Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
?
March 2, 2018 1:03 PM
|
A Gram-positive, fast-growing, endophytic bacterium was isolated from root nodules of Medicago polymorpha and identified as Bacillus megaterium. The isolate, named NMp082, co-inhabited nodules with the symbiotic rhizobium Ensifer medicae. B. megaterium NMp082 contained nifH and nodD genes that were 100% identical to those of Ensifer meliloti, an unusual event that suggested previous lateral gene transfer from a different rhizobial species. Despite the presence of nodulation and nitrogen fixation genes, the endophyte was not able to form effective nodules; however, it induced nodule-like unorganised structures in alfalfa roots. Axenic inoculation promoted plant growth in M. polymorpha, Medicago lupulina, Medicago truncatula and Medicago sativa, and co-inoculation with E. medicae enhanced growth and nodulation of Medicago spp. plants compared with inoculation with either bacterium alone. B. megaterium NMp082 also induced tolerance to salt stress in alfalfa and Arabidopsis plants. The ability to produce indole acetic acid (IAA) and the 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase activity displayed by the endophyte in vitro might explain the observed plant growth promotion and salt stress alleviation. The isolate was also highly tolerant to salt stress, water deficit and to the presence of different heavy metals. The newly characterised endophytic bacterium possessed specific characteristics that point at potential applications to sustain plant growth and nodulation under abiotic stress.

|
Scooped by
?
March 2, 2018 11:17 AM
|
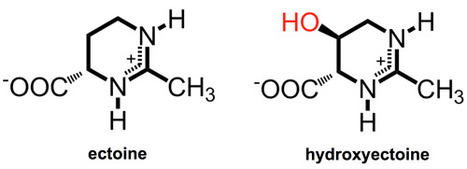
The ability to maintain physiologic and metabolic functions in response to changes in the salinity of the surrounding environment is critical for microorganisms. These organisms have adopted two strategies for dealing with fluctuations in environmental salinity: “salt in,” which occurs when the cells encounter hyperosmotic conditions, and “salt out.” A signature of organisms that use the “salt in” strategy is an acidic proteome that favors persistent high relative concentrations of cations. Organisms that use the “salt out” mechanism also import potassium in response to hyperosmotic shock; however, they do not maintain it for extended periods. Instead, they either import or synthesize compatible solutes that include ectoine and glycine-betaine

|
Scooped by
?
March 2, 2018 9:34 AM
|
We report the discovery that strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis produce 6- N -hydroxyaminopurine (6-HAP), a molecule that inhibits DNA polymerase activity. In culture, 6-HAP selectively inhibited proliferation of tumor lines but did not inhibit primary keratinocytes. Resistance to 6-HAP was associated with the expression of mitochondrial amidoxime reducing components, enzymes that were not observed in cells sensitive to this compound. Intravenous injection of 6-HAP in mice suppressed the growth of B16F10 melanoma without evidence of systemic toxicity. Colonization of mice with an S. epidermidis strain producing 6-HAP reduced the incidence of ultraviolet-induced tumors compared to mice colonized by a control strain that did not produce 6-HAP. S. epidermidis strains producing 6-HAP were found in the metagenome from multiple healthy human subjects, suggesting that the microbiome of some individuals may confer protection against skin cancer. These findings show a new role for skin commensal bacteria in host defense.

|
Scooped by
?
March 2, 2018 8:36 AM
|
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is a greenhouse gas that is also capable of destroying the ozone layer1. Agricultural soil is the largest source of N2O (ref. 2). Soybean is a globally important leguminous crop, and hosts symbiotic nitrogen-fixing soil bacteria (rhizobia) that can also produce N2O (ref. 3). In agricultural soil, N2O is emitted from fertilizer and soil nitrogen. In soybean ecosystems, N2O is also emitted from the degradation of the root nodules4. Organic nitrogen inside the nodules is mineralized to NH4+, followed by nitrification and denitrification that produce N2O. N2O is then emitted into the atmosphere or is further reduced to N2 by N2O reductase (N2OR), which is encoded by the nosZ gene. Pure culture and vermiculite pot experiments showed lower N2O emission by nosZ+ strains5 and nosZ++ strains (mutants with increased N2OR activity)6 of Bradyrhizobium japonicum than by nosZ− strains. A pot experiment using soil confirmed these results7. Although enhancing N2OR activity has been suggested as a N2O mitigation option8,9, this has never been tested in the field. Here, we show that post-harvest N2O emission from soybean ecosystems due to degradation of nodules can be mitigated by inoculation of nosZ+ and non-genetically modified organism nosZ++ strains of B. japonicum at a field scale.

|
Scooped by
?
March 1, 2018 11:52 PM
|
Microbes inhabiting the gut play an essential role in our biology, but could these gastrointestinal dwellers also shape our evolution?

|
Scooped by
?
March 1, 2018 8:35 AM
|
The soil bacterium Pseudomonas putida is rapidly becoming a platform of choice for applications that require a microbial host highly resistant to different types of stresses and elevated rates of reducing power regeneration. P. putida is capable of growing in a wide variety of carbon sources that range from simple sugars to complex substrates such as aromatic compounds. Interestingly, the growth of the reference strain KT2440 on glycerol as the sole carbon source is characterized by a prolonged lag phase, not observed with other carbon substrates. This macroscopic phenomenon has been shown to be connected with the stochastic expression of the glp genes, which encode the enzymes needed for glycerol processing. In this protocol, we propose a general procedure to examine bacterial growth in small-scale cultures while monitoring the metabolic activity of individual cells. Assessing the metabolic capacity of single bacteria by means of fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry, in combination with the analysis of the temporal takeoff of growth in single-cell cultures, is a simple and easy-to-implement approach. It can help to understand the link between macroscopic phenotypes (e.g., microbial growth in batch cultures) and stochastic phenomena at the genetic level. The implementation of these methodologies revealed that the adoption of a glycerol-metabolizing regime by P. putida KT2440 is not the result of a gradual change in the whole population, but it rather reflects a time-dependent bimodal switch between metabolically inactive (i.e., not growing) to fully active (i.e., growing) bacteria.

|
Scooped by
?
March 1, 2018 1:52 AM
|
In the absence of antibiotic-mediated selection, sensitive bacteria are expected to displace their resistant counterparts if resistance genes are costly. However, many resistance genes persist for long periods in the absence of antibiotics. Horizontal gene transfer (primarily conjugation) could explain this persistence, but it has been suggested that very high conjugation rates would be required. Here, we show that common conjugal plasmids, even when costly, are indeed transferred at sufficiently high rates to be maintained in the absence of antibiotics in Escherichia coli. The notion is applicable to nine plasmids from six major incompatibility groups and mixed populations carrying multiple plasmids. These results suggest that reducing antibiotic use alone is likely insufficient for reversing resistance. Therefore, combining conjugation inhibition and promoting plasmid loss would be an effective strategy to limit conjugation-assisted persistence of antibiotic resistance.

|
Scooped by
?
March 1, 2018 1:05 AM
|
The overwhelming majority of antibiotics in clinical use originate from Gram-positive Actinobacteria. In recent years, however, Gram-negative bacteria have become increasingly recognised as a rich yet underexplored source of novel antimicrobials, with the potential to combat the looming health threat posed by antibiotic resistance. In this article, we have compiled a comprehensive list of natural products with antimicrobial activity from Gram-negative bacteria, including information on their biosynthetic origin(s) and molecular target(s), where known. We also provide a detailed discussion of several unusual pathways for antibiotic biosynthesis in Gram-negative bacteria, serving to highlight the exceptional biocatalytic repertoire of this group of microorganisms.

|
Scooped by
?
March 1, 2018 12:51 AM
|
Pseudomonas protegens strain Pf-5 is a rhizosphere bacterium that suppresses soilborne plant diseases and produces at least seven different secondary metabolites with antifungal properties. We derived mutants of Pf-5 with single and multiple mutations in biosynthesis genes for seven antifungal metabolites: 2,4-diacetylphoroglucinol (DAPG), pyrrolnitrin, pyoluteorin, hydrogen cyanide, rhizoxin, orfamide A, and toxoflavin. These mutants were tested for inhibition of the pathogens Fusarium verticillioides and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi. Rhizoxin, pyrrolnitrin, and DAPG were found to be primarily responsible for fungal antagonism by Pf-5. Previously, other workers showed that the mycotoxin fusaric acid, which is produced by many Fusarium species, including F. verticillioides, inhibited the production of DAPG by Pseudomonas spp. In this study, amendment of culture media with fusaric acid decreased DAPG production, increased pyoluteorin production, and had no consistent influence on pyrrolnitrin or orfamide A production by Pf-5. Fusaric acid also altered the transcription of biosynthetic genes, indicating that the mycotoxin influenced antibiotic production by Pf-5 at the transcriptional level. Addition of fusaric acid to the culture medium reduced antibiosis of F. verticillioides by Pf-5 and derivative strains that produce DAPG but had no effect on antibiosis by Pf-5 derivatives that suppressed F. verticillioides due to pyrrolnitrin or rhizoxin production. Our results demonstrated the importance of three compounds, rhizoxin, pyrrolnitrin, and DAPG, in suppression of Fusarium spp. by Pf-5 and confirmed that an interspecies signaling system mediated by fusaric acid had parallel effects on antifungal metabolite production and antibiosis by the bacterial biological control organism.

|
Scooped by
?
February 28, 2018 11:37 PM
|
The increased use of the “omic” techniques, e.g., genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and fluxomics, as well as the systems biology approaches for addressing biological complexity from a holistic perspective, has contributed significantly to accelerate and complete our understanding on different aspects of the physiology, ecology, biochemistry, and regulatory mechanisms underlying the catabolism of aromatic compounds in bacteria of the Pseudomonas genus. Toxic aromatic compounds simultaneously serve as potential nutrients to be metabolized by bacteria but also as cellular stressors. When bacteria are exposed to these compounds they exhibit a multifactorial response that comprises three major intimately connected programs: (i) metabolic programs that involve not only the compound-specific pathways but also their integration within the global metabolism of the host cell; (ii) stress-response programs, e.g., changes in lipid metabolism, efflux pumps, or molecular chaperones, for adaptation to sub-optimal growth conditions; and (iii) a social program, including cell motility and chemotaxis, reorganization of the cell envelope, biofilm formation, and cell-to-cell interactions. As individual cells rarely metabolize a wide range of substrates, metabolic specialization within the bacterial population becomes a relevant trait in the assembly of efficient microbial biodegrader communities. Genome-scale metabolic models of several Pseudomonas strains have been performed. These models, when combined with the emergent synthetic biology approaches, can be used to explore the potential of Pseudomonas as cell factories in different biotechnological applications. Therefore, Pseudomonas becomes a paradigmatic bacterial genus both for increasing basic knowledge on the catabolism of aromatic compounds and for the bioremediation and/or biosensing of toxic pollutants and the valorization of aromatic compounds present in biowaste toward a sustainable knowledge-based bioeconomy with social and environmental rewards.

|
Scooped by
?
February 28, 2018 11:55 AM
|
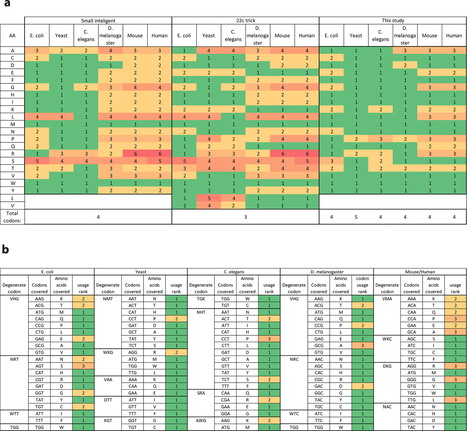
Saturation mutagenesis is employed in protein engineering and genome-editing efforts to generate libraries that span amino acid design space. Traditionally, this is accomplished by using degenerate/compressed codons such as NNK (N = A/C/G/T, K = G/T), which covers all amino acids and one stop codon. These solutions suffer from two types of redundancy: (a) different codons for the same amino acid lead to bias, and (b) wild type amino acid is included within the library. These redundancies increase library size and downstream screening efforts. Here, we present a dynamic approach to compress codons for any desired list of amino acids, taking into account codon usage. This results in a unique codon collection for every amino acid to be mutated, with the desired redundancy level. Finally, we demonstrate that this approach can be used to design precise oligo libraries amendable to recombineering and CRISPR-based genome editing to obtain a diverse population with high efficiency.

|
Scooped by
?
February 28, 2018 10:23 AM
|
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ST313 is a relatively newly emerged sequence type that is causing a devastating epidemic of bloodstream infections across sub-Saharan Africa. Analysis of hundreds of Salmonella genomes has revealed that ST313 is closely related to the ST19 group of S . Typhimurium that cause gastroenteritis across the world. The core genomes of ST313 and ST19 vary by only ∼1,000 SNPs. We hypothesized that the phenotypic differences that distinguish African Salmonella from ST19 are caused by certain SNPs that directly modulate the transcription of virulence genes. Here we identified 3,597 transcriptional start sites of the ST313 strain D23580, and searched for a gene-expression signature linked to pathogenesis of Salmonella . We identified a SNP in the promoter of the pgtE gene that caused high expression of the PgtE virulence factor in African S. Typhimurium, increased the degradation of the factor B component of human complement, contributed to serum resistance, and modulated virulence in the chicken infection model. We propose that high levels of PgtE expression by African S . Typhimurium ST313 promote bacterial survival and dissemination during human infection. Our finding of a functional role for an extragenic SNP shows that approaches used to deduce the evolution of virulence in bacterial pathogens should include a focus on noncoding regions of the genome.

|
Scooped by
?
February 28, 2018 9:18 AM
|
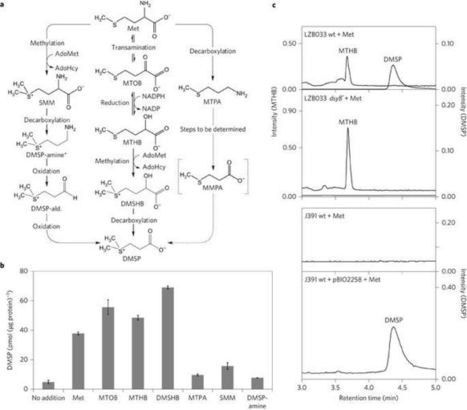
Dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP) is one of the Earth's most abundant organosulfur molecules, a signalling molecule, a key nutrient for marine microorganisms and the major precursor for gaseous dimethyl sulfide (DMS). DMS, another infochemical in signalling pathways, is important in global sulfur cycling and affects the Earth's albedo, and potentially climate, via sulfate aerosol and cloud condensation nuclei production. It was thought that only eukaryotes produce significant amounts of DMSP, but here we demonstrate that many marine heterotrophic bacteria also produce DMSP, probably using the same methionine (Met) transamination pathway as macroalgae and phytoplankton. We identify the first DMSP synthesis gene in any organism, dsyB, which encodes the key methyltransferase enzyme of this pathway and is a reliable reporter for bacterial DMSP synthesis in marine Alphaproteobacteria. DMSP production and dsyB transcription are upregulated by increased salinity, nitrogen limitation and lower temperatures in our model DMSP-producing bacterium Labrenzia aggregata LZB033. With significant numbers of dsyB homologues in marine metagenomes, we propose that bacteria probably make a significant contribution to oceanic DMSP production. Furthermore, because DMSP production is not solely associated with obligate phototrophs, the process need not be confined to the photic zones of marine environments and, as such, may have been underestimated.
|

|
Scooped by
?
March 2, 2018 11:21 AM
|
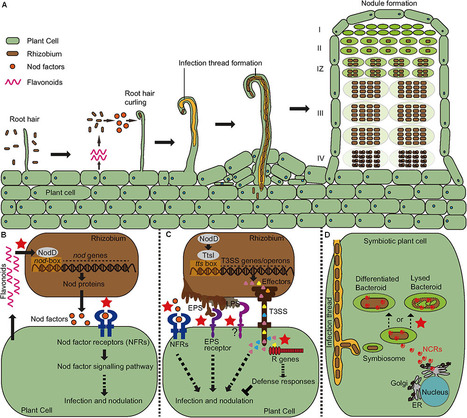
Legumes are able to form a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing soil bacteria called rhizobia. The result of this symbiosis is to form nodules on the plant root, within which the bacteria can convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia that can be used by the plant. Establishment of a successful symbiosis requires the two symbiotic partners to be compatible with each other throughout the process of symbiotic development. However, incompatibility frequently occurs, such that a bacterial strain is unable to nodulate a particular host plant or forms nodules that are incapable of fixing nitrogen. Genetic and molecular mechanisms that regulate symbiotic specificity are diverse, involving a wide range of host and bacterial genes and signals with various modes of action. In this review, we will provide an update on our current knowledge of how the recognition specificity has evolved in the context of symbiosis signaling and plant immunity.

|
Scooped by
?
March 2, 2018 11:05 AM
|
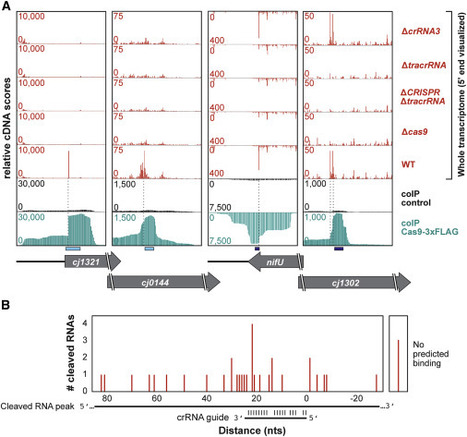
Cas9 nucleases naturally utilize CRISPR RNAs (crRNAs) to silence foreign double-stranded DNA. While recent work has shown that some Cas9 nucleases can also target RNA, RNA recognition has required nuclease modifications or accessory factors. Here, we show that the Campylobacter jejuni Cas9 (CjCas9) can bind and cleave complementary endogenous mRNAs in a crRNA-dependent manner. Approximately 100 transcripts co-immunoprecipitated with CjCas9 and generally can be subdivided through their base-pairing potential to the four crRNAs. A subset of these RNAs was cleaved around or within the predicted binding site. Mutational analyses revealed that RNA binding was crRNA and tracrRNA dependent and that target RNA cleavage required the CjCas9 HNH domain. We further observed that RNA cleavage was PAM independent, improved with greater complementarity between the crRNA and the RNA target, and was programmable in vitro. These findings suggest that C. jejuni Cas9 is a promiscuous nuclease that can coordinately target both DNA and RNA.

|
Scooped by
?
March 2, 2018 9:16 AM
|
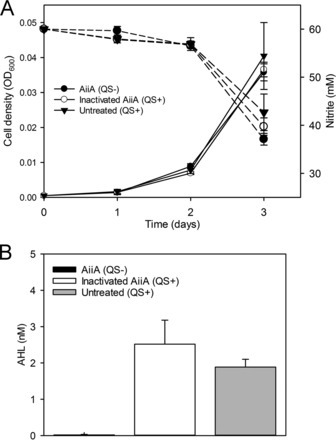
To date, most studies on QS have focused on model bacteria that are amenable to genetic manipulation and capable of high growth rates, but many environmentally important bacteria have been overlooked. For example, representatives of proteobacteria that participate in nitrification, the aerobic oxidation of ammonia to nitrate via nitrite, produce QS signals called acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs). Nitrification emits nitrogen oxide gases (NO, NO2, and N2O), which are potentially hazardous compounds that contribute to global warming. Despite considerable interest in nitrification, the purpose of QS in the physiology/ecology of nitrifying bacteria is poorly understood. Through a quorum quenching approach, we investigated the role of QS in a well-studied AHL-producing nitrite oxidizer, Nitrobacter winogradskyi. We added a recombinant AiiA lactonase to N. winogradskyi cultures to degrade AHLs to prevent their accumulation and to induce a QS-negative phenotype and then used mRNA sequencing (mRNA-Seq) to identify putative QS-controlled genes. Our transcriptome analysis showed that expression of nirK and nirK cluster genes (ncgABC) increased up to 19.9-fold under QS-proficient conditions (minus active lactonase). These data led to us to query if QS influenced nitrogen oxide gas fluxes in N. winogradskyi. Production and consumption of NOx increased and production of N2O decreased under QS-proficient conditions. Quorum quenching transcriptome approaches have broad potential to identify QS-controlle

|
Scooped by
?
March 1, 2018 11:54 PM
|
The acquisition of a virulence plasmid is sufficient to turn a beneficial strain of Rhodococcus bacteria into a pathogen. "Evolutionary transitions between beneficial and phytopathogenic Rhodococcus challenge disease management"

|
Scooped by
?
March 1, 2018 9:09 AM
|
Harnessing and controlling self-assembly is an important step in developing proteins as novel biomaterials. With this goal, here we report the design of a general genetically programmed system that covalently concatenates multiple distinct protein domains into specific assembled arrays. It is driven by iterative intein-mediated Native Chemical Ligation (NCL) under mild native conditions. The system uses a series of initially inert recombinant protein fusions that sandwich the protein modules to be ligated between one of a number of different affinity tags and an intein protein domain. Orthogonal activation at opposite termini of compatible protein fusions, via protease and intein cleavage, coupled with sequential mixing directs an irreversible and traceless stepwise assembly process. This gives total control over the composition and arrangement of component proteins within the final product, enabled the limits of the system - reaction efficiency and yield - to be investigated and led to the production of “functional” assemblies.

|
Scooped by
?
March 1, 2018 8:30 AM
|
The compartmentalization of enzymes into organelles is a promising strategy for limiting metabolic crosstalk and improving pathway efficiency; however, prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound organelles. To mimic this natural compartmentalization, we present here the targeting of the reductive tricarboxylic acid (rTCA) pathway to the periplasm to enhance the production of malate. A multigene combination knockout strategy was used to construct a phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) pool. Then, the genes encoding phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and malate dehydrogenase were combinatorially overexpressed to construct a cytoplasmic rTCA pathway for malate biosynthesis; however, the efficiency of malate production was low. To further enhance malate production, the rTCA pathway was targeted to the periplasm, which led to a 100% increase in malate production to 18.8 mM. Next, dual metabolic engineering regulation was adopted to balance the cytoplasmic and periplasmic pathways, leading to an increase in malate production to 58.8 mM. The final engineered strain, GL2306, produced 193 mM malate with a yield of 0.53 mol/mol in 5 L of pH-stat fed-batch culture. The strategy described here paves the way for the development of metabolic engineering and synthetic biology in the microbial production of chemicals. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.

|
Scooped by
?
March 1, 2018 1:12 AM
|
Pseudomonas is a diverse genus of Gammaproteobacteria with more than 60 species exhibiting varied life styles in a wide range of environments, including soil, water, plant surfaces, and animals. They are well known for their ubiquity in the natural world, capacity to utilize a striking variety of organic compounds as energy sources, resistance to a wide range of medically- and agriculturally-important antimicrobial compounds, and production of a remarkable array of secondary metabolites. Here, we provide an overview of the astonishing metabolic capacity of the Pseudomonads, summarize the knowledge of secondary metabolite biosynthesis in this group of organisms, and highlight the biological significance of these compounds to the diverse life styles exhibited by Pseudomonas spp. A consistent theme throughout this discussion is the central role of genomics in natural product discovery, characterization of metabolic gene clusters and patterns of their inheritance, and illuminaton of new aspects of Pseudomonas biology.

|
Scooped by
?
March 1, 2018 12:53 AM
|
Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) enhance plant health and growth using a variety of traits. Effective PGPR strains typically exhibit multiple plant-beneficial properties, but whether they are better adapted to the rhizosphere than PGPR strains with fewer plant-beneficial properties is unknown. Here, we tested the hypothesis that strains with higher numbers of plant-beneficial properties would be preferentially selected by plant roots. To this end, the co-occurrence of 18 properties involved in enhanced plant nutrition, plant hormone modulation, or pathogen inhibition was analyzed by molecular and biochemical methods in a collection of maize rhizosphere and bulk soil isolates of fluorescent Pseudomonas. Twelve plant-beneficial properties were found among the 698 isolates. Contrarily to expectation, maize preferentially selected pseudomonads with low numbers of plant-beneficial properties (up to five). This selection was not due to the predominance of strains with specific assortments of these properties, or with specific taxonomic status. Therefore, the occurrence of only few plant-beneficial properties appeared favorable for root colonization by pseudomonads.

|
Scooped by
?
March 1, 2018 12:39 AM
|
Secondary metabolites are synthesized by many microorganisms and provide a fitness benefit in the presence of competitors and predators. Secondary metabolism also can be costly, as it shunts energy and intermediates from primary metabolism. In Pseudomonas spp., secondary metabolism is controlled by the GacS-GacA global regulatory system. Intriguingly, spontaneous mutations in gacS or gacA (Gac− mutants) are commonly observed in laboratory cultures. Here we investigated the role of secondary metabolism in the accumulation of Gac− mutants in Pseudomonas protegens strain Pf-5. Our results showed that secondary metabolism, specifically biosynthesis of the antimicrobial compound pyoluteorin, contributes significantly to the accumulation of Gac− mutants. Pyoluteorin biosynthesis, which poses a metabolic burden on the producer cells, but not pyoluteorin itself, leads to the accumulation of the spontaneous mutants. Interspecific competition also influenced the accumulation of the Gac− mutants: a reduced proportion of Gac− mutants accumulated when P. protegens Pf-5 was cocultured with Bacillus subtilis than in pure cultures of strain Pf-5. Overall, our study associated a fitness trade-off with secondary metabolism, with metabolic costs versus competitive benefits of production influencing the evolution of P. protegens, assessed by the accumulation of Gac− mutants.

|
Scooped by
?
February 28, 2018 11:35 PM
|
Metabolic co-regulation between biosynthetic pathways for secondary metabolites is common in microbes and can play an important role in microbial interactions. Here, we describe a novel mechanism of metabolic co-regulation in which an intermediate in one pathway is converted into signals that activate a second pathway. Our study focused on the co-regulation of 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol (DAPG) and pyoluteorin, two antimicrobial metabolites produced by the soil bacterium Pseudomonas protegens. We show that an intermediate in DAPG biosynthesis, phloroglucinol, is transformed by a halogenase encoded in the pyoluteorin gene cluster into mono- and di-chlorinated phloroglucinols. The chlorinated phloroglucinols function as intra- and inter-cellular signals that induce the expression of pyoluteorin biosynthetic genes, pyoluteorin production, and pyoluteorin-mediated inhibition of the plant-pathogenic bacterium Erwinia amylovora. This metabolic co-regulation provides a strategy for P. protegens to optimize the deployment of secondary metabolites with distinct roles in cooperative and competitive microbial interactions.

|
Scooped by
?
February 28, 2018 10:35 AM
|
Compartmentalized partnered replication (CPR) is an emulsion-based directed evolution method based on a robust and modular phenotype–genotype linkage. In contrast to other in vivo directed evolution approaches, CPR largely mitigates host fitness effects due to a relatively short expression time of the gene of interest. CPR is based on gene circuits in which the selection of a 'partner' function from a library leads to the production of a thermostable polymerase. After library preparation, bacteria produce partner proteins that can potentially lead to enhancement of transcription, translation, gene regulation, and other aspects of cellular metabolism that reinforce thermostable polymerase production. Individual cells are then trapped in water-in-oil emulsion droplets in the presence of primers and dNTPs, followed by the recovery of the partner genes via emulsion PCR. In this step, droplets with cells expressing partner proteins that promote polymerase production will produce higher copy numbers of the improved partner gene. The resulting partner genes can subsequently be recloned for the next round of selection. Here, we present a step-by-step guideline for the procedure by providing examples of (i) selection of T7 RNA polymerases that recognize orthogonal promoters and (ii) selection of tRNA for enhanced amber codon suppression. A single round of CPR should take ∼3–5 d, whereas a whole directed evolution can be performed in 3–10 rounds, depending on selection efficiency.

|
Scooped by
?
February 28, 2018 10:15 AM
|
Secondary metabolites are a heterogeneous class of chemicals that often mediate interactions between species. The tryptophan-derived secondary metabolite, psilocin, is a serotonin receptor agonist that induces altered states of consciousness. A phylogenetically disjunct group of mushroom-forming fungi in the Agaricales produce the psilocin prodrug, psilocybin. Spotty phylogenetic distributions of fungal compounds are sometimes explained by horizontal transfer of metabolic gene clusters among unrelated fungi with overlapping niches. We report the discovery of a psilocybin gene cluster in three hallucinogenic mushroom genomes, and evidence for its horizontal transfer between fungal lineages. Patterns of gene distribution and transmission suggest that synthesis of psilocybin may have provided a fitness advantage in the dung and late wood-decay fungal niches, which may serve as reservoirs of fungal indole-based metabolites that alter behavior of mycophagous and wood-eating invertebrates. These hallucinogenic mushroom genomes will serve as models in neurochemical ecology, advancing the (bio)prospecting and synthetic biology of novel neuropharmaceuticals.
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...