Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 22, 9:38 AM
|
Ever wondered about monoclonal antibody applications? The image contains every FDA-approved monoclonal antibody arranged by therapeutic areas.
Bi- and tri-specific antibodies are hot topics, but classical monoclonals (mAbs) are the workhorses of modern biotherapeutics.
In 1975, Georges Köhler and César Milstein, working in Cambridge, unlocked a new era of medicine with the development of the hybridoma technique.
That was the first method for mass-producing mAbs.
The first therapeutic mAb (Orthoclone OKT3) was approved in 1986, but there are now >100 FDA-approved mAbs.
➟ Oncology and haematology remain dominant applications of mAbs.
➟ Neurology and dermatology are growing fast with CGRP blockers and IL-23/IL-17 inhibitors.
➟ Interestingly, nearly 40 % of approvals are outside of cancer. I thought it would have been less.
Do you think bi-specifics will catch up?
---
* Data source: The Antibody Society.
** Some antibodies are approved for multiple therapeutic areas, and commercial rights may vary across jurisdictions or under specific licensing agreements.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 20, 5:19 AM
|
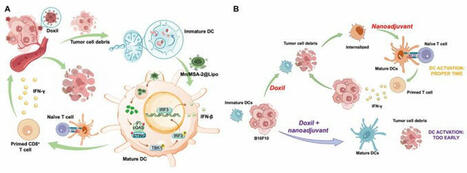
#Immunotherapy | "Right Time, Right Place" | Lymph Node-targeted temporally programmed #STING nanoadjuvant delivery unlocks synergistic chemotherapy-induced anti-#Tumor #Immunity | Breaking at Science Magazine Advances |
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) agonists have attracted notable attention for their potent immune activation capabilities. However, their clinical application is hindered by systemic toxicity and delivery inefficiencies.
Here*, researchers addressed these challenges by developing a lymph node–targeted STING agonist nanoadjuvant (Mn/MSA-2@Lipo) combined with a temporally optimized delivery strategy. Mn/MSA-2@Lipo uses manganese ions to amplify STING pathway activation while achieving efficient lymph node accumulation and antigen presentation.
They first induced immunogenic cell death (ICD) through chemotherapy to release tumor antigens, followed by the administration of the nanoadjuvant at an optimized time interval, the approach effectively synchronizes dendritic cell (DC) antigen uptake and maturation. This combination therapy notably enhanced antitumor immunity in melanoma and breast cancer models, achieving complete tumor regression and inducing long-lasting immune memory, all while demonstrating an excellent safety profile.
These findings highlight the critical importance of delivery timing optimization, offering a promising strategy for the clinical translation of STING agonists and the design of advanced immunotherapies.
*https://lnkd.in/epVJs-GE
Celentyx Ltd #immunooncology #drugdiscovery www.celentyx.com
Professor Nicholas Barnes PhD, FBPhS Omar Qureshi Catherine Brady
SUMMARY FIGURE | (A) Schematic of temporally programmed STING nanoadjuvant delivery unlocks synergistic chemotherapy-induced antitumor immunity | (B). Schematic representation of the temporally programmed delivery strategy. The top panel illustrates the optimal sequence of chemotherapy and nanoadjuvant delivery. Administering Mn/MSA-2@Lipo 48 hours after Doxil allows DCs to capture tumor antigens prior to maturation, enabling efficient cross-presentation to CD8+ T cells in the tdLNs. This strategy enhances CD8+ T cell activation, subsequent tumor cell destruction, and long-term immune memory. The bottom panel depicts premature adjuvant administration, leading to early DC maturation, reduced phagocytic capacity, and diminished antitumor immune responses |

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 8, 4:44 AM
|
gains économiques générés par l'achat de médicaments biosimilaires, étude réalisée par l'OMEDIT de la région Grand Est, PUI...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
June 25, 9:26 AM
|
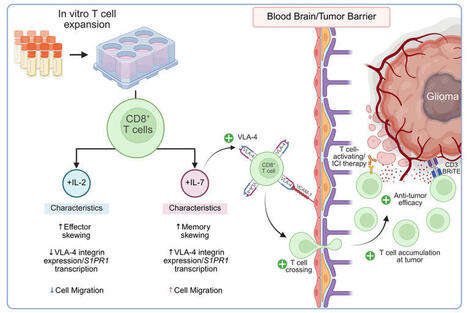
IL-7–expanded CD8+ T cells demonstrate increased accumulation within orthotopic glioblastoma models despite endogenous T cell sequestration in bone marrow. Though peripherally administered, activated autologous T cells have been shown to cross the BBB under physiologic conditions (28), their...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
June 20, 6:47 AM
|
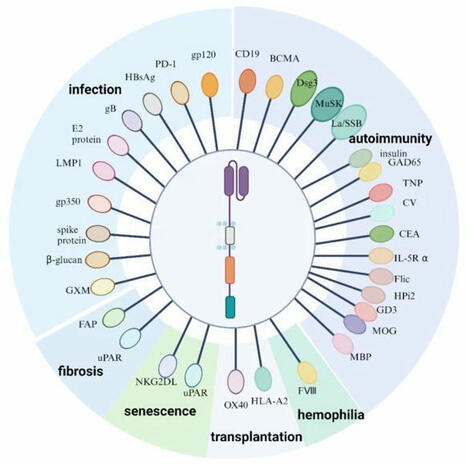
𝐂𝐀𝐑 𝐓 𝐓𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐩𝐲 𝐢𝐧 𝐍𝐨𝐧-𝐎𝐧𝐜𝐨𝐥𝐨𝐠𝐲 👇
CAR T cell therapy has transformed cancer treatment, but its potential extends far beyond oncology.
The figure below illustrates diverse CAR T cell targets in non-oncological diseases:
- Autoimmune diseases,
- Infections,
- Fibrosis,
- Haemophilia,
- Aging.
Exciting see the next-gen CARs tackle areas beyond oncology. Dual-targeting CARs (e.g., CD19-BCMA for lupus) are proving especially effective in tackling treatment-resistant diseases.
#oncology #immunology #celltherapy #CGTweekly

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 28, 3:47 AM
|
The response to vaccination depends on many factors and is based on the 4 Ws: Who, When, What, and Where.
In this article, the authors, focusing on the last W (Where), sought to identify the determinants associated with a better response to booster vaccination when administered at the same site as the initial vaccination.
They were able to show that in mice Bmems in dLNs reside in a subcapsular niche rich in CD169+ macrophages (SSMs) that interact closely with these cells, promoting their re-entry into germinative centers (GCs) after booster vaccination. Bmems in ndLNs (non-draining LNs) are more dispersed, migrate deeper into the follicles, and preferentially differentiate into plasma cells rather than GC cells.
The study in the mouse model was supplemented by a study in humans comparing, as has been done in the past, ipsilateral versus contralateral booster vaccination with a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine, demonstrating the superiority of ipsilateral vaccination.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 25, 3:57 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 20, 10:26 AM
|
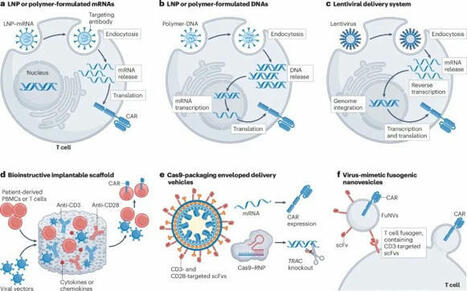
In vivo CAR engineering for immunotherapy
In this Review, the authors discuss current strategies for in vivo CAR engineering of T cells and other immune cells and explore future directions and potential applications for the advancement of in vivo CAR engineering technologies.
- Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered immune cell therapy represents an important advance in cancer treatments. However, the complex ex vivo cell manufacturing process and stringent patient selection criteria curtail its widespread use.
- In vivo CAR engineering is emerging as a promising off-the-shelf therapy, providing advantages such as streamlined production, elimination of patient-specific manufacturing, reduced costs and simplified logistics.
- Among the various approaches to in vivo CAR engineering, LNP–mRNA-based CARs have a strong chance of reaching the clinic first, leveraging the manufacturing and regulatory advancements established during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Preclinical proof-of-concept studies in cancer and cardiac injury models have demonstrated functional equivalence between therapeutic cells that were engineered in vivo and those produced via conventional ex vivo methods.
- Before taking in vivo CAR engineering to the clinic, it is essential to conduct a comparative analysis across the various vector technologies to identify those that provide an optimal balance among efficacy, immunogenicity and safety.
- Patient selection for in vivo CAR engineering would be likely to prioritize individuals with relatively intact immune systems, as endogenous T cells must respond to the in vivo gene delivery, expand and persist for therapeutic efficacy. This could exclude heavily pretreated patients with profound lymphopenia or those with a highly immunosuppressive TME.
https://lnkd.in/ePhBCVsS
#celltherapy #CART #immunotherapy

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 7, 11:19 AM
|
𝐁𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐤𝐭𝐡𝐫𝐨𝐮𝐠𝐡 𝐢𝐧 𝐆𝐞𝐧𝐞 𝐓𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐩𝐲:
Life-Changing Miracle for Baby with Fatal Disease 👇
Eisa Hussain, a four-year-old boy born with the severe form of leukocyte adhesion deficiency 1 (LAD-1), was given a "death sentence" without treatment.
This ultra rare disease cripples the immune system, often leading to death before age two.
👉 This innovative gene therapy, developed by Rocket Pharmaceuticals, used Eisa’s own stem cells at GOSH to replace the faulty gene responsible for the condition, restoring his immune system.
Now, several months after receiving the treatment, Eisa is thriving, playing football, attending school, and living a normal life something his family once thought impossible.
This incredible breakthrough is a beacon of hope for other families facing rare, life-threatening conditions.
Amazing to see just how powerful gene therapy is in saving lives 👏
#genetherapy #raredisease #celltherapy #CGTweekly | 26 commentaires sur LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 22, 5:33 AM
|
🚀 The Ultimate Guide to ADC Drugs 🚀
Want to know everything about the 17 approved ADC drugs worldwide in 2025? We've got you covered! From advanced cancer therapies to the latest treatment breakthroughs, this is the most comprehensive summary yet.
🔍 Discover:
✅ All 17 FDA-approved ADC drugs
✅ Key details on each drug's target and mechanism
✅ Global approval updates
Don't miss out on the full breakdown! Click below to read the full article. ⬇️
https://lnkd.in/gAjYyszC
#ADC #Pharma #DrugDevelopment #CancerTreatment #Biotech #Pharmaceuticals

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 19, 2:29 AM
|
Malaria vaccine research has progressed significantly, with RTS,S/AS01 and R21/Matrix-M receiving WHO endorsement in 2021 / 2023. These vaccines show promise, but challenges like vaccine adherence, strain variation, and resistance persist, highlighting the need for more effective, broad-reaching interventions.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 16, 7:32 AM
|
🚫 𝗡𝗼𝘁 𝗮𝗹𝗹 𝗺𝗥𝗡𝗔 𝗱𝗲𝗹𝗶𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘆 𝘀𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺𝘀 𝗮𝗿𝗲 𝗯𝘂𝗶𝗹𝘁 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝘀𝗮𝗺𝗲.
Some? Bare-bones.
Others? Engineered with surgical precision.
🧪 But every single one reveals something deeper—
---> Formulation strategy.
---> Biocompatibility.
---> How far we’ve come in drug delivery science.
👇 Here's a visual buffet of mRNA vaccine delivery platforms—each with its own size, mechanism, and logic:
📍 Naked mRNA – No carrier. Vulnerable. Fast degradation.
📍 Electroporation – A jolt to get inside cells. Effective, but tech-heavy.
📍 Protamine-complexed – Cationic peptide hugs mRNA. More stable, better uptake.
📍 Cationic nanoemulsion – Think oil-in-water with a positive twist.
📍 Dendrimer + PEG-lipid – Custom-designed for precision and low immunogenicity.
📍 Protamine in PEG-lipid NP – Double protection. Peptide inside, stealth outside.
📍 PEI-based – Potent. But needs careful formulation to avoid toxicity.
📍 PEI + lipids – A more balanced version for smoother biocompatibility.
📍 Polysaccharide-based – Like chitosan. Gentle and stable.
📍 Cationic lipid nanoparticles – Classic workhorses: DOTAP, DOPE, and friends.
📍 Cationic lipids + cholesterol ± PEG-lipid – Combo packs for optimal stability and immune modulation.
✨ And then there’s ex vivo dendritic cell loading:
💸 Pricey.
🕒 Time-consuming.
🎯 But unbeatable when precision targeting really matters.
💡 Bottom line:
In mRNA therapeutics, delivery isn’t just how you get there—it’s the whole mission.
It’s the difference between "potential" and "performance."
💬 What delivery tech are you watching (or working on) in this space?
👇 Let’s break down what works, what’s evolving, and what’s next.
#mRNADelivery #LipidNanoparticles #RNAFormulation #NonViralVectors #mRNATherapeutics #FormulationStrategy #TechnoPharmaSphere

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 10, 9:54 AM
|
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-based therapies developed for the treatment of haematological malignancies have recently been repurposed to treat refractory systemic autoimmune diseases.
📖 In a NEW Review Marc Scherlinger and colleagues critically discuss the current data available on the use of CAR-based therapy in systemic autoimmune diseases, the current challenges, and the potential next steps toward their implementation into clinical practice. Beyond the targeting of B cells via CD19, the advantages and potential pitfalls of targeting plasma cells (B-cell Maturation Antigen or CD138) and other non-immune targets, such as fibroblast activated protein, and of aiming to restore immune homeostasis using CAR T regulatory cells, are also discussed.
Read the full Review here 👉 https://lnkd.in/eB7cvhGG
Alt text: Current and future strategies for CAR use in humans
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 20, 5:21 AM
|
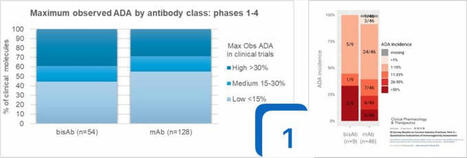
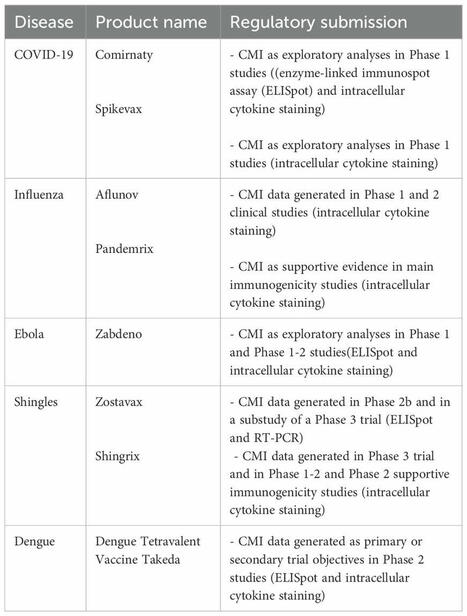
🚨#Immunogenicity can undermine any biologic, driven by anti-drug-antibodies (#ADA), from pre-clinical to post launch. This topic is so challenging due to the combination, intricacies and complexity of the molecules, human immunology, patient treatment journeys, assay standards and the vagaries of publishing. There is a ground truth but “for now we see through a glass, darkly”. Allowing for all that complexity, and briefly putting it to one side, are there any rules of thumbs we can see?
🫣What data shall we look at?
I decided to focus on the worst-case scenario and use the maximal ADA rates (the % of HV or patients across phase 1-4 reporting ADA post treatment) for #antibodies. With the help of a Deep Research tool I read the refs and extracted the published maximal ADA rates for these assets across all indications. So that’s:
• 54 #bisAb: 19 approved & 2 reg review, 13 phase 1-3, 20 terminated phase 1-3
• 129 #mAb: 75 approved | 16 phase 1-3 | 38 terminated phase 1-3
🎬 Findings:
1️⃣ mAb and bisAb clinical assets have a #similar spread of ADA profiles. The same observation was published this year in the IQ Survey Part 2 on immunogenicity for 46 mAb and 9 bisAb assets.
2️⃣ Mixtures of mAbs, co-formulated or co-administered, do not reduce immunogenicity risk.
3️⃣ Some targets do report higher ADA rates for almost all mAb and bisAb prosecuted in the clinic. This may primarily be MoA related but may also be due to the number of shots on goal the industry has tried.
🧐So what?
➡️ Each molecule is unique in its ADA risk profile. As we engineer our candidate drugs integrating an Immunogenicity Risk Assessment (#IRA) as part of our candidate target profile informs the risk and helps us select the candidate for IND.
🔂 The #translational #gap between the range of brilliant in vitro assays and patient response is still there.
↔️ Thank you to all the #patients, institutes and companies who put their data into the #public domain. As much as it’s in your remit please keep publishing the clinical ADA data. It’s part of enabling bedside to bench translation so we can do better next time💙
👍Over to #you🤔
❓What’s your view on de-risking preclinically and in vitro #assays?
🙋Who is curating this clinical data in a more robust way?
💬 it’s always good to chat the science through as “the truth is so obscure in these times… unless we love the truth, we can not know it” Blaise Pascal (1623-1662)

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 15, 4:14 AM
|
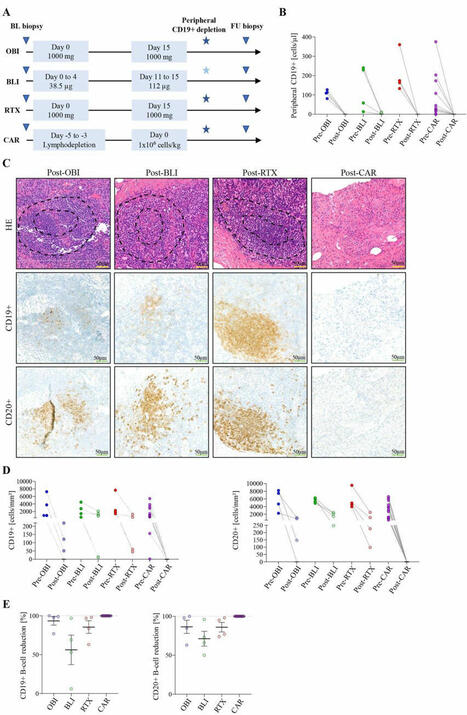
Effects of different B-cell-depleting strategies on the lymphatic tissue
- Advanced protein-based B cell depleters, such as glycoengineered CD20 monoclonal antibody obinutuzumab (OBI) and CD19/CD3 T cell engager blinatumomab (BLI), are promising new therapeutic instruments for treatment of autoimmune disease (AIDs).
- It has been speculated that such B cell-depleting modalities achieve better clearance of tissue B cells in patients.
- By performing sequential lymph node biopsies, this study shows that advanced protein-based B cell depleters, like OBI and BLI, reduce but do not consistently deplete B cells in the lymph nodes.
- These results stand in contrast to the consistent full depletion of B cells associated with the disruption of follicular lymph node architecture after CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy.
- B cell depletion was associated with stable drug-free remission, whereas a reduction in B cell numbers without depletion required retreatment with immunomodulatory drugs.
- Introducing lymph node biopsy as a clinical tool to assess B cell depletion could enhance treatment monitoring and play a pivotal role in tailoring therapeutic strategies. Larger-scale studies are needed to confirm whether B cell depletion in secondary lymphoid organs directly correlates with clinical outcomes in patients with AID.
https://lnkd.in/eDdFr-_7
#autoimmunity #celltherapy #immunology #rheumatology

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 5, 2:03 AM
|
The FLUniversal consortium, supported by the EU’s Horizon Europe programme, is pioneering the development of an intranasal universal influenza vaccine. Our goal is to create a vaccine that offers broad protection against all flu strains, reducing the need for annual updates.
Key highlights of our approach include:
- Innovative Vaccine Design: Utilizing a live, replication-deficient influenza strain lacking the NS1 protein to stimulate a robust and lasting immune response.
- Intranasal Delivery: Administering the vaccine through the nose to induce strong local immunity, potentially preventing infection at its entry point.
- Comprehensive Testing: Employing controlled human infection models (CHIMs) to assess vaccine efficacy and identify immune correlates of protection.
- Preclinical Validation: Animal studies have demonstrated promising safety and immunogenicity results, laying a solid foundation for future clinical development.
This collaborative effort brings together leading experts from academia and industry, aiming to revolutionize influenza prevention.
Read the full article here: https://lnkd.in/dpYwW-PV

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
June 24, 7:58 AM
|
Vaccines are complex biological medicinal products developed with the aim to generate protective immunity against specific infectious diseases in

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
June 20, 6:32 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 26, 3:34 AM
|
🚀 𝗖𝗲𝗹𝗹 𝗧𝗵𝗲𝗿𝗮𝗽𝘆 - 𝗧𝗵𝗲 (𝗥)𝗘𝘃𝗼𝗹𝘂𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻
𝘍𝘳𝘰𝘮 𝘪𝘯𝘧𝘶𝘴𝘪𝘰𝘯𝘴 𝘵𝘰 𝘪𝘯𝘫𝘦𝘤𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯𝘴?
Thrilled to have attended last week’s virtual "𝙄𝙣 𝙑𝙞𝙫𝙤 𝙀𝙣𝙜𝙞𝙣𝙚𝙚𝙧𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙤𝙛 𝙄𝙢𝙢𝙪𝙣𝙚 𝘾𝙚𝙡𝙡𝙨 (𝙄𝙑𝙀𝙄𝘾)" workshop hosted by the 𝗡𝗖𝗜! 🚀
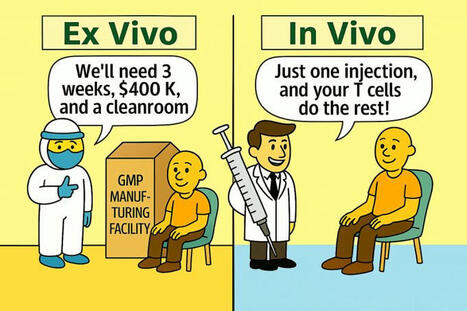
𝘐𝘯 𝘷𝘪𝘷𝘰 cell engineering is redefining the possibilities of immunotherapy—offering the potential for 𝗳𝗮𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗿, 𝗺𝗼𝗿𝗲 𝗮𝗰𝗰𝗲𝘀𝘀𝗶𝗯𝗹𝗲, 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗹𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝗿𝗲𝘀𝗼𝘂𝗿𝗰𝗲-𝗶𝗻𝘁𝗲𝗻𝘀𝗶𝘃𝗲 treatments compared to traditional 𝘦𝘹 𝘷𝘪𝘷𝘰 approaches.
𝗦𝗼𝗺𝗲 𝗸𝗲𝘆 𝗮𝗱𝘃𝗮𝗻𝘁𝗮𝗴𝗲𝘀 𝗶𝗻𝗰𝗹𝘂𝗱𝗲:
✅ No need for GMP manufacturing facilities
✅ Shorter and more scalable workflows
✅ Potential for outpatient or point-of-care delivery
⚠️ 𝗕𝘂𝘁 𝗰𝗵𝗮𝗹𝗹𝗲𝗻𝗴𝗲𝘀 𝗿𝗲𝗺𝗮𝗶𝗻:
- Reduced control over the engineering process
- Difficulties in targeting specific immune subsets
- Efficacy and safety still under active investigation
🔥 𝗬𝗲𝘁 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗺𝗼𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁𝘂𝗺 𝗶𝘀 𝘂𝗻𝗱𝗲𝗻𝗶𝗮𝗯𝗹𝗲! 🔥
🌟 𝗦𝗼𝗺𝗲 𝗵𝗶𝗴𝗵𝗹𝗶𝗴𝗵𝘁𝘀:
- Carl June (University of Pennsylvania) laid the groundwork with a visionary keynote on 𝘦𝘹 𝘷𝘪𝘷𝘰 and 𝘪𝘯 𝘷𝘪𝘷𝘰 CAR-T.
- Matthias Stephan (WHI CCC Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center) showcased the power of local reprogramming via 𝘪𝘯 𝘷𝘪𝘷𝘰 engineering of macrophages to secrete BiTEs.
- Yevgeny Brudno (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Chapel Hill) introduced implantable sponges enabling same-day CAR T therapy.
- Cristiana Pires (Asgard Therapeutics) proposed turning tumors into antigen-presenting cells through 𝘪𝘯 𝘷𝘪𝘷𝘰 reprogramming.
- Daniel G. (Myeloid Therapeutics) shared early clinical data on 𝘪𝘯 𝘷𝘪𝘷𝘰 mRNA CAR myeloid engineering.
- Adrian Bot, M.D., Ph.D. (Capstan Therapeutics) presented Capstan’s LNP platform tackling both oncology and autoimmunity.
👏 Kudos to all the speakers and organizers for advancing this paradigm-shifting field.
⁉️ 𝙒𝙝𝙖𝙩 𝙖𝙧𝙚 𝙮𝙤𝙪𝙧 𝙩𝙝𝙤𝙪𝙜𝙝𝙩𝙨?
⁉️ 𝙒𝙝𝙖𝙩 𝙧𝙚𝙘𝙚𝙣𝙩 𝙞𝙣 𝙫𝙞𝙫𝙤 𝙙𝙖𝙩𝙖 𝙤𝙧 𝙥𝙡𝙖𝙩𝙛𝙤𝙧𝙢𝙨 𝙝𝙖𝙫𝙚 𝙘𝙖𝙪𝙜𝙝𝙩 𝙮𝙤𝙪𝙧 𝙖𝙩𝙩𝙚𝙣𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣?
#Immunotherapy #InVivoEngineering #CellTherapy #CancerResearch #Biotech #CAR #GeneTherapy | 27 comments on LinkedIn

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
May 24, 5:15 AM
|
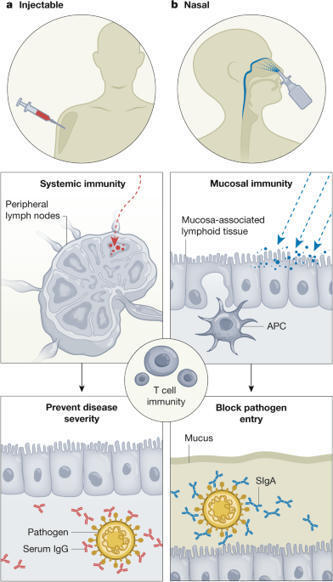
The search for potent malaria vaccine candidate has seen several twists and turns. Here, we provide a perspective on the current state of PfRH5-based malaria vaccine development, the progress, existing challenges, and future research directions. We discuss the clinical trials in endemic regions, immune correlates of protection, prospects of integrating PfRH5 into multi-antigen vaccine strategies and considerations on the onward development/deployment of PfRH5 vaccine from the laboratory to endemic communities.
Beginning with Edward Jenner’s discovery of the smallpox vaccine, the ever-expanding repertoire of vaccines against pathogens has saved many lives. During the COVID-19 pandemic, a revolutionary mRNA injectable vaccine emerged that effectively controlled the severity of disease caused by SARS-CoV-2. This vaccine induced potent antigen-specific neutralizing serum IgG antibodies, but was limited in its ability to prevent viral invasion at the respiratory surfaces. Nasal vaccines have attracted attention as a potential strategy to combat respiratory infections and prepare for future pandemics. Input from disciplines such as microbiology, biomaterials, bioengineering and chemistry have complemented the immunology to create innovative delivery systems. This approach to vaccine delivery has yielded nasal vaccines that induce secretory IgA as well as serum IgG antibodies, which are expected to prevent pathogen invasion, thereby diminishing transmission and disease severity. For a nasal vaccine to be successful, the complexity of the relevant anatomical, physiological and immunological properties, including the proximity of the central nervous system to the nasal cavity, must be considered. In this Review, we discuss past and current efforts as well as future directions for developing safe and effective nasal vaccines for the prevention of respiratory infections. This Review provides an overview of progress and future directions in the development of nasally administered vaccines for respiratory infections.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 30, 6:47 AM
|
#T2Evolve survey results on analytical methods for CAR T cells. A nice overview of the European landscape !

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 19, 4:24 AM
|
The effectiveness of intramuscular vaccines aimed at preventing severe COVID-19 remains limited due to waning immunity and the emergence of novel variants. Next-generation vaccines are needed for broader protection and blocking virus transmission. Here, we rationally designed an original nasal subunit vaccine composed of a fusion protein (SwFN) made of Wuhan spike and nucleoprotein combined with biocompatible mucosal nanocarriers (Nc). In mouse model, the nasal Nc-SwFN vaccine elicited multivalent serum and mucosal neutralizing antibodies. Robust spike and nucleoprotein cross-reactive immunity against variants was induced with a predominant phenotype of resident memory T cells in the lungs. Moreover, Nc-SwFN led to protective responses against Wuhan and Delta infection in relevant models with an absence of morbidity, mortality, and virus dissemination in the lungs and brain. Finally, Nc-SwFN drastically reduced host-to-host transmission. These promising results underscore the advantages of the nasal Nc-SwFN approach as a broad-spectrum vaccine candidate against current and emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 17, 7:03 AM
|
BMJ Publishing Group. Pancreatic Cancer. https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-us/265 Updated November 19, 2024. Accessed March 19, 2025. Yu B, et al. Frontiers in pancreatic cancer on biomarkers, microenvironment, and immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2025;610:217350.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 13, 7:52 AM
|
#highlyviewed
📢 An Update on Anti- #COVID19 #Vaccines and the Challenges to Protect Against New #SARSCoV2 Variants
👨🎓 by Fábio Mambelli et al.
🔗 Full article: mdpi.com/2076-0817/14/1/23
The COVID-19 pandemic has posed a significant threat to global health systems, with extensive impacts across many sectors of society. The pandemic has been responsible for millions of deaths worldwide since its first identification in late 2019. Several actions have been taken to prevent the disease, including the unprecedented fast development and global vaccination campaigns, which were pivotal in reducing symptoms and deaths. Given the impact of the pandemic, the continuous changes of the virus, and present vaccine technologies, this review analyzes how, so far, we have met the challenge posed by the emergence of new variants and discusses how next-generation pan-coronavirus vaccines, with enhanced longevity and breadth of immune responses, may be tackled with alternative administration routes and antigen delivery platforms. By addressing these critical aspects, this review aims to contribute to the ongoing efforts to achieve long-term control of COVID-19, stimulating the discussion and work on next-generation vaccines capable of facing future waves of infection.
|


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...