 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 31, 2025 4:13 PM
|
Arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) associations of plants and Glomeromycotina soil fungi play a crucial role in all terrestrial ecosystems. In this mutually beneficial interaction, obligate biotrophic fungi acquire photosynthetically fixed carbon from the plant, while the mutualistic fungi enhance plant access to soil nutrients. AM fungi colonize the inner tissues of host roots, where they form specialized symbiotic structures (arbuscules) within fully differentiated cortex cells that are reprogrammed to host the microbe. Given the intimate nature of the interaction, extensive partner communication at the interface of plant and fungal cells is crucial for the development and functioning of AM symbiosis. The peri-arbuscular space, a specialized apoplast compartment surrounding the arbuscules, supports not only nutrient exchange between the symbiotic partners but is also the site of extensive partner crosstalk mediated by cell wall components, receptors, signaling peptides, and extracellular vesicles. Such signaling processes in the apoplast modulate plant immune responses to enable colonization by beneficial fungi, making this compartment a key player for the establishment and maintenance of AM symbiosis. In this review, we discuss recent discoveries related to the role of partner communication in the apoplast, with a focus on peptide and cell wall signaling, as well as extracellular vesicles.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 31, 2025 4:10 PM
|
Ectomycorrhizal fungi form symbiotic relationships with a wide range of terrestrial plants, acquiring carbohydrates for themselves and promoting nutrient uptake in their host plants. However, some ectomycorrhizal fungi cannot effectively obtain the thiamine necessary for growth from their host or synthesize it themselves. Ectomycorrhizal fungi can recruit hypha-associated microorganisms, which play a vital role in promoting nutrient absorption and ectomycorrhizal root formation, ultimately colonizing within fruiting bodies to form a unique bacterial microbiota. In this study, non-targeted metabolomics and whole-genome sequencing were employed to investigate the colonization characteristics of the hyphae-associated bacterium Bacillus altitudinis B4 on the mycelial surface of ectomycorrhizal fungus Suillus clintonianus, as well as the synergistic promotion of thiamine synthesis and absorption by B. altitudinis B4 and the fungal mycelium, respectively. The results suggested that S. clintonianus first secreted ureidosuccinic acid and pregnenolone, recruiting the hyphae-associated bacterium B. altitudinis B4 to the mycelial surface. Subsequently, the ureidosuccinic acid secreted by S. clintonianus further stimulated B. altitudinis B4 to enhance thiamine production by increasing its biomass and upregulating the expression of related functional genes. Finally, S. clintonianus absorbed the thiamine secreted by the B. altitudinis B4, promoting fungal growth and increasing the colonization rate in association with Pinus massoniana. This study elucidates the thiamine acquisition mechanisms of ectomycorrhizal fungi, highlighting the critical role of bacterial partners in fungal nutrition and host-fungal interactions.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 31, 2025 3:43 PM
|
In the current context of climate change, there is a need to develop more sustainable agrifood strategies. As an alternative to the intensive use of chemically synthesized fertilizers and pesticides that pollute water and impact biodiversity, there is a growing interest in using beneficial microbes as biostimulants and/or bioprotection agents. However, their implementation in agriculture remains a challenge due to highly variable outcomes and benefits. Furthermore, there are major knowledge gaps about the molecular mechanisms that regulate different plant–microbe interactions. In the present review, we summarize current knowledge on the molecular mechanisms that control different beneficial plant root–microbe interactions; namely, arbuscular mycorrhiza, the rhizobium–legume symbiosis, ectomycorrhiza, and fungal and bacterial endophytic associations. This includes the signaling pathways required for recognition of microbes as beneficial, the metabolic pathways that provide nutritional benefits to the plant, and the regulatory pathways that modulate the extent of symbiosis establishment depending on soil nutrient availability and plant needs. Our aim is to highlight the main common mechanisms, as well as knowledge gaps, in order to promote the use of microbes, either individually or in consortia, within the framework of a sustainable agriculture that is less dependent on chemicals and more protective of biodiversity and water resources.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 28, 2025 4:57 PM
|
PerCon SFA project data dentification of spatially resolved biomarkers of drought in Sorghum bicolor rhizosphere molecular-microbe interactions using a novel root cartography "RhizoGrid" system for sampling plants under drought and control conditions across 10 equally sized root zone environments (4 quadrants each). Each quadrant was sampled and processed for 16S amplicon, metabolomics, and X-ray computed tomography (XCT). Data download includes experimental metadata and results files for 16S rRNA sequence analysis of microbial community assembly (processed data files), liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) metabolomics analysis of microbial community root exudates (processed data files), X-ray computed tomography (XCT) spatial gradient analysis (raw and processed data files) of microbial community composition, and related computational modeling outputs.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 25, 2025 9:34 PM
|
Background and aims
Mycorrhizal (AMF) benefits to ancient tetraploid and hexaploid wheats, particularly under saline conditions, are not sufficiently known.
Methods
A two-year field experiment and a pot experiment were carried out, where the field experiment encompassed non-saline and saline (120 mM NaCl) irrigation, presence and absence of AMF (Funneliformis mosseae) inoculation, and 10 wheat genotypes. The pot experiment encompassed four salinities (0, 40, 80, and 120 mM) and two levels of AMF inoculation (with and without of AMF inoculation) and 11 genotypes.
Results
Salinity suppressed the chlorophyll, carotenoids, K, and P, grains/m2, grain yield, harvest index, and dry mass. Though, it boosted the activities of antioxidative enzymes, Na, electrolyte leakage, Na/K, protein, wet gluten, and gluten index. Inoculation to AMF led to enhancement in the maximum quantum efficiency of photosystem II, chlorophyll, K, P, N, and total phenolic compounds concentrations, the activities of antioxidative enzymes, grains/m2, grain yield, dry mass, protein, wet gluten, and gluten index, while decreasing the Na concentration, Na/K, and electrolyte leakage, particularly in the salt-stricken plants; favorable responses to the AMF were more appreciable in the salt-stricken modern wheats, than the ancient emmer and spelt wheats.
Conclusion
Salinity and AMF exerted contrasting effects on physiological, growth, dry mass, and grain yield attributes of different genotypes, with a tendency of salt-induced suppressions and AMF-induced enhancements to be less notable in the ancient wheats, than the modern bread and durum wheats. Though, salinity and AMF inoculation shared a same trend in improving the grain and flour quality attributes.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 25, 2025 9:24 PM
|
This thesis tests the hypothesis that phosphorus (P) fertiliser addition can optimise nitrogen (N2) fixation processes and increase soybean yield. Using a combination of controlled environment studies, field trial and global meta-analysis, this thesis aids in achieving sustainable soybean production through building improved understanding of the effects of P fertiliser addition to inform future fertiliser guidelines, crop models and management practices. Global meta-analysis showed an increase in soybean response to P fertiliser addition with seed yield increasing by 25%. This also highlighted the complexity of soybean yield response to P fertiliser, with a several key management and environmental conditions having a significant effect, including soil P concentration, pH, fertiliser type and rate of application and climatic conditions – indicating soybean yield cannot be increased by single P fertiliser applications alone. Controlled environment studies revealed P addition significantly increased nitrogen (N2) fixation. Key nodule traits significantly correlated with shoot N; however, further work should examine the mechanistic pathways driving the increase in nodule formation. Interestingly, controlled environment studies revealed nodule function was not influenced by P fertiliser addition. Instead, regulatory mechanisms such as maintenance of nodule P concentration and leghaemoglobin concentration under low P conditions maintained N2 fixation. Through combined analysis of multiple growth parameters and measures of plant physiology, seed yield was found to increase under P fertiliser addition. Seed P concentration also increased following P fertiliser addition. Results of this thesis contribute to our understanding of soybean response to P fertiliser addition, particularly the improvement to key nodule traits to improve N2 fixation and the partitioning and remobilisation of resources to improve yield. This now needs to be upscaled at differing environmental and management conditions and incorporated into crop models to ensure the sustainable use of P fertiliser in soybean production globally.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 25, 2025 7:27 PM
|
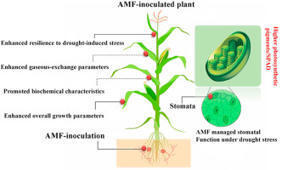
Drought-induced stress is a significant constraint for crop yields in semi-arid and arid areas.
Yield assessments under water stress indicate that mycorrhizae can alleviate the detrimental impacts of drought, placing them as sustainable options for agricultural practices in affected areas. Thus, we executed a two-year study to examine the effects of root colonization by two AMF species (Diversispora epigaea and Diversispora versiformis) under different drought stress conditions, assessing maize morpho-physiological and biochemical characteristics, nutrient absorption, yield components, oil percentage, and irrigation water efficiency. The research was conducted in a desolate region of Pakistan during the 2023 and 2024 growing seasons. Drought-induced stress was generated at two levels by irrigating after 80 % and 60 % water loss, categorized as severe and mild drought stress. Irrigation after a 40 % reduction in water was considered normal (without stress). The findings demonstrated that regardless of AMF species and level of drought stress, inoculated plants yielded heavier seeds, higher dry matter, chlorophyll (37 %) and carotenoids (41 %), phytohormone (27 %), enhanced oil yields (32 %) and seeds (24.2 %) compared to uninoculated plants. Notably, the maize seed yields of Diversispora epigaea-treated plants under every irrigation treatment surpassed those of Diversispora versiformis inoculated plants and uninoculated plants. Drought stress reduced nitrogen levels in seeds and leaves, whereas AMF enhanced nitrogen levels, particularly when crops were treated with Diversispora epigaea. Moreover, seed phosphorus percentages were not influenced by AMF in 2023. Conversely, the highest phosphorus percentages in seeds and leaves were recorded in crops inoculated with Diversispora epigaea in 2023. Our findings indicate that Diversispora epigaea exhibits greater efficiency under water stress and provides superior support to maize plants.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 25, 2025 7:17 PM
|
•Glomalin is widely used as a soil health and mycorrhizal fungi indicator.
•The extraction method raises concerns about its specificity to mycorrhizal fungi.
•Glomalin content correlates with plant litter decomposition and added organic matter.
•High-temperature citrate extracts include diverse compounds, not just glomalin.
•Glomalin is unsuitable for standardized measurements of mycorrhizal fungi.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 22, 2025 9:58 AM
|
Biofertilizers have become a viable substitute for chemical fertilizers. Biofertilizers contain the effective strains of potential organisms majorly included of bacterial and fungal strains providing desirable benefits to crop plants and soil. They are being prepared in different formulations suitable for diverse applications. Variations in production process, raw materials and storage conditions can lead to inconsistencies in microbial composition and nutrient levels, impacting their function in the fields. However, the shelf life and quality maintenance of biofertilizers are critical to their effectiveness and viability and present considerable hurdles throughout production, storage and application. Biofertilizers are easily affected by various factors resulting in eventual loss of viability. Variations in temperature, moisture content and exposure to UV radiation are a few examples of factors that might negatively impact microbial viability and activity. Furthermore, contamination by undesirable microorganism during production and storage can reduce the effectiveness of bio-fertilizers. To address these problems, innovative approaches such as different formulation techniques were developed. Addition of stabilizing agents to the formulation will add value to the products, since it gives protection to the cell, thus the efficacy and shelf life are maintained. Varied types of formulations have different issues with the maintenance of quality and shelf life. Widely used formulations and the problems and constrains with different formulations on application, in addition to shelf life and also the possible suggestions are discussed in this review.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 21, 2025 5:23 PM
|
Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis plays a pivotal role in nutrient acquisition and stress tolerance, making its regulation crucial for sustainable crop productivity. This review synthesizes current advances in understanding the molecular and physiological factors governing AM symbiosis, with emphasis on transcriptional, hormonal, and nutrient-mediated regulation. From pre-symbiotic signaling to root colonization and arbuscule development, AM formation is orchestrated by a complex network of molecular interactions. Transcription factors, including those with GRAS domains (e.g., NSP1, NSP2, RAM1, and DELLA), and other regulators such as MYB, SPX, WRKY, and CYCLOPS/IPD3, serve as central modulators of symbiosis-related gene expression. Phytohormones, including strigolactones, salicylic acid, and abscisic acid, generally promote symbiosis, whereas gibberellins and ethylene act as inhibitors; cytokinin exerts context-dependent effects. Nutrient status also modulates AM formation—low phosphorus and nitrogen promote, while high nutrient availability suppresses colonization. Collectively, these insights reveal the integrative regulatory networks driving AM symbiosis and offer new avenues to optimize symbiotic efficiency for enhanced plant growth and agricultural sustainability.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 21, 2025 5:21 PM
|
Climate change, a major threat to global food security, has been accelerated by increasing atmospheric CO2 levels over the last two centuries. Numerous studies indicate that high atmospheric CO2 (eCO2) enhances carbon (C) sequestration in plant biomass, potentially aiding in its mitigation. Plant root characteristics are critical regulators of underground C inputs, soil nutrient acquisition, and water uptake. Roots directly interface with soil, while shoots perceive atmospheric CO2 via β-carbonic anhydrase, triggering systemic signals, such as hormone pathways, that influence root functions, including strigolactone secretion and mycorrhizal colonization. Recent research has begun to elucidate how eCO2 influences root morphology, root system expansion, and overall root functionality, including increased root:shoot ratios, respiration rates, rhizodeposition, and fungal colonization. This review aims to synthesize the current understanding of eCO2 effects on plant roots, with a particular focus on arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) symbiosis. We highlight novel findings regarding the interactions between eCO2 and plant hormones, which play a crucial role in the systemic regulation of AM symbiosis. Finally, we outline potential future research directions that could enhance crop resilience to climate change, emphasizing the importance of integrating root biology and mycorrhizal interactions in sustainable agricultural practices.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 19, 2025 4:29 PM
|
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) play a crucial role in promoting plant health. They assist plants in absorbing nutrients and enhance their resistance to diseases and environmental stressors. In contrast, plant-parasitic nematodes (PPNs) pose a significant threat to global crop production. Both AMF and PPNs inhabit the soil surrounding plant roots, yet their interactions are not fully understood. They may compete directly or influence plants in indirect ways. This review examines the relationship between AMF and PPNs, emphasizing their interactions and suggesting that AMF could serve as a natural method to control PPN populations. Unlike previous studies that have focused on these organisms separately, this review integrates insights on the impact of AMF and nematode interactions on plants through nutrient availability, spatial competition, and rhizosphere dynamics. Additionally, it explores the mechanisms of systemic resistance that AMF may provide against nematodes, creating a comprehensive framework for future research and sustainable agriculture.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 17, 2025 4:48 PM
|
Central to the legume–rhizobium symbiosis is the formation of organelle-like symbiosomes where nitrogen-fixing bacteroids are enclosed by a host-derived symbiosome membrane. This creates the symbiosome space, which topologically resembles an apoplastic compartment within the cell. While the apoplast of plant cells is largely occupied by the cell wall, symbiosomes are devoid of cell wall polymers. Here, we describe a mechanism that functions to protect and maintain effective nitrogen fixation through the action of cell-wall-degrading enzymes that prevent accumulation of un-esterified pectin within symbiosomes. We identify two symbiotically-induced polygalacturonase (PG) genes in Medicago truncatula, SyPG1 and SyPG2, that are secreted into the symbiosome space. Silencing the expression of SyPG1/2 or editing SyPG1/2 via CRISPR-Cas9 both lead to nodule senescence and trigger excessive accumulation of un-esterified pectin in symbiosome containing cells. Additionally, we show that un-esterified pectins inhibit rhizobial growth both in vivo and in vitro. Together, our results provide evidence for a host-controlled cell wall clearance mechanism that is essential for symbiosome maintenance.
|

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 31, 2025 4:11 PM
|
Soil, the Earth's upper crust layer, is crucial for ecological processes, comprising mineral, organic, and biological components that determine fertility and multifuncionality. Human-induced degradation necessitates advancements in pedology and soil conservation. The rhizosphere, surrounding plant roots, houses a diverse microbial community, notably bacteria, which enhance plant growth and disease resistance. Root exudates fuel biological activity and nutrient cycling, supporting microbial growth, improving soil structure, and reducing plant stress. Plant-microorganism interactions in ecological and agricultural systems play a vital role for maintaining primary production and ecosystem sustainability. Moreover, arbuscular mycorrhizae and nitrogen-fixing bacteria are essential, influencing plant development, sustainability, and ecosystem health. Specific bacterial phyla populate the rhizosphere and endosphere, with Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR), such as Pseudomonas spp. and Bacillus spp., playing a prominent role. PGPR employ direct and indirect mechanisms, including phytohormone production, mineral solubilization, systemic resistance induction, antibiosis, competition for resources, and ACC deaminase activity, The amalgamation of these traits underscores the conceptual foundation for comprehending the ecological and agricultural implications of employing microbes. This inquiry is particularly relevant to sustainable agriculture, where the use of microbes, including PGPR, plays a crucial role in biofertilization and mitigating environmental stressors. Thus, investigating the ecological and agricultural implications through multi-omics approaches such as genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics offers valuable insights. The integration of these multi-omics data provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the complex interactions between plants, bacteria, and fungi. This holistic perspective not only deepens our understanding of soil ecology but also lays the groundwork for informed and sustainable agricultural practices, fostering resilience against environmental stresses.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 31, 2025 3:50 PM
|
Microbiota-mediated nutrient turnover in the rhizosphere determines nutrient bioavailability, thereby enhancing nutrient uptake, utilization, and ultimately crop productivity. Consequently, elucidating the functional core microbiota in rhizosphere nutrient turnover is of critical importance. In this study, we leveraged soybean germplasm core collections to investigate the tripartite relationship among host genotype, core microbiota and nutrient availability, with a focus on delineating the pivotal role of core microbiota in nutrient turnover. Our results suggest that phylogenetic variation significantly shape root-associated microbial communities and rhizosphere nutrient availability, explaining 11.75 % and 2.07 % of total variances, respectively. Core microbiota analysis identified 29 phylogenetic conserved core amplicon sequence variants (ASVs), the majority of which exhibited significant correlated with nutrient availability. Notably, three key core ASVs—ASV13, ASV14 and ASV12, positively correlated with alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen, available phosphorus, and soil organic matter, respectively. These taxa were subsequently incorporated into a Bradyrhizobium-based synthetic bacterial community (SynCom) to validate their functional roles. Further experiments confirmed that core microbiota-driven nutrient turnover directly facilitates host plant, as evidenced by SynCom inoculation assays. Collectively, this study establishes that phylogenetically conserved core microbiota critically regulate nutrient turnover and acquisition efficiency in the rhizosphere. These insights advance our understanding the ecological function of core microbiota in the rhizosphere and provide a framework for harnessing the beneficial traits in sustainable agriculture.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 28, 2025 5:02 PM
|
Transmission electron microscopy was the key for revealing structural similarities between intracellular plant-microbe interactions.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 25, 2025 9:43 PM
|
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) are obligate biotrophs that rely on host-derived symbiotic carbohydrates. However, it remains unclear whether symbiotic AMF can access exogenous non-symbiotic carbon sources, complicating our understanding of their relationship with host plants. Here, we investigated the direct uptake of exogenous 13C1-labeled myristate by three symbiotic AMF species (Rhizophagus irregularis, R. intraradices, and R. diaphanous) and assessed their growth responses using AMF-carrot hairy root co-culture systems. Furthermore, we explored the environmental distribution of myristate, and evaluated the impact of exogenous myristate on the carbon-phosphorus exchange between R. irregularis and alfalfa or rice in a greenhouse experiment. Symbiotic AMF can absorb exogenous myristate, as evidenced by 13C enrichment and transcriptional activation of fatty acid transport and metabolism genes in AMF extraradical hyphae. Myristate is commonly present in various soil and plant environments, and its application increased both intraradical and extraradical fungal biomass, possibly linked to suppressed mycorrhizal-activated defense responses in host roots. Unexpectedly, exogenous myristate reduced the mycorrhizal phosphorus benefits for both alfalfa and rice and decreased their symbiotic carbon allocation to root-colonizing AMF, although these effects varied with soil phosphorus conditions. These findings provide new insights into understanding and manipulating the nutritional interactions between AMF and host plants.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 25, 2025 9:27 PM
|
Crop rotation enhances agroecosystem sustainability by reducing nutrient loss, improving soil fertility, and decreasing crop evapotranspiration. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) inoculation further supports enhanced nutrient and water uptake by plants, potentially improving water use efficiency and soil health while reducing fertigation needs. However, crop species may respond differently to AMF inoculation under varying fertigation regimes. In this study, the response of four horticultural species to AMF inoculation was investigated under optimal (100 %) and deficit (25 % reduction) water and fertilizer (fertigation) availability. Leek, courgette, white bean, and celery were planted consecutively over the course of two years, with crop production and quality as well as leaf nutrients and soil parameters being measured at the end of each crop cycle. Mycorrhizal inoculation did not improve any agronomic parameter among the crops studied under either fertigation condition.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 25, 2025 9:16 PM
|
The symbiotic nitrogen fixation process between legume roots and rhizobia initiates at the root hairs. Rhizobia initially colonize the tip of the root hairs and induce its curling to become entrapped. However, the specific molecular mechanisms underlying root hair deformation and curling in response to rhizobial infection remain unclear. In this study, transcriptome analysis of wild-type JiMa389 and nodulation-deficient mutant jima61 of Melilotus albus, the Rho-like small GTPase MaROP10. Our results show that MaROP10 functions as an interacts with the Nod factor receptor NFR5 to regulate rhizobia-induced root hair deformation and infection thread formation during the early stages of rhizobial infection. To elucidate the mechanism of MaROP10, we further identified its downstream potential effector protein, MaRIC6, which positively regulates root hair deformation and infection thread formation. Taken together, MaROP10 likely integrates signals from the symbiotic receptor NFR5 to regulate downstream signaling pathways through its effector MaRIC6, thereby coordinating root hair deformation and infection thread development during the early stages of rhizobial infection.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 25, 2025 7:20 PM
|
Many plant endosymbionts are facultative, switching between host-associated and free-living stages. Extensive genomic and experimental studies suggest that adaptation during the saprophytic, off-host phase, rather than adaptation to hosts, primarily constrains the biogeographic distribution of these microbes. To test this hypothesis, we analyzed the growth capacities and genomic features of 38 Sinorhizobium and Ensifer strains isolated from the nodules of Medicago lupulina (black medic), collected from two regions with distinct thermal environments. The warmer region is predominantly inhabited by S. meliloti, while S. medicae and Ensifer strains are more common in the cooler region. Laboratory assays demonstrated that at 40 °C, the upper temperature limit of their region of origin, S. meliloti remained viable, albeit with reduced growth, whereas S. medicae and Ensifer strains failed to grow under heat stress. Comparative genomics revealed isolation-by-distance in both the core and accessory genomes, particularly in S. meliloti in the warmer region, which exhibits less within-region thermal variation. This is consistent with an isolation-by-distance model where population divergence is governed by restricted gene flow. These findings suggest that metabolic constraints shape the regional distribution of this facultative microbial symbiont, while limited gene flow influences local population structure.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 23, 2025 1:08 PM
|
Lateral roots (LR) and the root nodules (RN) of legumes are structurally related and the decision processes leading to RN formation involve signal exchange with the shoot. In order to disentangle these processes, we established a quantitative assay for LR formation in hairy root liquid cultures (HRLC) for the legume Lotus japonicus. In HRLC, ectopic expression of SymRK, or deregulated, auto-active versions of CCaMK and Cyclops stimulated LR formation in a NIN-dependent manner, but spontaneous RN were never observed. It appears that the previously described spontaneous RN formation induced by these versions requires the presence of the shoot. Interestingly, CCaMKT265D increased LR number in a cyclops mutant, revealing the presence of additional CCaMK targets mediating LR formation. Constitutive and ectopic expression of NIN under the ubiquitin promoter resulted in a significant increase in LR number. We compared the responsiveness of two Rosaceae that have either retained NIN (Dryas drummondii) or lost it (Fragaria vesca) to stimulation with the constitutively active variant CCaMK1−314. Intriguingly, CCaMK1−314 was able to increase LR formation in Dryas but not in Fragaria, pointing to consequences of the evolutionary loss of NIN on root architecture. Taken together our data provide evidence for NIN as a molecular link between symbiosis-signaling and LR formation. Non-inoculated nsp1 and nsp2 mutant plants as well as HRLC of these mutants exhibited increased LR densities that were no further increased by expression of CCaMK1-314. We propose a model in which LR density is balanced by the activation of NIN expression by SymRK and CCaMK and the LR suppressing activity of NSP1 and NSP2.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 22, 2025 9:42 AM
|
Legume Nod Factor Receptors (NFRs) are LysM-Receptor-Like Kinases (LysM-RLKs) that initiate host nodulation signaling upon perception of Nod Factors produced by rhizobia. Structural and functional characterization of NFRs from the model legumes Medicago truncatula and Lotus japonicus have unravelled crucial domains/motifs that are indispensable for nodulation signaling. Due to a partial homology of NFRs with that of LysM-RLKs in cereals, the identified domains/motifs have helped in the engineering of these receptors in non-nodulating crop plants like barley.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 21, 2025 5:22 PM
|
Phosphorus (P) is a primary mineral nutrient essential for the growth and productivity of many crop plants. Although abundant in nature, its bioavailability is limited due to the prevalence of insoluble forms. An alternative for meeting agricultural P demand is the application of P-solubilizing microorganisms (PSMs), which mobilize it. Although progress has been made in the study of PSMs, knowledge gaps still exist regarding their role in sustainable agriculture. Therefore, this review examines the barriers to P acquisition in low-solubility soils and highlights recent advances in understanding the mechanisms of P solubilization mediated by plant-associated bacteria and fungi. The molecular strategies involved in the uptake and transport of P from soil in plants are also analyzed. Bacteria from genera such as Bacillus, Pseudomonas, and Streptomyces, as well as fungi including arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, Aspergillus spp., and Penicillium spp., employ various approaches to solubilize P, leading to improved plant nutrition. These mechanisms, which include the production of organic acids, cation chelation, proton exudation, and phosphatase activity, can be inferred from experimental approaches or genome mining strategies. The role of PSMs as plant growth promoters and enhancers of plant nutrition across diverse environmental conditions are also discussed. Finally, we propose the integration of PSM consortia as multifunctional bioinoculants to promote sustainable agricultural practices.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 21, 2025 5:20 PM
|
The advent of endosymbiosis underlies evolutionary innovation and ecosystem function. However, whether free-living partners tend to benefit or exploit each other during incipient endosymbiosis remains a dilemma. Rhizobia bacteria are plant endosymbionts capable of initiating root nodules and fixing nitrogen due to genes carried on mobile genetic elements (MGEs) such as the symbiosis island (SI). We conjugated marked SIs into the genomes of nonnodulating strains, which was sufficient to generate de novo root nodule-forming endosymbionts. Most novel endosymbionts originated as commensals that incurred no detectable costs to host plants, in contrast to predictions of exploitation. In fact, a third of endosymbionts originated as nitrogen fixing mutualists. Consistent with phylogenetic limits to transfer of MGE function, novel endosymbionts derived from more closely related SI donor and recipient strains showed greater nitrogen fixation. However, we did not detect phylogenetic limits to SI transmission, which could reflect selfish selection for generalized horizontal transfer of this MGE. In fact, the SI was able to displace other genomic elements residing at its characteristic tRNA gene insertion site. We thus provide genetic, genomic, and functional evidence of how MGEs can potentiate and constrain major evolutionary transitions to expand bacterial niches, with cascading effects on host organisms.

|
Scooped by
Jean-Michel Ané
December 19, 2025 4:26 PM
|
The genetic basis for the adaptive advantages of polyploids over their diploid relatives remains poorly understood. To address this knowledge gap, we generate a haplotype-resolved autotetraploid alfalfa (Medicago sativa subsp. sativa) genome and construct a super-pangenome from 13 genomes across seven Medicago taxa. We discover substantial gene content variation in alfalfa, with only 20.1% of genes present on all four haplotypes. Within this group, 53.3% are core genes conserved across the Medicago genus, which we term ‘tetra-copy core genes’. We find these genes are significantly enriched in climate-adaptation-associated genes (1.60-fold) and stress-responsive differentially expressed genes (1.61-fold). Paradoxically, they also carry a high genetic burden, with 80.1% of deleterious variants located in coding regions. Indeed, overexpressing a representative tetra-copy core gene, the glycine decarboxylase (MsGDC), improves both biomass and nitrogen use efficiency, despite its high genetic burden. Our study reveals the trade-off between adaptation and evolutionary constraints mediated by tetra-copy core genes, facilitating polyploid genetics and alfalfa breeding.
|






 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...



















Awesome paper... I love it.