Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
?
April 10, 2018 12:08 AM
|
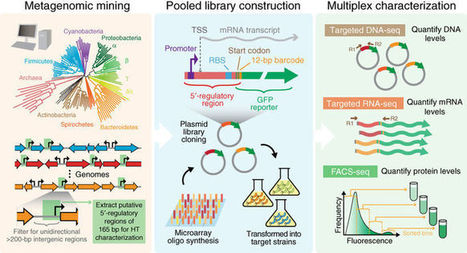
Robust and predictably performing synthetic circuits rely on the use of well-characterized regulatory parts across different genetic backgrounds and environmental contexts. Here we report the large-scale metagenomic mining of thousands of natural 5′ regulatory sequences from diverse bacteria, and their multiplexed gene expression characterization in industrially relevant microbes. We identified sequences with broad and host-specific expression properties that are robust in various growth conditions. We also observed substantial differences between species in terms of their capacity to utilize exogenous regulatory sequences. Finally, we demonstrate programmable species-selective gene expression that produces distinct and diverse output patterns in different microbes. Together, these findings provide a rich resource of characterized natural regulatory sequences and a framework that can be used to engineer synthetic gene circuits with unique and tunable cross-species functionality and properties, and also suggest the prospect of ultimately engineering complex behaviors at the community level.

|
Scooped by
?
April 9, 2018 11:56 AM
|
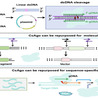
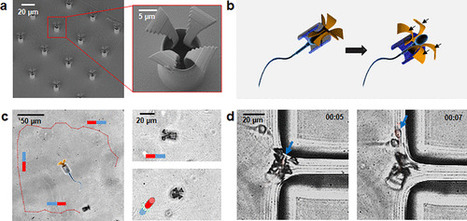
A sperm-driven micromotor is presented as a targeted drug delivery system, which is appealing to potentially treat diseases in the female reproductive tract. This system is demonstrated to be an efficient drug delivery vehicle by first loading a motile sperm cell with an anticancer drug (doxorubicin hydrochloride), guiding it magnetically, to an in vitro cultured tumor spheroid, and finally freeing the sperm cell to deliver the drug locally. The sperm release mechanism is designed to liberate the sperm when the biohybrid micromotor hits the tumor walls, allowing it to swim into the tumor and deliver the drug through the sperm–cancer cell membrane fusion. In our experiments, the sperm cells exhibited a high drug encapsulation capability and drug carrying stability, conveniently minimizing toxic side effects and unwanted drug accumulation in healthy tissues. Overall, sperm cells are excellent candidates to operate in physiological environments, as they neither express pathogenic proteins nor proliferate to form undesirable colonies, unlike other cells or microorganisms. This sperm-hybrid micromotor is a biocompatible platform with potential application in gynecological healthcare, treating or detecting cancer or other diseases in the female reproductive system.

|
Scooped by
?
April 8, 2018 11:10 PM
|
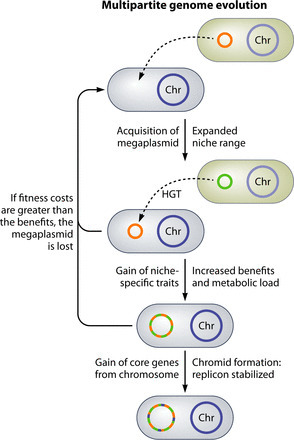
Approximately 10% of bacterial genomes are split between two or more large DNA fragments, a genome architecture referred to as a multipartite genome. This multipartite organization is found in many important organisms, including plant symbionts, such as the nitrogen-fixing rhizobia, and plant, animal, and human pathogens, including the genera Brucella, Vibrio, and Burkholderia. The availability of many complete bacterial genome sequences means that we can now examine on a broad scale the characteristics of the different types of DNA molecules in a genome. Recent work has begun to shed light on the unique properties of each class of replicon, the unique functional role of chromosomal and nonchromosomal DNA molecules, and how the exploitation of novel niches may have driven the evolution of the multipartite genome. The aims of this review are to (i) outline the literature regarding bacterial genomes that are divided into multiple fragments, (ii) provide a meta-analysis of completed bacterial genomes from 1,708 species as a way of reviewing the abundant information present in these genome sequences, and (iii) provide an encompassing model to explain the evolution and function of the multipartite genome structure. This review covers, among other topics, salient genome terminology; mechanisms of multipartite genome formation; the phylogenetic distribution of multipartite genomes; how each part of a genome differs with respect to genomic signatures, genetic variability, and gene functional annotation; how each DNA molecule may interact; as well as the costs and benefits of this genome structure.

|
Scooped by
?
April 5, 2018 5:14 PM
|
Glycoside Hydrolase Family 7 cellobiohydrolases (GH7 CBHs) catalyze cellulose depolymerization in cellulolytic eukaryotes, making them key discovery and engineering targets. However, there remains a lack of robust structure–activity relationships for these industrially important cellulases. Here, we compare CBHs from Trichoderma reesei (TrCel7A) and Penicillium funiculosum (PfCel7A), which exhibit a multi-modular architecture consisting of catalytic domain (CD), carbohydrate-binding module, and linker. We show that PfCel7A exhibits 60% greater performance on biomass than TrCel7A. To understand the contribution of each domain to this improvement, we measure enzymatic activity for a library of CBH chimeras with swapped subdomains, demonstrating that the enhancement is mainly caused by PfCel7A CD. We solve the crystal structure of PfCel7A CD and use this information to create a second library of TrCel7A CD mutants, identifying a TrCel7A double mutant with near-equivalent activity to wild-type PfCel7A. Overall, these results reveal CBH regions that enable targeted activity improvements.

|
Scooped by
?
April 5, 2018 11:47 AM
|
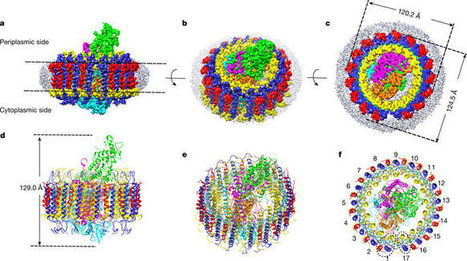
The light-harvesting 1–reaction centre (LH1–RC) complex is a key functional component of bacterial photosynthesis. Here we present a 2.9 Å resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of the bacteriochlorophyll b-based LH1–RC complex from Blastochloris viridisthat reveals the structural basis for absorption of infrared light and the molecular mechanism of quinone migration across the LH1 complex. The triple-ring LH1 complex comprises a circular array of 17 β-polypeptides sandwiched between 17 α- and 16 γ-polypeptides. Tight packing of the γ-apoproteins between β-polypeptides collectively interlocks and stabilizes the LH1 structure; this, together with the short Mg–Mg distances of bacteriochlorophyll b pairs, contributes to the large redshift of bacteriochlorophyll b absorption. The ‘missing’ 17th γ-polypeptide creates a pore in the LH1 ring, and an adjacent binding pocket provides a folding template for a quinone, Q P, which adopts a compact, export-ready conformation before passage through the pore and eventual diffusion to the cytochrome bc1 complex.

|
Scooped by
?
April 5, 2018 12:56 AM
|
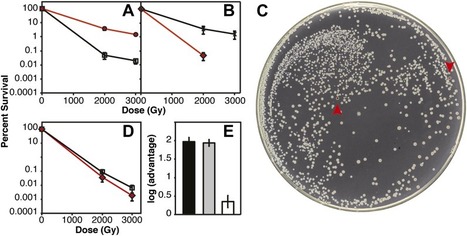
By directed evolution in the laboratory, we previously generated populations of Escherichia coli that exhibit a complex new phenotype, extreme resistance to ionizing radiation (IR). The molecular basis of this extremophile phenotype, involving strain isolates with a 3-4 order of magnitude increase in IR resistance at 3000 Gy, is now addressed. Of 69 mutations identified in one of our most highly adapted isolates, functional experiments demonstrate that the IR resistance phenotype is almost entirely accounted for by only three of these nucleotide changes, in the DNA metabolism genes recA, dnaB, and yfjK. Four additional genetic changes make small but measurable contributions. Whereas multiple contributions to IR resistance are evident in this study, our results highlight a particular adaptation mechanism not adequately considered in studies to date: Genetic innovations involving pre-existing DNA repair functions can play a predominant role in the acquisition of an IR resistance phenotype.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 9:57 PM
|
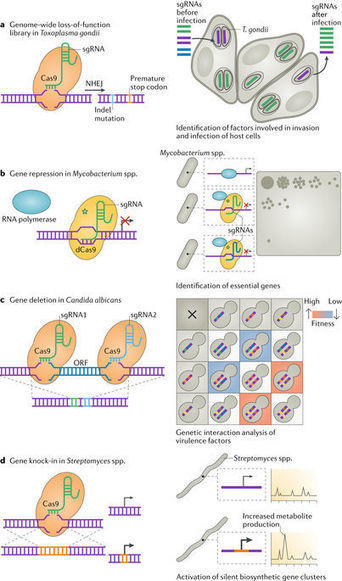
Genetic manipulation of microorganisms has been crucial in understanding their biology, yet for many microbial species, robust tools for comprehensive genetic analysis were lacking until the advent of CRISPR–Cas-based gene editing techniques. In this Progress article, we discuss advances in CRISPR-based techniques for the genetic analysis of genetically intractable microorganisms, with an emphasis on mycobacteria, fungi and parasites. We discuss how CRISPR-based analyses in these organisms have enabled the discovery of novel gene functions, the investigation of genetic interaction networks and the identification of virulence factors.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 2:44 PM
|
How will the farms of the future feed a projected 9.8 billion people by 2050? A 'smart farm' project marries microbiology and machine learning in an effort to reduce the need for chemical fertilizers and enhance soil carbon uptake, thus improving the long-term viability of the land while increasing crop yields.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 2:36 PM
|
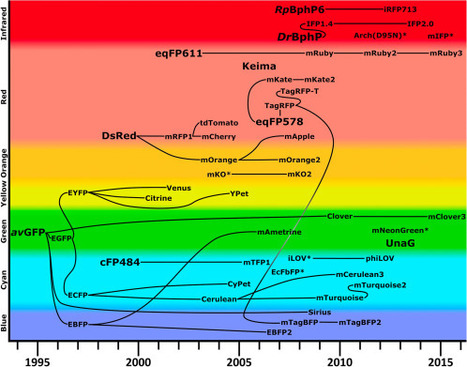
Genetically encoded fluorescent sensors are essential tools in modern biological research, and recent advances in fluorescent proteins (FPs) have expanded the scope of sensor design and implementation. In this review we compare different sensor platforms, including Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) sensors, fluorescence-modulated single FP-based sensors, translocation sensors, complementation sensors, and dimerization-based sensors. We discuss elements of sensor design and engineering for each platform, including the incorporation of new types of FPs and sensor screening techniques. Finally, we summarize the wide range of sensors in the literature, exploring creative new sensor architectures suitable for different applications.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 2:25 PM
|
Plants associated with symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria play important roles in early successional, riparian and semidry ecosystems. These so‐called nitrogen fixing plants are widely used for reclamation of disturbed vegetation and improvement of soil fertility in agroforestry. Yet, available information about plants that are capable of establishing nodulation is fragmented and somewhat outdated. This article introduces the NodDB database of nitrogen fixing plants based on morphological and phylogenetic evidence (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.15156/BIO/587469) and discusses plant groups with conflicting reports and interpretation such as certain legume clades and the Zygophyllaceae family. During angiosperm evolution, nitrogen fixing plants became common in the fabid rather than in the ‘nitrogen fixing’ clade. The global GBIF plant species distribution data indicated that nitrogen fixing plants tend to be relatively more diverse in savanna and semidesert biomes. The compiled and re‐interpreted information about nitrogen fixing plants enables accurate analyses of biogeography and community ecology of biological nitrogen fixation.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 2:04 PM
|
In this special issue, the state of the art on several of those relatively new microbial biotechnologies are summarized and critically evaluated.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 2:00 PM
|
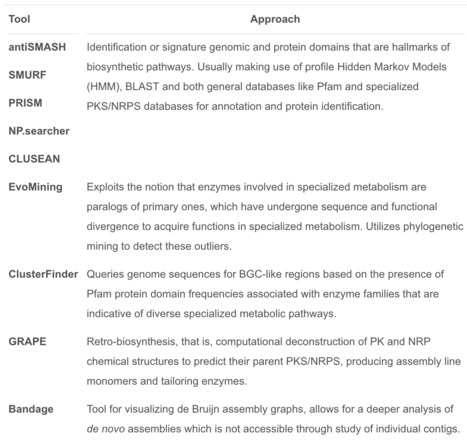
Microorganisms are Nature's little engineers of a remarkable array of bioactive small molecules that represent most of our new drugs. The wealth of genomic and metagenomic sequence data generated in the last decade has shown that the majority of novel biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) is identified from cultivation-independent studies, which has led to a strong expansion of the number of microbial taxa known to harbour BGCs. The large size and repeat sequences of BGCs remain a bioinformatic challenge, but newly developed software tools have been created to overcome these issues and are paramount to identify and select the most promising BGCs for further research and exploitation. Although heterologous expression of BGCs has been the greatest challenge until now, a growing number of polyketide synthase (PKS) and non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS)-encoding gene clusters have been cloned and expressed in bacteria and fungi based on techniques that mostly rely on homologous recombination. Finally, combining ecological insights with state-of-the-art computation and molecular methodologies will allow for further comprehension and exploitation of microbial specialized metabolites.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 8:16 AM
|
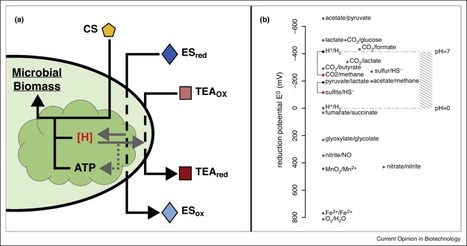
Microbial communities present the next research frontier. We argue here that understanding and engineering microbial communities requires a holistic view that considers not only species–species, but also species–environment interactions, and feedbacks between ecological and evolutionary dynamics (eco-evo feedbacks). Due this multi-level nature of interactions, we predict that approaches aimed soley at altering specific species populations in a community (through strain enrichment or inhibition), would only have a transient impact, and species–environment and eco-evo feedbacks would eventually drive the microbial community to its original state. We propose a higher-level engineering approach that is based on thermodynamics of microbial growth, and that considers specifically microbial redox biochemistry. Within this approach, the emphasis is on enforcing specific environmental conditions onto the community. These are expected to generate higher-level thermodynamic bounds onto the system, which the community structure and function can then adapt to. We believe that the resulting end-state can be ecologically and evolutionarily stable, mimicking the natural states of complex communities. Toward designing the exact nature of the environmental enforcement, thermodynamics and redox biochemistry can act as coarse-grained principles, while the use of electrodes — as electron providing or accepting redox agents — can provide implementation with spatiotemporal control.
|

|
Scooped by
?
April 9, 2018 10:20 PM
|
Model ecosystems could provide significant insight into the evolution and behavior of real ecosystems. We discuss the advantages and limitations of common approaches like mesocosms. In this context, we highlight recent breakthroughs that allow for the creation of networks of organisms with independently controlled environments and rates of chemical exchange.

|
Scooped by
?
April 9, 2018 11:35 AM
|
The demand for cellulosic biofuels is on the rise because of the anticipation for sustainable energy and less greenhouse gas emissions in the future. However, production of cellulosic biofuels, especially cellulosic butanol, has been hampered by the lack of potent microbes that are capable of converting cellulosic biomass into biofuels. We report a wild-type Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum strain TG57, which is capable of using microcrystalline cellulose directly to produce butanol (1.93 g/liter) as the only final product (without any acetone or ethanol produced), comparable to that of engineered microbes thus far. Strain TG57 exhibits significant advances including unique genes responsible for a new butyrate synthesis pathway, no carbon catabolite repression, and the absence of genes responsible for acetone synthesis (which is observed as the main by-product in most Clostridium strains known today). Furthermore, the use of glucose analog 2-deoxyglucose posed a selection pressure to facilitate isolation of strain TG57 with deletion/silencing of carbon catabolite repressor genes—the ccr and xylR genes—and thus is able to simultaneously ferment glucose, xylose, and arabinose to produce butanol (7.33 g/liter) as the sole solvent. Combined analysis of genomic and transcriptomic data revealed unusual aspects of genome organization, numerous determinants for unique bioconversions, regulation of central metabolic pathways, and distinct transcriptomic profiles. This study provides a genome-level understanding of how cellulose is metabolized by T. thermosaccharolyticum and sheds light on the potential of competitive and sustainable biofuel production.

|
Scooped by
?
April 7, 2018 10:10 PM
|
Nitrogen availability is a central controller of terrestrial plant growth and, thereby, of the carbon cycle and global climate change. It has been widely assumed that the atmosphere is the main source of terrestrial nitrogen input. Surprisingly, Houlton et al. now show that bedrock is just as large a nitrogen source across major sectors of the global terrestrial environment. They used three diverse and largely independent assessments of the nitrogen mobility and reactivity of rocks in the surface environment. These approaches yielded convergent estimates pointing to the equal importance of the atmosphere and bedrock as nitrogen sources.

|
Scooped by
?
April 5, 2018 4:52 PM
|
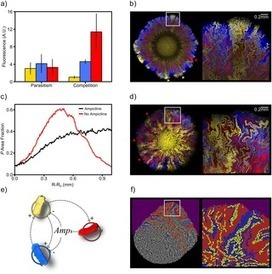
In order to achieve greater levels of complexity, complex systems often display cooperative interactions that enable the formation and stabilisation of mutualisms. Theoretical models have shown that closed chains of cooperative species or hypercycles might have been crucial in the evolution towards complexity in early molecular replicators. However, parasites can easily destroy the cooperative loop, unless the system is embedded in a spatial context where interactions are limited to nearest neighbours. A dynamically similar phenomenon occurs in ecological webs, where closed positive feedback loops contribute to global stability and ecophysiology. Here we explore this problem by engineering synthetic cooperative strains of microbes that grow and interact in a cell culture under the absence and presence of a synthetic parasitic strains. By analysing the impact of cooperation under different conditions, we find that cooperative replication is successful and overcomes competitive interactions in nutrient-poor environments. However, the same closed loop fails to establish in nutrient-rich media. Moreover, parasitic entities that jeopardise cooperation under well-mixed conditions can be overcome by hypercycles when growing in a two-dimensional space.

|
Scooped by
?
April 5, 2018 9:28 AM
|
In legume-Rhizobium symbioses, specialised soil bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen in return for carbon. However, ineffective strains can arise, making discrimination essential. Discrimination can occur via partner choice, where legumes prevent ineffective strains from entering, or via sanctioning, where plants provide fewer resources. Several studies have inferred that legumes exercise partner choice, but the rhizobia compared were not otherwise isogenic. To test when and how plants discriminate ineffective strains we developed sets of fixing and non-fixing strains that differed only in the expression of nifH – essential for nitrogen fixation – and could be visualised using marker genes. We show that the plant is unable to select against the non-fixing strain at the point of entry, but that non-fixing nodules are sanctioned. We also used the technique to characterise mixed nodules (containing both a fixing and a non-fixing strain), whose frequency could be predicted using a simple diffusion model. We discuss that sanctioning is likely to evolve in preference to partner choice in any symbiosis where partner quality cannot be adequately assessed until goods or services are actively exchanged.

|
Scooped by
?
April 5, 2018 12:16 AM
|
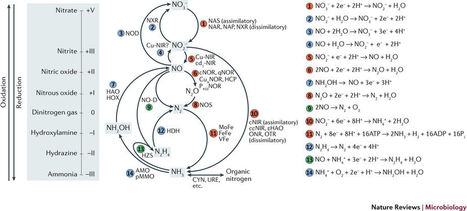
Nitrogen is an essential component of all living organisms and the main nutrient limiting life on our planet. By far, the largest inventory of freely accessible nitrogen is atmospheric dinitrogen, but most organisms rely on more bioavailable forms of nitrogen, such as ammonium and nitrate, for growth. The availability of these substrates depends on diverse nitrogen-transforming reactions that are carried out by complex networks of metabolically versatile microorganisms. In this Review, we summarize our current understanding of the microbial nitrogen-cycling network, including novel processes, their underlying biochemical pathways, the involved microorganisms, their environmental importance and industrial applications.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 3:52 PM
|
We examined succession of the rhizosphere microbiota of three model plants (Arabidopsis, Medicago and Brachypodium) in compost and sand and three crops (Brassica, Pisum and Triticum) in compost alone. We used serial inoculation of 24 independent replicate microcosms over three plant generations for each plant/soil combination. Stochastic variation between replicates was surprisingly weak and by the third generation, replicate microcosms for each plant had communities that were very similar to each other but different to those of other plants or unplanted soil. Microbiota diversity remained high in compost, but declined drastically in sand, with bacterial opportunists and putative autotrophs becoming dominant. These dramatic differences indicate that many microbes cannot thrive on plant exudates alone and presumably also require carbon sources and/or nutrients from soil. Arabidopsis had the weakest influence on its microbiota and in compost replicate microcosms converged on three alternative community compositions rather than a single distinctive community. Organisms selected in rhizospheres can have positive or negative effects. Two abundant bacteria are shown to promote plant growth, but in Brassicathe pathogen Olpidium brassicae came to dominate the fungal community. So plants exert strong selection on the rhizosphere microbiota but soil composition is critical to its stability. microbial succession/ plant–microbe interactions/rhizosphere microbiota/selection.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 2:42 PM
|
Here, all the RNA assembled de novo from roots of 12 willow trees, pot-grown in either contaminated or non-contaminated soil from a former petroleum refinery, was annotated and differential gene expression from any and all organisms identified was explored to see if the functionality of a successful phytoremediation system can be elucidated.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 2:33 PM
|
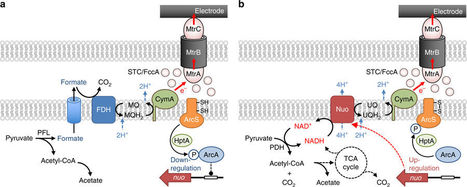
Electrochemically active bacteria (EAB) receive considerable attention for their utility in bioelectrochemical processes. Although electrode potentials are known to affect the metabolic activity of EAB, it is unclear whether EAB are able to sense and respond to electrode potentials. Here, we show that, in the presence of a high-potential electrode, a model EAB Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 can utilize NADH-dependent catabolic pathways and a background formate-dependent pathway to achieve high growth yield. We also show that an Arc regulatory system is involved in sensing electrode potentials and regulating the expression of catabolic genes, including those for NADH dehydrogenase. We suggest that these findings may facilitate the use of EAB in biotechnological processes and offer the molecular bases for their ecological strategies in natural habitats.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 2:16 PM
|
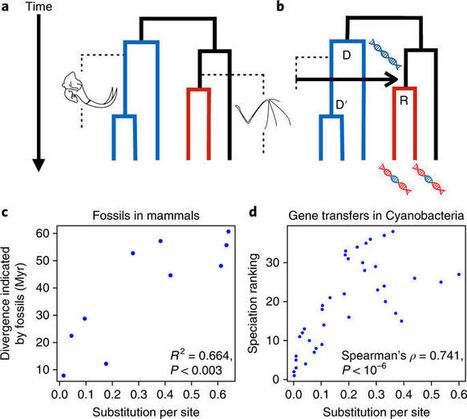
Biodiversity has always been predominantly microbial, and the scarcity of fossils from bacteria, archaea and microbial eukaryotes has prevented a comprehensive dating of the tree of life. Here, we show that patterns of lateral gene transfer deduced from an analysis of modern genomes encode a novel and abundant source of information about the temporal coexistence of lineages throughout the history of life. We use state-of-the-art species tree-aware phylogenetic methods to reconstruct the history of thousands of gene families and demonstrate that dates implied by gene transfers are consistent with estimates from relaxed molecular clocks in Bacteria, Archaea and Eukarya. We present the order of speciations according to lateral gene transfer data calibrated to geological time for three datasets comprising 40 genomes for Cyanobacteria, 60 genomes for Archaea and 60 genomes for Fungi. An inspection of discrepancies between transfers and clocks and a comparison with mammalian fossils show that gene transfer in microbes is potentially as informative for dating the tree of life as the geological record in macroorganisms.Article

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 2:02 PM
|
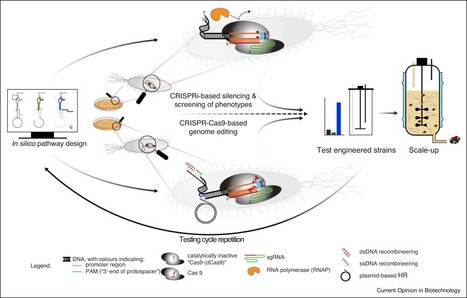
High engineering efficiencies are required for industrial strain development. Due to its user-friendliness and its stringency, CRISPR-Cas-based technologies have strongly increased genome engineering efficiencies in bacteria. This has enabled more rapid metabolic engineering of both the model host Escherichia coli and non-model organisms like Clostridia, Bacilli, Streptomycetes and cyanobacteria, opening new possibilities to use these organisms as improved cell factories. The discovery of novel Cas9-like systems from diverse microbial environments will extend the repertoire of applications and broaden the range of organisms in which it can be used to create novel production hosts. This review analyses the current status of prokaryotic metabolic engineering towards the production of biotechnologically relevant products, based on the exploitation of different CRISPR-related DNA/RNA endonuclease variants.

|
Scooped by
?
April 3, 2018 8:18 AM
|
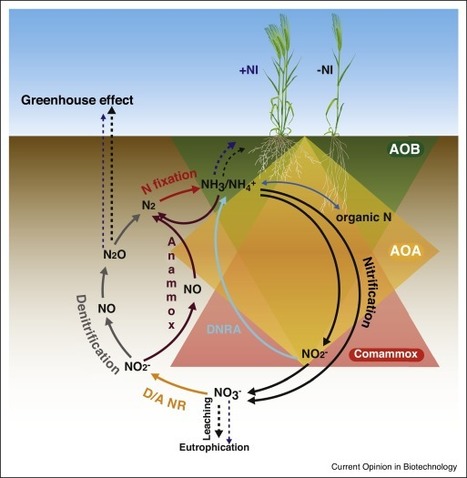
Nitrogen is one of the most important nutrients for plant growth and hence heavily applied in agricultural systems via fertilization. Nitrification, that is, the conversion of ammonium via nitrite to nitrate by soil microorganisms, however, leads to nitrate leaching and gaseous nitrous oxide production and as such to an up to 50% loss of nitrogen availability for the plant. Nitrate leaching also results in eutrophication of groundwater, drinking water and recreational waters, toxic algal blooms and biodiversity loss, while nitrous oxide is a greenhouse gas with a global warming potential 300× greater than carbon dioxide. Logically, inhibition of nitrification is an important strategy used in agriculture to reduce nitrogen losses, and contributes to a more environmental-friendly practice. However, recently identified and crucial players in nitrification, that is, ammonia-oxidizing archaea and comammox bacteria, seem to be under-investigated in this respect. In this review, we give an update on the different pathways in ammonia oxidation, the relevance for agriculture and the interaction with nitrification inhibitors. As such, we hope to pinpoint possible strategies to optimize the efficiency of nitrification inhibition.
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...