Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
January 23, 2023 2:22 AM
|
Improved second-tier assays are needed to reduce the number of false positives in newborn screening (NBS) for inherited metabolic disorders including those on the Recommended Uniform Screening Pane

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
January 16, 2023 8:06 AM
|
Paris, le lundi 16 janvier 2023 - L’amyotrophie spinale infantile* est une maladie génétique (autosomique récessive) rare qui touche les neurones moteurs entraînant une atrophie progressive des muscles. Dans sa forme la plus sévère (SMA type I, 60 % cas), 95 % des enfants atteints meurent avant l’âge [...]

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
January 3, 2023 7:52 AM
|
Projects in the U.K. and New York City face questions of cost and ethics

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
December 21, 2022 3:56 AM
|
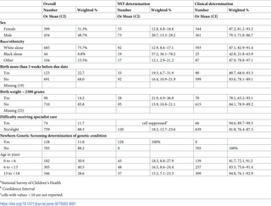
Newborn screening tests (NST) are important public health procedures with potential to improve quality of life, and decrease morbidity/mortality by identifying metabolic, genetic, enzymatic, and endocrinological diseases/conditions. In the United States (U.S.), Hawaii conducts the fewest NST (28) and Connecticut conducts the most (75). The purpose of this research is to determine if difficulty receiving specialty care for children with genetic diseases is associated with NST determination of the genetic condition. The research hypothesis is that parents/guardians of children with determination of genetic disease from NST are more likely to report no/slight difficulty accessing specialty care versus parents/guardians of children with genetic diseases whose determination was other than NST. This study has a cross-sectional design with National Survey of Children’s Health, 2020 data. Data were analyzed for frequency, Rao Scott Chi square, and logistic regression analyses. Of 833 children with genetic diseases, most parents/guardians reported no/slight difficulty in receiving needed specialty care; however, children whose determination of a genetic condition was other than NST were 4.82 times as likely (95%CI: 1.66, 14.02; p = 0.0040) to have difficulty. In analysis adjusted for sex, race, age, premature birth, and birthweight, the adjusted odds ratio was 6.71 (95% CI:1.91, 23.60 p = 0.0031). Parents/guardians of children screened with a positive NST reported less difficulty in receiving needed specialist care as compared with reports of parents/guardians of children with genetic conditions who were diagnosed later. The implication is there would be greater population level benefits realized in the U.S. if NST were expanded in states conducting minimal testing.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
December 12, 2022 2:50 AM
|
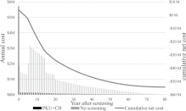
To evaluate the long-term costs and health effects of the Swedish newborn screening program for classic phenylketonuria (PKU) alone and in combination…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
December 5, 2022 4:54 AM
|
Now that targeted therapies for spinal muscular atrophy are available, attempts are being made worldwide to include screening for spinal muscular atrophy in general newborn screening. In Germany, after a pilot project from 2018–2021, it was included

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
November 30, 2022 8:21 AM
|
Parents increasingly utilise the internet to obtain information on health practices, but the quality of online information about screening for inherited metabolic diseases (IMD) needs to be improved. A content analysis examined how IMD blood and urine tests were described online in local healthcare sectors between May and June 2021. Among the nine resources, four were blood test providers and five were urine test providers. All mentioned the test benefits and procedures. Other information, such as false-positive/negative or risk of pain, was infrequently mentioned. The descriptions of urine tests are advertised as outperforming blood tests and can be purchased from commercial laboratory sites without medical guidance. Two urine test providers claimed no false results were reported. A few commercial advertisements highlighted the simplicity of the urine test and potentially overstated the invasiveness of the blood test. We found that some advertisements described IMD as “silent killers” and emphasised the advantage of getting “reassurance” in controlling the child’s developmental health and well-being. To better protect the parents, or broadly, the public interest, regulatory and oversight measures on the urine tests should be implemented to promote the proper use of genetic tests. Without timely regulation and oversight, the incorrect descriptions might create a public misconception about utilising these commercial laboratory tests to inform health decisions.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
November 29, 2022 7:36 AM
|
PurposeCystic Fibrosis (CF) was added to the German newborn bloodspot screening (NBS) panel in 2016. This study assesses parental perceptions of CF-NBS and confirmatory testing. MethodsProspectiv

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
November 23, 2022 4:48 AM
|
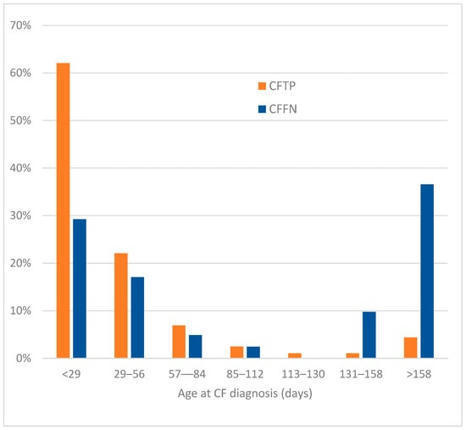
Testing immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT) is the first step in cystic fibrosis (CF) newborn screening. While high IRT is associated with CF, some cases are missed. This survey aimed to find factors associated with missed CF cases due to IRT levels below program cutoffs. Twenty-nine states responded to a U.S-wide survey and 13 supplied program-related data for low IRT false screen negative cases (CFFN) and CF true screen positive cases (CFTP) for analysis. Rates of missed CF cases and odds ratios were derived for each factor in CFFNs, and two CFFN subgroups, IRT above (“high”) and below (“low”) the CFFN median (39 ng/mL) compared to CFTPs for this entire sample set. Factors associated with “high” CFFN subgroup were Black race, higher IRT cutoff, fixed IRT cutoff, genotypes without two known CF-causing variants, and meconium ileus. Factors associated with “low” CFFN subgroup were older age at specimen collection, Saturday birth, hotter season of newborn dried blood spot collection, maximum ≥ 3 days laboratories could be closed, preterm birth, and formula feeding newborns. Lowering IRT cutoffs may reduce “high” IRT CFFNs. Addressing hospital and laboratory factors (like training staff in collection of blood spots, using insulated containers during transport and reducing consecutive days screening laboratories are closed) may reduce “low” IRT CFFNs.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
November 14, 2022 7:37 AM
|
A pilot newborn screening (NBS) program for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) study proposes to assess the feasibility of the screening procedure, temporal course of the various steps of screening and the public acceptability of the program. This is

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
November 10, 2022 2:15 AM
|
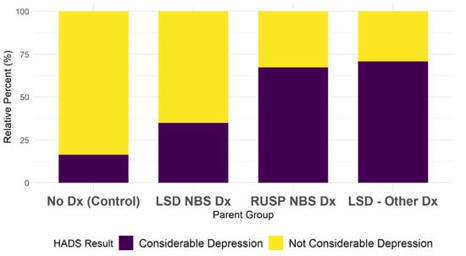
The ability to screen newborns for a larger number of disorders, including many with variable phenotypes, is prompting debate regarding the psychosocial impact of expanded newborn bloodspot screening (NBS) on parents. This study compares psychological outcomes of parents of children with a range of NBS/diagnostic experiences, with a particular focus on lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs) and X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) as representative disorders with complex presentations. An online cross-sectional survey with six domains was completed in 2019 by a volunteer sample of parents with at least one child born between 2013 and 2018. Parents were classified in the analysis stage into four groups based on their child’s rare disorder and means of diagnosis. Stress and depression were estimated using dichotomous measures of the depression subscale of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and the Parental Stress Scale. Logistic regression models were estimated for the relationship between the parent group and stress/depression, controlling for demographic variables (region of the US, income, education, major life events, relationship to the child, number of children, parent age, and race/ethnicity). One hundred seventy-four parents were included in this analysis. Parents of children with an LSD or X-ALD diagnosis clinically may have higher odds of depression (OR: 6.06, 95% CI: 1.64–24.96) compared to parents of children with the same disorders identified through NBS, controlling for covariates. Although a similar pattern was observed for parental stress (OR: 2.85, 95% CI: 0.82–10.37), this did not reach statistical significance. Ethically expanding NBS and genome sequencing require an understanding of the impacts of early detection for complex disorders on families. These initial findings are reassuring, and may have implications as NBS expands. Given our small sample size, it is difficult to generalize these findings to all families. These preliminary trends warrant further investigation in larger and more diverse populations.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
November 8, 2022 3:23 AM
|
Pompe disease (PD) is a progressive neuromuscular disorder caused by a lysosomal acid α-glucosidase (GAA) deficiency. Enzymatic replacement therapy is…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
October 24, 2022 5:33 AM
|
Health economic assessments are used to determine whether the resources needed to generate net benefit from a screening programme, driven by multiple …
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
January 18, 2023 2:13 AM
|
Newborn screening for SMA, coupled with early access to disease-modifying therapies,
effectively ameliorates the functional burden and associated comorbidities for affected
children. For children diagnosed through newborn screening, motor score, CMAP, and
disease status at diagnosis has clinical utility to determine functional independence.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
January 9, 2023 1:53 AM
|
Galactosemia is an inborn metabolic disorder caused by a deficient activity in one of the enzymes involved in the metabolism of galactose. The first description of galactosemia in newborns dates from 1908, ever since complex research has been performed on cell and animal models to gain more insights into the molecular and clinical bases of this challenging disease. In galactosemia, the newborn appears to be born in proper health, having a window of opportunity before developing major morbidities that may even be fatal following ingestion of milk that contains galactose. Galactosemia cannot be cured, but its negative consequences on health can be avoided by establishing precocious diagnosis and treatment. All the foods that contain galactose should be eliminated from the diet when there is a suspicion of galactosemia. The neonatal screening for galactosemia can urge early diagnosis and intervention, preventing complications. All galactosemia types may be detected during the screening of newborns for this disorder. The major target is, however, galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GALT) deficiency galactosemia, which is diagnosed by applying a combination of total galactose and GALT enzyme analysis as well as, in certain programs, mutation screening. Most critically, infants who exhibit symptoms suggestive of galactosemia should undergo in-depth testing for this condition even when the newborn screening shows normal results. The decision to enroll global screening for galactosemia among the specific population still faces many challenges. In this context, the present narrative review provides an updated overview of the incidence, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, therapy, and prognosis of galactosemia, questioning under the dome of these aspects related to the disease the value of its neonatal monitoring.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
January 3, 2023 7:49 AM
|
We aimed to evaluate cutoff values of immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT)/IRT and determine relationship between IRT values and clinical characteristics of children with cystic fibrosis (CF). This study is cross-sectional study. Data of children with positive newborn screening (NBS) between 2015 and 2021 were evaluated in three pediatric pulmonology centers. Age at admission, sex, gestational age, presence of history of meconium ileus, parental consanguinity, sibling with CF, and doll-like face appearance, first and second IRT values, sweat chloride test, fecal elastase, fecal fat, biochemistry results, and age at CF diagnosis were recorded. Sensitivity and specificity of IRT cutoff values were evaluated. Of 815 children with positive NBS, 58 (7.1%) children were diagnosed with CF. Median values of first and second IRT were 157.2 (103.7–247.6) and 113.0 (84.0–201.5) μg/L. IRT values used in current protocol, sensitivity was determined as 96.6%, specificity as 17.2% for first IRT, and 96.6% sensitivity, 20.5% specificity for second IRT. Positive predictive value (PPV) was determined as 7.1%. When cutoff value for first IRT was estimated as 116.7 μg/L, sensitivity was 69.0% and specificity was 69.6%, and when cutoff value was set to 88.7 μg/L for second IRT, sensitivity was 69.0% and specificity was 69.0%. Area under curve was 0.757 for first and 0.763 for second IRT (p < 0.001, p < 0.001, respectively). PPV was calculated as 4.3%. Conclusion: Although sensitivity of CF NBS is high in our country, its PPV is significantly lower than expected from CF NBS programs. False-positive NBS results could have been overcome by revising NBS strategy. What is Known: • Although immunoreactive trypsinogen elevation is a sensitive test used in cystic fibrosis newborn screening, its specificity is low. • In countries although different algorithms are used, all strategies begin with the measurement of immunoreactive trypsinogen in dried blood spots. What is New: • In our study, it was shown that use of the IRT/IRT protocol for cystic fibrosis newborn screening is not sufficient for the cut-off values determined by the high number of patients. • Newborn screening strategy should be reviewed to reduce false positive newborn screening results.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
December 13, 2022 2:33 AM
|
RationaleCystic fibrosis (CF) newborn screening (NBS) algorithms in the USA vary by state. Differences in CF NBS algorithms could potentially affect the detection rate of CF newborns and lead t

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
December 9, 2022 1:54 AM
|
Newborn screening (NBS) has been developed for years to identify newborns with severe but treatable conditions. Taiwan's NBS system, after the initial…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
December 1, 2022 5:32 AM
|
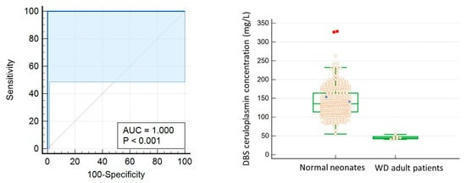
In this study, we modified a fully automatic immunoassay on ceruloplasmin concentration on dried blood spots (DBS) to increase its analytical sensitivity in order to accurately differentiate newborns from true Wilson disease (WD) patients. Modifications to the assay parameters of the Roche/Hitachi Cobas c systems immunoturbidimetric assay are adjusted to lower the limit of quantitation to 0.60 mg/L from 30 mg/L. This enables sensitive measurement of ceruloplasmin in eluent after DBS extraction. In addition, reference intervals and receiver operating characteristic curve analysis for diagnostic cut-off were established using DBS of neonates and WD adult patients. After DBS whole blood calibration, the 95th percentile of the reference interval for newborns was 86–229 mg/L. The cut-off value of 54 mg/L was found to be the most optimal point for differentiating true adult WD from newborn controls. This test shows a high area under curve of 1.000 with 100% sensitivity and specificity in differentiating normal newborns from WD adult samples. However, the results should be further validated with true newborn WD patient samples together with the consideration of other factors that can also lead to low ceruloplasmin levels. This test shows application potential in newborn screening for WD, which can save lives through early identification and timely treatment.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
November 30, 2022 4:59 AM
|
Mucopolysaccharidosis type II (MPS II), also known as Hunter syndrome, is an X-linked condition caused by pathogenic variants in the iduronate-2-sulfa…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
November 23, 2022 7:24 AM
|
BackgroundNewborn screening (NBS) for cystic fibrosis (CF) has been underway universally in the USA for more than a decade, as well in most European countries, and algorithms have been evolvin

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
November 15, 2022 2:29 AM
|
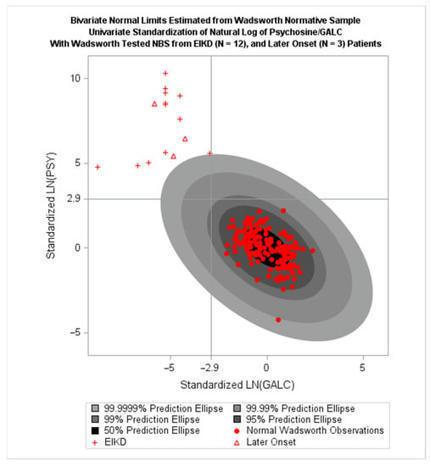
The mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS), Pompe Disease (PD), and Krabbe disease (KD) are inherited conditions known as lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs) The resulting enzyme deficiencies give rise to progressive symptoms. The United States Department of Health and Human Services’ Recommended Uniform Screening Panel (RUSP) suggests LSDs for inclusion in state universal newborn screening (NBS) programs and has identified screening deficiencies in MPS I, KD, and PD NBS programs. MPS I NBS programs utilize newborn dried blood spots and assay alpha L-iduronidase (IDUA) enzyme to screen for potential cases. Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) offer potential as a confirmatory test. KD NBS programs utilize galactocerebrosidase (GaLC) as an initial test, with psychosine (PSY) activity increasingly used as a confirmatory test for predicting onset of Krabbe disease, though with an excessive false positive rate. PD is marked by a deficiency in acid α-glucosidase (GAA), causing increased glycogen, creatine (CRE), and other biomarkers. Bivariate normal limit (BVNL) methods have been applied to GaLC and PSY activity to produce a NBS tool for KD, and more recently, to IDUA and GAG activity to develop a NBS tool for MPS I. A BVNL tool based on GAA and CRE is in development for infantile PD diagnosis. Early infantile KD, MPS I, and PD cases were pre-symptomatically identified by BVNL-based NBS tools. This article reviews these developments, discusses how they address screening deficiencies identified by the RUSP and may improve NBS more generally.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
November 14, 2022 2:52 AM
|
The aim of this study was to record the current status of newborn bloodspot screening (NBS) for CF across Europe and assess performance.Survey of repr…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
November 8, 2022 3:27 AM
|
Metachromatic Leukodystrophy (MLD) is a rare, autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme arylsulfatase A (ARSA). MLD causes progressive loss of motor function and severe decline in cognitive function, leading to premature death. Early diagnosis of MLD provides the opportunity to begin treatment before the disease progresses and causes severe disability. MLD is not currently included in newborn screening (NBS) in the UK. This study consisted of an online survey, and follow-up semi-structured interviews open to MLD patients or caregivers, aged 18 years and over. The aims of the study were to understand the importance of early diagnosis and to establish the views of families and caregivers of patients with MLD on NBS. A total of 24 patients took part in the survey, representing 20 families (two families had two children with MLD, one family had three children with MLD). Following on from the survey, six parents participated in the interviews. Our data showed diagnostic delay from first symptoms was between 0 and 3 years, with a median of 1 year (n = 18); during this time deterioration was rapid, especially in earlier onset MLD. In patients with late infantile MLD (n = 10), 50% were wheelchair dependent, 30% were unable to speak, and 50% were tube fed when a diagnosis of MLD was confirmed. In patients with early juvenile MLD (n = 5), over half used a wheelchair some of the time, had uncontrollable crying, and difficulty speaking (all 60%) before or at the time of diagnosis. A high degree of support was expressed for NBS among caregivers, 95% described it as very or extremely important and 86% believed detection of MLD at birth would have changed their child’s future. One parent expressed their gratitude for an early diagnosis as a result of familial MLD screening offered at birth and how it had changed their child’s future: “It did and it absolutely has I will be forever grateful for his early diagnosis thanks to his older sister.” The rapid rate of deterioration in MLD makes it an essential candidate for NBS, particularly now the first gene therapy (Libmeldy™) has been approved by the European Medicines Agency. Libmeldy™ has also been recommended as a treatment option in England and Wales by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) and is being made available to patients in Scotland via the Scottish Medicines Consortium’s ultra-orphan pathway.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
October 24, 2022 7:58 AM
|
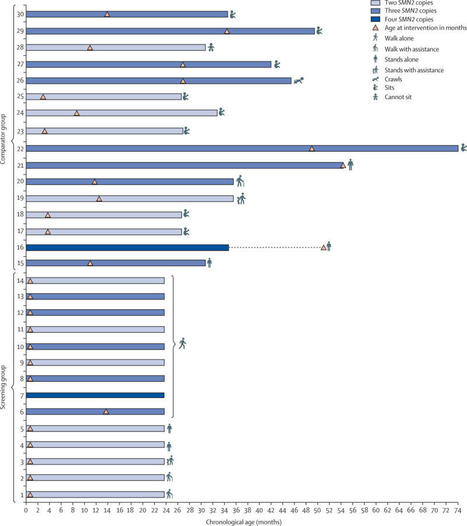
Background: Universal spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) newborn screening was implemented in California on June 24, 2020. Objective: We describe California’s experience with the first 18 months of SMA newborn screening, including our assay methodology, t
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...