue densities of M. leprae and more robust, but ineffective, antibody responses.38,39 T Cells and Their Effector Functions Ruben C. Fragoso, ... Steven J. Burakoff, in Encyclopedia of Cancer (Second Edition), 2002 IV.B.2 Th2 T Cells Th2 cells promote IgE production and eosinophil function, which are the key players in the pathogenesis of allergic inflammation and immunity against parasitic infections. Cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-5 released by Th2 cells stimulate, respectively, B-cell switching to the production of IgE antibody and activation of eosinophils. The coordinate actions of these effector mechanisms result in heightened immunity against, for example, helminthic parasites, which can be coated with IgE and destroyed by the toxic granular contents of eosinophils. The balance between Th1 and Th2 cells may serve to determine the outcome of an infection. The Th1-mediated response is an effective deterrent for the protozoan parasite Leishmania major. In strains of mice with a genetic predisposition to mount predominately Th2 responses, infection by L. major results in a severe cutaneous and systemic disease that cannot be eliminated effectively. In contrast, if mice were vaccinized with leishmania antigens coadministered with IL-12 to induce a Th1 response, the mice are protected from subsequent challenges with L. major. In an analogous manner, responses to Mycobacterium leprae in humans can have two sharply different outcomes depending on the polarization of Th cells. In lepromatous leprosy, a Th2-dominated response can result in diffuse and destructive lesions due to an ineffective response against M. leprae antigens. In contrast, patients who develop a strong Th1-mediated immunity have a less destructive disease called tuberculoid leprosy. T-Cell Immunity Shannon A. Carty, ... Gary A. Koretzky, in Hematology (Seventh Edition), 2018 Th2 Cells Th2 cells are critical for the immune response against extracellular parasites, such as helminths, through production of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. At initial sites of parasitic infection, epithelial cells of the target organs, including the skin, lungs, and intestines, and resident cells of the innate immune system sense parasite-derived products and produce Th2-inducing cytokines, including thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), IL-4, IL-25, and IL-33. These cytokines then act on innate immune cells, including basophils and DCs, as well as directly on naive CD4+ cells to promote Th2 differentiation. Recent work has provided insight into how cytokine signaling, particularly IL-4 signaling, promotes Th2 differentiation. Through interaction with its receptor, IL-4 activates STAT6. STAT6 plays a vital role in Th2 differentiation, as evidenced by the profound reduction in development of this lineage in Stat6-deficient mice. STAT6 activation leads to its nuclear translocation and subsequent induction of the transcription factor GATA3, which, like T-bet for Th1 cells, is considered the master regulator of Th2 differentiation. GATA3 regulates Th2 cytokine production by binding and activating the “Th2 locus,” which includes the genes encoding IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. When GATA3 function is abrogated, Th2 differentiation is virtually absent both in vitro and in vivo. In mature differentiated Th2 cells, GATA3 deficiency results in loss of IL-5 and IL-13 production. GATA3 is both necessary and sufficient for Th2 differentiation because forced expression either by retroviral constructs or transgenic expression promotes Th2 differentiation and represses Th1 differentiation. Repression of Th1 development occurs at least partially through GATA3-dependent inhibition of STAT4, thus interfering with Ifng gene transcription. TCR signal strength also is involved in determining if a naive T cell will differentiate into a Th1 or Th2 cell. Studies in mice using altered peptide ligands that have decreased affinity for particular TCRs and experiments using limiting doses of antigen have demonstrated that diminished TCR stimulation promotes Th2 cell differentiation. Differences in costimulation also affect Th2 pathway differentiation. Mice deficient in CD28 or its ligand have a more pronounced defect in Th2 responses, suggesting that these molecules may play a greater role in promoting Th2 differentiation than Th1 differentiation. IL-4 produced by mature Th2 cells acts in a positive feedback loop to promote further Th2 cell differentiation in naive T cells as they encounter antigen. Th2-derived IL-4 also mediates IgE class switching in B cells. Soluble IgE binds to and crosslinks its high-affinity receptor FcεRI on basophils and mast cells, promoting production of histamine and serotonin as well as several cytokines, including IL-4, IL-13, and TNF-α. IL-5 produced from Th2 cells recruits eosinophils, whereas Th2-derived IL-13 promotes both the expulsion of helminths during parasitic infection and also the induction of airway hypersensitivity. Th2 responses are critical for immunity against extracellular parasites, but excessive Th2 responses are associated with the pathologic conditions of allergy and airway hypersensitivity. The increase in asthma in the developed world has been linked to an imbalance of Th subsets with skewing toward “Th2-ness” in the population. Additional work is necessary to more firmly establish a molecular immunologic link to the epidemiology of these diseases. Chronic Inflammation and Atherosclerosis Jan Nilsson, ... Andreas Edsfeldt, in Early Vascular Aging (EVA), 2015 Interleukin-10 Th2 cells, Tregs, B-cells, monocytes, and macrophages are all potential sources of IL-10. The anti-inflammatory effects of IL-10 are mediated by inhibition of T-cell proliferation, macrophage apoptosis, antigen presentation, collagenase expression, and inflammatory cytokine production. In mice, IL-10 deficiency is associated with increased inflammatory cell invasion, a greater plaque burden, and an increased inflammatory cytokine response [40]. Human studies on circulating IL-10 revealed that high plasma levels of IL-10 are associated with an improved outcome and a lower risk for recurrent events in patients with acute coronary syndromes [41,42]. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in the Regulation of Immune Responses Ben Roediger, Wolfgang Weninger, in Advances in Immunology, 2015 7.8 IL-4/IL-4Rα Like Th2 cells, ILC2 cells express a functional IL-4 receptor (Doherty et al., 2012; Motomura et al., 2014), at least in the lung, and have been shown to produce IL-13 and IL-9 in response to IL-4 in vitro (Motomura et al., 2014). IL-4 was also shown to augment IL-2-driven proliferation of ILC2 cells in vitro (Motomura et al., 2014), which may relate to the STAT6 dependency of ILC2 cell proliferation in vivo (discussed further below). Animal Models of Immunity to Female Genital Tract Infections and Vaccine Development Charu Kaushic, ... Kenneth W. Beagley, in Mucosal Immunology (Fourth Edition), 2015 Th2 Cells CD4+ Th2 cells do not protect against chlamydial infection (Wang et al., 1999; Yang, 2001; Hawkins et al., 2002) and can exacerbate pathology (Chen et al., 2010; Wang et al., 1999; Perry et al., 1997) because of suppression of Th1 immunity. However, activation of Th2 cells is important for the production of IgG and IgA, both of which reduce infection in vivo. Th2 cells also may act as regulators of the Th1 response to limit tissue pathology after resolution of infection (Debattista et al., 2003). Indeed, it has been suggested that a human vaccine to prevent ascending infection and tissue inflammation should aim to elicit primarily a Th2 response to limit collateral damage (Vicetti Miguel and Cherpes, 2012). This approach would certainly be contrary to the current dogma driving vaccine research (see below).

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
onto Immunology August 2, 2021 4:00 AM
|
No comment yet.
Sign up to comment




 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...