Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 19, 4:35 AM
|
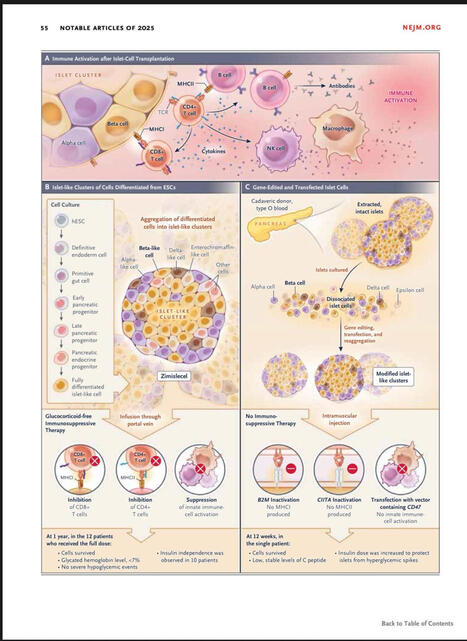
The NEJM has just released the usual end-of-the-year list of most influential papers of 2025.
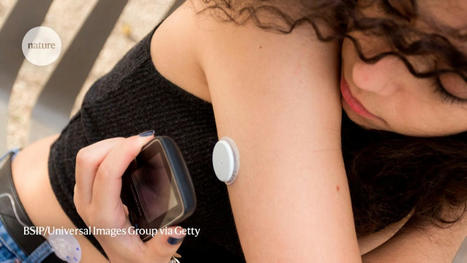
I found particularly amazing the paper and the editorial concerning allogeneic transplantation of CRISPR genetically-modified Beta cells for type 1 diabetes. A groundbreaking clinical observation that could revolutionise completely this deadly disease. More to come in 2026!
You can download it for free.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 21, 4:24 AM
|
Researchers at Academia Sinica have developed the first population-specific polygenic risk score (PRS) models for people of Han Chinese ancestry, achieving unprecedented accuracy in predicting risks for common diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, autoimmune disorders.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 10, 11:24 AM
|
Each November, we observe National Diabetes Month and engage in discussions surrounding prevention, management and the impact of this increasingly common autoimmune disease.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 3, 2024 5:17 AM
|
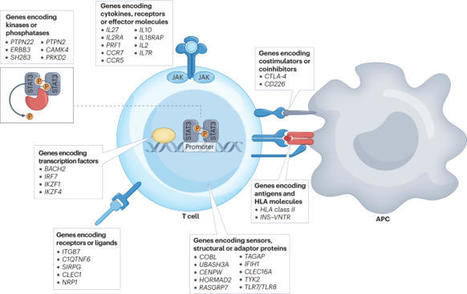
Following the seminal discovery of insulin a century ago, treatment of individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D) has been largely restricted to efforts to monitor and treat metabolic glucose dysregulation. The recent regulatory approval of the first immunotherapy that targets T cells as a means to delay the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic β-cells highlights the critical role of the immune system in disease pathogenesis and tends to pave the way for other immune-targeted interventions for T1D. Improving the efficacy of such interventions across the natural history of the disease will probably require a more detailed understanding of the immunobiology of T1D, as well as technologies to monitor residual β-cell mass and function. Here we provide an overview of the immune mechanisms that underpin the pathogenesis of T1D, with a particular emphasis on T cells. The first immune-targeted drug for type 1 diabetes (T1D), teplizumab, received regulatory approval by the US FDA in 2022. In this Review, Herold, Walker and colleagues examine the immune mechanisms that underpin T1D and provide an overview of immune-targeted strategies for T1D that are currently in development.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 9, 2023 10:17 AM
|
In young children with high genetic risk of type 1 diabetes, SARS-CoV-2 infection was temporally associated with the development of islet autoantibodies.

|
Rescooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
from Virus World
June 30, 2023 1:43 PM
|
Background Enteroviruses are routinely detected with molecular methods within large cohorts that are at risk of type 1 diabetes. We aimed to examine the association between enteroviruses and either islet autoimmunity or type 1 diabetes. Methods For this systematic review and meta-analysis, we searched PubMed and Embase for controlled observational studies from inception until Jan 1, 2023. Cohort or case-control studies were eligible if enterovirus RNA or protein were detected in individuals with outcomes of islet autoimmunity or type 1 diabetes. Studies in pregnancy or other types of diabetes were excluded. Data extraction and appraisal involved author contact and deduplication, which was done independently by three reviewers. Study quality was assessed with the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale and National Health and Medical Research Council levels of evidence. Pooled and subgroup meta-analyses were done in RevMan version 5.4, with random effects models and Mantel-Haenszel odds ratios (ORs; 95% CIs). The study is registered with PROSPERO, CRD42021278863. Findings The search returned 3266 publications, with 897 full texts screened. Following deduplication, 113 eligible records corresponded to 60 studies (40 type 1 diabetes; nine islet autoimmunity; 11 both), comprising 12077 participants (5981 cases; 6096 controls). Study design and quality varied, generating substantial statistical heterogeneity. Meta-analysis of 56 studies showed associations between enteroviruses and islet autoimmunity (OR 2·1, 95% CI 1·3–3·3; p=0·002; n=18; heterogeneity χ2/df 2·69; p=0·0004; I2=63%), type 1 diabetes (OR 8·0, 95% CI 4·9–13·0; p<0·0001; n=48; χ2/df 6·75; p<0·0001; I2=85%), or within 1 month of type 1 diabetes (OR 16·2, 95% CI 8·6–30·5; p<0·0001; n=28; χ2/df 3·25; p<0·0001; I2=69%). Detection of either multiple or consecutive enteroviruses was associated with islet autoimmunity (OR 2·0, 95% CI 1·0–4·0; p=0·050; n=8). Detection of Enterovirus B was associated with type 1 diabetes (OR 12·7, 95% CI 4·1–39·1; p<0·0001; n=15). Interpretation These findings highlight the association between enteroviruses and islet autoimmunity or type 1 diabetes. Our data strengthen the rationale for vaccine development targeting diabetogenic enterovirus types, particularly those within Enterovirus B. Prospective studies of early life are needed to elucidate the role of enterovirus timing, type, and infection duration on the initiation of islet autoimmunity and the progression to type 1 diabetes. Published in The Lancet (June 27, 2023):
Via Juan Lama

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 2, 2023 6:59 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 7, 2023 2:33 AM
|
pathophysiological components. Information garnered through many large multicenter cohort studies, multi-integration of bio-information obtained using genomics, epigenomics, proteomics and metabolomics approaches, and the utilization of datadriven classification strategies have drastically altered...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 11, 2022 4:09 AM
|
I recently got a diabetes diagnosis, and it was a surprise to me that diabetes type I is classified as an autoimmune disorder. I know diabetes is an epidemic in the U.S., but how common is it? What is the most common autoimmune disease?

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
October 28, 2022 1:37 PM
|
The study by Warncke et al. (13) raises several questions about the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. First, what is the true role of autoimmunity, an important precipitating factor or a mere epiphenomenon?

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 8, 2022 4:16 AM
|
Diabetes is a general term for disorders characterised by polyuria. It usually refers to diabetes mellitus, a common chronic syndrome of impaired carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism owing to insufficient secretion of insulin and/or target-tissue insulin resistance.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 20, 2022 4:31 AM
|
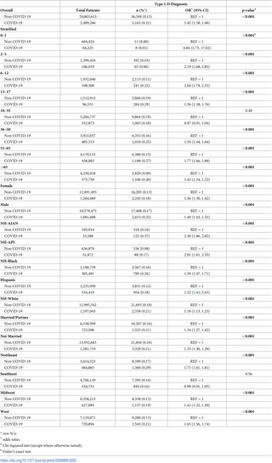
Objective To assess the risk of new-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D) diagnosis following COVID-19 diagnosis and the impact of COVID-19 diagnosis on the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in patients with prior T1D diagnosis.

|
Suggested by
LIGHTING
January 8, 2022 2:41 AM
|
Abstract Emerging evidence indicates a bi-directional relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and diabetes. The possibility exists that SARS-CoV-2 could induce diabetes, but it is not yet clear whether thi...
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 18, 4:42 AM
|
Fatty liver disease is not just a liver problem.
It is a whole-body metabolic disease.
A major review by Prof. Norbert Stefan, Hannele Yki-Järvinen and Brent A. Neuschwander-Tetri shows that metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease affects nearly 4 in 10 adults worldwide and most people with it do not die from liver failure, but from heart disease and cancer…
Important:
• Fatty liver comes in different types, driven by metabolism, fat distribution, or genetics
• The liver actively worsens blood sugar, cholesterol, and clotting risk
• Weight loss helps many…but not everyone responds the same way
• Some treatments improve liver health even without weight loss
The key message is simple:
One-size-fits-all medicine does not work for fatty liver disease!!!
Prevention, early detection and treatment need to focus on metabolic health across the whole body, not just liver enzymes…
If we treat fatty liver early, we also reduce diabetes, heart attacks and strokes later 🤞🏼
What should come first in routine care: liver screening, metabolic screening or both?
If useful, save, share or add your perspective below.
Read original review in The Lancet Group: https://lnkd.in/g3m4tA3k
#metabolichealth #fattyliver #cardiovascularhealth #prevention #publichealth

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 15, 5:20 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 7, 2:32 AM
|
The age of immunotherapy for type 1 diabetes is upon us! Thrilled by the opportunity to contribute to this review led by Remi Creusot at Columbia University!#immunologymatters #endt1d https://lnkd.in/eQ_E2j5d

|
Scooped by
Eva Feigerlova
November 26, 2023 6:24 AM
|
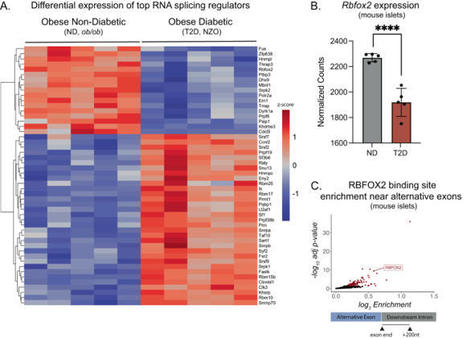
Insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta cell is a tightly regulated process that is vital for maintaining blood glucose homeostasis. Here, the authors show that the RNA binding protein RBFOX2 is a regulator of insulin secretion through the alternative splicing of genes required for insulin...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 22, 2023 2:05 AM
|
The spike in childhood type 1 diabetes opened new avenues for researchers to explore the cause of the disease.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 17, 2023 3:09 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
January 17, 2023 4:22 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 17, 2022 1:58 AM
|
Background The gastrointestinal ecosystem is a highly complex environment with a profound influence on human health. Inflammation in the gut, linked to an altered gut microbiome, has been associated with the development of multiple human conditions including type 1 diabetes (T1D).

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 14, 2022 11:43 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
October 15, 2022 11:04 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 30, 2022 1:10 AM
|
Autoimmune diabetes arises spontaneously in Non-Obese Diabetic (NOD) mice, and the pathophysiology of this disease shares many similarities with human type 1 diabetes. Since its generation in 1980, the NOD mouse, derived from the Cataract Shinogi strain, has represented the gold standard of spontaneous disease models, allowing to investigate autoimmune diabetes disease progression and susceptibility traits, as well as to test a wide array of potential treatments and therapies. Beyond autoimmune diabetes, NOD mice also exhibit polyautoimmunity, presenting with a low incidence of autoimmune thyroiditis and Sjögren’s syndrome. Genetic manipulation of the NOD strain has led to the generation of new mouse models facilitating the study of these and other autoimmune pathologies. For instance, following deletion of specific genes or via insertion of resistance alleles at genetic loci, NOD mice can become fully resistant to autoimmune diabetes; yet the newly generated diabetes-resistant NOD strains often show a high incidence of other autoimmune diseases. This suggests that the NOD genetic background is highly autoimmune-prone and that genetic manipulations can shift the autoimmune response from the pancreas to other organs. Overall, multiple NOD variant strains have become invaluable tools for understanding the pathophysiology of and for dissecting the genetic susceptibility of organ-specific autoimmune diseases. An interesting commonality to all autoimmune diseases developing i

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 19, 2022 3:15 AM
|
Information on a number of conditions that are associated with diabetes including coeliac disease, thyroid disease and dental health complications.
|

 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...