Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 9, 2022 3:37 AM
|
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a progressive, fatal neuromuscular disorder typically diagnosed between 4 and 5 years of age. DMD currently has five FDA approved therapies, which has led t

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 2, 2022 2:14 AM
|
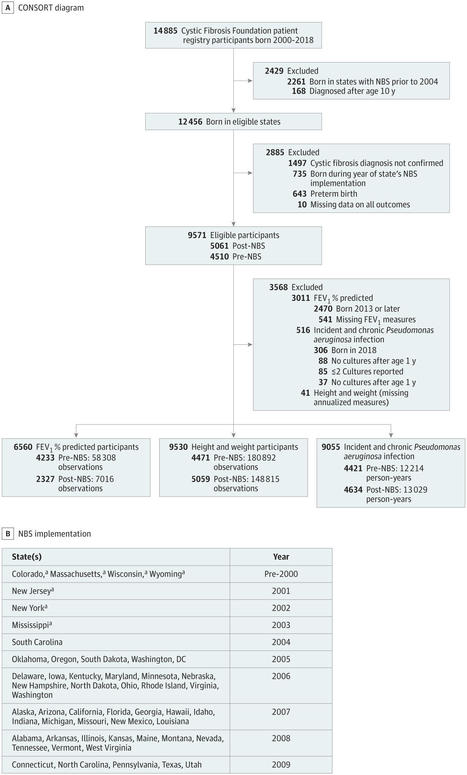
This cohort study investigates the association of newborn screening for cystic fibrosis with child outcomes up to age 10 years in the US.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 1, 2022 11:28 AM
|
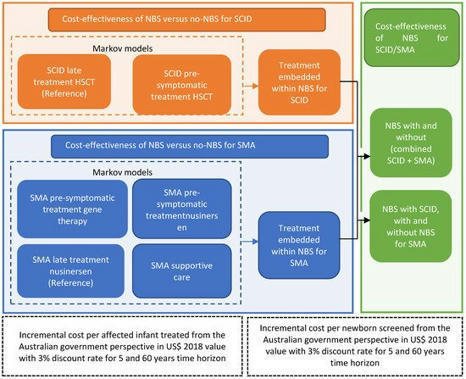
Evidence on the cost-effectiveness of newborn screening (NBS) for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) in the Australian policy context is lacking. In this study, a pilot population-based screening program in Australia was used to model the cost-effectiveness of NBS for SCID from the government perspective. Markov cohort simulations were nested within a decision analytic model to compare the costs and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) over a time horizon of 5 and 60 years for two strategies: (1) NBS for SCID and treat with early hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT); (2) no NBS for SCID and treat with late HSCT. Incremental costs were compared to incremental QALYs to calculate the incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICER). Sensitivity analyses were performed to assess the model uncertainty and identify key parameters impacting on the ICER. In the long-term over 60 years, universal NBS for SCID would gain 10 QALYs at a cost of US $0.3 million, resulting in an ICER of US$33,600/QALY. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis showed that more than half of the simulated ICERs were considered cost-effective against the common willingness-to-pay threshold of A$50,000/QALY (US$35,000/QALY). In the Australian context, screening for SCID should be introduced into the current NBS program from both clinical and economic perspectives.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 1, 2022 11:27 AM
|
Pompe disease was added to the United States recommended uniform screening panel in 2015 to avoid diagnostic delay and implement prompt treatment, specifically for those with infantile-onset Pompe disease (IOPD). However, most newborns with abnormal newborn screening (NBS) for Pompe disease have late-onset Pompe disease (LOPD). An early diagnosis of LOPD raises the question of when symptoms will arise which is challenging for parents, patients, and providers managing an LOPD diagnosis. This study aimed to characterize mothers’ experiences of their child’s LOPD diagnosis and medical monitoring. A qualitative descriptive approach was chosen to gain an in-depth understanding of parental experiences. Eight mothers were interviewed about their experiences with positive NBS and diagnosis, experiences with living with the diagnosis, and experiences with medical monitoring. Interview transcripts were analyzed through conventional content analysis. Negative emotions like fear were more frequent with communication of NBS results. Participants expressed uncertainty surrounding age of symptom onset and the future. The medical monitoring experience increased worry but participants expressed that being vigilant with management reassured them. Parental emotions shifted to thankfulness and reassurance with time and education. These findings can provide guidance to providers about the psychosocial implications of receiving positive NBS results and an LOPD diagnosis.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 1, 2022 11:23 AM
|
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) and severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) are rare, inherited genetic disorders with severe mortality and morbidity. The benefits of early diagnosis and initiation of treatment are now increasingly recognized, with the most benefits in patients treated prior to symptom onset. The aim of the economic evaluation was to investigate the costs and outcomes associated with the introduction of universal newborn screening (NBS) for SCID and SMA, by generating measures of cost-effectiveness and budget impact. A stepwise approach to the cost-effectiveness analyses by decision analytical models nested with Markov simulations for SMA and SCID were conducted from the government perspective. Over a 60-year time horizon, screening every newborn in the population and treating diagnosed SCID by early hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and SMA by gene therapy, would result in 95 QALYs gained per 100,000 newborns, and result in cost savings of USD 8.6 million. Sensitivity analysis indicates 97% of simulated results are considered cost-effective against commonly used willingness-to-pay thresholds. The introduction of combined NBS for SCID and SMA is good value for money from the long-term clinical and economic perspectives, representing a cost saving to governments in the long-term, as well as improving and saving lives.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 1, 2022 11:20 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 23, 2022 7:26 AM
|
Cystic fibrosis (CF) newborn screening (NBS) was universally adopted in 2009 in the United States. Variations in NBS practices between states may impact the timing of diagnosis and intervention. Quantitative metrics can provide insight into NBS programs (NBSP), but the nuances cannot be elucidated without additional feedback from programs. This study was designed to determine facilitators and barriers to timely diagnosis and intervention following NBS for CF. The median age at the first CF event for infants with CF within each state was used to define early and late states (n = 15 per group); multiple CF centers were invited in states with more than two CF centers. Thirty states were eligible, and 61 NBSP and CF centers were invited to participate in structured interviews to determine facilitators and barriers. Once saturation of themes was reached, no other interviews were conducted. Forty-five interviews were conducted (n = 16 early CF center, n = 12 late CF center, n = 11 early NBSP, and n = 6 late NBSP). Most interviewees reported good communication between CF centers and NBSP. Communication between primary care providers (PCPs) and families was identified as a challenge, leading to delays in referral and subsequent diagnosis. The misperception of low clinical risk in infants from racial and ethnic minority groups was a barrier to early diagnostic evaluation for all groups. NBSP and CF centers have strong relationships. Early diagnosis may be facilitated through more engagement with PCPs. Quality improvement initiatives should focus on continuing strong partnerships between CF centers and NBS programs, improving education, communication strategies, and partnerships with PCPs, and improving CF NBS timeliness and accuracy.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 16, 2022 4:34 AM
|
Bloodspot screening in newborns is an exemplary public health intervention as it is essential secondary prevention with proven efficacy and benefit fo …

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 16, 2022 10:14 AM
|
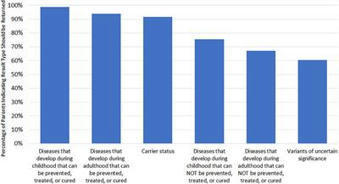
Introduction: With increasing utility and decreasing cost of genomic sequencing, augmentation of standard newborn screening (NBS) programs with newborn genomic sequencing (nGS) has been proposed. Before nGS can be integrated into newborn screening, parents’ perspectives must be better understood.Objective: Using data from surveys administered to parents of healthy newborns who were enrolled in the BabySeq Project, a randomized clinical trial of nGS alongside NBS, this paper reports parents’ attitudes regarding population-based NBS and nGS assessed 3 months after results disclosure.Methods: Parental attitudes regarding whether all newborns should receive, and whether informed consent should be required for, NBS and nGS, as well as whether nGS should be mandated were assessed using 5-point scales from strongly disagree (=1) to strongly agree (=5). Parents’ interest in receiving types of results from nGS was assessed on a 5-point scale from not at all interested (=1) to very interested (=5). Survey responses were analyzed using Fisher’s exact tests, paired t-tests, and repeated measures ANOVA.Results: At 3 months post-disclosure, 248 parents of 174 healthy newborns submitted a survey. Support for every newborn receiving standard NBS (mean 4.67) was higher than that for every newborn receiving nGS (mean 3.60; p < 0.001). Support for required informed consent for NBS (mean 3.44) was lower than that for nGS (mean 4.27, p < 0.001). Parents’ attitudes toward NBS and nGS were no

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 10, 2022 9:49 AM
|
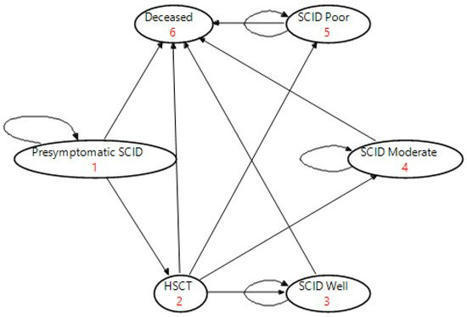
Screening for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) was added to the New Zealand national newborn screening programme in December 2017. Documentation pertaining to the application to add SCID to the panel and screening results over the first three years were reviewed. Screening evaluation metrics were shown to differ according to site of collection (babies in a neonatal intensive care unit vs. the community), definition of a positive test (out-of-range result vs. result leading to a further action on baby), and screening target/case definition (primary SCID vs. non-SCID T-cell lymphopenia). Our experience demonstrates both the value of close clinical involvement during the implementation phase of SCID screening and that the use of standard definitions will facilitate international comparison.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 9, 2022 4:43 AM
|
Although individual rare disorders are uncommon, it is estimated that, together, 6000+ known rare diseases affect more than 30 million people in Europe, and present a substantial public health burden. Together with the psychosocial burden on affected families, rare disorders frequently, if untreated, result in a low quality of life, disability and even premature death. Newborn screening (NBS) has the potential to detect a number of rare conditions in asymptomatic children, providing the possibility of early treatment and a significantly improved long-term outcome. Despite these clear benefits, the availability and conduct of NBS programmes varies considerably across Europe and, with the increasing potential of genomic testing, it is likely that these differences may become even more pronounced. To help improve the equity of provision of NBS and ensure that all children can be offered high-quality screening regardless of race, nationality and socio-economic status, a technical meeting, endorsed by the Slovenian Presidency of the Council of the European Union, was held in October 2021. In this article, we present experiences from individual EU countries, stakeholder initiatives and the meeting’s final conclusions, which can help countries attempting to establish new NBS programmes or expand existing provision.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 3, 2022 8:10 AM
|
INESSS, Institut national d'excellence en santé et services sociaux

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
April 19, 2022 3:14 AM
|
The development and continuous optimization of newborn screening (NBS) programs remains an important and challenging task due to the low prevalence of screened diseases and high sensitivit
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 3, 2022 4:06 AM
|
Newborn screening (NBS) for Pompe disease (PD) was added to the Recommended Uniform Screening Panel (RUSP) in the United States in 2015 because there was compelling evidence of health benefits fo

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 1, 2022 11:31 AM
|
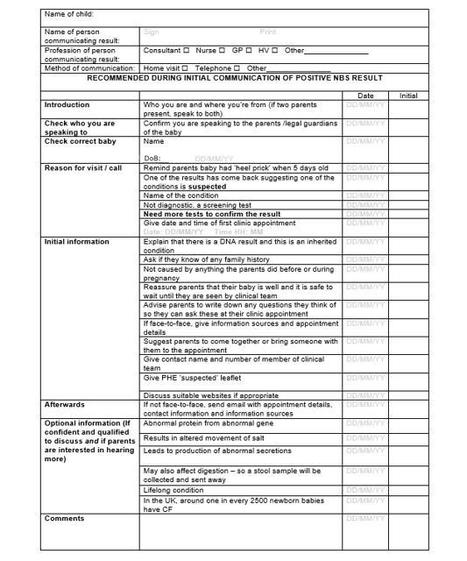
Background: Each year in England, almost 10,000 parents are informed of their child’s positive newborn bloodspot screening (NBS) results. This occurs approximately 2 to 8 weeks after birth depending on the condition. Communication of positive NBS results is a subtle and skillful task, demanding thought, preparation, and evidence to minimize potentially harmful negative sequelae. Evidence of variability in the content and the way the result is currently communicated has the potential to lead to increased parental anxiety and distress.
Objective: This study focused on the development of co-designed interventions to improve the experiences of parents receiving positive NBS results for their children and enhance communication between health care professionals and parents.
Conclusions: Parents and health professionals were able to successfully work together to identify priorities and develop co-designed interventions to improve communication of positive NBS results to parents. The resulting co-designed interventions address communication at different stages of the communication pathway to improve the experiences of parents receiving positive NBS results for their children.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 1, 2022 11:27 AM
|
Newborn screening for treatable disorders is one of the great public health success stories of the twentieth century worldwide. This commentary examines the potential use of a new technology, next generation sequencing, in newborn screening through the lens of the Wilson and Jungner criteria. Each of the ten criteria are examined to show how they might be applied by programmes using genomic sequencing as a screening tool. While there are obvious advantages to a method that can examine all disease-causing genes in a single assay at an ever-diminishing cost, implementation of genomic sequencing at scale presents numerous challenges, some which are intrinsic to screening for rare disease and some specifically linked to genomics-led screening. In addition to questions specific to routine screening considerations, the ethical, communication, data management, legal, and social implications of genomic screening programmes require consideration.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 1, 2022 11:25 AM
|
Progress in newborn screening (NBS) has been driven for 60 years by developments in science and technology, growing consumer advocacy, the actions of providers involved in the care of rare disease patients, and by federal and State government funding and policies. With the current explosion of clinical trials of treatments for rare diseases, the pressure for expansion has grown, and concerns about the capacity for improvement and growth are being expressed. Genome and exome sequencing (GS/ES) have now opened more opportunities for early identification and disease prevention at all points in the lifespan. The greatest challenge facing NBS stems from the conditions most amenable to screening, and new treatment development is that we are screening for rare genetic diseases. In addition, understanding the spectrum of severity requires vast amounts of population and genomic data. We propose recommendations on improving the NBS system and addressing specific demands to grow its capacity by: better defining the criteria by which screening targets are established; financing the NBS system’s responsiveness to opportunities for expansion, including engagement and funding from stakeholders; creating a national quality assurance, data, IT, and communications infrastructure; and improving intra-governmental communications. While our recommendations may be specific to the United States, the underlying issues should be considered when working to improve NBS programs globally.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 1, 2022 11:22 AM
|
Health and Social Care Delivery Research Volume: 10, Issue: 19, Published in July 2022

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 28, 2022 10:32 AM
|
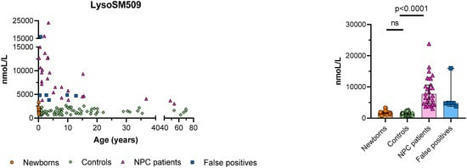
Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) is a lysosomal disorder caused by impaired cholesterol metabolism. Levels of lysosphingomyelin 509 (LysoSM509) have been shown elevated in dried blood spots (DBS) of NPC and acid sphingomyelinase deficiency patients. In this study, we report our experience using a two-tier approach (1st tier is the quantification of lysoSM509 by ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry followed by the 2nd tier with next-generation sequencing of the NPC1 and NPC2 genes). DBS samples from 450 suspected patients were received by the NPC Brazil network. Of these, 33 samples had elevated levels of lysoSM509, and in 25 of them, variants classified as pathogenic, likely pathogenic, or of unknown significance were identified in the NPC1 or NPC2 genes by next-generation sequencing. The quantification of lysoSM509 in DBS as a first-tier test for the diagnosis of NPC followed by molecular analysis of the NPC1 and NPC2 genes almost doubled the detection rate when compared to the performance of chitotriosidase activity as a first-tier biomarker, and it could likely be increased with the addition of a third tier with MLPA of the two genes involved. This strategy seems suitable for the neonatal screening (NBS) of NPC if this disease is eventually adopted by NBS programs.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 22, 2022 3:50 AM
|
The authors discuss the need for newborn screening in the context of the migration policy of the European Union, and particularly, the European Asylum, Migration and Integration Fund.The author

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 23, 2022 11:09 AM
|
With the expansion of newborn screening conditions globally and the increased use of genomic technologies for early detection, there is a need for ethically nuanced policies to guide the future integration of ever-more comprehensive genomics into population-based newborn screening programs. In the current paper, we consider the lived experiences of 169 family caregivers caring for 77 children with NBS-related conditions to identify lessons learned that can inform policy and practice related to population-based newborn screening using genomic technologies. Based on caregiver narratives obtained through in-depth interviews, we identify themes characterizing these families’ diagnostic odyssey continuum, which fall within two domains: (1) medical management implications of a child diagnosed with an NBS-related condition and (2) psychological implications of a child diagnosed with an NBS-related condition. For Domain 1, family caregivers’ experiences point to the need for educational resources for both health care professionals that serve children with NBS-related conditions and their families; empowerment programs for family caregivers; training for providers in patient-centered communication; and access to multi-disciplinary specialists. For Domain 2, caregivers’ experiences suggest a need for access to continuous, long-term counseling resources; patient navigator resources; and peer support programs. These lessons learned can inform policy recommendations for the benefit of the child, the family, the healthcare system, and society.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 11, 2022 8:23 AM
|
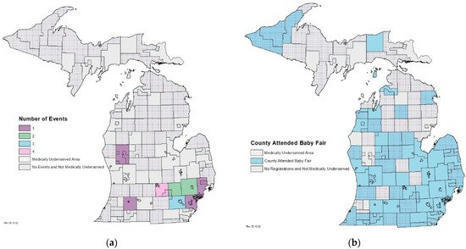
Educating parents about the newborn screening (NBS) process is critical in ensuring that families are aware of their child’s NBS, which could contribute to better outcomes for the baby and experiences for the family. Successful education efforts result in expecting parents understanding the importance of NBS, feeling comfortable with the NBS process, and being aware of their choices after NBS is complete. Educating parents prenatally is challenging for many NBS programs for a variety of reasons. The COVID-19 pandemic added additional barriers to NBS programs’ ability to educate parents prenatally about NBS. By initiating a department-wide partnership among other programs with a similar target audience, Michigan’s NBS Program was able to host a virtual baby fair. Since the inaugural event, Michigan’s NBS Program has hosted seven virtual fairs with 15 participating programs. A total of 692 participants registered for the baby fair and received a resource packet, over 157 participants joined one of the live presentations, and 211 have viewed the YouTube videos of recorded fairs. Virtual baby fairs are a cost-effective and convenient approach to education that could be implemented in any NBS program to educate parents prenatally about NBS.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 9, 2022 4:52 AM
|
Cystic fibrosis (CF) has been included within the UK national newborn screening programme since 2007. The approach uses measures of immunoreactive trypsin (IRT) in dried blood spot samples obtained at day 5 of life. Samples which reveal IRT results >99.5th centile go on to be tested for a limited panel of CF mutations. While the programme works well and achieves a high level of sensitivity and specificity, it relies upon repeat testing in some cases and identifies probable carriers, both potentially provoking parental anxiety. In addition, the limited CF mutation panel may not fully reflect the ethnic diversity within the UK population. The use of wider genomic screening, made possible by next-generation sequencing to replace more limited panels, can be used to avoid these shortcomings. However, the way in which this approach is employed can either be designed to maximise specificity by limiting reporting to combinations of known pathogenic mutations or can maximise sensitivity by also reporting combinations of pathogenic mutations together with variants of uncertain significance. The latter approach also increases the number of Cystic Fibrosis Screen-Positive Inconclusive Diagnosis (CFSPID) designations reported, resulting in uncertainty for parents. To help consider the design of the programme, a dialogue was commissioned by the UK National Screening Committee (UKNSC) to elicit the views of members of the public without direct experience of CF, to determine if there was a preference for maximising the sensitivity or the specificity of CF screening. The participants initially expressed a clear preference to maximise sensitivity and avoid missing CF cases, but after time to reflect and consider the implications of their choice, a number changed their views so as to tolerate some missed cases if this resulted in greater certainty of outcome; this became the majority view. It is proposed that it may be a generalisable finding that the public, when facing whole-population screening programmes, may require significant time and information to inform and make their choices and may attach great importance to clarity and certainty of outcome in the screening process.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 5, 2022 4:20 AM
|
Molecular diagnostics and therapies play a central role in an era of precision medicine, with the promise of more accurate diagnoses and more effective treatments. Universal newborn screening (NBS) identifies those health conditions that must be treated in early life and before clinical symptoms become apparent, to maximize effectiveness, prevent morbidity, and reduce or eliminate mortality. However, enthusiasm about NBS as the logical platform for early identification is tempered by the realization that NBS under public health authority exists in a complex ecology in which technology and medicine intersect with politics, ethics, advocacy, and resource constraints—a classic translational challenge that is exacerbated when considering the possible introduction of genome sequencing and molecular therapies in NBS. Substantial change is inevitable if the current model of NBS can be prepared for an envisioned future of greatly expanded molecular diagnostics and therapies. A window of opportunity for modernization now exists, but what changes are needed? The purpose of this commentary is to identify five major initiatives to stimulate focused discussion on how modernization might be achieved: (1) build systems for more rapid collection and integration of extant data relevant to NBS; (2) establish a national network of NBS research centers to design and conduct prospective research studies addressing critical NBS questions; (3) create a network of regional NBS laboratories to expedite state implementation of new methodologies or screening for newly recommended conditions; (4) establish a new stream of federal funding to provide financial support for states and incentivize national harmonization; and (5) integrate solutions in a way that is strategic and effective. Some aspects of these recommendations suggest that radical policy changes are needed to implement molecular testing in NBS and take advantage of emerging molecular therapies. I focus on recommendations for modernizing NBS in the US, some of which may be applicable in other countries.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
May 2, 2022 6:21 AM
|
Implementation of newborn screening (NBS) programs for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) have advanced diagnosis and management of affected infa…
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...