|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
onto Immunology and Biotherapies March 28, 6:50 AM
|
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
|

|
Rescooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
from Hésitations Vaccinales: Observatoire HESIVAXs
May 8, 5:25 AM
|
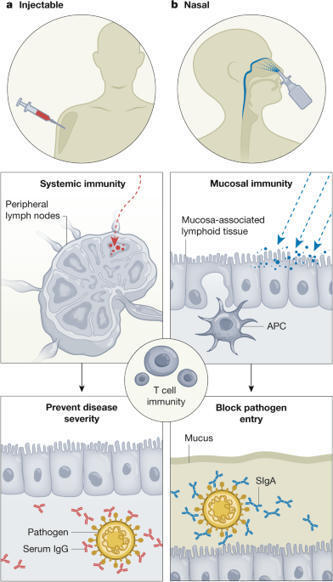
Beginning with Edward Jenner’s discovery of the smallpox vaccine, the ever-expanding repertoire of vaccines against pathogens has saved many lives. During the COVID-19 pandemic, a revolutionary mRNA injectable vaccine emerged that effectively controlled the severity of disease caused by SARS-CoV-2. This vaccine induced potent antigen-specific neutralizing serum IgG antibodies, but was limited in its ability to prevent viral invasion at the respiratory surfaces. Nasal vaccines have attracted attention as a potential strategy to combat respiratory infections and prepare for future pandemics. Input from disciplines such as microbiology, biomaterials, bioengineering and chemistry have complemented the immunology to create innovative delivery systems. This approach to vaccine delivery has yielded nasal vaccines that induce secretory IgA as well as serum IgG antibodies, which are expected to prevent pathogen invasion, thereby diminishing transmission and disease severity. For a nasal vaccine to be successful, the complexity of the relevant anatomical, physiological and immunological properties, including the proximity of the central nervous system to the nasal cavity, must be considered. In this Review, we discuss past and current efforts as well as future directions for developing safe and effective nasal vaccines for the prevention of respiratory infections. This Review provides an overview of progress and future directions in the development of nasally administered vaccines for respiratory infections.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 30, 6:47 AM
|
#T2Evolve survey results on analytical methods for CAR T cells. A nice overview of the European landscape !

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 19, 4:24 AM
|
The effectiveness of intramuscular vaccines aimed at preventing severe COVID-19 remains limited due to waning immunity and the emergence of novel variants. Next-generation vaccines are needed for broader protection and blocking virus transmission. Here, we rationally designed an original nasal subunit vaccine composed of a fusion protein (SwFN) made of Wuhan spike and nucleoprotein combined with biocompatible mucosal nanocarriers (Nc). In mouse model, the nasal Nc-SwFN vaccine elicited multivalent serum and mucosal neutralizing antibodies. Robust spike and nucleoprotein cross-reactive immunity against variants was induced with a predominant phenotype of resident memory T cells in the lungs. Moreover, Nc-SwFN led to protective responses against Wuhan and Delta infection in relevant models with an absence of morbidity, mortality, and virus dissemination in the lungs and brain. Finally, Nc-SwFN drastically reduced host-to-host transmission. These promising results underscore the advantages of the nasal Nc-SwFN approach as a broad-spectrum vaccine candidate against current and emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 17, 7:03 AM
|
BMJ Publishing Group. Pancreatic Cancer. https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-us/265 Updated November 19, 2024. Accessed March 19, 2025. Yu B, et al. Frontiers in pancreatic cancer on biomarkers, microenvironment, and immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2025;610:217350.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 13, 7:52 AM
|
#highlyviewed
📢 An Update on Anti- #COVID19 #Vaccines and the Challenges to Protect Against New #SARSCoV2 Variants
👨🎓 by Fábio Mambelli et al.
🔗 Full article: mdpi.com/2076-0817/14/1/23
The COVID-19 pandemic has posed a significant threat to global health systems, with extensive impacts across many sectors of society. The pandemic has been responsible for millions of deaths worldwide since its first identification in late 2019. Several actions have been taken to prevent the disease, including the unprecedented fast development and global vaccination campaigns, which were pivotal in reducing symptoms and deaths. Given the impact of the pandemic, the continuous changes of the virus, and present vaccine technologies, this review analyzes how, so far, we have met the challenge posed by the emergence of new variants and discusses how next-generation pan-coronavirus vaccines, with enhanced longevity and breadth of immune responses, may be tackled with alternative administration routes and antigen delivery platforms. By addressing these critical aspects, this review aims to contribute to the ongoing efforts to achieve long-term control of COVID-19, stimulating the discussion and work on next-generation vaccines capable of facing future waves of infection.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 7, 3:40 AM
|
Australia approves its first non-COVID mRNA vaccine, Moderna’s mresvia, for RSV in older adults. The U.S. FDA clears a freeze-dried Jynneos for mpox and smallpox, boosting biodefense readiness. Pfizer expands RSV vaccine Abrysvo use in Europe to at-risk adults. Desentum reports positive Phase 1 results for birch pollen allergy vaccine DM-101PX. NEC unveils a secure workflow for personalized cancer vaccine delivery. Novavax awaits FDA approval for its protein-based COVID-19 vaccine, offering a non-mRNA alternative backed by Phase 3 safety and efficacy data.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 3, 6:02 AM
|
#Immunotherapy | #AutoimmuneDiseases | #Cancer | #Transplantation | The Role of #RegulatoryTcells ↔ #Endothelial Cells Crosstalk | Breaking Perspective at…

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 27, 5:10 AM
|
🧬 𝗡𝗲𝘄 𝗦𝘁𝘂𝗱𝘆 𝗥𝗲𝘃𝗲𝗮𝗹𝘀 𝗛𝗼𝘄 𝗺𝗥𝗡𝗔 𝗖𝗢𝗩𝗜𝗗-𝟭𝟵 𝗩𝗮𝗰𝗰𝗶𝗻𝗲𝘀 𝗧𝗿𝗮𝗶𝗻 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗜𝗺𝗺𝘂𝗻𝗲 𝗦𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺’𝘀 '𝗟𝗼𝗻𝗴-𝗧𝗲𝗿𝗺…

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 18, 5:52 AM
|
I'm pleased to share with you the first of two publications with Arti Rai on the legal and regulatory landscape around biologics manufacturing patents. Using…

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 10, 5:06 AM
|
𝐂𝐀𝐑 𝐓 𝐓𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐩𝐲 𝐢𝐧 𝐍𝐨𝐧-𝐎𝐧𝐜𝐨𝐥𝐨𝐠𝐲 👇
CAR T cell therapy has transformed cancer treatment, but its potential extends far beyond oncology.… | 24 comments on LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 20, 6:40 AM
|
A fundamental challenge for cancer vaccines is to generate long-lived functional T cells that are specific for tumour antigens. Here we find that mRNA–lipoplex vaccines against somatic mutation-derived neoantigens may solve this challenge in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), a lethal cancer with few mutations. At an extended 3.2-year median follow-up from a phase 1 trial of surgery, atezolizumab (PD-L1 inhibitory antibody), autogene cevumeran1 (individualized neoantigen vaccine with backbone-optimized uridine mRNA–lipoplex nanoparticles) and modified (m) FOLFIRINOX (chemotherapy) in patients with PDAC, we find that responders with vaccine-induced T cells (n = 8) have prolonged recurrence-free survival (RFS; median not reached) compared with non-responders without vaccine-induced T cells (n = 8; median RFS 13.4 months; P = 0.007). In responders, autogene cevumeran induces CD8+ T cell clones with an average estimated lifespan of 7.7 years (range 1.5 to roughly 100 years), with approximately 20% of clones having latent multi-decade lifespans that may outlive hosts. Eighty-six percent of clones per patient persist at substantial frequencies approximately 3 years post-vaccination, including clones with high avidity to PDAC neoepitopes. Using PhenoTrack, a novel computational strategy to trace single T cell phenotypes, we uncover that vaccine-induced clones are undetectable in pre-vaccination tissues, and assume a cytotoxic, tissue-resident memory-like T cell state up to three years post-vaccination with preserved neoantigen-specific effector function. Two responders recurred and evidenced fewer vaccine-induced T cells. Furthermore, recurrent PDACs were pruned of vaccine-targeted cancer clones. Thus, in PDAC, autogene cevumeran induces de novo CD8+ T cells with multiyear longevity, substantial magnitude and durable effector functions that may delay PDAC recurrence. Adjuvant mRNA–lipoplex neoantigen vaccines may thus solve a pivotal obstacle for cancer vaccination. In a phase 1 trial, patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma who were treated with surgery and bespoke neoantigen mRNA vaccines combined with anti-PD-L1 and chemotherapy exhibited marked long-lived persistence of neoantigen-specific CD8+ T cell clones, which correlated with prolonged recurrence-free survival at a 3.2-year follow-up.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 20, 10:26 AM
|
In vivo CAR engineering for immunotherapy
In this Review, the authors discuss current strategies for in vivo CAR engineering of T cells and other immune cells and explore future directions and potential applications for the advancement of in vivo CAR engineering technologies.
- Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered immune cell therapy represents an important advance in cancer treatments. However, the complex ex vivo cell manufacturing process and stringent patient selection criteria curtail its widespread use.
- In vivo CAR engineering is emerging as a promising off-the-shelf therapy, providing advantages such as streamlined production, elimination of patient-specific manufacturing, reduced costs and simplified logistics.
- Among the various approaches to in vivo CAR engineering, LNP–mRNA-based CARs have a strong chance of reaching the clinic first, leveraging the manufacturing and regulatory advancements established during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Preclinical proof-of-concept studies in cancer and cardiac injury models have demonstrated functional equivalence between therapeutic cells that were engineered in vivo and those produced via conventional ex vivo methods.
- Before taking in vivo CAR engineering to the clinic, it is essential to conduct a comparative analysis across the various vector technologies to identify those that provide an optimal balance among efficacy, immunogenicity and safety.
- Patient selection for in vivo CAR engineering would be likely to prioritize individuals with relatively intact immune systems, as endogenous T cells must respond to the in vivo gene delivery, expand and persist for therapeutic efficacy. This could exclude heavily pretreated patients with profound lymphopenia or those with a highly immunosuppressive TME.
https://lnkd.in/ePhBCVsS
#celltherapy #CART #immunotherapy

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 7, 11:19 AM
|
𝐁𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐤𝐭𝐡𝐫𝐨𝐮𝐠𝐡 𝐢𝐧 𝐆𝐞𝐧𝐞 𝐓𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐩𝐲:
Life-Changing Miracle for Baby with Fatal Disease 👇
Eisa Hussain, a four-year-old boy born with the severe form of leukocyte adhesion deficiency 1 (LAD-1), was given a "death sentence" without treatment.
This ultra rare disease cripples the immune system, often leading to death before age two.
👉 This innovative gene therapy, developed by Rocket Pharmaceuticals, used Eisa’s own stem cells at GOSH to replace the faulty gene responsible for the condition, restoring his immune system.
Now, several months after receiving the treatment, Eisa is thriving, playing football, attending school, and living a normal life something his family once thought impossible.
This incredible breakthrough is a beacon of hope for other families facing rare, life-threatening conditions.
Amazing to see just how powerful gene therapy is in saving lives 👏
#genetherapy #raredisease #celltherapy #CGTweekly | 26 commentaires sur LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 22, 5:33 AM
|
🚀 The Ultimate Guide to ADC Drugs 🚀
Want to know everything about the 17 approved ADC drugs worldwide in 2025? We've got you covered! From advanced cancer therapies to the latest treatment breakthroughs, this is the most comprehensive summary yet.
🔍 Discover:
✅ All 17 FDA-approved ADC drugs
✅ Key details on each drug's target and mechanism
✅ Global approval updates
Don't miss out on the full breakdown! Click below to read the full article. ⬇️
https://lnkd.in/gAjYyszC
#ADC #Pharma #DrugDevelopment #CancerTreatment #Biotech #Pharmaceuticals

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 19, 2:29 AM
|
Malaria vaccine research has progressed significantly, with RTS,S/AS01 and R21/Matrix-M receiving WHO endorsement in 2021 / 2023. These vaccines show promise, but challenges like vaccine adherence, strain variation, and resistance persist, highlighting the need for more effective, broad-reaching interventions.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 16, 7:32 AM
|
🚫 𝗡𝗼𝘁 𝗮𝗹𝗹 𝗺𝗥𝗡𝗔 𝗱𝗲𝗹𝗶𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘆 𝘀𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺𝘀 𝗮𝗿𝗲 𝗯𝘂𝗶𝗹𝘁 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝘀𝗮𝗺𝗲.
Some? Bare-bones.
Others? Engineered with surgical precision.
🧪 But every single one reveals something deeper—
---> Formulation strategy.
---> Biocompatibility.
---> How far we’ve come in drug delivery science.
👇 Here's a visual buffet of mRNA vaccine delivery platforms—each with its own size, mechanism, and logic:
📍 Naked mRNA – No carrier. Vulnerable. Fast degradation.
📍 Electroporation – A jolt to get inside cells. Effective, but tech-heavy.
📍 Protamine-complexed – Cationic peptide hugs mRNA. More stable, better uptake.
📍 Cationic nanoemulsion – Think oil-in-water with a positive twist.
📍 Dendrimer + PEG-lipid – Custom-designed for precision and low immunogenicity.
📍 Protamine in PEG-lipid NP – Double protection. Peptide inside, stealth outside.
📍 PEI-based – Potent. But needs careful formulation to avoid toxicity.
📍 PEI + lipids – A more balanced version for smoother biocompatibility.
📍 Polysaccharide-based – Like chitosan. Gentle and stable.
📍 Cationic lipid nanoparticles – Classic workhorses: DOTAP, DOPE, and friends.
📍 Cationic lipids + cholesterol ± PEG-lipid – Combo packs for optimal stability and immune modulation.
✨ And then there’s ex vivo dendritic cell loading:
💸 Pricey.
🕒 Time-consuming.
🎯 But unbeatable when precision targeting really matters.
💡 Bottom line:
In mRNA therapeutics, delivery isn’t just how you get there—it’s the whole mission.
It’s the difference between "potential" and "performance."
💬 What delivery tech are you watching (or working on) in this space?
👇 Let’s break down what works, what’s evolving, and what’s next.
#mRNADelivery #LipidNanoparticles #RNAFormulation #NonViralVectors #mRNATherapeutics #FormulationStrategy #TechnoPharmaSphere

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 10, 9:54 AM
|
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-based therapies developed for the treatment of haematological malignancies have recently been repurposed to treat refractory systemic autoimmune diseases.
📖 In a NEW Review Marc Scherlinger and colleagues critically discuss the current data available on the use of CAR-based therapy in systemic autoimmune diseases, the current challenges, and the potential next steps toward their implementation into clinical practice. Beyond the targeting of B cells via CD19, the advantages and potential pitfalls of targeting plasma cells (B-cell Maturation Antigen or CD138) and other non-immune targets, such as fibroblast activated protein, and of aiming to restore immune homeostasis using CAR T regulatory cells, are also discussed.
Read the full Review here 👉 https://lnkd.in/eB7cvhGG
Alt text: Current and future strategies for CAR use in humans

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 4, 11:51 AM
|
Gavi and its partners have identified 11 needle-free vaccine patches that should be prioritised to boost immunisation coverage in low- and middle-income countries.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 2, 12:22 PM
|
🏭 𝐌𝐚𝐧𝐮𝐟𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐒𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐠𝐢𝐞𝐬 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐂𝐀𝐑 𝐍𝐊 𝐂𝐞𝐥𝐥 𝐓𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐩𝐢𝐞𝐬: 𝐂𝐡𝐚𝐥𝐥𝐞𝐧𝐠𝐞𝐬 & 𝐈𝐧𝐧𝐨𝐯𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬
Manufacturing CAR NK cells at sufficient scale and quality for clinical use is no easy feat. Robust GMP-compliant protocols are essential, but strategies vary depending on the starting material and proprietary technologies.
Here’s a look at how different companies are tackling this challenge:
🩸 𝐏𝐁-𝐍𝐊 (𝐏𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐩𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐁𝐥𝐨𝐨𝐝-𝐃𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐝 𝐍𝐊 𝐂𝐞𝐥𝐥𝐬)
Companies like Nkarta, Inc. use healthy donor NK cells, activated with feeder cells and genetically modified using γ-retrovirus to introduce a CAR and IL-15. Cells are expanded and cryopreserved for off-the-shelf use.
🧬 𝐂𝐁-𝐍𝐊 (𝐂𝐨𝐫𝐝 𝐁𝐥𝐨𝐨𝐝-𝐃𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐝 𝐍𝐊 𝐂𝐞𝐥𝐥𝐬)
Artiva Biotherapeutics and Takeda leverage donor CB units, selecting for high-affinity CD16 variants or KIR ligand mismatches to enhance anti-tumor activity. Genetic engineering (via lentivirus/retrovirus) introduces CAR and IL-15, followed by expansion and storage.
🦠 𝐢𝐏𝐒𝐂-𝐍𝐊 (𝐈𝐧𝐝𝐮𝐜𝐞𝐝 𝐏𝐥𝐮𝐫𝐢𝐩𝐨𝐭𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐦 𝐂𝐞𝐥𝐥-𝐃𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐝 𝐍𝐊 𝐂𝐞𝐥𝐥𝐬)
Fate Therapeutics Inc. uses a clonal iPSC master bank to generate NK cells, incorporating genetic modifications such as IL-15RF expression and CD38 knockout, enabling high-scale production.
⚡ 𝐍𝐊-𝟗𝟐 (𝐈𝐦𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐭𝐚𝐥𝐢𝐳𝐞𝐝 𝐍𝐊 𝐂𝐞𝐥𝐥 𝐋𝐢𝐧𝐞)
Trials like NCT03383978 explore NK-92-based CAR NK cells, expanded under GMP conditions. Due to their tumorigenic nature, γ-irradiation is applied before infusion to prevent proliferation while maintaining potency.
Each approach presents unique advantages and challenges, shaping the future of off-the-shelf cell therapy. As technology advances, optimizing manufacturing efficiency and scalability will be key to ensuring broader patient access.
💬 What do you think is the most promising approach for CAR NK therapies ? Let’s discuss !
#CellTherapy #CellandGeneTherapy #CARNK #GMP #Manufacturing #Immunotherapy #Oncology

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 28, 4:50 AM
|
📚🔬Innovation médicale et prix des médicaments : un équilibre économique à trouver
Nouveaux traitements, thérapies géniques, accès aux soins… Derrière chaque…

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 27, 5:00 AM
|
Vaccines are one of the most effective #PublicHealth tools in our toolbox. Combination vaccines, where one vaccine covers multiple diseases or strains, could…

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 14, 4:35 AM
|
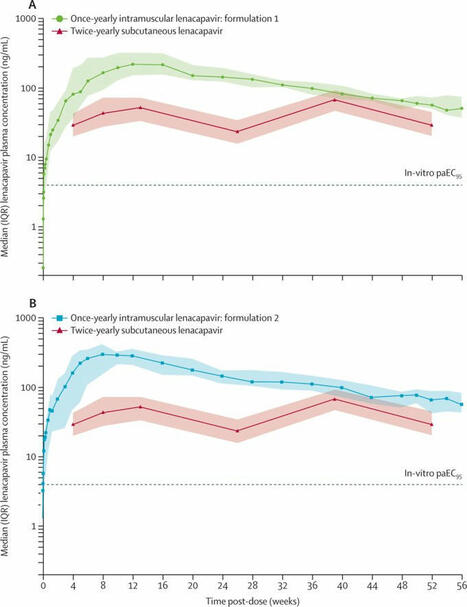
Un médicament administré par injection une fois par an a la possibilité de prévenir l'infection par le VIH.
Ceci pourrait changer complétement la donne en…

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 9, 5:36 AM
|
CAR-T vs CAR-NK therapies:
How do they compare?
Let's break it down:
1. Relative Abundance in the Body
- CAR-T: T cells = ~30-60% of lymphocytes (easier… | 80 comments on LinkedIn