 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 27, 2013 5:57 AM
|
Pathology, Diagnosis and Therapy

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 15, 6:01 AM
|
🔥Hot paper on #NonAlcoholicFattyLiverDisease
Title: Identifying Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Primary Care: How and for What Benefit?
👥Authors: Dr. Andrew D. Schreine

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 12, 4:53 AM
|
The human immune system has a formidable arsenal of defenses to detect and eliminate threats. One of its most powerful guardians is the complement system — a dynamic network of proteins that tirelessly patrols our body, looking ever vigilantly for signs of infection or injury. In the presence of danger, these proteins spring into action, unleashing a cascade of inflammatory signals that mobilizes the body’s defenses to neutralize the threats.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 28, 5:02 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 15, 1:38 PM
|
#Autoimmunity | #Tregs | Differential roles of human CD4+ & CD8+ regulatory T cells in controlling self-reactive immune responses | Fundamental new insights by… | 10 comments on LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 2, 8:30 AM
|
Stem cells reside in specialized microenvironments, termed niches, at several different locations in tissues1–3. The differential functions of heterogeneous stem cells and niches are important given the increasing clinical applications of stem-cell transplantation and immunotherapy. Whether hierarchical structures among stem cells at distinct niches exist and further control aspects of immune tolerance is unknown. Here we describe previously unknown new hierarchical arrangements in haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and bone marrow niches that dictate both regenerative potential and immune privilege. High-level nitric oxide-generating (NOhi) HSCs are refractory to immune attack and exhibit delayed albeit robust long-term reconstitution. Such highly immune-privileged, primitive NOhi HSCs co-localize with distinctive capillaries characterized by primary ciliated endothelium and high levels of the immune-checkpoint molecule CD200. These capillaries regulate the regenerative functions of NOhi HSCs through the ciliary protein IFT20 together with CD200, endothelial nitric oxide synthase and autophagy signals, which further mediate immunoprotection. Notably, previously described niche constituents, sinusoidal cells and type-H vessels2–10 co-localize with less immune-privileged and less potent NOlow HSCs. Together, we identify highly immune-privileged, late-rising primitive HSCs and characterize their immunoprotective niches comprising specialized vascular domains. Our results indicate that the niche orchestrates hierarchy in stem cells and immune tolerance, and highlight future immunotherapeutic targets. Previously undescribed hierarchical arrangements in haematopoietic stem cells and their niches that mediate both regenerative potential and immune privilege are identified.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 4, 2024 1:56 PM
|
𝐂𝐞𝐥𝐥 𝐓𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐩𝐲 𝐋𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐬𝐜𝐚𝐩𝐞 𝐢𝐧 𝐀𝐮𝐭𝐨𝐢𝐦𝐦𝐮𝐧𝐢𝐭𝐲 🏄♂️
30 companies below categorised by 12 disease areas and other/undiscovered… | 26 comments on LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 29, 2024 10:33 AM
|
Myositis-specific autoantibodies (MSAs) have become pivotal biomarkers for idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and have revolutionized understanding of the heterogeneous disease spectrum that affects both adults and children. The discovery and characterization of MSAs have substantially enhanced patient stratification based on clinical phenotype, thereby facilitating more precise diagnosis and ultimately improving management strategies. Advances in immunoassay technologies in the past 20 years have further propelled the field forward, enabling the detection of a growing repertoire of autoantibodies with high specificity and sensitivity; however, evolving research over the past decade has revealed that even within antibody-defined subsets, considerable clinical diversity exists, suggesting a broader spectrum of disease manifestations than previously acknowledged. Challenges persist, particularly among patients who are seronegative, where the failure to identify certain rare MSAs stems from the use of diverse detection methodologies and inadequate consensus-guided standardization and validation protocols. Bridging these diagnostic gaps is crucial for optimizing patient care and refining prognostic stratification in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. This Review provides an update on autoantibodies associated with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies in both adults and children. The authors also discuss methods of autoantibody detection and the advantages and limitations of each technique.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 9, 2024 4:37 AM
|
BCR-independent memory B cell reactivation via TLR7 or TLR8 activation, type I interferon production, immune complex formation and T helper cell signalling is central in SLE pathogenesis. Dörner and Lipsky discuss the potential of targeting these pathways to eliminate autoreactive memory B cells...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
October 3, 2024 4:54 AM
|
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) encompass a spectrum of autoimmune diseases characterized by muscle inflammation and systemic involvement. This review aimed to synthesize current evidence on the clinical significance and pathogenic mechanism

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 14, 2024 3:31 AM
|
Guest Blog: A Major Health Crisis: The Alarming Rise of Autoimmune Disease By Molly Murray, President and CEO, Autoimmune Association Observed every March, Autoimmune Awareness Month aims to enhance awareness […]

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 10, 2024 5:31 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 3, 2024 2:35 AM
|
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 30, 5:40 AM
|
The ACR has released its 2025 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) treatment guidelines and consensus-based good practice statements, applicable to children and adults with SLE. Overall, the goals of SLE management are to achieve remission or a low level disease activity, reduce morbidity and mortality, and minimize treatment-related adverse events. For treatment of SLE, they recommend universal use of hydroxychloroquine, minimizing glucocorticoid exposure, and early introduction of conventional and/or biologic immunosuppressive therapies.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 22, 8:57 AM
|
Patients with Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) positive dermatomyositis (DM) are complicated and prone to interstitial lung disease, poor prognosis, and a high mortality. A new study suggests a risk prediction model that may identify of high-risk patients to promote timely diagnosis and treatment.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 21, 4:37 AM
|
Here we analyzed the relative contributions of CD4+ regulatory T cells expressing Forkhead box protein P3 (FOXP3) and CD8+ regulatory T cells expressing killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors to the control of autoreactive T and B lymphocytes in human tonsil-derived immune organoids. FOXP3 and GZMB respectively encode proteins FOXP3 and granzyme B, which are critical to the suppressive functions of CD4+ and CD8+ regulatory T cells. Using CRISPR–Cas9 gene editing, we were able to achieve a reduction of ~90–95% in the expression of these genes. FOXP3 knockout in tonsil T cells led to production of antibodies against a variety of autoantigens and increased the affinity of influenza-specific antibodies. By contrast, GZMB knockout resulted in an increase in follicular helper T cells, consistent with the ablation of CD8+ regulatory T cells observed in mouse models, and a marked expansion of autoreactive CD8+ and CD4+ T cells. These findings highlight the distinct yet complementary roles of CD8+ and CD4+ regulatory T cells in regulating cellular and humoral responses to prevent autoimmunity. Here the authors use a tonsil organoid culture model system to investigate the roles of human CD4+ and CD8+ regulatory T cells in controlling self-reactive immune responses. CD4+ regulatory T cells were stronger regulators of autoreactive B cells, autoantibodies and antigen-specific antibody affinity, whereas CD8+ regulatory T cells predominantly controlled expansion of follicular helper cells and autoreactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.

|
Rescooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
from Virus World
January 5, 5:31 AM
|
Aberrant immune responses to viral pathogens contribute to pathogenesis, but our understanding of pathological immune responses caused by viruses within the human virome, especially at a population scale, remains limited. We analyzed whole-genome sequencing datasets of 6,321 Japanese individuals, including patients with autoimmune diseases (psoriasis vulgaris, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) or multiple sclerosis) and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), or healthy controls. We systematically quantified two constituents of the blood DNA virome, endogenous HHV-6 (eHHV-6) and anellovirus. Participants with eHHV-6B had higher risks of SLE and PAP; the former was validated in All of Us. eHHV-6B-positivity and high SLE disease activity index scores had strong correlations. Genome-wide association study and long-read sequencing mapped the integration of the HHV-6B genome to a locus on chromosome 22q. Epitope mapping and single-cell RNA sequencing revealed distinctive immune induction by eHHV-6B in patients with SLE. In addition, high anellovirus load correlated strongly with SLE, RA and COVID-19 status. Our analyses unveil relationships between the human virome and autoimmune and infectious diseases. Analysis of the blood DNA virome in patients with COVID-19 and autoimmune disease associates endogenous HHV-6 (eHHV-6) and high anellovirus load with increased disease risk, most notably for systemic lupus erythematosus. eHHV-6 carriers show a distinct immune response. Published in NAt. Genetics (Jan. 3, 2025): https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-024-02022-z
Via Juan Lama

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 5, 2024 4:04 AM
|
WEDNESDAY, Dec. 4, 2024 (HealthDay News) -- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in older adults has become a global public health burden, according to a study published in the Jan. 31, 2025, issue of Autoimmunity Reviews.

|
Rescooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
from Immunology
December 3, 2024 4:37 AM
|
As a pivotal cytokine, IL-22 plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. In this comprehensive review, we initially provide an overvie

|
Suggested by
LIGHTING
November 16, 2024 5:00 AM
|
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial to prevent disease development and define therapeutic strategies. Due to predominantly unspecific symptoms, diagnosis of autoimmune diseases (AID) is notoriously challenging. Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) are a promising method with the potential to enhance and expedite precise diagnostics by physicians. However, due to the difficulties of integrating and encoding multi-omics data with clinical values, as well as a lack of standardization, such systems are often limited to certain data types. Accordingly, even sophisticated data models fall short when making accurate disease diagnoses and presenting data analyses in a user-friendly form. Therefore, the integration of various data types is not only an opportunity but also a competitive advantage for research and industry. We have developed an integration pipeline to enable the use of machine learning for patient classification based on multi-omics data in combination with clinical values and laboratory results. The application of our framework resulted in up to 96% prediction accuracy of autoimmune diseases with machine learning models. Our results deliver insights into autoimmune disease research and have the potential to be adapted for applications across disease conditions.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 5, 2024 3:55 AM
|
Sixteen presentations of preclinical studies funded by the Lupus Research Alliance (LRA) to advance understanding of lupus and potential treatment pathways,...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 7, 2024 2:55 AM
|
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a prototypic autoimmune disease that primarily affects young women and causes a wide range of inflammatory manifestations. The hallmark of SLE is the production of antibodies to components of the cell nucleus (anti-nuclear antibodies [ANAs]).

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 12, 2024 4:27 AM
|
Myositis with anti-Ku-autoantibodies is a rare inflammatory myopathy associated with various connective tissue diseases. Histopathological studies have identified inflammatory and necrotizing aspects, but a precise morphological analysis and pathomechanistic disease model are lacking. We therefore aimed to carry out an in-depth morpho-molecular analysis to uncover possible pathomechanisms. Muscle biopsy specimens from 26 patients with anti-Ku-antibodies and unequivocal myositis were analyzed by immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, transcriptomics, and proteomics and compared to biopsy specimens of non-disease controls, immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), and inclusion body myositis (IBM). Clinical findings and laboratory parameters were evaluated retrospectively and correlated with morphological and molecular features. Patients were mainly female (92%) with a median age of 56.5 years. Isolated myositis and overlap with systemic sclerosis were reported in 31%, respectively. Isolated myositis presented with higher creatine kinase levels and cardiac involvement (83%), whereas systemic sclerosis-overlap patients often had interstitial lung disease (57%). Histopathology showed a wide spectrum from mild to pronounced myositis with diffuse sarcolemmal MHC-class I (100%) and -II (69%) immunoreactivity, myofiber necrosis (88%), endomysial inflammation (85%), thickened capillaries (84%), and vacuoles (60%). Conspicuous sarcoplasmic protein aggregates were p62, BAG3, myotilin, or immunoproteasomal beta5i-positive. Proteomic and transcriptomic analysis identified prominent up-regulation of autophagy, proteasome, and hnRNP-related cell stress. To conclude, Ku + myositis is morphologically characterized by myofiber necrosis, MHC-class I and II positivity, variable endomysial inflammation, and distinct protein aggregation varying from IBM and IMNM, and it can be placed in the spectrum of scleromyositis and overlap myositis. It features characteristic sarcoplasmic protein aggregation on an acquired basis being functionally associated with altered chaperone, proteasome, and autophagy function indicating that Ku + myositis exhibit aspects of an acquired inflammatory protein-aggregate myopathy.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 7, 2024 9:13 AM
|
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells are highly effective at targeting and eliminating cells of the B cell lineage. CAR T cell therapy has become a standard-of-care treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory B cell malignancies. In addition, the administration of genetically modified T cells with the capacity to deplete B cells and/or plasma cells has tremendous therapeutic potential in autoimmune diseases. In the past few years, CD19-based and B cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-based CAR T cell therapies have been applied to various B cell-mediated autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus, idiopathic inflammatory myopathy, systemic sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, myasthenia gravis and multiple sclerosis. The scientific rationale behind this approach is that deep depletion of B cells, including autoreactive B cell clones, could restore normal immune function, referred to as an immune reset. In this Review, we discuss important aspects of CAR T cell therapy in autoimmune disease, including considerations relating to patient selection, safety, efficacy and medical management. These considerations are based on the early experiences of CAR T cell therapy in autoimmune diseases, and as the field of CAR T cell therapy in autoimmune diseases continues to rapidly evolve, these issues will remain subject to ongoing refinement and adaptation. CAR T cell therapy shows promise for achieving long-term drug-free remission in various autoimmune diseases. This Review discusses the ongoing challenges and unanswered questions of CAR T cell therapy in autoimmune diseases, including pre-procedural, procedural and post-procedural considerations.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 2, 2024 1:04 PM
|
|
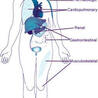




Autoimmunity is indeed one of the biggest challenge of Immunology!
Understanding the mechanisms of this physiological immune phenomenon inducing such a diverse array of diseases, joint and muscular, digestive, endocrinological, neurological, cutaneous..
Among covered diseases
Diabetes (>400 posts)
https://www.scoop.it/topic/autoimmunity?q=diabetes
Mutiple sclerosis (>100 posts)
https://www.scoop.it/topic/autoimmunity?q=multiple+sclerosis
Thyroid disorders
https://www.scoop.it/topic/autoimmunity?q=thyroid
Improving the molecular and cellular tools in use for a few decades for diagnosis and follow-up of patients, perhaps screening in the future
Autoantibodies
https://www.scoop.it/topic/autoimmunity?q=autoantibody
Mastering the molecular and cellular therapies to treat patients.
You can also find relevant informations on some other topics curated here such as
Rheumatology
http://www.scoop.it/t/rheumatology-rhumatologie
Immunology and biotherapies
http://www.scoop.it/t/immunology-and-biotherapies