Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
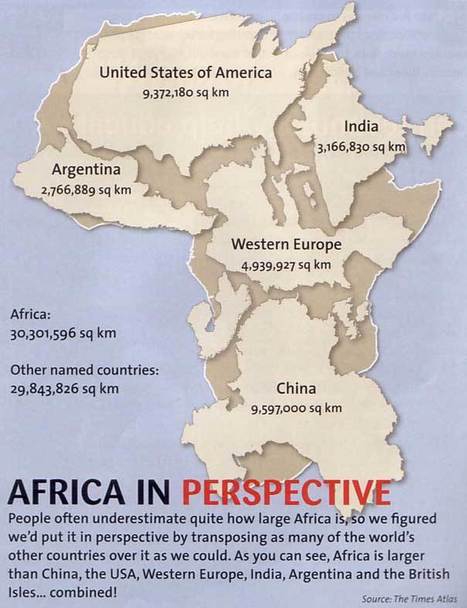
Digital textbook company Kno has created an infographic called “College Kids Digital Study Habits Revealed,” exploring some key statistics about how university students study... According to the infographic, social science students search for terms 2x as much during the semester as math students and medical and nursing students highlight 15x more than math and 2x more than social science students.
Via EDTECH@UTRGV

|
Rescooped by
Dr. Russ Conrath
from Into the Driver's Seat
September 22, 10:22 AM
|
From Internet Scout Report "Staff at the State University of New York's University at Buffalo's Map Collection have worked to bring the general public this top-notch guide to teaching with maps. The resources are culled from the University at Buffalo, digital collections from other institutions, and the Internet. The materials are organized into 14 thematic categories, such as Gazetteers, GIS Maps and Sites, and Satellite and Remote-Sensing Images. Visitors will note that each resource has a brief annotation along with a direct link to the resource. "Locating Maps on the World Wide Web is a great resource, as it features high-quality links to collections at the University of Texas at Austin, the United Nations, and the US Geological Survey. Moving on, the Teaching Resources and Other Materials area is another great find. Here visitors can make their way through over two dozen resources, including the Using Historic Maps in College and University Courses site from the Newberry Library in Chicago."
Via Jim Lerman
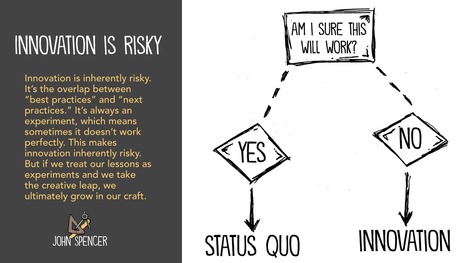
"Over the last few years, I’ve had the honor of leading PBL and design thinking workshops all over the world. Early on in each workshop, I ask participants to identify the challenges that they face when trying to implement innovative teaching strategies. Whether they teach in Australia or the Netherlands or Hong Kong or the U.S., certain challenges always emerge."
Via EDTECH@UTRGV
Online learning has become increasingly popular in recent years, especially due to the global pandemic. However, engaging students in this type of learning can be challenging. In this article, we explore seven innovative teaching strategies to help educators engage their students in online learning.
Via EDTECH@UTRGV
"AssemblyAI enhances its speech-to-text services by introducing support for 99 languages, offering advanced features at a single price point. Explore the latest developments in AI-driven language recognition. In a significant advancement for language recognition technology, AssemblyAI has announced the expansion of its speech-to-text services to support 99 languages. The company is offering these enhanced capabilities alongside advanced features at a unified price point, according to assemblyai.com. Key Features and Updates AssemblyAI's latest update introduces a universal model that not only accommodates a wide array of languages but also incorporates advanced contextual text formatting. This feature is particularly beneficial for languages like Spanish and German, enhancing the accuracy and usability of transcriptions. The company has also streamlined its pricing model, making these features more accessible to a broader audience. Technological Integration and Implementation In addition to the language expansion, AssemblyAI has integrated OpenAI's Whisper technology for offline speech recognition. This integration supports browser and Node.js implementations, allowing developers to utilize powerful transcription capabilities in various environments. The Whisper API also facilitates audio transcription using JavaScript, broadening the scope for developers to create innovative applications. Industry Impact and Future Prospects The expansion to 99 languages positions AssemblyAI as a formidable player in the AI-driven speech-to-text market. By offering comprehensive language support and advanced features at a competitive price, the company is poised to attract a diverse clientele ranging from individual developers to large enterprises. Furthermore, the inclusion of free speech-to-text APIs and open-source engines underscores AssemblyAI's commitment to fostering innovation and accessibility in AI technology. This strategic move is likely to stimulate growth and adoption of AI-driven language solutions across various sectors.AI-powered search engine As AssemblyAI continues to enhance its offerings, the company is set to play a pivotal role in the evolution of speech recognition technology, driving forward the capabilities and applications of AI in everyday communication and business operations. Image source: Shutterstock" AssemblyAI Expands Speech-to-Text Capabilities with 99 Languages Iris Coleman Aug 26, 2025 05:08 https://blockchain.news/news/assemblyai-expands-speech-to-text-capabilities-with-99-languages #Metaglossia #metaglossia_mundus
Via Charles Tiayon
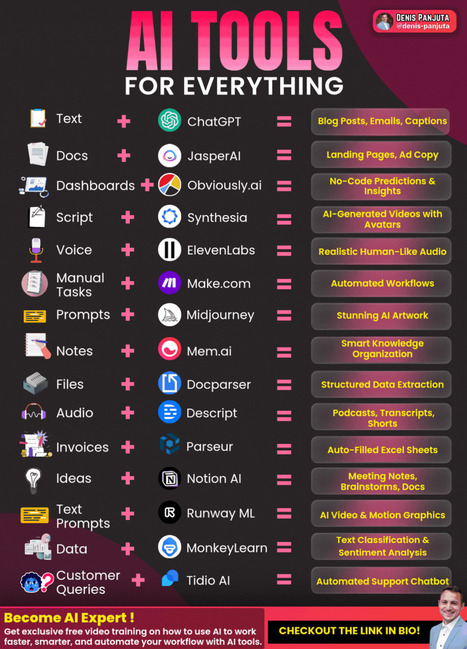
Every CEO knows the struggle: too many tasks, too little time. From managing teams to making data-driven decisions, time is your most valuable asset. That’s where AI tools step in. They automate repetitive tasks, provide actionable insights, and keep you focused on what truly matters: growth and strategy. Here’s a cheat sheet of AI Tools for Everything you can plug into your workflow today: 1. Text → ChatGPT → Blog posts, emails, captions 2. Docs → JasperAI → Landing pages, ad copy 3. Dashboards → Obviouslyai → No-code predictions & insights 4. Script → Synthesia → AI-generated videos with avatars 5. Voice → ElevenLabs → Realistic human-like audio 6. Manual Tasks → Makecom → Automated workflows 7. Prompts → Midjourney → Stunning AI artwork 8. Notes → Memai → Smart knowledge organization 9. Files → Docparser → Structured data extraction 10. Audio → Descript → Podcasts, transcripts, shorts 11. Invoices → Parseur → Auto-filled Excel sheets 12. Ideas → Notion AI → Meeting notes, brainstorms, docs 14. Text Prompts → Runway ML → AI video & motion graphics 15. Data → MonkeyLearn → Text classification & sentiment analysis 16. Customer Queries → Tidio AI → Automated support chatbot 👉 Ready to build AI workflows that run your business on autopilot? Let’s make it happen! [Explore More In The Post] If you found this helpful don’t forget to save this for later and comment your thoughts. Get exclusive free video training on how to use AI to work faster, smarter, and automate your workflow with AI tools : https://lnkd.in/eWTUNUYxFollow Denis Panjuta on Linkedin : https://lnkd.in/eUHjTBUi | 64 comments on LinkedIn
Via Dennis Swender
The CHLOE 10 report, focusing on online learning, reveals a boom in short-term credentials, along with uneven progress on AI across higher ed
Via EDTECH@UTRGV
"The power of translation services in patient care
When communication barriers impede care, Penn nurses play a role in bridging language and cultural gaps. Aparticular patient in the emergency room at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania wasn’t assigned to resource nurse Monica Phann, but colleagues had asked for her help because the man and his wife had limited English proficiency, and they couldn’t immediately locate a translator. Phann grew up speaking Khmer with her parents and grandparents in South Philadelphia. View large image
Image: Doug Chayka
“When I stepped in, they let go of all their formalities and [the patient was] finally able to say, ‘yes, I don’t feel good, and I need to be able to have someone understand the pain that I’m in,’” Phann recalls. With her as a go-between, the hospital team was able to run the appropriate tests and quickly diagnose the patient with lung cancer. He started radiation treatment within a week. Though the diagnosis was unsettling, Phann knew she had made a positive impact on his course of care. “When there’s a language barrier, patients aren’t able to fully express what they’ve been feeling. It was really empowering to see how eliminating that barrier allowed this patient to then get further care,” Phann says. “It speaks to how powerful it is to have bilingual or multilingual nurses when other resources aren’t available. We need more of us at the bedside.” Around the country, Penn Nursing alumni are using multilingualism to improve patient outcomes in hospitals, doctor’s offices, and community health settings. They reduce longer lengths of stay and readmissions and increase patient satisfaction. They foster trust with patients and their families, and serve as strong advocates for multilingual patients and those with limited English proficiency. “We live in a multilingual world. I say this to colleagues in the United States and in Latin America. We have to develop those skills,” says School of Nursing professor and Margaret Bond Simon Dean of Nursing Antonia M. Villarruel. Federal law requires free translation services be offered to those who need it—in person or remotely through, for example, a videoconference on a tablet. And even multilingual providers call on certified medical interpreters to navigate complex topics. However, Villarruel says, when a nurse converses and tends to basic needs in the patient’s native language, “there’s a benefit to that one-on-one connection. To be able to say ‘hi, how are you’ humanizes care.” Bilingual nurse scientists also contribute with more inclusive research. For decades, studies left out people who aren’t fluent in English. Penn Nursing faculty and alumni are addressing that gap, designing solutions with everyone in mind. Still, multilingual day-to-day communication is valuable, says Phann. “You’re not always going to be able to predict that you need a translator or an interpreter at the bedside. When I started working in the health care system, I realized that my languages were a huge bonus … and needed in this world.” This story is by Janine White.
https://penntoday.upenn.edu/news/penn-nursing-translation-services-patient-care
#metaglossia_mundus
Via Charles Tiayon
AI teacher assistant tools generated more-punitive recommendations for students with Black-coded names, a study finds.
Via EDTECH@UTRGV
A new report shows AI teaching assistants could be beneficial in the classroom — but may also bring invisible bias.
Via EDTECH@UTRGV
"TYSONS, Va., May 15, 2025 -- The Academy of Interpretation (AOI) proudly announces the launch of its highly anticipated Training of Trainers (ToT) for the Professional Medical Interpreter (PMI) course. The first class debut was this past March, and this initiative aims to empower language professionals and organizations with the skills, tools, and strategies to deliver AOI's signature PMI course and elevate the standards of medical interpretation nationwide. The PMI course is widely recognized for preparing interpreters to meet the rigorous demands of healthcare settings by developing essential skills in medical terminology, ethics, and real-time interpretation techniques. The new Training of Trainers program will prepare qualified educators with in-depth knowledge and teaching methods to guide future interpreters successfully. The AOI offers flexible licensing packages for educational institutions, healthcare providers, and language service companies interested in incorporating PMI training into their professional development programs. The ToT is a hybrid program and includes asynchronous material and live sessions with trainers. Partners will gain exclusive access to:
Comprehensive training materials and instructional guides
Expert-led workshops and support sessions
Certification options for both trainers and their students Sameh Abdelkader, Director of Education at the AOI, shared, "We are thrilled to launch this program and expand the reach of high-quality interpreter training through strong partnerships. By empowering other organizations to teach PMI, we aim to set a new standard for medical interpreting excellence and improve patient outcomes through better communication." The ToT initiative helps organizations meet the growing demand for qualified medical interpreters and strengthens their role in shaping the next generation of language professionals. Maria Teresa Buendia, Assistant Director of Education at AOI, added, "This program is designed to create a ripple effect of knowledge and expertise in the field of medical interpretation. We’ve just signed our first licensing agreement, and they already have a full class. We look forward to working with other organizations that share our passion for bridging language barriers in healthcare." Contact AOI at support@academyofinterpretation.com or visit https://www.academyofinterpretation.com/trainingoftrainers/pmi The Academy of Interpretation (AOI) is a leading organization in the language services industry, dedicated to professionalizing the field and maintaining high-quality standards. AOI offers education, training, and credentialing to interpreters, translators, and language professionals to ensure effective communication across linguistic and cultural divides."
https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/05/15/3082414/0/en/Academy-of-Interpretation-Launches-Professional-Medical-Interpreting-PMI-Training-of-Trainers-Program.html
#metaglossia_mundus
Via Charles Tiayon
If there's one good thing that has come out of COVID, it has to be the increasing awareness about immunity. For the medical world although, especially the front liners handling COVID patients, it's been a one-of-a-kind experience. Every prognosis took wrong turns, with little to almost no respite in mitigating recurring symptoms. Since then, doctors have been harping on the importance of immunity in the wake of lengthy infections and beyond. A "Better safe than sorry" scenario, you see. Although there have been some steadfast developments across countries producing early vaccines to boost immunity, there’s a still lot to wait for with bated breath. In serious COVID cases, it was hypoxaemic respiratory failure along with organ dysfunction that seemed to have contributed largely to the mortality rate. As such, alternative treatment options like Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy were sought to help mitigate moderate to heavy symptoms. The very first instance, in this case, can be traced back to Wuhan, the source center for COVID, where doctors resorted to using hyperbaric chambers in treating serious COVID patients and successfully improved their condition.
Via Natalia Smith
|

|
Rescooped by
Dr. Russ Conrath
from The 21st Century
September 22, 10:22 AM
|
Newberry College in Newberry, South Carolina has created an undergraduate major dedicated to social media.
Via Dr. Susan Bainbridge

|
Rescooped by
Dr. Russ Conrath
from Affiliate Marketing
September 22, 10:21 AM
|
Master in-demand digital skills that top companies seek—and let Cyberinfomines turn your potential into a powerful career advantage. Let’s face it. In 2025, job interviews don’t start with “What degree do you have?” anymore. They begin with “What can you do?” Gone are the days when a piece of paper from a university could guarantee a seat in a company. Today, the competition is fierce, attention spans are shorter, and companies want results — not just resumes. The real question is simple but life-changing: Should you spend years earning a degree or months mastering job-ready digital skills? In this blog, we’ll decode the answer — straight, honest, and human. No fluff. Only what truly matters. 1. What Changed Between 2015 and 2025? In 2015, you could survive with a B.Tech, MBA, or BCA degree. Companies still believed in training you after hiring. But by 2025, the game has changed. AI can scan 1000 resumes in seconds. Recruiters search LinkedIn, GitHub, Behance before your CV. Startups and MNCs want "doers," not just "knowers." So who’s winning in this new hiring era? People who know how to work, not just those who studied work. 2. Why Degrees Alone Don’t Guarantee Jobs Anymore Let’s be clear — degrees are not useless, but they are not enough anymore. Here’s why: 📌 Too Generic College curriculums often don’t match what’s happening in real companies. You might learn Java in theory, but never write a real-world API. 📌 No Practical Projects In most degrees, there’s a huge gap between what’s taught and what’s expected. You graduate, but don’t know how to work in a live team. 📌 No Industry Connect You’re not taught how to crack interviews, build a LinkedIn presence, or understand client briefs — the things that actually matter. 3. What Are 'Digital Skills' and Why Are They Game-Changers? Digital skills are the actual tools and techniques companies use every day. Whether you want to be a developer, designer, digital marketer, or even a cybersecurity expert, you need to know how things work, not just what they are. Examples of In-Demand Digital Skills in 2025: Field Skills Development Java, Python, Full Stack, APIs, Git Design UI/UX, Figma, Prototyping, Responsive Design Marketing SEO, Google Ads, Meta Ads, Analytics Cybersecurity Network Defense, SOC, Threat Hunting Cloud & DevOps AWS, Docker, CI/CD The best part? You can learn these in 3–6 months with proper mentorship and project-based training. 4. What Do Companies Really Want in 2025? We asked hiring managers, and here’s what they said: “We don’t care where someone studied. We care whether they can deliver.” – Senior HR, Bengaluru-based SaaS firm “If you’ve built even one real project with a team, that tells me more than a degree.” – Tech Lead, Pune Startup In short, companies hire: Problem solvers Team players Portfolio builders People who are trained for the job, not just qualified on paper 5. Meet the Hybrid Hero: Skills + Smart Certifications Here’s a smarter formula for 2025: 🎯 Degree + Real-World Skills + Guided Mentorship = Job-Ready Professional That’s where Cyberinfomines comes in. We’re not here to replace your college. We’re here to complete your career with: 🔸 Industry-Ready Training (Java, Full Stack, UI/UX, Digital Marketing) 🔸 Live Projects, Not Just Notes 🔸 Certifications with Credibility 🔸 100% Interview Training & Placement Support In short, we help you skip the confusion and start the career. 6. The ROI of Learning Smart in 2025 Let’s talk numbers — because let’s be honest, they matter. Path Time Cost Results Traditional Degree 3–4 years ₹3–6 Lakhs Maybe job-ready Skill-based Training 4–6 months ₹25,000–₹60,000 Job-ready in 6 months The ROI is massive when you learn smart — you save time, money, and start earning faster. 7. True Stories: From Confused to Career-Ready (Cyberinfomines Learners) 🌟 Aman (2023 Batch) "I had a BCA degree but zero coding confidence. Cyberinfomines trained me in Full Stack Development. Today, I work at a startup in Gurugram and lead my own small team!" 🌟 Priya (2024 Batch) "I was good at art but didn’t know design tools. After UI/UX training with Cyberinfomines, I now freelance and earn ₹50K+ a month." 🌟 Ravi (Corporate Client) "We upskilled our marketing team via Cyberinfomines’ Corporate Training Solutions. Their Digital Marketing program gave instant ROI — our ad campaigns improved by 3x!" Real people. Real growth. Real proof. 8. Still Confused? Ask Yourself These 5 Questions Can I build a project from scratch in my field? Do I understand how to crack real interviews? Is my LinkedIn or GitHub impressive enough? Can I explain my skills without a degree? If I were the hiring manager, would I hire myself? If your answer is “maybe” — then it’s time to upskill. 9. How Cyberinfomines Makes Learning Human Again We don’t treat learners like "batches" or "numbers." We work like mentors, career guides, and skill coaches. ✅ Personalized Learning Paths ✅ Industry Mentors ✅ Interview Bootcamps ✅ Job Support That Doesn’t Quit — even after course completion, we assist with resumes, LinkedIn, and real referrals. 10. Final Verdict: In 2025, Skills Speak Louder Than Degrees We’ll say it once more — degrees are fine. But if you rely only on them, you’re gambling with your career. The winners in 2025 are those who: ✅ Learn smart ✅ Stay curious ✅ Build real skills ✅ Present themselves well And Cyberinfomines is here to help you do exactly that. Ready to Rewrite Your Career Story? If you’re tired of waiting, confused by options, or stuck in a degree with no direction — talk to us. 📞 Call: +91-8587000904-906, 9643424141 🌐 Visit: www.cyberinfomines.com 📧 Email: vidhya.chandel@cyberinfomines.com Let’s make your career future-proof — together.
Via cyberinfominessss@gmail.com
Inspired by past educators, Aida Hadzovic has built a reputation for innovative teaching strategies for English. Hadzovic earned a degree in English education and later pursued a science degree in part because of the demand for science teachers in Brooklyn, New York. Her diverse background in teaching writing, science and coding positioned her well to participate in the Project Topeka pilot, a multifaceted AI program that gave real-time feedback to students to support the development of argumentative writing skills.
Via EDTECH@UTRGV
The Rise of Article Rewriting Tools: A Comprehensive Guide If you’ve ever struggled with writer’s block or faced a heavy workload, an article rewriting tool can be a game-changer. With the advancement of artificial intelligence, paraphrasing written content has become easier than ever before. In this article, we will explore what these tools are, how they work, and how to effectively use the HIX.AI article rewriter tool in your daily workflow. Why Use Article Rewriting? Article rewriting is a common practice in academic and professional settings. It allows for the same content to be written in a different context, which can help boost SEO and maximize audience reach. It can also improve content structure and delivery, as well as eliminate plagiarism. However, this process often requires repetitive creativity and effort. This is where article rewriter tools like HIX.AI come in handy. These tools can instantly alter already written words to create unique content in a fraction of the time it takes human writers. For busy content writers, repurposing content can save time brainstorming new ideas, writing text, and editing content. The HIX.AI rewriting tool replaces inputted words with synonyms, adjusts the tone to suit the intended reader, and even accurately alters the language. All of this is done using AI-based algorithms and natural language processing. The Benefits of Article Rewriting Using an article rewriting tool can help you engage more readers, improve your SEO rankings, and boost your marketing campaigns. The quality of the tool you use determines the dissimilarity between the original and rewritten content. In most cases, plagiarism checkers will be unable to detect any similarities. The Ethics of Article Rewriting The ethics of using an article rewriting tool fall into a gray area. These tools utilize previously written content, which increases the likelihood of including plagiarized text from the original source. Plagiarism can have serious consequences for individuals, negatively impacting their reputation as students or working professionals. To ensure ethical use of a rewriting tool, it is best to feed it your own original texts. Tools like HIX.AI can help you quickly create multiple variations of your own writing. As long as the writing has not been published before, there is little chance of accidental plagiarism. However, if you intend to paraphrase content from another source, proper citation is essential to avoid plagiarism. Common Users of Article Rewriting Tools Online marketing experts often need to create multiple variations of blog posts for different platforms to promote products, services, or websites. Social media managers use these tools to prevent repetitive posting and increase user engagement. PR professionals rely on article rewriting tools to craft different pitches for various news outlets and publications. College students frequently use these tools to paraphrase content for research papers. Considerations When Using an Article Rewriter While article rewriting tools can be useful, they are not foolproof. AI-based tools often lack the ability to craft text in a natural tone or sentence structure. Proofreading the paraphrased content is crucial to ensure readability and accuracy. Choosing the right AI rewriting tool can minimize the need for constant correction. HIX.AI’s article rewriting tool generates plagiarism-free text that requires minimal editing. It also offers a personalized content-creating experience, allowing users to tailor the tone and content to a specific audience. In conclusion, HIX.AI’s article rewriting tools are designed to speed up the content creation process without compromising the original context. They are useful for generating multiple blog article variations, paraphrasing academic papers, and creating unique social media posts. However, it is important to use these tools ethically by avoiding spinning and publishing someone else’s content as your own. If you use your own content, article rewriters can be a valuable asset. When paraphrasing someone else’s work, always include proper citations. Overall, article rewriting tools can be a valuable addition to your writing toolkit, helping you save time and produce high-quality content. © 2023 | Email: contact@globalvillagespace.com
Via Charles Tiayon
Google has rolled out new Gmail and Chat features to improve search experience with labels and related results. The tech giant has introduced three features for accurate and customized search suggestions and results -- 'Search suggestions', 'Gmail labels' and 'Related results'. These features do not have an admin control, the company said in a blogpost. With 'Search suggestions' users can see search-query as they type in the Chat search field based on their prior search history. Additionally, it help users to quickly recall important messages, files, and more on mobile. The Search suggestions feature is available on Android devices and will roll out to iOS devices by the end of October. 'Gmail labels' allow users to search messages under a specific Gmail label in the app to give results only under that label. Additionally, users can refine label searches using search chips in the Gmail search bar. The labels feature is available on Android and iOS devices. 'Related results'Ais for Gmail search-queries that give no results, related results will be displayed to improve the overall search experience. The result feature is only available on the web, the company said. Meanwhile, recently, the company had announced that over 250 million monthly active devices were powered by Android Go, after the company declared the release of Android 13. --IANS aj/ksk/
Via Charles Tiayon

|
Rescooped by
Dr. Russ Conrath
from Virus World
September 2, 11:04 AM
|
The Trump administration moved on Tuesday to accelerate vaccinations of Americans against COVID-19, releasing the rest of the doses it had been keeping in reserve and recommending states immediately open inoculations to those aged 65 and over. Federal and state health officials have scrambled in recent days to step up vaccination programs that had given shots to only 9.3 million Americans as coronavirus infections remain at record highs in many U.S. states nearly two weeks into the new year. Many U.S. states had strict rules in place giving shots to healthcare workers and nursing home residents first, telling “non-essential workers” they might wait months for their turn. “We’ve already distributed more vaccine than we have healthcare workers and people in nursing homes,” U.S. Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar told ABC News. “We’ve got to get to more channels of administration.” Roughly 27.5 million doses have been distributed by the U.S. government to states so far, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.Azar said the outgoing administration, which had been keeping doses in reserve to make sure that all those who got a first inoculation receive their second shot on schedule, was now confident enough in the supply chain to release that stockpile. Last week, a spokesman for Joe Biden said the president-elect, who takes office on Jan. 20, would release more of the reserved doses. The pace of vaccinations has risen to 700,000 a day nationwide and was expected to hit 1 million a day within 10 days, officials said. “Michigan and states across the country remain ready to get more shots in arms, which is why the Trump Administration’s decision to grant our request and release millions of doses of the vaccine is so crucial,” Michigan Governor Gretchen Whitmer said in a statement. Whitmer, who had backed the lower vaccination age, is seeking permission from the U.S. government to purchase 100,000 vaccine doses directly from manufacturer Pfizer Inc. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has authorized the vaccine from Pfizer and partner BioNTech SE and a second vaccine from Moderna Inc for emergency use. As of Monday night, the United States had reported a total of 22.5 million coronavirus infections and 376,188 deaths during the pandemic, the most of any country. Nearly 130,000 Americans were hospitalized with COVID-19 at midnight on Monday. GRIM SCENES AT CALIFORNIA HOSPITAL A Reuters tally has shown that the number of COVID-19 patients requiring hospitalization may have leveled off, at least temporarily, although public health officials warn that further spread may still be seen from holiday gatherings. California Health and Human Services Secretary Dr. Mark Ghaly cited several promising trends in COVID metrics statewide in recent days, including a slowing in confirmed daily case numbers and a leveling off in positive tests. The number of new COVID hospitalizations statewide has fallen to about 2,500 admissions a day over the past two days from a daily average of about 3,500 admissions in previous days. Ghaly called that “the biggest signal to me that things are beginning to flatten and potentially improve." Despite the encouraging statistics, staff at Providence St. Mary Medical Center in Apple Valley, California, said that the situation was grim. “Where in the beginning we were overloaded with a lot of patients - we still have a lot of patients - but now it seems like they’re sicker than they’ve ever been before,” said Mary Mendy, executive director of acute care services at the hospital some 90 miles northeast of Los Angeles. “And every day there’s Code Blues on the floor and more and more patients are updated to ICU. It’s devastating,” Mendy said. The latest surge has potentially been compounded by a more infectious variant of the virus first seen in the UK and now found in at least 10 U.S. states - California, Florida, New York, Colorado, Georgia, Indiana, Connecticut, Minnesota, Pennsylvania and Texas.
Via Juan Lama
"This year is the first time that more U.S. college students will learn entirely online compared to being fully in-person. And research shows most online programs cost as much or more than in-person."
Via EDTECH@UTRGV

|
Rescooped by
Dr. Russ Conrath
from Assignment
August 26, 2:30 PM
|
Public Health Care Assignment Help
Our Public health challenge assistance is a provider that focuses entirely on assisting students from various colleges and universities with their assignments. We've specialists in specific topics who're to be had 24 hours a day, 7 days per week, to help with dissertations, theses, essays, reviews, and extra. We also assist college students at numerous universities make or create academic posters and presentations to assist them to get the finest scores. We support students in a couple of areas, consisting of Public fitness, to assist them in performing better and demonstrating a deeper knowledge of critical ideas. Why do You need Public health task assist services? Online public health assignment assistance is a novel manner to examine more about the challenge's various facets, which might also assist to put in writing the fine assignment and all needs in connection with the subject or name. On any occasion, some of the requirements of public healthcare, in step with the professionals who offer public healthcare assignments resources. Investigating national healthcare is a giant topic that is not constrained to 1 sickness or course of treatment. It is essentially concerned with categorizing human services for huge implementation via authorities schemes. Distinctive Fields of Public health in which you may Take Our assistance Lease community health Helper online Network fitness experts support the groups they deal with by arranging services and teaching citizens about the way to improve their fitness and great lifestyles. They run outreach projects to train and contain the community on subjects of fitness. Avail international fitness assignment help from Us The countrywide Institutes of fitness describe international health because of the study, research, and training that broadens the scope of public health to consist of a worldwide angle for people everywhere. Help with Epidemiology mission Epidemiologists look at the distribution, etiology, and effects of illnesses and accidents within a populace or demographic. They gain this thru studies, network outreach, and help with health coverage to decrease the hazard and occurrence of damaging fitness effects. Why should You choose Us for your Public fitness mission help? The following are some of the reasons why you have to choose us: Value-effective - Our Public fitness undertaking assistance is fairly priced. We recognize that some students cannot afford to pay for high-priced offerings. However, they require to assist with Public fitness assignments from our specialists, that's why we've got stored our pricing modest. Writers who're experts - The utility manner for our Public Healthcare writing is a little challenging. For your Public Healthcare venture, we continually rent a certified character. Professionals cowl each challenge. Content is free of plagiarism - don't worry approximately plagiarism, as our expert writers will provide you with 100% unique and unique Public health task assistance. Plagiarism is exactly prohibited at our business enterprise. On-time shipping -every project is usually introduced on time. We positioned up all efforts to finish the process by way of the closing date. Now's the time to e-book our Public Healthcare challenge assist and sit return and loosen up. https://www.thetutorshelp.com/public-health-care-assignment-help.php
Via Adomlaramaxa
The field of communication is vast and ever-changing, making it an exciting area of study for those interested in a career in journalism. Communication and journalism programs are typically interdisciplinary, providing students with a well-rounded education in the liberal arts while also teaching them the skills they need to succeed in the competitive world of journalism. While communication and journalism may seem like two very different fields, they are actually quite closely related. Both disciplines focus on the exchange of information between people, whether it be through the written word, spoken word, or nonverbal communication. This shared focus makes communication and journalism an ideal combination for those interested in pursuing a career in the media. Communication programs typically focus on the theories and principles of human communication, while journalism programs emphasize the practical application of these theories. Students in communication programs learn about the various ways in which people communicate and the barriers that can prevent effective communication. They also study the different ways that messages can be delivered, such as through the mass media or interpersonal relationships. Journalism programs, on the other hand, focus on the skills and techniques needed to gather, report, and write news stories. Students in journalism programs learn how to conduct interviews, write compelling copy, and use various news sources. They also learn about the ethical considerations involved in journalism and the legal rights of journalists. While communication and journalism programs differ in their focus, they both provide students with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in the field of media. Those who complete a communication or journalism program will be prepared to enter the workforce as reporters, editors, producers, and more. Professionals with a communication degree can enter fields such as public relations, journalism, marketing, fundraising, and other areas requiring strong communication skills. Publishing and writing are two of the most important aspects of being a writer and publisher. Despite the fact that digital media is now the norm, effective written communication is still required. As a result of your communications degree, you will have opportunities to work in journalism, technical writing, book authoring, and publishing based on your writing skills. One of the most important distinctions between journalism and other types of non-fiction writing is a desire for objectivity. Journalists are expected to maintain an objective mindset throughout the course of their interviews, research, and reporting on the stories they report. This form of communication helps us stay informed of events, issues, and characters taking place outside of the news. The most important purpose of news, no matter how interesting or entertaining it may be, is to empower the informed. What Is Communication Journalism And Related Programs? Credit: www.colum.edu Communication journalism is the study of how people communicate with each other through the medium of journalism. It includes the study of how journalists communicate with their audiences, how news is produced and distributed, and how journalism affects society. Communication journalism programs typically include courses in journalism, communication, and media studies. The Importance Of A Communications Degree Even though digital media has taken on a new role as the new norm, effective written communication has not. With your communication degree, you will develop writing skills that will aid in the development of careers in journalism, technical writing, book writing, or publishing. Is Communications Related To Journalism? Credit: www.varsityscope.com There is no one answer to this question as it can be interpreted in a number of ways. However, generally speaking, communications is the process of exchanging information between individuals or groups, while journalism is the profession or activity of collecting, writing, and editing news stories for publication in newspapers, magazines, or news websites. Therefore, it is possible to say that communications is related to journalism in that both involve the exchange of information. The Iowa School of Journalism and Mass Communication, one of the top five college newspapers in the country, publishes The Iowan. Students will be taught by faculty members who specialize in books and publishing, cultural studies, documentary and podcast creation, and investigative journalism. Within six months of graduation, the rate of Iowa graduates finding work or attending graduate school is 95 percent. A BA degree is required in journalism and mass communication. Iowa students have access to more than 100 study abroad programs and numerous undergraduate research opportunities. National organizations are ideal for gaining leadership experience as well as preparing for careers. Every year, more than $200,000 in scholarships and awards are awarded to journalism and Mass Communication majors. Journalism and mass communication are the core areas of study in the undergraduate major in media writing and visual storytelling. The study of the media’s historical, legal, cultural, and institutional roles in society can help students develop professional skills. This degree can be earned in the university’s four-year graduation plan if the second concentration is not a second major. It is a noble profession in which everyone is expected to be skilled, courageous, and perseverent. We must protect and report the news objectively, as well as protect journalistic sources. Journalists should always be on the lookout for official actions and hold them to account when they violate the law. Journalists are essential to democracy and should not be held hostage at all costs. Journalists should not be afraid to report the news in an open manner and without fear of retribution. Is Communications Related To Journalism? Communications, as a broad field, frequently serves a narrow audience. A narrower focus on news and current events is commonly employed by journalism, but it is frequently targeted toward a larger audience. What Are The Types Of Communication In Journalism? A person has four communication channels: verbal, nonverbal, written, and visual. Is A Communication Degree The Same As Journalism? A communication degree and journalism degree may have some similarities, but they are not the same. A communication degree may focus on areas such as public relations, advertising, or organizational communication, while a journalism degree may focus on areas such as news writing, reporting, or photojournalism. Communication majors study advertising, media production, technical communication, and mass media. They learn to write press releases, long-form articles, and technical documents. Graduates can work in fields where they excel at communicating, such as advertising, politics, technology, and healthcare. Career paths for communication majors are detailed in this section, which includes information on median salaries and educational requirements. Depending on the career they wish to pursue, students may be able to pursue an undergraduate or graduate degree in communication. This section will walk you through the various types of communication degrees, as well as the various career paths available to those pursuing them. Students are managed by postsecondary education administrators who handle their services at colleges and universities. A bachelor’s degree typically takes four years to complete for a full-time student. The master’s degree in communication provides a thorough understanding of public relations, applied communication, and communication theory. A doctorate in communication is a degree that prepares graduates to work in the most demanding fields. Graduate students of MA or MS in communication can pursue careers in public relations, marketing, or consultant roles. A communication degree will help you improve your writing, interpersonal, and critical-thinking abilities. In addition to journalism, technical writing, mass communication, and public relations, communication majors can specialize in other fields. Professionals with a communication degree can pursue careers in public relations, marketing, fundraising, and other fields, among other things. A successful journalist must have a few things in order to succeed. To begin, you must be able to write. Storytelling is at the heart of journalism. You must be able to keep the reader interested from the start, and you must be able to make them pay attention to everything that you say. A good second step is to thoroughly research the topic. If you want to write about a financial issue, you must be able to get a basic understanding of how it works. In third, you must be able to work well with others. To be a good journalist, you are always willing to try new things and collaborate with others to bring your stories to life. A successful journalist will always be able to demonstrate the necessary skills and passion for journalism. There are a few things you must do before you can begin the path to success. To begin, you must have a strong writing ability. Journalism Degree Vs Communications Degree There is a big debate raging on about which degree is better for students who want to pursue a career in journalism: a journalism degree or a communications degree. While both options offer a great education, there are some key differences that students should be aware of before making their decision. A journalism degree will typically offer a more focused education on the field of journalism, with classes covering topics such as news writing, reporting, and ethics. Communications degrees, on the other hand, offer a more well-rounded education that can prepare students for a variety of roles in the communications field, including public relations, marketing, and event planning. So, which degree is right for you? If you have your heart set on a career in journalism, then a journalism degree is probably the way to go. But if you’re interested in communications and want to keep your options open, then a communications degree may be the better choice. Marketing and communication are the two most common undergraduate degree paths. Economics and public relations are typically taught as part of the marketing degree program. Students must take mass communication and writing courses in order to communicate effectively. Graduates of marketing programs go on to work in advertising or media. Students can pursue a wide range of career options after graduating from a communication program, including journalism. Journalism and law are two of the many fields of study available to communication graduates. As a result of this course, students gain valuable collaboration experience by honing their problem-solving and interpersonal skills. Bachelor’s degrees in communication cover a variety of forms of interpersonal communication. Marketing programs have a greater emphasis on business and finance, which has numerous opportunities but is limited in scope. Graduates of a communication degree frequently enter a field of law or journalism. A Master of Business Administration (MBA) in marketing is a good option for those who want to work in sales, advertising, or brand management. Graduate students must be able to think strategically and creatively, as well as interpersonally, in any discipline.
Via Charles Tiayon
How to spark AI creativity. Discover 5 unconventional AI prompting tactics to get bold, creative results. Plus 10 odd prompts to push AI beyond boring responses
Via Nik Peachey
Don’t let ancient languages die They illuminate our own blind spots
The Rosetta Stone transformed our understanding of Ancient Egypt.... Joseph Justus Scaliger. If you’re not a classicist or a historical linguist, you likely don’t know him. But if you are, he is a giant on whose shoulders you stand. Born in France, in 1540, he made his name at the Dutch university of Leiden. Here, at the lofty peak of the Renaissance, he reimagined what language could do. A polyglot — proficient in French, Italian, Latin, Greek, Hebrew and Arabic — only someone like Scaliger could have achieved something like De emendatione temporum (“On correcting dates”). Freeing the ancient world from slavish Biblical interpretations, he utterly transformed Europe’s sense of deep history. With him, the continent first began to realise that the cultures of Egypt and Mesopotamia predated Greece and Israel by millennia. It would take centuries to properly decipher their scripts and languages, but that was the beginning of a revolution in historical understanding as profound as the Darwinian revolution in biology. Scaliger showed that linguistic and textual scholarship is about far more than mere verbs or adjectives: it is a key to unlock our world. Now, though, his legacy is in danger of being abandoned. Over recent months, academics everywhere have been shocked by the news of cuts to long-established language programmes, including at Leiden. Among other languages, Turkish, Persian and Hebrew may all stop being offered. Arabic could soon vanish too: especially shocking at Leiden, home to the oldest chair of the language on earth. Yet if the decline has many causes, monoglot academic environments and budget cuts among them, the consequences are far from mundane. For if the trend continues, we will lose some of the best tools for cultural and historical understanding we have. Modern academia is dominated by the sciences. No one can deny that STEM subjects dominate the public conversation, followed by the more quantitative social sciences. On those rare occasions that the linguistic study of the human past does get a look in, it’s often just because AI is involved — and even then the returns are often dubious. It’s a similar story financially. In the UK, only £70 million of government research funding was allocated to the humanities in 2024-5. In a sense, meanwhile, this retreat is self-sustaining. Quite apart from the psychological impact on university administrators — the more humanities retreat from the front pages, the harder it is for bean-counters to take them seriously — it’s much easier to irretrievably lose knowledge of rarer languages once the chain of transmission is broken. Let me put it like this: how many experts in Lycian, Palmyrean, Aramaic or Tocharian are there in the world today? I don’t want to sound defeatist here. There are more than enough people interested to keep these studies alive — if the resources are there. Just one case in point is OxLat. Our Oxford programme teaching Latin to school students, it has twice as many applicants as spaces, despite the Government’s plan to scrap the Latin Excellence Programme for state schools. Yet even within the humanities, the most eye-catching work is often dealing in images rather than words: just think of how much media attention each new fresco in Pompeii gets compared to new finds in manuscripts or inscriptions. As far as language is concerned, meanwhile, there have surely been spectacular exceptions: yet they only serve to show what we usually miss. Perhaps the last time a historical linguistic discovery truly gripped the public imagination was the decipherment of Linear B in 1953. Yet who really remembers that discovery of the earliest form of Greek in a year that also saw the conquest of Everest and the detection of DNA? More to the point, how many people know anything about the deciphering of Mayan hieroglyphs, let alone the recent epic advances in the history of early writing? How things change. As Scaliger so vividly proves, linguistics could once change the world — literally. As the Renaissance bubbled on, scholars on both sides of Europe’s sectarian divide built a new community of scholarship aimed at understanding ancient texts. Encompassing Greek, Latin and Hebrew, among other tongues, the litterae humaniores (“more human letters”) were not a theological project per se, and indeed sought to bring bickering Protestants and Catholics closer together. They did, nonetheless, have a deep moral dimension. As the later German scholar Rudolf Pfeiffer remarked, luminaries like Erasmus linked Europe’s “spiritual decline” to the related deterioration of language. “And so,” he added, “it was with language that spiritual and moral renaissance must begin.” Pfeiffer, one of the refugees from Hitler’s Germany who transformed the study of classics in Britain, was no doubt feeling the same moral urgency himself. “Linguistics could once change the world — literally.” Erasmus and Scaliger were only two names in the wider “republic of letters”, an international community of thought and scholarship in active correspondence across Europe. Mostly writing in Latin, Scaliger was not a lone figure even at Leiden himself. Consider Justus Lipsius, the great editor of the Roman historian Tacitus and the Stoic philosopher Seneca, who distilled his learning into bestselling books on political ethics. Another example is Hugo Grotius, the father of international law as we know it. In England, Thomas More with his Utopia was part of the same community. We shouldn’t idolise these curious Renaissance minds. With modern departments now boasting a far subtler appreciation of Syriac or Aramaic, no scholar today would agree with Scaliger that someone “who knows no Greek knows nothing”. Nor should we resent the integration of visual culture into the study of the ancient world: it is no better to approach another culture by closing your eyes than closing your ears. New quantitative methods, too, have plenty to contribute. We can now understand the living standards, the flow of trade, the size of the population, the impact of disease in the ancient world in ways impossible even half a century ago. Yet if we doubtless gain by quantitative methods, we also lose something when straightforward knowledge of ancient tongues falls away. That’s true enough for early modern writers: even English authors like Milton or Hobbes can’t truly be appreciated without an intimate understanding of Latin. Not only was it the language in which all of them constantly read, but a large part of their work was simply written in Latin first. For ancient historians or medievalists, meanwhile, a large share of new knowledge still comes from texts in ancient languages, often fragmentary, and which require considerable linguistic expertise to interpret. To give you a sense of the scale, consider the Supplementum Epigraphicum Graecum, a publication covering newly published ancient inscriptions in Greek. Published annually, the Supplementum contains over 2,000 entries each year. Nor is Greek the only relevant language here. In 2013, for instance, a University of Warwick academic discovered a medieval Arabic translation of long-lost Greek text. Covering the financial management of farm estates, and written by a Greco-Roman philosopher called Bryson, it shows understanding of “need” as the driver of exchange and economy, and represents the earliest attempt to explain the price of things by supply and demand. One of my favourite examples here comes from Jane Lightfoot’s edition of the Apotelesmatica, a set of astrological poems ascribed to an Ancient Egyptian priest. Not only is this translation a major source on ancient astrology and astronomy, but also an encyclopaedia of the social world of Roman Egypt. Keen to know under what star sign the craftsmen of “marvellous machines past mortal ken” were born, and whether it was good to be one? Or “speakers of words, in public fora best at mending strife, and aiding the oppressed”? Or, for that matter, vagabonds in foreign lands, or “failures in business”? There’s no better place to start your research. I appreciate, of course, that in a world enraptured by AI decipherings in places like Herculaneum, texts like the Apotelesmatica can easily be ignored. Yet if that’s a shame in itself — which sane person wouldn’t want to learn about marvellous machines past mortal ken? — the decline of ancient languages matters for a yet more fundamental reason. To quote Mikhail Gasparov, a Russian classicist whose translations introduced me to Greece and Rome as a teenager, the study of ancient languages is “a service of understanding”. Our own time and our own culture represent only a tiny fraction of what the human mind is capable of. And, unless we get out of that familiar circle, we never get to see ourselves with some detachment, to detect the blind spots of our own time. From decrees of ancient cities offering a reflection on civic virtue, to Mesopotamian moral proverbs on clay tablets, to sermons discovered in medieval manuscripts, different takes on morality and society continue to appear from ancient sources. And just as we would never be content to rely on ChatGPT, or Google Translate, to understand another human being we truly cared for, why shouldn’t we go back to the original source to study some vanished culture — just as rich, in its way, as any lover or friend? In both cases, learning the language teaches us that they and their thoughts matter, no less than our own. That is more difficult than just making facile claims on behalf of other cultures, but it is still the thing that makes our studies “more human” than most. We may not think, with Scaliger, that “all divisions in religion arise from ignorance of grammar” — but we would understand each other infinitely better if we paid enough attention to language.
Via Charles Tiayon

|
Rescooped by
Dr. Russ Conrath
from Daily Magazine
August 11, 3:11 PM
|
Tectonic shifts in society and business occur when unexpected events force widespread experimentation around a new idea. During World War II, for instance, when American men went off to war, women proved that they could do “men’s” work — and do it well. Women never looked back after that. Similarly, the Y2K problem demanded the extensive use of Indian software engineers, leading to the tripling of employment-based visas granted by the U.S. Fixing that bug enabled Indian engineers to establish their credentials, and catapulted them as world leaders in addressing technology problems. Alphabet, Microsoft, IBM, and Adobe are all headed by India-born engineers today.
Right now, the Coronavirus pandemic is forcing global experimentation with remote teaching. There are many indicators that this crisis is going to transform many aspects of life. Education could be one of them if remote teaching proves to be a success. But how will we know if it is? As this crisis-driven experiment launches, we should be collecting data and paying attention to the following three questions about higher education’s business model and the accessibility of quality college education.
Do students really need a four-year residential experience?
Answering this question requires an understanding of which parts of the current four-year model can be substituted, which parts can be supplemented, and which parts complemented by digital technologies.
In theory, lectures that require little personalization or human interaction can be recorded as multi-media presentations, to be watched by students at their own pace and place. Such commoditized parts of the curriculum can be easily delivered by a non-university instructor on Coursera, for example; teaching Pythagoras’ theorem is pretty much the same the world over. For such courses, technology platforms can deliver the content to very large audiences at low cost, without sacrificing one of the important benefits of the face-to-face (F2F) classroom, the social experience, because there is hardly any in these basic-level courses.
By freeing resources from courses that can be commoditized, colleges would have more resources to commit to research-based teaching, personalized problem solving, and mentorship. The students would also have more resources at their disposal, too, because they wouldn’t have to reside and devote four full years at campuses. They would take commoditized courses online at their convenience and at much cheaper cost. They can use precious time they spend on campus for electives, group assignments, faculty office hours, interactions, and career guidance, something that cannot be done remotely. In addition, campuses can facilitate social networking, field-based projects, and global learning expeditions — that require F2F engagements. This is a hybrid model of education that has the potential to make college education more affordable for everybody.
But can we shift to a hybrid model? We’re about to find out. It is not just the students who are taking classes remotely, even the instructors are now forced to teach those classes from their homes. The same students and instructors that met until a few weeks back for the same courses, are now trying alternative methods. So, both parties can compare their F2F and remote experiences, all else held equal.
With the current experiment, students, professors, and university administrators must keep a record of which classes are benefiting from being taught remotely and which ones are not going so well. They must maintain chat rooms that facilitate anonymized discussions about the technology issues, course design, course delivery, and evaluation methods. These data points can inform future decisions about when — and why — some classes should be taught remotely, which ones should remain on the campus, and which within-campus classes should be supplemented or complemented by technology.
What improvements are required in IT infrastructure to make it more suitable for online education?
As so many of us whose daily schedules have become a list of virtual meetings can attest, there are hardware and software issues that must be addressed before remote learning can really take off. We have no doubt that digital technologies (mobile, cloud, AI, etc.) can be deployed at scale, yet we also know that much more needs to be done. On the hardware side, bandwidth capacity and digital inequalities need addressing. The F2F setting levels lots of differences, because students in the same class get the same delivery. Online education, however, amplifies the digital divide. Rich students have the latest laptops, better bandwidths, more stable wifi connections, and more sophisticated audio-visual gadgets.
Software for conference calls may be a good start, but it can’t handle some key functionalities such as accommodating large class sizes while also providing a personalized experience. Even in a 1,000-student classroom, an instructor can sense if students are absorbing concepts, and can change the pace of the teaching accordingly. A student can sense whether they are asking too many questions, and are delaying the whole class. Is our technology good enough to accommodate these features virtually? What more needs to be developed? Instructors and students must note and should discuss their pain points, and facilitate and demand technological development in those areas.
In addition, online courses require educational support on the ground: Instructional designers, trainers, and coaches to ensure student learning and course completion. Digital divide also exists among universities, which will become apparent in the current experiment. Top private universities have better IT infrastructure and higher IT support staff ratio for each faculty compared to budget-starved public universities.
What training efforts are required for faculty and students to facilitate changes in mindsets and behaviors?
Not all faculty members are comfortable with virtual classrooms and there is a digital divide among those who have never used even the basic audio-visual equipment, relying on blackboards and flipcharts, and younger faculty who are aware of and adept in newer technology. As students across the nation enter online classrooms in the coming weeks, they’re going to learn that many instructors are not trained to design multimedia presentations, with elaborate notations and graphics. Colleges and universities need to use this moment to assess what training is needed to provide a smooth experience.
Students also face a number of issues with online courses. Committing to follow the university calendar forces them to finish a course, instead of procrastinating it forever. And online they can feel as they don’t belong to a peer group or a college cohort, which in real life instils a sense of competition, motivating all to excel. Anything done online suffers from attention span, because students multi-task, check emails, chat with friends, and surf the Web while attending online lectures. We’re parents and professors; we know this is true.
Can these mindsets change? Right now we are (necessarily, due to social distancing) running trial and error experiments to find out. Both teachers and students are readjusting and recalibrating in the middle of teaching semesters. The syllabus and course contents are being revised as the courses are being taught. Assessment methods, such as exams and quizzes are being converted to online submissions. University administrators and student bodies are being accommodative and are letting instructors innovate their own best course, given such short notice. Instructors, students, and university administrators should all be discussing how the teaching and learning changes between day 1 of virtual education and day X. This will provide clues for how to train future virtual educators and learners.
A Vast Experiment
The ongoing coronavirus pandemic has forced a global experiment that could highlight the differences between, and cost-benefit trade off of, the suite of services offered by a residential university and the ultra low-cost education of an online education provider like Coursera. Some years ago, experts had predicted that massive open online courses (MOOCs), such as Khan Academy, Coursera, Udacity, and edX, would kill F2F college education — just as digital technologies killed off the jobs of telephone operators and travel agents. Until now, however, F2F college education has stood the test of time.
The current experiment might show that four-year F2F college education can no longer rest on its laurels. A variety of factors — most notably the continuously increasing cost of tuition, already out of reach for most families, implies that the post-secondary education market is ripe for disruption. The coronavirus crisis may just be that disruption. How we experiment, test, record, and understand our responses to it now will determine whether and how online education develops as an opportunity for the future. This experiment will also enrich political discourse in the U.S. Some politicians have promised free college education; what if this experiment proves that a college education doesn’t have to bankrupt a person?
After the crisis subsides, is it best for all students to return to the classroom, and continue the status quo? Or will we have found a better alternative?
Via Inovação Educacional, juandoming, THE OFFICIAL ANDREASCY
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...