 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 16, 2013 2:45 AM
|
Resources for DIU Immunologie et Biothérapies
DIU Immunologie et Biotherapies is a french diploma associating french universities and immunology laboratories. It is dedicated to the involvement of immunology in new biotherapies, either molecular or cellular.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 6, 11:25 AM
|
Check out my latest #ScienceSpeaks blog at Infectious Diseases Society of America #IDSA. #Tick-borne diseases like #Lyme are rising and spreading to more places, so clinicians and the public need to stay alert. I break down what’s in the #vaccine pipeline, especially the progress of late-stage #Lyme vaccine development, and what that could mean for prevention in the near future. I also highlight what we can do right now, including practical prevention such as avoiding bites, prompt tick removal, and timely evaluation and treatment.
The key message is that while better tools are coming, reducing risk today still depends on awareness, prevention, and early action.
📑 See comments section for link.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 6, 4:57 AM
|
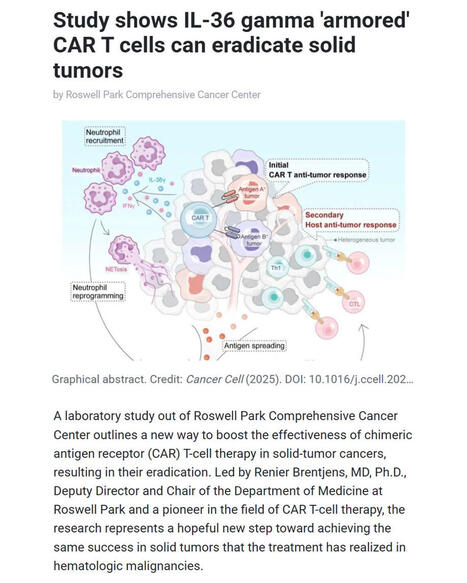
🚀 Breakthrough in CAR T-cell therapy for solid tumors
Researchers at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center report a major advance in overcoming one of #cancer #immunotherapy’s biggest challenges: treating solid #tumors with #CARTcells.
▪️ Led by Renier Brentjens, MD, PhD (Deputy Director and Chair of Medicine at Roswell Park), the team demonstrates that IL-36γ–armored CAR #Tcells can eradicate solid tumors in preclinical models by reprogramming #neutrophils to mount a powerful innate and adaptive anti-tumor #immuneresponse.
▪️ The study - published in Cancer Cell - was led by Yihan Zuo, PhD (first author) with Scott Abrams, PhD (Jacobs Family Endowed Chair of Immunology). The work shows that IL-36γ CAR T cells not only attack tumor cells directly but also drive antigen spreading, overcome tumor heterogeneity, and bypass the need for lymphodepletion, preserving neutrophils as key immune allies.
🧬 This approach offers a promising path toward extending the transformative success of CAR T-cell therapy from hematologic malignancies to solid tumors, where curative options remain limited.
🗃️ See comments for reference.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 4, 12:58 PM
|
Researchers at Texas Biologics, The University of Texas at Austin with international collaborators from the The University of Freiburg and Cardiff University / Prifysgol Caerdydd, have developed a novel engineered #antibody that prevents human #cytomegalovirus HMCV from hiding from the #immunesystem.
▪️ HCMV infects over 80% of the global population and, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), is the leading infectious cause of birth defects in the United States. Despite this, there is NO approved #vaccine, and current #antivirals can be toxic and prone to resistance.
▪️ Led by Prof. Jennifer Maynard with key contributions from Ahlam Qerqez and Prof. Jason McLellan, the team redesigned IgG1 #antibodies so they evade viral Fc receptors (vFcγRs) used by #HCMV to neutralize #immuneresponses while still activating natural killer (NK) cells to eliminate infected cells.
💡 Why this study is important: This work represents a paradigm shift in antiviral therapy - moving beyond targeting the #virus alone to empowering the immune system to clear infected cells. The approach could transform HCMV treatment for newborns, transplant recipients, cancer patients, and other immunocompromised populations, and may be applicable to other herpesviruses and pathogens with similar immune-evasion strategies.
🗃️ See comments section for reference.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 4, 5:05 AM
|
DÉCRYPTAGE - Accélérée par la pandémie de Covid-19, la recherche explore désormais des vaccins capables non plus seulement de prévenir les …

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 4, 3:51 AM
|
Restoring youth to old immune cells: mRNA therapy turns back the clock
A twice-weekly cocktail of three messenger RNAs can rejuvenate the weary immune systems of aged mice and boost responses to vaccination and cancer treatments.
- Ageing has a profound effect on the immune system, including the T cell repertoire, leading to reduced immune resilience. Central to this decline in humans and most other mammals is the involution of the thymus.
- Efforts to counter immune ageing have primarily focused on reversing thymic involution and although these strategies have provided valuable insights into immune ageing, they have been limited by effect size, toxicity or clinical feasibility.
- Here, the authors describe an approach for reconstituting thymus-derived factors in the liver to address age-related immune decline.
- First they identified signalling pathways in the thymus and peripheral blood T cells that decline with age. Then they delivered mRNAs encoding these factors (DLL1, FLT3-L and IL-7) to the liver using lipid nanoparticles (LNPs).
- Treatment with these mRNAs improved peptide vaccine responses and restored antitumour immunity in aged mice by increasing tumour-specific CD8+ infiltration and clonal diversity and synergizing with immune checkpoint blockade.
- These effects were reversible after dosing ceased and did not breach self-tolerance, in contrast to the inflammatory and autoimmune liabilities of recombinant cytokine treatment.
- These results highlight the potential of this approach to improve immune function and, more broadly, to use the liver as a transient ‘factory’ for replenishing factors that decline with age.
https://lnkd.in/eCijzNPH
https://lnkd.in/eujJmE2Z
#immunology #aging #immunity #science

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 3, 2:04 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 2, 12:58 PM
|
T cell egress technolog (S1PR1 Expression in T Cells)
T cell egress technology manipulates the exit of T cells from lymph nodes (LNs) and tissues into the bloodstream, primarily by targeting the sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 (S1PR1) pathway.
Drugs like FTY720 (fingolimod) block this pathway to trap autoimmune T cells in LNs. Conversely, manipulating (S1PR1) or CCR7 can modulate the trafficking of CAR T-cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) for improved immunotherapy.
T cell egress is the highly regulated process by which mature T cells exit lymphoid organs (like lymph nodes) into the blood, driven primarily by the S1P1 receptor (S1PR1) gradient. S1PR1 on T cells binds to high concentrations of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) in the lymph/blood compared to low levels in the lymph node, triggering migration out.
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 (S1PR1) pathway is a critical G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling mechanism that regulates immune cell trafficking (lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs), vascular development, and endothelial barrier integrity.
T cell expression of (S1PR1) enables them to follow an S1P gradient out of lymph nodes.
Spinster homolog 2 (SPNS2)
a specialized transmembrane protein acting as the primary exporter of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) from cells into the blood and lymph. It regulates immune cell trafficking, vascular development, and, when inhibited, can modulate cancer metastasis and autoimmune diseases.
Role of SPNS2: The transporter SPNS2 is crucial, as it supplies S1P to the lymph, enabling the exit.
CCR7-CCL21 Axis: CCR7 acts as a "tissue exit receptor" that promotes the movement of effector T cells from inflamed sites into the lymphatics.
CXCR4/CXCL12 Inhibition: In tumors, the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis can limit T cell egress, allowing them to remain and fight cancer. Disrupting this axis can influence the retention vs. exit of CAR T-cells.
Clinical Applications
Autoimmune Diseases: Trapping autoreactive T cells in lymph nodes using (S1PR1) modulators (e.g., multiple sclerosis treatment).
Cancer Immunotherapy (CAR T/TILs): Enhancing the retention of effector T cells within tumor tissues to improve tumor control.
Transplant Rejection: Controlling T cell migration to reduce the immune response against transplanted organs.
Current Research Directions
Targeting SPNS2: Developing inhibitors for the SPNS2 transporter for more precise control over S1P signaling than broad (S1PR1) agonists.
Controlling Effector T Cell Trafficking: Investigating how to maintain high levels of tumor-specific T cells within tumors by inhibiting their premature egress.
Regulation of Memory T Cells: Understanding how Tissue-Resident Memory (T_RM) cells are kept in place, as opposed to recirculating T cells that use the S1P-dependent egress route.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 1, 8:47 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 29, 2025 9:23 AM
|
CAR gamma-delta T Cells, Dual Targeting Immune Therapy And Can Significantly Extend Survival In Animal Model of Solid Tumor
Conventional CAR alpha-beta T cell therapy involves genetically engineering a patient's T cells to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) that binds directly to tumor surface antigens, bypassing the need for MHC antigen presentation. Upon binding, the CAR triggers T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytotoxic destruction of cancer cells via perforin/granzyme release.
But CAR T cells often become dysfunctional in the tumor microenvironment (TME) due to chronic antigen stimulation, immunosuppressive signaling, and metabolic stress, leading to T cell exhaustion and reduced persistence,
particularly in solid tumors.
CAR gamma, delta T cells engineered with Chimeric Antigen Receptors (CARs) combined with natural killer (NK) receptor NKG2D signaling offer a potent, dual-targeting immunotherapy.
They merge MHC-independent tumor recognition (via NKG2D, gamma/delta, TCR) with CAR-mediated specificity, enhancing cytotoxicity against solid tumors, reducing exhaustion, and enabling off-the-shelf, low-GVHD therapies.
CAR Design: Most constructs use the extracellular domain of NKG2D (amino acids 73-216) linked to intracellular signaling domains, such as CD3 zeta (1st generation) or combined with co-stimulatory domains like 4-1BB or CD28.
Gamma 9 delta 2 T Cell Advantages: These T cells possess natural, MHC-independent anti-tumor activity and can be easily engineered using non-viral approaches like mRNA electroporation to express NKG2D-CARs.
Direct Cytotoxicity: Upon activation, they release cytotoxic granules, including perforin and granzyme, to induce apoptosis in target cells.
Cytokine Production: They rapidly produce large amounts of inflammatory cytokines such as Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) and Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), which directly kill tumors and recruit other immune cells.
Infiltration and Persistence: CAR-gamma delta T cells, particularly Vdelta subsets, have a high capacity to infiltrate solid tumors and can persist to prevent recurrence.
Reduced Alloreactivity: They exhibit low reactivity against healthy donor tissue, making them suitable for "off-the-shelf" allogeneic CAR-T therapies.
Key Advantages:
Solid Tumor Homing: Gamma \delta T cells naturally infiltrate solid tumor microenvironments more effectively than alpha \beta T cells.
Lower risk of Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD).
Dual Killing: Combined CAR and NK receptor (NKG2D) signaling provides a more robust, multi-pronged attack.
Clinical Potential:
Preclinical studies, including work with CytoMed Therapeutics, have demonstrated that these engineered cells can significantly extend survival in animal models of solid tumors.
Research indicates that using CAR constructs with NKG2D-based mechanisms in gamma 9 delta 2 T cells is a highly promising strategy to improve the efficacy of cell-based cancer immunotherapies.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 28, 2025 5:31 AM
|
The treatment landscape for multiple myeloma is rapidly evolving, driven by T-cell-mediated tumor responses through CAR T-cell therapies and bispecific antibodies. Since KarMMa and CARTITUDE-1 established the activity of idecabtagene vicleucel and ciltacabtagene autoleucel in heavily pretreated...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 26, 2025 1:32 PM
|
The race for in vivo CAR therapy is heating up. I mapped out some of the key players.
While composing this chart, one question kept coming back: 𝗶𝘀 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝘄𝗶𝗻𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗱𝗲𝗹𝗶𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘆 𝘁𝗲𝗰𝗵𝗻𝗼𝗹𝗼𝗴𝘆 𝗮𝗺𝗼𝗻𝗴 𝘁𝗵𝗲𝘀𝗲 𝗼𝗻𝗲𝘀?
Because precise delivery is everything.
Whoever cracks cell-specific targeting doesn't just win one indication. They unlock access to every tissue with specificity. Ex vivo CAR-T would starts looking extremely limited in comparison by 𝘪𝘯 𝘷𝘪𝘷𝘰 believers.
Right now, two camps dominate:
• Non-viral mRNA-LNPs (transient or stable expression)
• LVV platforms (stable integration)
Most carry similar therapeutic payloads: CD19, CD20, or BCMA CARs to treat B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases.
But here's the problem though. The fundamental delivery challenges remain largely unsolved.
LNPs uptake is naturally liver-biased. Efficiently targeting the right T cell subsets in vivo hasn't been cracked yet. And matching the expansion and persistence of ex vivo products is still being proven out.
This is why the expression strategy matters right now.
With delivery still uncertain, transient expression through xRNA platforms offers a cleaner risk profile:
• No insertional mutagenesis risk
• Repeat dosing gives you control
• Safety profile regulators actually like
Stable integration sounds appealing until you're explaining genotoxicity concerns in a Phase 3 trial.
I'm not saying transient CAR expression solves delivery, no. But while delivery remains the bottleneck, transient expression keeps the risk manageable.
The clinical data will tell us who got it right.
But the company that solves cell-specific delivery with a clean safety profile doesn't just capture a market. They own the platform for the next decade of cell therapy.
I'll add a few companies I couldn't fit into the chart (for space reasons) in the comments, along with further readings.
What's your take? Are we looking at the winner already, or is the breakthrough still in someone's lab?
-----------------------------------------------------------
I share insights on all things xRNA, CAR-X and CGT innovation. Follow me for more biotech insights | 47 comments on LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 26, 2025 4:47 AM
|
💉 Malaria vaccines and long-acting monoclonal antibodies are moving from pipeline to programs – but how do we compare their full value across products and use cases?
📄 A new WHO-commissioned vaccine value profile brings together evidence on public health impact, economic value, and programmatic feasibility for malaria vaccines and prophylactic mAbs. It’s designed to help countries, funders, and manufacturers align R&D, financing, and introduction strategies with real-world priorities.
🔗 Read the article here: https://lnkd.in/eSyDqW95
Authors: Ashley Birkett, EVELYN KORKOR ANSAH, W. Scott Gordon, Margaret Gyapong, Shanelle Hall, Sherrie Kelly, Matt Laurens, Melissa Penny, Meredith Shirey, MIA, MPH, Larry Slutsker, Erin Sparrow, Sally Ethelston, Nelli Westercamp, Lindsey Wu, Mary Hamel. PATH, University of Health and Allied Sciences, The Yellow House, Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute, University of Maryland, The Kids Research Institute Australia, University of Basel, The University of Western Australia, World Health Organization, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 8, 7:32 AM
|
🦠rHVT IBD
🐔Protection of the "Immune Engine" (Bursa of Fabricius)-
The Bursa of Fabricius is the primary organ where a chicken’s B-lymphocytes (cells that produce antibodies) develop.Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD or Gumboro) targets and destroys these cells, leading to permanent immunosuppression.
The HVT-IBD Role: Because it uses a non-pathogenic HVT vector, the vaccine does not cause bursal atrophy or lesions.By preventing the IBD virus from damaging the bursa, the vaccine preserves the bird’s "immune engine," allowing it to produce antibodies effectively against all other diseases.
📊Overcoming the "Immunity Gap"-
One of the biggest challenges in young chicks is Maternally Derived Antibodies (MDA). In traditional vaccination, high levels of MDA can neutralize a live vaccine, leaving a "gap" where the chick is unprotected once maternal immunity fades but before vaccine immunity kicks in.[3]
The HVT-IBD Role: The HVT vector is not neutralized by IBD maternal antibodies.This allows the vaccine to be administered in the hatchery (either in ovo or at day-old), ensuring that active immunity begins to develop immediately.[1][5] This "closes the gap" and provides a seamless transition from maternal protection to vaccine-induced protection.
🐣💪Early and Lifelong Foundation-
The "immune foundation" must be established as early as possible to protect the bird during its most vulnerable stage.
Early Onset: Immunity against IBD typically begins as early as 12–14 days of age.[6]
Lifelong Duration: The HVT virus stays in the bird's system for life, continuously expressing the IBD antigen (VP2 protein). This provides a permanent immune memory without the need for repeated boosters in the field, which can be stressful and costly.
💉 Enabling "Vaccine Take" for Other Diseases-
A bird with a compromised immune foundation (due to subclinical IBD) will respond poorly to other essential vaccinations, such as those for Newcastle Disease (ND) or Infectious Bronchitis (IB). The HVT-IBD Role: By preventing immunosuppression, the HVT-IBD vaccine ensures that the bird’s immune system is "primed" and healthy enough to respond vigorously to subsequent vaccines.[5] This improves the overall "take" and efficacy of the entire vaccination program.
🪬Broad Spectrum Protection-
Field strains of IBDV are constantly evolving into variant and very virulent (vvIBDV) forms.The HVT-IBD Role: Recombinant HVT-IBD vaccines provide broad protection against a wide range of strains, including classic, variant, and very virulent strains.This ensures the immune foundation is robust enough to withstand diverse environmental challenges.
🥔Reduction of Viral Shedding-
By establishing a strong immunity early, vaccinated birds shed significantly less of the field virus into the environment. This reduces the "infection pressure" in the poultry house, protecting future flocks and further stabilizing the health foundation of the entire farm.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 6, 11:21 AM
|
⚠️ Reduced childhood vaccination policies will likely cause spikes in preventable diseases AND may reduce uptake of recommended vaccines....
👉 Reduced coverage of Diphtheria toxoid vaccine has resulted in a resurgence in cases with a high case-fatality rate in young children and treatment relying on antitoxin (DAT) ☝ most countries lack stockpiles!
It's therefore incredibly topical and important to see this study now out in Emerging Infectious Diseases highlighting the current challenges in DAT production and procurement.
🔊 https://lnkd.in/eh3Y6jzZ
Market, Manufacturing, Procurement and Stockpiling challenges (akin to those of antivenoms), threaten global health security!
We highlight an urgent need for improved coordination, financing, and innovation in DAT supply.
⏩ A transition to monoclonal antibody therapies offers a best-in-class solution to many of these challenges........ But remains neglected!
Caroline Marshall Erin Sparrow Julien Potet World Health Organization Wellcome Trust

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 5, 4:14 AM
|
Therapeutic T cell products and immunotherapies that target T cells require the manipulation of T cells ex vivo or in situ. Endogenous T cell functions are guided by their physical and biological interactions with other cells and tissues, occurring at the T cell membrane. Such T cell interfaces can be recapitulated using nanotechnologies and microtechnologies to precisely modulate and control T cell function. In this Review, we first discuss the structural and biochemical features of T cell interfaces at the cell and tissue levels, outlining how these interfaces dictate T cell function and fate. We then examine how T cell interfaces can be engineered at the nanoscale and microscale to create models for mechanistic studies, as well as scalable platforms for identifying, engineering, screening and sorting therapeutic T cells. Finally, we highlight key challenges and opportunities in the scaling and translation of these platforms for their integration into T cell therapy manufacturing processes. The function and fate of T cells are dictated by their various dynamic interactions with cells and tissues. This Review discusses the recreation of key T cell interfaces using nanotechnologies and microtechnologies for the mechanistic study of T cell biology, as well as the manufacturing and sorting of T cell products.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 4, 8:56 AM
|
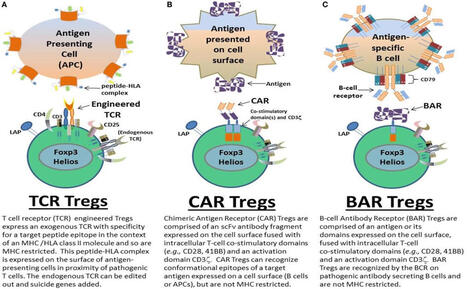
BAR T cells (B-cell Antibody Receptor T cells)
BAR T cells are engineered Regulatory T cells (Tregs) designed to treat autoimmune diseases by targeting specific antibody-producing B cells.
BAR T cells (B-cell Antibody Receptor T cells) are a type of engineered regulatory T cell (Treg) a specific receptor designed to recognize and target B-cell antigens,
notably in autoimmune diseases like hemophilia A. They function by suppressing B-cells that produce inhibitory antibodies, offering a therapeutic approach for treating harmful immune responses.
Targeting Mechanism: Similar to Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T cells, BAR T cells are engineered to bind specific pathogenic B-cell receptors (BCRs) rather than tumor antigens, allowing for highly precise, targeted immunotherapy.
BAR T cells utilize specific antigen domains (e.g., FVIII C2 domain) to bind to and suppress B-cells, often reducing the production of unwanted autoantibodies.
Process
Researchers use B-cell antibody components to create a custom receptor that allows the T-cell to bind directly to a specific autoantibody on a B-cell, rather than requiring traditional MHC antigen presentation.
The engineered BAR T cells are grown in large numbers in a laboratory, ensuring a high concentration of cells that can specifically target the disease-causing B cells.
The expanded BAR T cells are infused back into the patient.
Mechanism of action
Unlike CAR T cells that kill target cells, BAR T cells act as "living drugs" that suppress the immune response.
Upon binding the target antigen, the engineered receptor activates the regulatory T cell, which then suppresses the targeted B-cell antibody formation and immune response.
Clinical Applications
Applications: Besides hemophilia, this technology is being investigated for managing various autoimmune diseases, allergies, and other conditions involving B-cell dysfunction.
This approach is advantageous because it provides a more specific and potent alternative to broad immunosuppression, potentially leading to long-term remission in autoimmune disease patients.
Disclaimer: The information above is for informational purposes based on research studies and does not constitute medical advice.
https://lnkd.in/guctEiAc.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 4, 4:42 AM
|
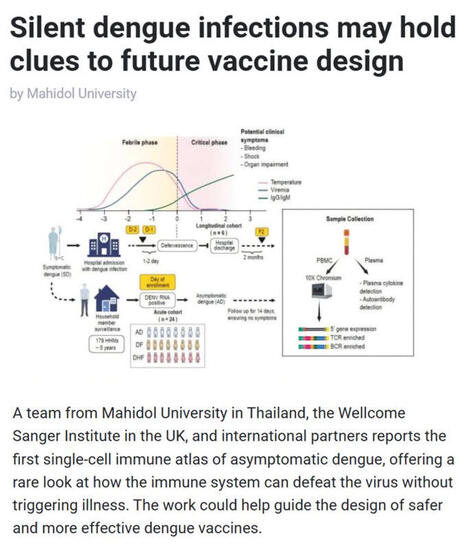
🦟 #Dengue is one of the world’s fastest-spreading #mosquito-borne diseases, with half of the global population now at risk and #climatechange is accelerating transmission. While most research focuses on people who become sick, scientists have long wondered how some individuals clear #denguevirus #DENV without ever developing symptoms.
▪️ A new study in Science Translational Medicine led by Mahidol University (Thailand), the Wellcome Sanger Institute (UK), and international partners provides the first single-cell immune atlas of asymptomatic dengue, revealing how the immune system defeats the virus without triggering illness.
▪️ Through a five-year household surveillance program in #Thailand, the team - including Assoc. Prof. Ponpan Matangkasombut, Dr. Waradon Sungnak, Dr. Tiraput Poonpanichakul, Dr. Natnicha Jiravejchakul, Prof. Sarah Teichmann FMedSci FRS, and Assoc. Prof. Varodom Charoensawan - captured extremely rare asymptomatic #infections and analyzed over 134,000 immune cells using cutting-edge single-cell RNA and immune receptor sequencing.
▪️ They found that people without symptoms showed distinct immune signatures involving CD8 #Tcells, natural killer cells, and #antibody-producing cells, while symptomatic #denguefever showed stronger inflammatory and antibody-driven processes associated with disease.
💡 Why is this research important? This work reveals how the #immunesystem can eliminate dengue without illness, provides an unprecedented dataset for global researchers, and offers a roadmap for designing safer, more effective dengue #vaccines that mimic naturally protective immune responses.
🗃️ See comments for reference.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 3, 2:05 AM
|
mRNA vaccines (including those used against #COVID19) are exceptionally good at generating #antibody responses largely because they drive germinal center formation, the immune “training hubs” that produce high-quality #antibodies and long-lived memory.
In a Cell study, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine show that the two core components of mRNA vaccines work together as built-in immune stimulators:
✅ The #mRNA (even with chemical modifications) isn’t fully “invisible” - it triggers low but meaningful type I interferon signaling that helps steer helper #Tcells toward germinal-center–supporting functions.
✅ The lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) activate dendritic cells and help position them in lymph nodes to effectively instruct T cells and support #Bcell help.
✅ Led by Michela Locci, PhD (Associate Professor of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania), the team also identifies IL-1 as a critical, independent signal shaping these responses.
Bottom line: understanding how #mRNA + LNPs cooperate to promote germinal centers and durable #immunememory can inform the design of next-generation mRNA #vaccines.
🗃️ See comments section for reference.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 2, 1:16 PM
|
The US FDA approved 46 new drugs in 2025, despite a tumultuous year at the regulatory agency.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 2, 4:38 AM
|
Over the past century, #vaccines have transformed #publichealth, most recently playing a critical role in combating the #COVID19 #pandemic. While prophylactic #cancer vaccines have successfully prevented malignancies caused by infectious agents, we are now seeing real clinical promise from therapeutic #cancervaccines designed to train the #immunesystem to eliminate established tumors.
Emerging data show encouraging outcomes:
▪️ Adjuvant setting: vaccines in #melanoma and #pancreaticcancer may reduce minimal residual disease and relapse
▪️Macrometastatic setting: in-situ vaccines have induced systemic tumor regressions in advanced #lungcancer, #breastcancer, and #lymphoma
▪️Advances are being driven by deeper understanding of tumor #immunology, incorporation of smarter vaccine components, integration of omics and #AI in vaccine design, and synergy with #immune #checkpointinhibitors
This work highlights the potential of next-generation cancer vaccines to improve outcomes and quality of life for patients worldwide. A fascinating and hopeful step forward for #cancerimmunotherapy.
Authors: Orrin Pail, MD • Matthew Lin, PhD • Theodora Anagnostou, MD • Brian Brown, PhD • Joshua Brody, MD.
Institutions: The Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA, Precision Immunology Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA, Icahn Genomics Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA, Perlmutter Cancer Center, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY, USA
🗃️ See comments section for reference.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 30, 2025 1:31 PM
|
To spur an immune response to fentanyl, a synthetic compound, the University of Houston's Colin Haile, an ARMR co-founder and scientific adviser, and his colleagues tied the opioid to something else.
They combined fentanyl fragments with deactivated diphtheria toxin and a nontoxic portion of the e-coli bacterium. This new compound builds antibodies that react to real fentanyl. These antibodies bind to the opioid, keeping it from crossing the brain's protective membrane — the blood-brain barrier — and then clearing it from the body.
In rat studies, the vaccine blocked fentanyl from entering the rodents' brain and also blocked the drug from depressing respiration and causing overdose.
Learn more about how vaccines are being used to address drug addiction.
https://lnkd.in/g2UUrZDd
#immunizations #vaccines #publichealth #fentanyl
Donate
https://lnkd.in/g2cKWfre

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 29, 2025 6:12 AM
|
Pandemic Preparedness: Key Considerations for Future Vaccine Development
As global health threats continue to evolve, the development of next-generation vaccines remains a cornerstone of pandemic preparedness. Recent analyses highlight several priorities the ecosystem must integrate to ensure rapid, scalable and equitable response in the event of a worldwide pandemic.
What must be taken into account?
1️⃣ Anticipating emerging pathogens
Zoonotic influenza, SARS-like coronaviruses and vector-borne viruses remain high-risk candidates. Vaccine platforms must be adaptable to new viral families and support rapid antigen redesign.
2️⃣ Accelerating timelines through flexible technologies
mRNA, viral vectors and recombinant platforms have demonstrated their value. Their modularity and scalability are essential to shorten development and production cycles.
3️⃣ Strengthening surveillance to guide vaccine targets
Real-time genomic and epidemiological data are critical to detect variants, adjust immunogenic targets and adapt vaccination strategies during global spread.
4️⃣ Ensuring manufacturing resilience
Distributed production capacities, standardized processes and secure supply chains will be essential to meet global demand and avoid bottlenecks seen during COVID-19.
5️⃣ Integrating One Health upstream
Climate change, biodiversity loss and urbanization increase spillover risks. Vaccine strategies must be developed in connection with environmental and animal-health surveillance.
6️⃣ Guaranteeing equitable access
Global deployment requires early planning for regulatory harmonization, technology transfer, and fair allocation frameworks to avoid widening health disparities.
At Infectious Diseases Cluster 🇫🇷 , we continue to support collaborative initiatives that bring together research, industry and public health stakeholders to strengthen preparedness capacities and accelerate vaccine innovation for future global threats.
Source: The Lancet Group Microbe
https://lnkd.in/evkgHuyt

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 27, 2025 5:21 AM
|
🧬 Lessons from Working on TILs — Part 2
T-Cell Exhaustion Is Not Just PD-1
One of the biggest misconceptions in cancer immunotherapy is that T-cell exhaustion = PD-1 expression.
Working with TILs quickly shows that exhaustion is not a single switch, but a progressive and often irreversible state. PD-1 marks early or intermediate dysfunction. But deeper exhaustion is driven by layered biology, including:
• Chronic antigen stimulation
• Transcriptional reprogramming (e.g., TOX-driven states)
• Epigenetic fixation that limits reinvigoration
• Metabolic stress within the tumor microenvironment
• Sustained inflammatory signaling that paradoxically suppresses function
This explains why checkpoint blockade can produce dramatic responses in some patients and minimal benefit in others, even when TILs are present.
In many tumors, T cells are no longer “off”; they are reprogrammed.
That distinction matters.
It reminds us that restoring anti-tumor immunity isn’t just about blocking checkpoints, but about understanding where a T cell sits along the exhaustion trajectory, and whether it’s still biologically recoverable.
#CancerImmunotherapy #TCellExhaustion #TILTherapy #ImmunoOncology #TumorMicroenvironment #CancerResearch #TNBC #TranslationalScience #ScientistsOfLinkedIn
Image Reference- Andrews LP et al. LAG-3 and PD-1 synergize on CD8⁺ T cells to drive T cell exhaustion and hinder autocrine IFN-γ-dependent anti-tumor immunity. Cell187, 4355–4372 (2024). doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.07.016 | 11 comments on LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 26, 2025 1:28 PM
|
🟥 Why Has CAR-T Cell Therapy Repeatedly Failed in Solid Tumors?
The success of CAR-T cell therapy in leukemia and lymphoma led researchers to believe that immune cells could potentially "eradicate" cancer. However, reality quickly dampened these hopes – CAR-T cell therapy has yet to achieve any significant breakthroughs in solid tumors.
Most discussions attribute the reasons to three "old problems": insufficient target specificity, strong immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment, and the difficulty of CAR-T cells entering tumor tissue. But these are merely superficial explanations. A less frequently mentioned, yet more crucial fact is that solid tumors are not a "target that can be eliminated by single cells," but rather a living, retaliatory ecosystem.
In hematological malignancies, CAR-T cells face a single population of cells floating in the blood; in solid tumors, they enter a highly organized "society"—cancer cells, fibroblasts, blood vessels, immunosuppressive cells, and metabolic waste collectively create an extremely hostile environment for outsiders. More importantly, CAR-T cells quickly "lose their identity" after entering solid tumors. Continuous antigen stimulation, hypoxia, and nutrient deprivation transform them from "killers" into "exhausted bystanders." This is not an engineering problem, but a biological one.
There's another reality that is not often discussed publicly: what solid tumors may need is not "stronger CAR-T cells," but a "reorganized immune system." This is precisely why people are turning to new approaches such as CAR-NK, CAR-M, in vivo CAR-T, microenvironment remodeling, and combined metabolic and vascular regulation.
CAR-T cell therapy hasn't failed; it has simply revealed a deeper truth: cancer is not a single enemy, but a whole set of uncontrolled tissue structures. Therefore, the real breakthrough may come from our willingness to move beyond the "single-cell weapon" mindset. Follow us (www.csteamus.com) to learn more about the latest advancements and trends in immune cell and stem cell therapies.
Reference
[1] Giulia Escobar et al, Cell Rep Med 2025 (doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102353)

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 24, 2025 4:39 AM
|
One CAR-T cell. Seven cancer cells. Seven hours.
This video captures ONE single CAR-T serially killing 7 tumor cells, triggering apoptosis after brief contacts and immediately moving on to the next target—no labels, no endpoints, no phototoxicity.
Then comes the part that matters most: only ONE cancer cell survives.
That heterogeneity—why some targets succumb while others resist sustained CAR-T pressure—is a central challenge in immuno-oncology and a key limiter of long-term therapeutic success.
Recorded using Nanolive’s label-free live-cell imaging platform, this dataset reveals continuous T-cell behavior at high spatial and temporal resolution—showing real dynamics, not assay artifacts.
🎥 Full breakdown with Dr. Roddy O’Connor (UPenn): https://bit.ly/4iYBj4l
🔬 Learn more about Nanolive’s IO imaging workflows: https://bit.ly/4povsaK
#ImmunoOncology #CAR_T #TCellBiology #CancerResearch #LiveCellImaging | 52 comments on LinkedIn
|


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...




























We use Scoop.it as preferred curation tool to collect, select, comment informations flowing on the web in this rapidly evolving theme to keep teachers abreast of scientific knowledge and help students surf the wave... Feel free to be a follower!
If you are interested
in Immunology also use http://www.scoop.it/t/immunology
in Mucosal Immunity http://www.scoop.it/t/mucosal-immunity
in Flow Cytometry and Cytomics http://www.scoop.it/t/from-flow-cytometry-to-cytomics
in Allergy an Clinical Immunology http://www.scoop.it/t/allergy-and-clinical-immunology
in Autoimmunity http://www.scoop.it/t/autoimmunity
Looking for cancer applications inside this topic, use
http://www.scoop.it/t/immunology-and-biotherapies?q=cancer
Looking for cytokines and chemokines, use
http://www.scoop.it/t/cytokines-et-chimiokines
Thanks to K Maggon for joining us. @Krishan Maggon