Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 7, 2023 4:05 AM
|
Newborn genomic sequencing (NBSeq) to screen for medically important genetic information is of considerable interest but data characterizing the actio…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 6, 2023 2:00 AM
|
Fabry disease is an X-linked progressive lysosomal disorder, due to α-galactosidase A deficiency. Patients with a classic phenotype usually present in childhood as a multisystemic disease. Patients presenting with the later onset subtypes have cardiac, renal and neurological involvements in adulthood. Unfortunately, the diagnosis is often delayed until the organ damage is already irreversibly severe, making specific treatments less efficacious. For this reason, in the last two decades, newborn screening has been implemented to allow early diagnosis and treatment. This became possible with the application of the standard enzymology fluorometric method to dried blood spots. Then, high-throughput multiplexable assays, such as digital microfluidics and tandem mass spectrometry, were developed. Recently DNA-based methods have been applied to newborn screening in some countries. Using these methods, several newborn screening pilot studies and programs have been implemented worldwide. However, several concerns persist, and newborn screening for Fabry disease is still not universally accepted. In particular, enzyme-based methods miss a relevant number of affected females. Moreover, ethical issues are due to the large number of infants with later onset forms or variants of uncertain significance. Long term follow-up of individuals detected by newborn screening will improve our knowledge about the natural history of the disease, the phenotype prediction and the patients’ management, allowing a better evaluation of risks and benefits of the newborn screening for Fabry disease.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 5, 2023 3:29 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 31, 2023 4:19 AM
|
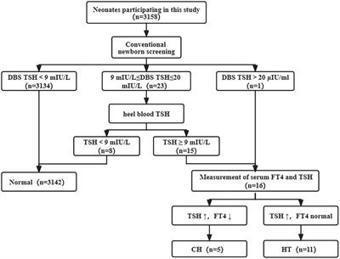
BackgroundCongenital hypothyroidism (CH) is an neonatal endocrine disorder. Traditional newborn screening is the mainstream method of CH screening, so as to ensure the early detection and treatment of CH. This method is limited as it has high rates of false positives and negatives. Genetic screening can be used to address the shortcomings of traditional newborn Screening (NBS); however, the comprehensive clinical value of genetic screening is yet to be systematically studied.MethodsA total of 3,158 newborns who accepted the newborn screening and genetic screening were recruited for this study. Biochemical screening and genetic screening were performed at the same time. The level of TSH with the DBS was detected by time-resolved immunofluorescence assay. High-throughput sequencing technology based on targeted gene capture was used for genetic screening. The suspected neonatal was recalled and tested serum TSH, and FT4. Finally, the effectiveness of traditional NBS and combined screening was compared.ResultsIn this study, 16 cases were diagnosed by traditional NBS. 10 cases of DUOX2 mutation were found in newborn CH-related genetic screening, including 5 homozygous and 5 compound heterozygous variations. We found that the c.1588A > T mutations in DUOX2 constituting the predominant site in the present cohort.Compared with NBS and genetic screening, the sensitivity of combined screening increased by 11.1% and 55.6%, respectively. Compared with NBS and genetic screening, th

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 26, 2023 6:54 AM
|
AbstractContext. Males with adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) have an 80% lifetime risk of developing adrenal insufficiency (AI), which can be life-threatening when un

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 16, 2023 2:12 AM
|
Background
Newborn screening (NBS) has largely eliminated the physical and neurodevelopmental effects of untreated congenital hypothyroidism (CH). Many countries, including Australia, hav

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 8, 2023 6:56 AM
|
Introduction Tandem mass spectrometry (TMS) has emerged an important screening tool for various metabolic disorders in newborns. However, there is inherent risk of false positive outcomes. Objective To establish analyte-specific cutoffs in TMS by integrating metabolomics and genomics data to avoid false positivity and false negativity and improve its clinical utility. Methods TMS was performed on 572 healthy and 3000 referred newborns. Urine organic acid analysis identified 23 types of inborn errors in 99 referred newborns. Whole exome sequencing was performed in 30 positive cases. The impact of physiological changes such as age, gender, and birthweight on various analytes was explored in healthy newborns. Machine learning tools were used to integrate demographic data with metabolomics and genomics data to establish disease-specific cut-offs; identify primary and secondary markers; build classification and regression trees (CART) for better differential diagnosis; for pathway modeling. Results This integration helped in differentiating B12 deficiency from methylmalonic acidemia (MMA) and propionic acidemia (Phi coefficient=0.93); differentiating transient tyrosinemia from tyrosinemia type 1 (Phi coefficient=1.00); getting clues about the possible molecular defect in MMA to initiate appropriate intervention (Phi coefficient=1.00); to link pathogenicity scores with metabolomics profile in tyrosinemia (r2=0.92). CART model helped in establishing differential diagnosis of urea cycle disorders (Phi coefficient=1.00). Conclusion Calibrated cut-offs of different analytes in TMS and machine learning-based establishment of disease-specific thresholds of these markers through integrated OMICS have helped in improved differential diagnosis with significant reduction of the false positivity and false negativity rates.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 3, 2023 5:49 AM
|
Biotinidase deficiency (BD) is an autosomal recessively inherited disorder that was first described in 1982. Forty years after its first description, …

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
April 13, 2023 4:00 AM
|
Newborn screening (NBS) is a state or territory-based public health system that screens newborns for congenital diseases that typically do not present with clinical symptoms at birth but can cause significant mortality and morbidity if not detected or treated quickly. NBS continues to be one of the most successful public health interventions in the US, providing early detection and intervention to all infants. The increase in overall birth prevalence of core Recommended Uniform Screening Panel (RUSP) diseases detected via dried blood spot (DBS) specimens from 2015–2017 (17.50–18.31 per 10,000) to 2018–2020 (20.07 per 10,000), as reported into the APHL NewSTEPs database, affirms the importance and impact of NBS programs. This report presents aggregate numbers and birth prevalence of diseases detected by DBS on the RUSP from 2018–2020, including data from fifty US states and two territories.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
April 11, 2023 8:10 AM
|
Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a group of diseases characterized by low T-cell count and impaired T-cell function, resulting in severe cellular and humoral immune defects. If no

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
April 6, 2023 4:59 AM
|
The Recommended Uniform Screening Panel (RUSP) is the list of conditions recommended by the US Secretary of Health and Human Services for inclusion in state newborn screening (NBS). During 2010–2022, seven conditions were added to the RUSP: severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) (2010), critical congenital heart disease (CCHD) (2011), glycogen storage disease, type II (Pompe) (2015), mucopolysaccharidosis, type I (MPS I) (2016), X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) (2016), spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) (2018), and mucopolysaccharidosis, type II (MPS II) (2022). The adoption of SCID and CCHD newborn screening by programs in all 50 states and three territories (Washington, D.C.; Guam; and Puerto Rico) took 8.6 and 6.8 years, respectively. As of December 2022, 37 programs screen for Pompe, 34 for MPS I, 32 for X-ALD, and 48 for SMA. The pace of implementation based on the average additional number of NBS programs per year was most rapid for SMA (11.3), followed by CCHD (7.8), SCID (6.2), MPS I (5.4), Pompe (4.9), and X-ALD (4.7).

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 28, 2023 1:31 AM
|
Individuals with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), a group of rare, genetic conditions, are at risk for life-threatening illnesses unless diagnosed and treated early. Even after early identification through newborn screening, parents of children with SCID embark on a complex journey marked by a variety of informational and emotional support needs. This paper explored the types of uncertainties experienced by parents of a child with SCID diagnosed through newborn screening. We conducted semi-structured interviews with 26 parents to discuss the types of uncertainty experienced, including scientific, practical, personal, and existential. Each interview was recorded, transcribed, and coded. Using deductive and inductive content analysis, we describe the type of uncertainty experienced across each stage of the SCID journey. We found that uncertainties in the SCID journey were chronic and multifaceted. Some uncertainties were more prominent at certain points of the journey whereas others spanned multiple stages. Parents expressed a variety of negative emotional reactions to uncertainty, from anxiety, worry, and fear, to doubt, guilt, or grief, and even anger, frustration, and depression. The results speak to the need for healthcare providers to prepare parents for the SCID journey by providing resources to help manage and cope with uncertainty.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 27, 2023 3:17 AM
|
Background Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is an inherited disease which causes premature atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. However, less than 10% of individuals with FH have been identified. Objective To assess parental perspectives for inclusion of FH on routine newborn screening (NBS) and to highlight potential benefits, harms, and ethical concerns. Methods Telephone interviews of two groups were conducted: 1) parents of children diagnosed with FH, and 2) parents of children diagnosed with a genetic condition through NBS. Stratified purposive sampling was used to ensure adequate representation. The 11 telephone interviews were conducted in 30-min sessions guided by a semi-structured interview script. At the beginning of the interview, participants were educated on the NBS process and FH. The interviews were transcribed verbatim, and a thematic analysis was performed in multiple steps. Results All interviewees indicated that they would be interested in having their child be screened for FH on the newborn screen. Reasons supporting screening during the newborn period included knowing their child’s diagnosis, the ability to screen family members for FH, incorporation of lifestyle changes, and access to preventive care. Negatives surrounding screening during the newborn period included increased stress or anxiety, knowledge, stigma, and the delay from diagnosis to initiation of pharmacotherapy for FH. Conclusion While these interviewees were in favor of NBS for FH, further education of parents and clinicians is needed to ensure proper implementation. The results of this study may be useful to formulate family notification and care protocols for newborns diagnosed with FH and other diseases.
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 6, 2023 9:34 AM
|
The British Journal of Haematology publishes original research papers in clinical, laboratory and experimental haematology. The Journal also features annotations, reviews, short reports, images in haematology and Letters to the Editor.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 5, 2023 3:30 AM
|
Background Primary carnitine deficiency is an inborn error of metabolism, which can lead to life-threating complications early in life. Low carnitine levels can be detected by newborn bloodspot screening (NBS). However, NBS can also identify, mostly asymptomatic, mothers with primary carnitine deficiency. To identify mothers’ needs and areas for improving screening practice, this study explored the experiences with, and opinions on primary carnitine deficiency screening in NBS among women diagnosed through NBS of their newborn. Methods Twelve Dutch women were interviewed, 3–11 years after diagnosis. Data were analysed using a thematic approach. Results Four main themes were derived: 1) psychological impact of primary carnitine deficiency diagnosis, 2) becoming a patient and “patient-in-waiting”, 3) information issues and care provision, and 4) primary carnitine deficiency as part of the NBS panel. Mothers shared that they did not experience major psychological distress of the diagnosis. They did experience (recall) various emotions following the initial abnormal NBS result, including fear and anxiety as well as relief, and emotions regarding their own diagnosis, including uncertainty about health risks and treatment effectiveness. Some felt a patient-in-waiting. Many participants experienced a lack of information, especially shortly after receiving the abnormal NBS result. All shared the belief that screening for primary carnitine deficiency in NBS is beneficial for the newborn, and, given the information they received, also considered the knowledge beneficial for their own health. Conclusions Psychological burden following diagnosis was experienced by women as limited, although the experienced lack of information amplified feelings of uncertainty and anxiety. Most mothers believed that benefits of knowing about primary carnitine deficiency outweighed the disadvantages. Mothers’ perspectives should be incorporated in policy-making about primary carnitine deficiency in NBS.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 1, 2023 4:29 AM
|
AbstractContext. Treatment of children with classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency is challenging. Linear growth and ad

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 26, 2023 6:55 AM
|
Introduction We sought to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of newborn screening (NBS) versus no NBS for 5q spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) in England. Methods A cost-utility analysis using a combination of decision tree and Markov model structures was developed to estimate the lifetime health effects and costs of NBS for SMA, compared with no NBS, from the perspective of the National Health Service (NHS) in England. A decision tree was designed to capture NBS outcomes, and Markov modeling was used to project long-term health outcomes and costs for each patient group following diagnosis. Model inputs were based on existing literature, local data, and expert opinion. Sensitivity and scenario analyses were conducted to assess the robustness of the model and the validity of the results. Results The introduction of NBS for SMA in England is estimated to identify approximately 56 (96% of cases) infants with SMA per year. Base-case results indicate that NBS is dominant (less costly and more effective) than a scenario without NBS, with a yearly cohort of newborns accruing incremental savings of £62,191,531 and an estimated gain in quality-adjusted life-years of 529 years over their lifetime. Deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses demonstrated the robustness of the base-case results. Conclusions NBS improves health outcomes for patients with SMA and is less costly compared with no screening; therefore, it is a cost-effective use of resources from the perspective of the NHS in England.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 22, 2023 4:46 AM
|
INESSS, Institut national d'excellence en santé et services sociaux

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 9, 2023 2:25 AM
|
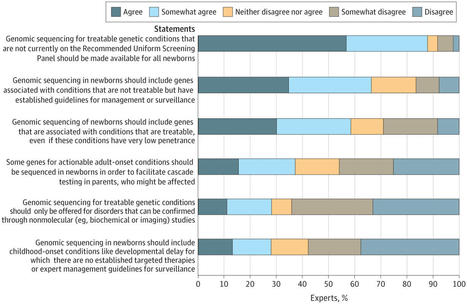
This survey study examines rare disease expert perspectives on newborn genome sequencing and which gene-disease pairs they consider appropriate for screening in newborns.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 4, 2023 4:14 AM
|
Neonatal screening has excellent coverage in France. Data from the foreign literature raise questions about the informed consent to this screening. The Neonatal Screening and Informed Consent Dépistage Néonatal Information et Consentement Eclairé (DENICE) study was designed to assess whether information on neonatal screening provided for families in Brittany allows for informed consent. A qualitative methodology was chosen to collect parents’ opinions on this topic. Twenty semi-structured interviews were conducted with twenty-seven parents whose children had positive neonatal screening for one of six diseases. The five main themes from the qualitative analysis were knowledge of neonatal screening, information received by parents, parental choice, the experience of the screening process, and parents’ perspectives and wishes. Informed consent was weakened by parents’ lack of knowledge regarding choice and the absence of a parent after birth. The study found that more information about screening during pregnancy would be preferable. The information should be repeated and accessible and should make it clear that neonatal screening is not mandatory, but informed consent should be obtained from parents who choose to screen their newborns.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 3, 2023 5:47 AM
|
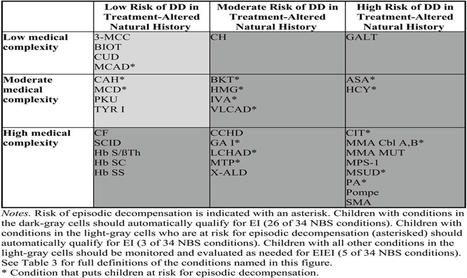
Despite benefiting from NBS and timely treatment, many children diagnosed with NBS conditions are at risk for developmental delays and significant medical complexity. The results demonstrate a need for more clarity and guidance regarding which children should qualify for EI. We suggest that most NBS conditions should automatically qualify based on the probability of resulting in a developmental delay. These findings suggest a future opportunity for collaboration between NBS and EI programs to create a consistent set of Established Conditions, potentially expediate referrals of eligible children, and streamline children's access to E

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
April 12, 2023 8:35 AM
|
This paper focuses on the question of, “When is the best time to identify an individual at risk for a treatable genetic condition?” In this review, we describe a framework for considering th

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
April 11, 2023 8:09 AM
|
Inborn errors of immunity (IEI) are a group of over 450 genetically distinct conditions associated with significant morbidity and mortality, for which early diagnosis and treatment improve outcomes. Newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is currently underway in several countries, utilising a DNA-based technique to quantify T cell receptor excision circles (TREC) and kappa-deleting recombination excision circles (KREC). This strategy will only identify those infants with an IEI associated with T and/or B cell lymphopenia. Other severe forms of IEI will not be detected. Up-front, first-tier genomic-based newborn screening has been proposed as a potential approach by which to concurrently screen infants for hundreds of monogenic diseases at birth. Given the clinical, phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity of IEI, a next-generation sequencing-based newborn screening approach would be suitable. There are, however, several ethical, legal and social issues which must be evaluated in detail prior to adopting a genomic-based newborn screening approach, and these are discussed herein in the context of IEI.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 30, 2023 4:09 AM
|
INESSS, Institut national d'excellence en santé et services sociaux

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 27, 2023 5:39 AM
|
In April 2019, the Alberta Newborn Screening Program expanded to include screening for classic galactosemia using a two-tier screening approach. This approach secondarily identifies infants with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. The goals of this study were (i) to evaluate the performance of a two-tier galactosemia screening protocol, (ii) to explore the impact on and acceptability to families of reporting G6PD deficiency as a secondary finding, and (iii) assess the communication and follow-up process for positive G6PD deficiency screening results. The two-tiered galactosemia approach increased the positive predictive value (PPV) for galactosemia from 8% to 79%. An additional 119 positive newborn screen results were reported for G6PD deficiency with a PPV of 92%. The results show that there may be utility in reporting G6PD deficiency results. Most parents who participated in the study reported having some residual worry around the unexpected diagnosis; however, all thought it was helpful to know of their child’s diagnosis of G6PD deficiency. Finally, the communication process for reporting G6PD deficiency newborn screen results was determined to result in appropriate follow up of infants.
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...