Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 20, 2023 8:17 AM
|
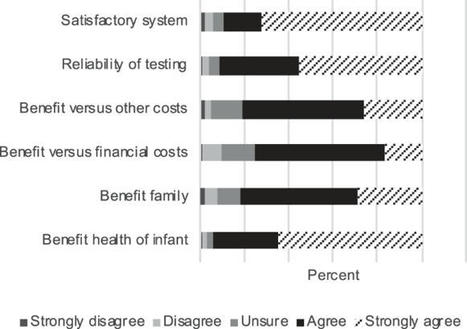
Since the introduction of genome sequencing in medicine, the factors involved in deciding how to integrate this technology into population screening programs such as Newborn Screening (NBS) have been widely debated. In Australia, participation in NBS is not mandatory, but over 99.9% of parents elect to uptake this screening. Gauging stakeholder attitudes towards potential changes to NBS is vital in maintaining this high participation rate. The current study aimed to determine the knowledge and attitudes of Australian parents and health professionals to the incorporation of genomic sequencing into NBS programs. Participants were surveyed online in 2016 using surveys adapted from previous studies. The majority of parents (90%) self-reported some knowledge of NBS, with 77% expressing an interest in NBS using the new technology. This was significantly lower than those who would utilise NBS using current technologies (99%). Although, many health professionals (62%) felt that new technologies should currently not be used as an adjunct to NBS, 79% foresaw the use of genomic sequencing in NBS by 2026. However, for genomic sequencing to be considered, practical and technical challenges as well as parent information needs were identified including the need for accurate interpretation of data; pre-and post-test counselling; and appropriate parental consent and opt-out process. Therefore, although some support for implementing genomic sequencing into Australian NBS does exist, there is a need for further investigation into the ethical, social, legal and practical implications of introducing this new technology as a replacement to current NBS methods.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 17, 2023 2:22 AM
|
In 1963, Robert Guthrie’s pioneering work developing a bacterial inhibition assay to measure phenylalanine in dried blood spots, provided the means for whole-population screening to detect phenylketonuria in the USA. In the following decades, NBS became firmly established as a part of public health in developed countries. Technological advances allowed for the addition of new disorders into routine programmes and thereby resulted in a paradigm shift. Today, technological advances in immunological methods, tandem mass spectrometry, PCR techniques, DNA sequencing for mutational variant analysis, ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC), iso-electric focusing, and digital microfluidics are employed in the NBS laboratory to detect more than 60 disorders. In this review, we will provide the current state of methodological advances that have been introduced into NBS. Particularly, ‘second-tier’ methods have significantly improved both the specificity and sensitivity of testing. We will also present how proteomic and metabolomic techniques can potentially improve screening strategies to reduce the number of false-positive results and improve the prediction of pathogenicity. Additionally, we discuss the application of complex, multiparameter statistical procedures that use large datasets and statistical algorithms to improve the predictive outcomes of tests. Future developments, utilizing genomic techniques, are also likely to play an increasingly important role, possibly combined with artificial intelligence (AI)-driven software. We will consider the balance required to harness the potential of these new advances whilst maintaining the benefits and reducing the risks for harm associated with all screening.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 13, 2023 7:44 AM
|
We describe our experience with population-based newborn screening for mucopolysaccharidosis type II (MPS II) in 586,323 infants by measurement of idu…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 6, 2023 9:26 AM
|
Newborn screening (NBS) for classical galactosaemia (CG) facilitates early diagnosis and treatment to prevent life-threatening complications, but remains controversial, and screening protocols var

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 1, 2023 4:39 AM
|
The prevalence of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) within the Caribbean region remains second only to that of West Africa. The Newborn Screening (NBS) Program in Antigua and Barbuda remains heavily dependent on grants, therefore ultimately facing sustainability challenges. Early intervention and implementation of preventative measures post-NBS result in significant improvements in morbidity, quality of life, and survival. This audit reviewed the pilot SCD NBS Program in Antigua and Barbuda from September 2020 to December 2021. A conclusive result was received by 99% of babies eligible for screening, 84.3% of which were HbFA, whilst 9.6% and 4.6% were HbFAS and HbFAC, respectively. This was comparable to other Caribbean countries. Sickle Cell Disease was noted in 0.5% of babies screened, which translates to 1 in 222 live births. Eighty-two percent of mothers were aware of their sickle cell status, compared to 3% of fathers. The importance of instituting a quality improvement team post the initiation of a screening program and the need for a robust public education program have been demonstrated by this audit.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 10:00 AM
|
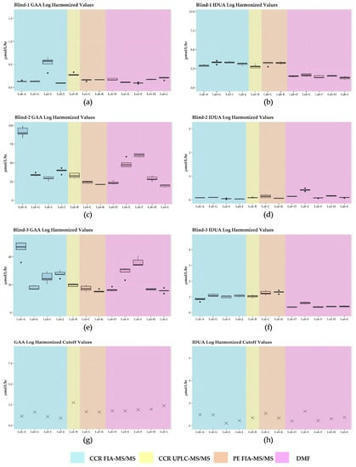
In newborn screening, false-negative results can be disastrous, leading to disability and death, while false-positive results contribute to parental anxiety and unnecessary follow-ups. Cutoffs are set conservatively to prevent missed cases for Pompe and MPS I, resulting in increased falsepositive results and lower positive predictive values. Harmonization has been proposed as a way to minimize false-negative and false-positive results and correct for method differences, so we harmonized enzyme activities for Pompe and MPS I across laboratories and testing methods (Tandem Mass Spectrometry (MS/MS) or Digital Microfluidics (DMF)). Participating states analyzed proofof- concept calibrators, blanks, and contrived specimens and reported enzyme activities, cutoffs, and other testing parameters to Tennessee. Regression and multiples of the median were used to harmonize the data. We observed varied cutoffs and results. Six of seven MS/MS labs reported enzyme activities for one specimen for MPS I marginally above their respective cutoffs with results classified as negative, whereas all DMF labs reported this specimen’s enzyme activity below their respective cutoffs with results classified as positive. Reasonable agreement in enzyme activities and cutoffs was achieved with harmonization; however, harmonization does not change how a value would be reported as this is dependent on the placement of cutoffs.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 8:20 AM
|
Abstract. Untreated congenital hypothyroidism (CH) leads to intellectual disabilities. Prompt diagnosis by newborn screening (NBS) leading to early and adequate treatment results in grossly normal neurocognitive outcomes in adulthood. However, NBS for hypothyroidism is not yet established in all countries globally. Seventy percent of neonates worldwide do not undergo NBS.The initial treatment of CH is levothyroxine, 10 to 15 mcg/kg daily. The goals of treatment are to maintain consistent euthyroidism with normal thyroid-stimulating hormone and free thyroxine in the upper half of the age-specific reference range during the first 3 years of life. Controversy remains regarding detection of thyroid dysfunction and optimal management of special populations, including preterm or low-birth weight infants and infants with transient or mild CH, trisomy 21, or central hypothyroidism.Newborn screening alone is not sufficient to prevent adverse outcomes from CH in a pediatric population. In addition to NBS, the management of CH requires timely confirmation of the diagnosis, accurate interpretation of thyroid function testing, effective treatment, and consistent follow-up. Physicians need to consider hypothyroidism in the face of clinical symptoms, even if NBS thyroid test results are normal. When clinical symptoms and signs of hypothyroidism are present (such as large posterior fontanelle, large tongue, umbilical hernia, prolonged jaundice, constipation, lethargy, and/or hypothermia), measurement of serum thyroid-stimulating hormone and free thyroxine is indicated, regardless of NBS results.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 8:16 AM
|
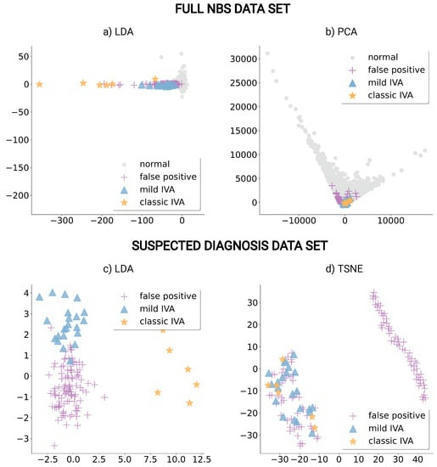
Isovaleric aciduria (IVA) is a rare disorder of leucine metabolism and part of newborn screening (NBS) programs worldwide. However, NBS for IVA is hampered by, first, the increased birth prevalence due to the identification of individuals with an attenuated disease variant (so-called “mild” IVA) and, second, an increasing number of false positive screening results due to the use of pivmecillinam contained in the medication. Recently, machine learning (ML) methods have been analyzed, analogous to new biomarkers or second-tier methods, in the context of NBS. In this study, we investigated the application of machine learning classification methods to improve IVA classification using an NBS data set containing 2,106,090 newborns screened in Heidelberg, Germany. Therefore, we propose to combine two methods, linear discriminant analysis, and ridge logistic regression as an additional step, a digital-tier, to traditional NBS. Our results show that this reduces the false positive rate by 69.9% from 103 to 31 while maintaining 100% sensitivity in cross-validation. The ML methods were able to classify mild and classic IVA from normal newborns solely based on the NBS data and revealed that besides isovalerylcarnitine (C5), the metabolite concentration of tryptophan (Trp) is important for improved classification. Overall, applying ML methods to improve the specificity of IVA could have a major impact on newborns, as it could reduce the newborns’ and families’ burden of false positives or over-treatment.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 8:10 AM
|
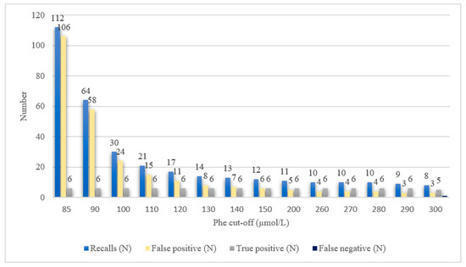
Phenylketonuria (PKU) was the first disease to be identified by the newborn screening (NBS) program. Currently, there are various methods for determining phenylalanine (Phe) values, with tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) being the most widely used method worldwide. We aimed to compare the MS/MS method with the fluorometric method (FM) for measuring Phe in the dried blood spot (DBS) and the efficacy of both methods in the NBS program. The FM was performed using a neonatal phenylalanine kit and a VICTOR2TM D fluorometer. The MS/MS method was performed using a NeoBaseTM 2 kit and a Waters Xevo TQD mass spectrometer. The Phe values measured with the MS/MS method were compared to those determined by the FM. The cut-off value for the NBS program was set at 120 µmol/L for FM and 85 µmol/L for MS/MS. We analyzed 54,934 DBS. The measured Phe values varied from 12 to 664 µmol/L, with a median of 46 µmol/L for the MS/MS method and from 10 to 710 µmol/L, with a median of 70 µmol/L for the FM. The Bland–Altman analysis indicated a bias of −38.9% (−23.61 µmol/L) with an SD of 21.3% (13.89 µmol/L) when comparing the MS/MS method to the FM. The Phe value exceeded the cut-off in 187 samples measured with FM and 112 samples measured with MS/MS. The FM had 181 false positives, while the MS/MS method had 106 false positives. Our study showed that the MS/MS method gives lower results compared to the FM. Despite that, none of the true positives would be missed, and the number of false-positive results would be significantly lower compared to the FM.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 6, 2023 7:24 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 3, 2023 2:56 AM
|
Population newborn genetic screening for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is feasible, but its benefits, harms, and cost effectiveness are uncertain.…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
January 30, 2023 8:51 AM
|
Newborn screening (NBS) assays for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) typically use a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based assay to identify individuals with homozygous deletion in exon 7 of the SMN1 gene. Due to high DNA sequence homology between SMN1 and SMN2, it has previously been difficult to accurately bioinformatically map short reads from next-generation DNA sequencing (NGS) to SMN1, resulting in low analytical performance and preventing NGS being used for SMA screening. Advances in bioinformatics have allowed NGS to be used in diagnostic settings, but to date these assays have not reached the scale required for high volume population newborn screening and have not been performed on the dried blood spot samples that NBS programs currently use. Here we integrate an NGS assay using hybridisation-based capture with a customised bioinformatics algorithm and purpose designed high throughput reporting software into an existing NBS program to achieve a laboratory workflow for population SMA screening. We tested the NGS assay on over 2500 newborns born over 2 weeks in a NBS program in a technical feasibility study and show high sensitivity and specificity. Our results suggest NGS may be an alternate method for SMA screening by NBS programs, providing a multiplex testing platform on which potentially hundreds of inherited conditions could be simultaneously tested.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
January 26, 2023 4:25 AM
|
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 20, 2023 8:16 AM
|
Inborn errors of metabolism (IEM) can lead to severe motor and neurological developmental disorders and even disability and death in children due to untimely treatment. In this study, we used tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) for primary screening and recall of those with positive primary screening for rescreening. Further diagnosis was based on biochemical tests, imaging and clinical presentation as well as accurate genetic testing using multi-gene panel with high-throughput sequencing of 130 IEM-related genes. The screening population was 16,207 newborns born between July 1, 2019, and December 31, 2021. Based on the results, 8 newborns were diagnosed with IEM, constituting a detection rate of 1:2,026. Phenylketonuria was the most common form of IEM. In addition, seven genes associated with IEM were detected in these eight patients. All eight patients received standardized treatment starting in the neonatal period, and the follow-up results showed good growth and development. Therefore, our study suggests that MS/MS rescreening for IEM pathogenic variants in high-risk areas, combined with a sequencing validation strategy, can be highly effective in the early detection of affected children. This strategy, combined with early intervention, can be effective in preventing neonatal morbidity and improving population quality.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 15, 2023 9:04 AM
|
Most rare diseases are caused by single-gene mutations, and as such, lend themselves to a host of new gene-targeted therapies and technologies including antisense oligonucleotides

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 13, 2023 5:45 AM
|
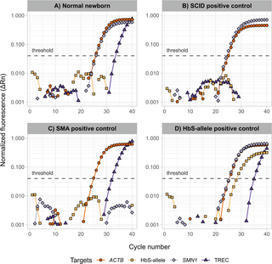
Early diagnosis of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), and sickle cell disease (SCD) improves health outcomes by providing a specific treatment before the onset of symptoms. A high-throughput nucleic acid-based method in newborn screening (NBS) has been shown to be fast and cost-effective in the early detection of these diseases. Screening for SCD has been included in Germany’s NBS Program since Fall 2021 and typically requires high-throughput NBS laboratories to adopt analytical platforms that are demanding in terms of instrumentation and personnel. Thus, we developed a combined approach applying a multiplexed quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) assay for simultaneous SCID, SMA, and 1st-tier SCD screening, followed by a tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) assay for 2nd-tier SCD screening. DNA is extracted from a 3.2-mm dried blood spot from which we simultaneously quantify T-cell receptor excision circles for SCID screening, identify the homozygous SMN1 exon 7 deletion for SMA screening, and determine the integrity of the DNA extraction through the quantification of a housekeeping gene. In our two-tier SCD screening strategy, our multiplex qPCR identifies samples carrying the HBB: c.20A>T allele that is coding for sickle cell hemoglobin (HbS). Subsequently, the 2nd tier MS/MS assay is used to distinguish heterozygous HbS/A carriers from samples of patients with homozygous or compound heterozygous SCD. Between July 2021 and March 2022, 96,015 samples were screened by applying the newly implemented assay. The screening revealed two positive SCID cases, while 14 newborns with SMA were detected. Concurrently, the qPCR assay registered HbS in 431 samples which were submitted to 2nd-tier SCD screening, resulting in 17 HbS/S, five HbS/C, and two HbS/β thalassemia patients. The results of our quadruplex qPCR assay demonstrate a cost-effective and fast approach for a combined screening of three diseases that benefit from nucleic-acid based methods in high-throughput NBS laboratories.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 1, 2023 7:22 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 10:02 AM
|
Technological advances and decreasing costs of genomic sequencing have paved the way for the increased incorporation of genomics into newborn screening (NBS). Genomic sequencing may complement current NBS laboratory analyses or may be used as a first-tier screening tool to identify disorders not detected by current approaches. As a large proportion of infant deaths occur in children with an underlying genetic disorder, earlier diagnosis of these disorders may improve neonatal and infant mortality rates. This lends an additional layer of ethical consideration regarding genomic newborn screening. We review the current understanding of genomic contributions to infant mortality and explore the potential implications of expanded access to genomic screening for infant mortality rates.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 8:22 AM
|
Untreated congenital hypothyroidism (CH) leads to intellectual disabilities. Newborn screening (NBS) for CH should be performed in all infants. Prompt diagnosis by NBS leading to early and adequate treatment results in grossly normal neurocognitive outcomes in adulthood. However, NBS for hypothyroidism is not yet practiced in all countries globally. Seventy percent of neonates worldwide do not undergo NBS.The recommended initial treatment of CH is levothyroxine, 10 to 15 mcg/kg daily. The goals of treatment are to maintain consistent euthyroidism with normal thyroid-stimulating hormone and with free thyroxine in the upper half of the age-specific reference range during the first 3 years of life. Controversy remains regarding the detection of thyroid dysfunction and optimal management of special populations, including preterm or low-birth-weight infants and infants with transient or mild CH, trisomy 21, or central hypothyroidism.NBS alone is not sufficient to prevent adverse outcomes from CH in a pediatric population. In addition to NBS, the management of CH requires timely confirmation of the diagnosis, accurate interpretation of thyroid function testing, effective treatment, and consistent follow-up. Physicians need to consider hypothyroidism in the face of clinical symptoms, even if NBS thyroid test results are normal. When clinical symptoms and signs of hypothyroidism are present (such as large posterior fontanelle, large tongue, umbilical hernia, prolonged jaundice, constipation, lethargy, and/or hypothermia), measurement of serum thyroid-stimulating hormone and free thyroxine is indicated, regardless of NBS results.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 8:17 AM
|
Background: An inconclusive diagnosis of cystic fibrosis (CF) after positive newborn screening (NBS) may cause parental distress. We compared the psychological impact of CF transmembrane conductance regulator-related metabolic syndrome (CRMS)/CF screen-positive, inconclusive diagnosis (CFSPID), and clear CF diagnosis, on parents. Methods: The participants were administered the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale, Patient Health Questionnaire-9, and the Italian version of the Impact of Event Scale-Revised as quantitative tools and semi-structured interviews as qualitative tools. Parental experience, child representation, relationships, future information, and perception of health status were investigated. Interviews were recorded and transcribed verbatim maintaining anonymity. Results: Thirty-two families were enrolled: sixteen with CF and CRMS/CFSPID, respectively. Anxiety and depression values were high in both groups, as were the measurement of traumatic impact subscales: avoidance, intrusiveness, and hyperarousal. The children’s health was evaluated by respective parents as being nearly healthy. Conclusions: Our results highlight negative psychological impacts, including emotional and affective representations, on parents of children with inconclusive CF diagnosis compared with those with clear diagnosis.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 8:12 AM
|
Background
The process of receiving a communication of positivity for metabolic diseases at expanded newborn screening (ENBS) is extremely articulated, involves a variety of actors (parents

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 8:09 AM
|
Purpose of developing the guidelines: Newborn screening (NBS) for congenital hypothyroidism (CH) was started in 1979 in Japan, and early diagnosis and …

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 3, 2023 2:57 AM
|
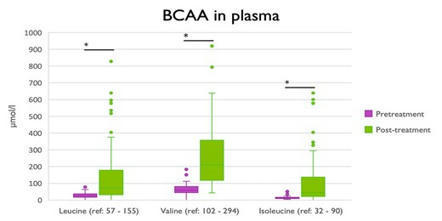
Tangeraas et al. describe the largest series of BCKDK deficiency patients to date, including responses to dietetic treatment. Early introduction of BCAA amelior

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 1, 2023 4:55 AM
|
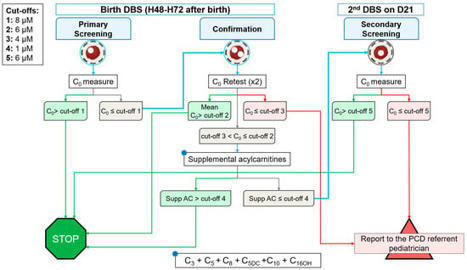
Primary Carnitine Deficiency (PCD) is a fatty acid oxidation disorder that will be included in the expansion of the French newborn screening (NBS) program at the beginning of 2023. This disease is of high complexity to screen, due to its pathophysiology and wide clinical spectrum. To date, few countries screen newborns for PCD and struggle with high false positive rates. Some have even removed PCD from their screening programs. To understand the risks and pitfalls of implementing PCD to the newborn screening program, we reviewed and analyzed the literature to identify hurdles and benefits from the experiences of countries already screening this inborn error of metabolism. In this study, we therefore, present the main pitfalls encountered and a worldwide overview of current practices in PCD newborn screening. In addition, we address the optimized screening algorithm that has been determined in France for the implementation of this new condition.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
January 30, 2023 4:09 AM
|
IntroductionX-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is the most common inherited peroxisomal disorder caused by variants in the ABCD1 gene. The main phenotypes observed in men with X-ALD are primary adrenal insufficiency, adrenomyeloneuropathy, and cerebral ALD (cALD). Cerebral ALD consists of a demyelinating progressive cerebral white matter (WM) disease associated with rapid clinical decline and is fatal if left untreated. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is the standard treatment for cALD as it stabilizes WM degeneration when performed early in the disease. For this reason, early diagnosis is crucial, and several countries have already implemented their newborn screening programs (NBS) with the assessment of C26:0-lysophosphatidylcholine (C26:0-LPC) values as screening for X-ALD.MethodsIn June 2021, an Italian group in Lombardy launched a pilot study for the implementation of X-ALD in the Italian NBS program. A three-tiered approach was adopted, and it involved quantifying the values of C26:0-LPC and other metabolites in dried blood spots with FIA-MS/MS first, followed by the more specific ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) technique and, finally, the genetic confirmation via focused NGS.DiscussionGenetically confirmed patients are set to undergo a follow-up protocol and are periodically evaluated to promptly start a specific treatment if and when the first signs of brain damage appear, as suggested by internationa
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...