Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
April 15, 2022 8:13 AM
|
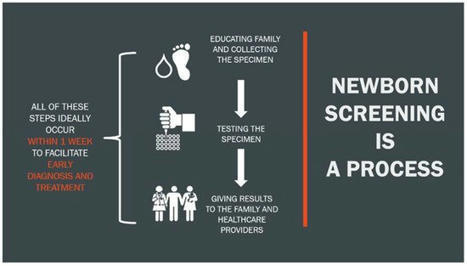
Newborn screening (NBS) is an essential public health service that performs screening to identify those newborns at increased risk for a panel of disorders, most of which are genetic. The goal of screening is to link those newborns at the highest risk to timely intervention and potentially life-saving treatment. The global COVID-19 pandemic led to disruptions within the United States public health system, revealing implications for the continuity of newborn screening laboratories and follow-up operations. The impacts of COVID-19 across different states at various time points meant that NBS programs impacted by the pandemic later could benefit from the immediate experiences of the earlier impacted programs. This article will review the collection, analysis, and dissemination of information during the COVID-19 pandemic facilitated by a national, centralized technical assistance and resource center for NBS programs.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
April 13, 2022 8:17 AM
|
Newborn screening (NBS) programmes are considered to be one of the most successful secondary prevention measures in childhood to prevent or reduce morbidity and/or mortality via early disease identification and subsequent initiation of therapy. However, while many rare diseases can now be detected at an early stage using appropriate diagnostics, the introduction of a new target disease requires a detailed analysis of the entire screening process, including a robust scientific background, analytics, information technology, and logistics. In addition, ethics, financing, and the required medical measures need to be considered to allow the benefits of screening to be evaluated at a higher level than its potential harm. Infantile nephropathic cystinosis (INC) is a very rare lysosomal metabolic disorder. With the introduction of cysteamine therapy in the early 1980s and the possibility of renal replacement therapy in infancy, patients with cystinosis can now reach adulthood. Early diagnosis of cystinosis remains important as this enables initiation of cysteamine at the earliest opportunity to support renal and patient survival. Using molecular technologies, the feasibility of screening for cystinosis has been demonstrated in a pilot project. This review aims to provide insight into NBS and discuss its importance for nephropathic cystinosis using molecular technologies.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
April 1, 2022 7:55 AM
|
Background & Objectives This study aims to explore and elucidate parents’ experience of newborn screening [NBS], with the overarching goal of identifying desiderata for the development of informatics-based educational and health management resources. Methods We conducted four focus groups and four one-on-one qualitative interviews with a total of 35 participants between March and September 2020. Participants were grouped into three types: parents who had received true positive newborn screening results; parents who had received false positive results; and soon-to-be parents who had no direct experience of the screening process. Interview data were subjected to analysis using an inductive, constant comparison approach. Results Results are divided into five sections: (1) experiences related to the process of receiving NBS results and prior knowledge of the NBS program; (2) approaches to the management of a child’s medical data; (3) sources of additional informational and emotional support; (4) barriers faced by parents navigating the health system; and (5) recommendations and suggestions for new parents experiencing the NBS process. Conclusion Our analysis revealed a wide range of experiences of, and attitudes towards the newborn screening program and the wider newborn screening system. While parents’ view of the screening process was – on the whole – positive, some participants reported experiencing substantial frustration, particularly related to how results are initially communicated and difficulties in accessing reliable, timely information. This frustration with current information management and education resources indicates a role for informatics-based approaches in addressing parents’ information needs.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 28, 2022 7:31 AM
|
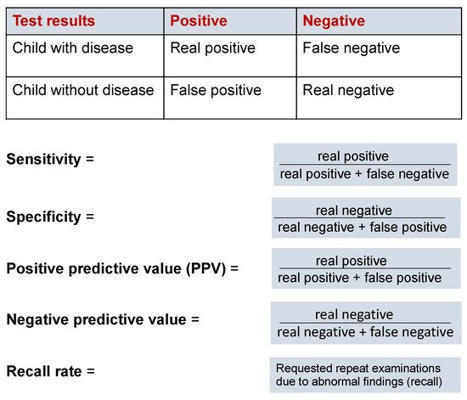
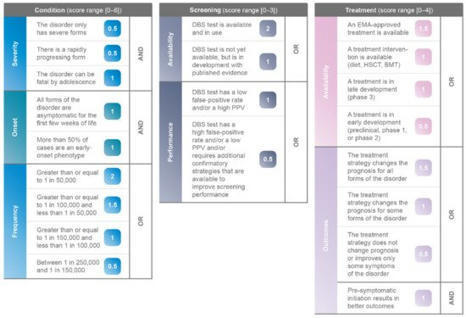
Newborn screening (NBS) programmes are essential in the diagnosis of inherited metabolic diseases (IMDs) and for access to disease modifying treatment. Most European countries follow the World Health Organisation (WHO) criteria to determine which disorders are appropriate for screening at birth; however, these criteria are interpreted and implemented by individual countries differently, creating disparities. Advances in research and diagnostics, together with the promise of new treatments, offer new possibilities to accelerate the expansion of evidence-based screening programmes. A novel and robust algorithm was built to objectively assess and prioritise IMDs for inclusion in NBS programmes. The Wilson and Jungner classic screening principles were used as a foundation to develop individual and measurable criteria. The proposed algorithm is a point-based system structured upon three pillars: condition, screening, and treatment. The algorithm was tested by applying the six IMDs currently approved in the United Kingdom NBS programme. The algorithm generates a weight-based score that could be used as the first step in the complex process of evaluating disorders for inclusion on NBS programmes. By prioritising disorders to be further evaluated, individual countries are able to assess the economic, societal and political aspects of a potential screening programme.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 21, 2022 7:44 AM
|
Introduction/Aims
Creatine kinase-MM (CK-MM) is a marker of skeletal muscle damage. Detection of elevated levels of CK-MM in newborns can enable an early suspicion of the diagnosis of Duchenn

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 18, 2022 2:25 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 14, 2022 6:48 AM
|
Although the communication pathways of Newborn Bloodspot Screening (NBS) are a delicate task, these pathways vary across different conditions and are often not evidence-based. The ReSPoND interventions were co-designed by healthcare professionals alongside parents who had received a positive NBS result for their child. To calculate the cost of these co-designed strategies and the existing communication pathways, we interviewed 71 members of the clinical and laboratory staff of the 13 English NBS laboratories in the English National Health Service. Therefore, a scenario analysis was used to compare the cost of the existing communication pathways to the co-designed strategies delivered by (i) home-visits and (ii) telecommunications. On average, the existing communication pathway cost £447.08 per infant (range: £237.12 to £628.51) or £234,872.75 (£3635.99 to £1,932,986.23) nationally. Implementing the new interventions relying on home-visits exclusively would cost on average £521.62 (£312.84 to £646.39) per infant and £297,816.03 (£4506.37 to £2,550,284.64) nationally, or £447.19 (£235.79 to £552.03) and £231,342.40 (£3923.7 to £1,922,192.22) if implemented via teleconsultations, respectively. The new strategies delivered are not likely to require additional resources compared with current practice. Further research is needed to investigate whether this investment represents good value for money for the NHS budget.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 3, 2022 9:54 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 1, 2022 1:33 AM
|
This study assesses the benefits and challenges of using genomics in Newborn Screening Programs (NBS) from the perspectives of State program officials. This project aims to help programs develop policies that will aid in the integration of genomic technology. Discussion groups were conducted with the NBS Program and Laboratory Directors in the seven HRSA Regional Genomics Collaboratives (August 2014–March 2016). The discussion groups addressed expected uses of genomics, potential benefits, and challenges of integrating genomic technology, and educational needs for parents and other NBS stakeholders: Twelve focus groups were conducted, which included participants from over 40 state programs. Benefits of incorporating genomics included improving screening modalities, supporting diagnostic procedures, and screening for a wider spectrum of disorders. Challenges included the costs of genomics, the ability to educate parents and health care providers about results, and the potential negative psychosocial impact of genomic information. Attempts to address the challenges of integrating genomics must focus on preserving the child welfare goals of NBS programs. Health departments will need to explore how genomics could be used to enhance programs while maintaining universal access to screening.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2022 2:49 AM
|
An open-access, peer-reviewed, international journal in the field of precision medicine. Articles in the journal present genomic and molecular analyses of individuals or cohorts alongside their clinical presentations and phenotypic information.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 24, 2022 4:58 AM
|
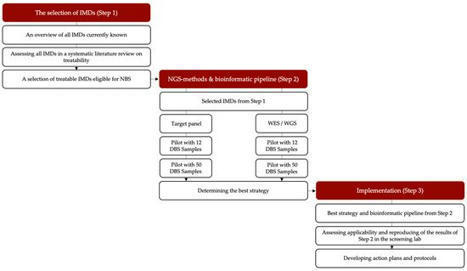
Newborn screening (NBS) aims to identify neonates with severe conditions for whom immediate treatment is required. Currently, a biochemistry-first approach is used to identify these disorders, which are predominantly inherited meta1bolic disorders (IMD). Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is expected to have some advantages over the current approach, for example the ability to detect IMDs that meet all screening criteria but lack an identifiable biochemical footprint. We have now designed a technical study to explore the use of NGS techniques as a first-tier approach in NBS. Here, we describe the aim and set-up of the NGS-first for the NBS (NGSf4NBS) project, which will proceed in three steps. In Step 1, we will identify IMDs eligible for NGS-first testing, based on treatability. In Step 2, we will investigate the feasibility, limitations and comparability of different technical NGS approaches and analysis workflows for NBS, eventually aiming to develop a rapid NGS-based workflow. Finally, in Step 3, we will prepare for the incorporation of this workflow into the existing Dutch NBS program and propose a protocol for referral of a child after a positive NGS test result. The results of this study will be the basis for an additional analytical route within NBS that will be further studied for its applicability within the NBS program, e.g., regarding the ethical, legal, financial and social implications.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 23, 2022 9:20 AM
|
Background Newborn screening (NBS) has been implemented for neonatal inborn disorders using various technology platforms, but false-positive and false-negative results are still common. In addition, target diseases of NBS are limited by suitable biomarkers. Here we sought to assess the feasibility of further improving the screening using next-generation sequencing technology. Methods We designed a newborn genetic sequencing (NBGS) panel based on multiplex PCR and next generation sequencing to analyze 134 genes of 74 inborn disorders, that were validated in 287 samples with previously known mutations. A retrospective cohort of 4986 newborns was analyzed and compared with the biochemical results to evaluate the performance of this panel. Results The accuracy of the panel was 99.65% with all samples, and 154 mutations from 287 samples were 100% detected. In 4986 newborns, a total of 113 newborns were detected with biallelic or hemizygous mutations, of which 36 newborns were positive for the same disorder by both NBGS and conventional NBS (C-NBS) and 77 individuals were NBGS positive/C-NBS negative. Importantly, 4 of the 77 newborns were diagnosed currently including 1 newborn with methylmalonic acidemia, 1 newborn with primary systemic carnitine deficiency and 2 newborns with Wilson’s disease. A total of 1326 newborns were found to be carriers with an overall carrier rate of 26.6%. Conclusion Analysis based on next generation sequencing could effectively identify neonates affected with more congenital disorders. Combined with C-NBS, this approach may improve the early and accurate identification of neonates with inborn disorders. Our study lays the foundation for prospective studies and for implementing NGS-based analysis in NBS.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 14, 2022 11:03 AM
|
Thoroughly phenotype children with late-onset Pompe disease (LOPD) diagnosed via newborn screening (NBS) to provide guidance for long-term follow up.T…
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
April 14, 2022 6:59 AM
|
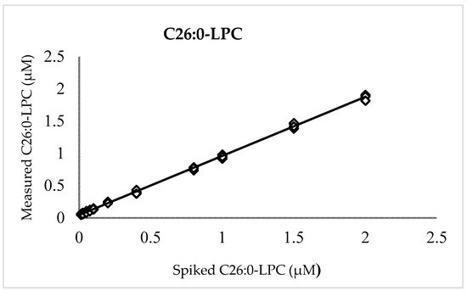
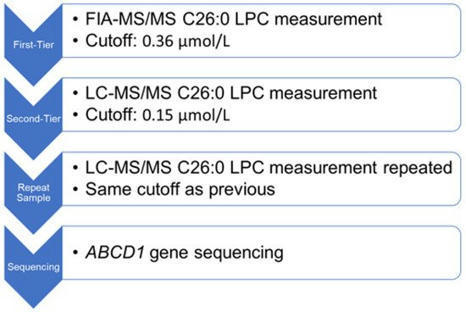
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is a genetic disorder caused by pathogenic variants in the ATP-binding cassette subfamily D member 1 gene (ABCD1) that encodes the adrenoleukodystrophy protein (ALDP). Defects in ALDP result in elevated cerotic acid, and lead to C26:0-lysophosphatidylcholine (C26:0-LPC) accumulation, which is the primary biomarker used in newborn screening (NBS) for X-ALD. C26:0-LPC levels were measured in dried blood spot (DBS) NBS specimens using a flow injection analysis (FIA) coupled with electrospray ionization (ESI) tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) performed in negative ion mode. The method was validated by assessing and confirming linearity, accuracy, and precision. We have also established C26:0-LPC cutoff values that identify newborns at risk for X-ALD. The mean concentration of C26:0-LPC in 5881 de-identified residual routine NBS specimens was 0.07 ± 0.02 µM (mean + 1 standard deviation (SD)). All tested true X-ALD positive and negative samples were correctly identified based on C26:0-LPC cutoff concentrations for borderline between 0.15 µM and 0.22 µM (mean + 4 SD) and presumptive screening positive at ≥0.23 µM (mean + 8 SD). The presented FIA method shortens analysis run-time to 1.7 min, while maintaining the previously established advantage of utilizing negative mode MS to eliminate isobaric interferences that could lead to screening false positives.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
April 5, 2022 7:31 AM
|
Inborn errors of metabolism (IEMs) are rare hereditary or acquired disorders resulting from an enzymatic deformity in biochemical and metabolic pathways influencing proteins, fats, carbohydrate metabolism, or hampered some organelle function. Even though individual IEMs are uncommon, together, they represent a diverse class of genetic diseases, with new issues and disease mechanisms being portrayed consistently. IEM includes the extraordinary multifaceted nature of the fundamental pathophysiology, biochemical diagnosis, molecular level investigation, and complex therapeutic choices. However, due to the molecular, biochemical, and clinical heterogeneity of IEM, screening alone will not detect and diagnose all illnesses included in newborn screening programs. Early diagnosis prevents the emergence of severe clinical symptoms in the majority of IEM cases, lowering morbidity and death. The appearance of IEM disease can vary from neonates to adult people, with the more serious conditions showing up in juvenile stages along with significant morbidity as well as mortality. Advances in understanding the physiological, biochemical, and molecular etiologies of numerous IEMs by means of modalities, for instance, the latest molecular-genetic technologies, genome engineering knowledge, entire exome sequencing, and metabolomics, have prompted remarkable advancement in detection and treatment in modern times. In this review, we analyze the biochemical basis of IEMs, clinical manifestations, the present status of screening, ongoing advances, and efficiency of diagnosis in treatment for IEMs, along with prospects for further exploration as well as innovation.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 31, 2022 4:22 AM
|
Neonatal screening for congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is based on the measurement of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in whole dried blood samples on…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 23, 2022 8:28 AM
|
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is the most common peroxisomal disorder. It results from pathogenic variants in ABCD1, which encodes the peroxisomal very-long-chain fatty acid transporter, causing a spectrum of neurodegenerative phenotypes. The childhood cerebral form of the disease is particularly devastating. Early diagnosis and intervention improve outcomes. Because newborn screening facilitates identification of at-risk individuals during their asymptomatic period, X-ALD was added to the Pennsylvania newborn screening program in 2017. We analyzed outcomes from the first four years of X-ALD newborn screening, which employed a two-tier approach and reflexive ABCD1 sequencing. There were 51 positive screens with elevated C26:0-lysophosphatidylcholine on second-tier screening. ABCD1 sequencing identified 21 hemizygous males and 24 heterozygous females, and clinical follow up identified four patients with peroxisomal biogenesis disorders. There were two false-positive cases and one false-negative case. Three unscreened individuals, two of whom were symptomatic, were diagnosed following their young siblings’ newborn screening results. Combined with experiences from six other states, this suggests a U.S. incidence of roughly 1 in 10,500, higher than had been previously reported. Many of these infants lack a known family history of X-ALD. Together, these data highlight both the achievements and challenges of newborn screening for X-ALD.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 18, 2022 2:28 AM
|
Medium-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency is the most common disorder of mitochondrial β-oxidation of fatty acids resulting in hypoketotic hypoglycemia, hepatopathy, and often fatal outcome in undiagnosed children. Introduction of tandem mass spectrometry–based newborn screening programs in the late 1990s has significantly reduced morbidity and mortality in MCAD deficiency; however, neonatal death in individuals with early disease manifestation and severe hypoglycemia may still occur. We describe the fatal disease course in eight newborns with MCAD deficiency, aiming to raise awareness for early clinical symptoms and the life-saving treatment, and promote systematic post-mortem protocols for biochemical and genetic testing, necessary for correct diagnosis and counselling of the family if unexpected death occurred in the neonatal period.Conclusion: Early newborn screening and awareness for clinical symptoms is lifesaving in MCAD deficiency, which may present with fatal neonatal crisis. Systematic post-mortem diagnostic protocols are needed for sudden neonatal deaths.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 15, 2022 9:10 AM
|
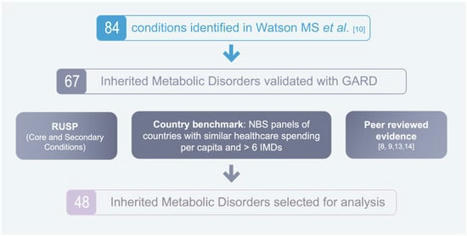
Inherited metabolic disorders (IMDs) are mostly rare, have overlapping symptoms, and can be devastating and progressive. However, in many disorders, early intervention can improve long-term outcomes, and newborn screening (NBS) programmes can reduce caregiver stress in the journey to diagnosis and allow patients to receive early, and potentially pre-symptomatic, treatment. Across Europe there are vast discrepancies in the number of IMDs that are screened for and there is an imminent opportunity to accelerate the expansion of evidence-based screening programmes and reduce the disparities in screening programmes across Europe. A comprehensive list of IMDs was created for analysis. A novel NBS evaluation algorithm, described by Burlina et al. in 2021, was used to assess and prioritise IMDs for inclusion on expanded NBS programmes across Europe. Forty-eight IMDs, of which twenty-one were lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs), were identified and assessed with the novel NBS evaluation algorithm. Thirty-five disorders most strongly fulfil the Wilson and Jungner classic screening principles and should be considered for inclusion in NBS programmes across Europe. The recommended disorders should be evaluated at the national level to assess the economic, societal, and political aspects of potential screening programmes.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 7, 2022 1:26 AM
|
The introduction of massive parallel sequencing has contributed to a decline in sequencing costs. In recent years, whole-exome sequencing (WES) and wh…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 1, 2022 10:01 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 1, 2022 1:32 AM
|
During the COVID-19 pandemic, state newborn screening programs faced challenges to ensure this essential public health program continued to function at a high level. In December 2020, the EveryLife Foundation for Rare Diseases held a workshop to discuss these common challenges and solutions. Newborn screening officials described challenges including short staffing across the entire program, collection and transport of specimens, interrupted follow-up activities, and pilot study recruitment. To address these challenges, state programs implemented a wide variety of solutions to maintain the high standards of newborn screening. To address staffing issues, newborn screening programs, public health laboratories, and hospitals all cross-trained personnel, worked to manage staff stress, and established essential functions. Other solutions included working with courier companies to ensure the timely pick-up of specimen, creating educational materials for hospital staff, and the creation of hybrid recruitment models for pilot studies. Implementing the lessons discussed throughout this paper can help to prepare for the next public health emergencies to ensure that a program that interacts with millions of families every year and saves the lives of thousands of children every year is minimally impacted.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 24, 2022 7:35 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 24, 2022 4:57 AM
|
Newborn screening for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy began in New York in 2013. Prior to this start, there was already significant information on the diagnosis and monitoring of asymptomatic individuals. Methods needed to be developed and validated for the use of dried blood spots. Following its institution in New York, its acceptance as a disorder on the Recommended Uniform Screening occurred. With it has come published recommendations on the surveillance and care of boys detected by newborn screening. There still remain challenges, but it is hoped that with periodic review, they may be overcome.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 14, 2022 11:08 AM
|
Background and objectives Projections that 60 transformative cell and gene therapies could be approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) within 10 years underscore an urgent need to modernize the newborn screening (NBS) system. This study convened expert stakeholders to assess challenges to the NBS system and propose solutions for its modernization.s This study engaged representatives from multiple stakeholder groups to generate potential solutions to challenges facing NBS in the United States. These solutions provide a rich starting point for policy makers and other stakeholders who desire to maximize the impact of new transformative therapies for babies, families, and society.
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...