Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 8, 2023 5:45 AM
|
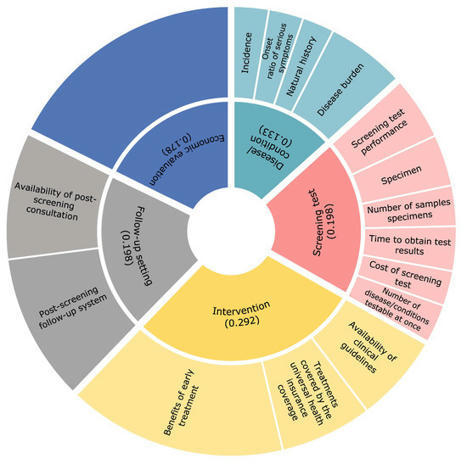
Whether or not conditions should be included in publicly funded newborn screening (NBS) programs should be discussed according to objective and transparent criteria. Certain criteria have been developed for the introduction of NBS programs in the context of individual countries; however, there are no standard selection criteria for NBS programs in Japan. This study aimed to develop a quantitative scoring model to assess newborn screening that incorporates the views of a variety of stakeholders in Japan. The five recommended eligibility criteria for NBS were stratified based on previous studies and expert opinions, using the analytic hierarchy process. We conducted a cross-sectional, web-based questionnaire targeting a wide range of people involved in NBS to investigate pairwise comparisons of the evaluation items between February and April of 2022. There were 143 respondents. Most of our respondents (44.1%) were physicians. Fifty-eight respondents (40.6%) had been engaged in NBS-related research or work for more than 10 years. The distribution of allocation points was the highest for ‘intervention’, ‘screening test’, ‘follow-up setting’, ’economic evaluation’, and ’disease/condition’, in that order. The algorithm in this study will guide decision makers in collecting and evaluating objective data, thus enabling transparent discussions to occur.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 8, 2023 5:37 AM
|
Purpose
Dried blood spot succinylacetone (SA) is often used as biomarker for newborn screening (NBS) for Tyrosinemia type 1 (TT1). However, false-positive SA results are often observed. Elevated S

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 8, 2023 5:28 AM
|
Background: Lysosomal diseases (LDs) are progressive life-threatening disorders that are usually asymptomatic at birth. Specific treatments are availa…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 8, 2023 5:19 AM
|
Guanidinoacetate methyltransferase (GAMT) deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder of creatine biosynthesis due to pathogenic variants in the GAMT gene that lead to cerebral creatine deficiency and neurotoxic levels of guanidinoacetate. Untreated, GAMT deficiency is associated with hypotonia, significant intellectual disability, limited speech development, recurrent seizures, behavior problems, and involuntary movements. The birth prevalence of GAMT deficiency is likely between 0.5 and 2 per million live births. On the basis of small case series and sibling data, presymptomatic treatment with oral supplements of creatine, ornithine, and sodium benzoate, and a protein-restricted diet to reduce arginine intake, appear to substantially improve health and developmental outcomes. Without newborn screening, diagnosis typically happens after the development of significant impairment, when treatment has limited utility. GAMT deficiency newborn screening can be incorporated into the tandem-mass spectrometry screening that is already routinely used for newborn screening, with about 1 per 100 000 newborns screening positive. After a positive screen, diagnosis is established by finding an elevated guanidinoacetate concentration and low creatine concentration in the blood. Although GAMT deficiency is significantly more rare than other conditions included in newborn screening, the feasibility of screening, the low number of positive results, the relative ease of diagnosis, and the expected benefit of presymptomatic dietary therapy led to a recommendation from the Advisory Committee on Heritable Disorders in Newborns and Children to the Secretary of Health and Human Services that GAMT deficiency be added to the Recommended Uniform Screening Panel. This recommendation was accepted in January 2023.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 7, 2023 10:07 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 11, 2023 2:10 AM
|
Newborn screening (NBS) allows early identification of individuals with rare disease, such as isovaleric aciduria (IVA). Reliable early prediction of disease severity of positively screene

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 6, 2023 3:50 AM
|
Population Newborn Screening (NBS) for phenylketonuria began in the United States in 1963. In the 1990s electrospray ionization mass spectrometry permitted an array of pathognomonic metabolites t

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 23, 2023 7:52 AM
|
Objective
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is an X-linked disorder resulting in progressive muscle weakness and atrophy, cardiomyopathy, and in late stages, cardiorespiratory impairment, an

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 21, 2023 7:36 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 21, 2023 6:01 AM
|
Research funded and jointly led by NIH may prompt more countries to screen for SCID.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 19, 2023 2:52 AM
|
Thieme E-Books & E-Journals

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 13, 2023 1:57 AM
|
AbstractObjective. To evaluate the neonatal screening for congenital hypothyroidism (CH) and the diagnosis CH in the national health registers. To study the eff

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 12, 2023 1:40 AM
|
Assessment of T cell receptor excision circles (TRECs) in dried blood spots of newborns allows detection of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) (T…
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 8, 2023 5:43 AM
|
The assumption of this study is strictly connected to the need to focus and to know more about the impact on the psychological state of the parents whose newborn babies get a positive result at Expanded Newborn Screening (ENS). As clinical experience shows us, this aspect seems to have a potentially lasting resonance on the way the disease will be managed and handled in the family, leading to potential negative effects and repercussions on the child’s wellbeing and on the quality of life within the family. On the basis of this and on the evidence emerging from a review of the literature, this study aims to investigate and objectify possible distress indicators elicited at the moment of the communication of a positive result at ENS. Questionnaires containing the Beck Depression Inventory-II, the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory-Y, and the Short Form 36 Health Survey tests were administered to the parents of 87 newborns who received positive results at ENS. The parents of 32 babies expressed the presence of discomfort potentially related to the communication of a positive result at ENS.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 8, 2023 5:30 AM
|
To report on the first three years of mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I) newborn screening (NBS) in the large and diverse state of California.The Ca…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 8, 2023 5:21 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 8, 2023 5:16 AM
|
AbstractBackground. Newborn screening (NBS) is an effective public health intervention that reduces death and disability from treatable genetic diseases, but ma

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 12, 2023 4:18 AM
|
This prospective multicenter study of 400 hospitalized infants with a suspected genetic disorder evaluated rates of molecular diagnostic yield, time to return of results, and clinical utility by comparing between genomic sequencing and targeted neonatal gene-sequencing testing.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 7, 2023 1:23 AM
|
Pompe disease (PD) results from a deficiency of lysosomal acid α-glucosidase that leads to glycogen accumulation in lysosomes in multiple tissues. The…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 3, 2023 3:00 AM
|
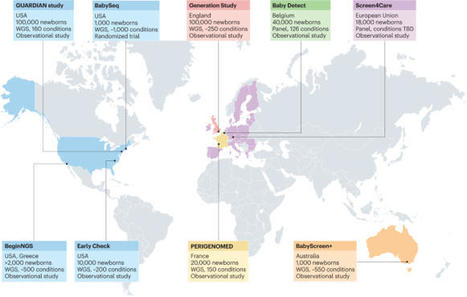
Rare diseases are a leading cause of infant mortality and lifelong disability. To improve outcomes, timely diagnosis and effective treatments are needed. Genomic sequencing has transformed the traditional diagnostic process, providing rapid, accurate and cost-effective genetic diagnoses to many. Incorporating genomic sequencing into newborn screening programmes at the population scale holds the promise of substantially expanding the early detection of treatable rare diseases, with stored genomic data potentially benefitting health over a lifetime and supporting further research. As several large-scale newborn genomic screening projects launch internationally, we review the challenges and opportunities presented, particularly the need to generate evidence of benefit and to address the ethical, legal and psychosocial issues that genomic newborn screening raises. In this Review, the authors summarize the current evidence for the use of genomic sequencing in newborn screening for rare diseases. As several large-scale studies launch internationally, the authors discuss major challenges and opportunities that lie ahead and identify key research priorities.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 23, 2023 3:18 AM
|
Newborn screening using dried blood spots (NBS) is widely acknowledged as a highly successful procedure in secondary prevention. For a number of congenital disorders, severe disability or death are impressively prevented by early detection and early treatment through NBS. However, as with any other screening, NBS can also cause harm, and the principle that “the overall benefits of screening should outweigh the harms” must be considered when introducing and implementing NBS programmes. This publication compiles the results of a systematic literature research on requirements for NBS infrastructure and procedures which was conducted as part of a research project on the quality and shortcomings of the NBS pathway in Germany. The compilation contains the requirements and recommendations for realising the principle of “maximise benefits and minimise harms” in relevant NBS pathway components such as parental education and information, coverage, timeliness, laboratory quality assurance, follow-up of abnormal results, confirmatory diagnostics, documentation, and evaluation. The results reflect the complexity of NBS infrastructure, and thus, they illustrate the importance of considering and implementing NBS as a well-coordinated public health programme with continuous quality management. Special attention should be paid to the perspectives of parents and families. Some NBS issues can substantially benefit from digital instruments or international cooperation. The literature review presented here has contributed to a concept of proposals for the advancement of NBS in Germany, and despite different settings, it may as well be of interest for other countries to achieve the best possible course and outcome of NBS for each child.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 21, 2023 7:35 AM
|
Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is fatal unless durable adaptive immunity is established, most commonly through allogeneic haematopoietic cell…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 19, 2023 2:53 AM
|
Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is an x-linked genetic condition with a high risk of adrenal dysfunction recommended for newborn screening. This review aim…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 19, 2023 2:47 AM
|
Thyroid hormone (TH) is indispensable for brain development in utero and during the first two to three years of life, and the negative effects of TH deficiency on brain development are irreversible. Detection of TH deficiency early in life by neonatal screening allows early treatment, thereby preventing brain damage. Inborn shortage of TH, also named congenital hypothyroidism (CH), can be the result of defective thyroid gland development or TH synthesis (primary or thyroidal CH (CH-T)). Primary CH is characterized by low blood TH and elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) concentrations. Less frequently, CH is due to insufficient stimulation of the thyroid gland because of disturbed hypothalamic or pituitary function (central CH). Central CH is characterised by low TH concentrations while TSH is normal, low or slightly elevated. Most newborn screening (NBS) programs for CH are primarily TSH-based thereby do not detect central CH. Only a few NBS programs worldwide aim to detect both forms of CH by different strategies. In the Netherlands, we have a unique T4-TSH-thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) NBS algorithm for CH which enables detection of primary and central CH. Although the necessity of central CH detection by NBS is still under debate, it has been shown that most central CH patients have moderate-to-severe hypothyroidism instead of mild, and that early detection of central CH by NBS problably improves its clinical outcome and clinical care for central CH patients with multiple pituitary hormone deficiency. We are therefore convinced that detection of central CH by NBS is of utmost importance.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 12, 2023 7:57 AM
|
Increased acylcarnitine ratio indices in newborn screening for carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency shows increased sensitivity and reduced false-positivity
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...