Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 29, 2023 7:44 AM
|
With over one million deaths per year in the world, suicide is a major public health problem that could be significantly reduced by effective prevention programs. E-health tools are of particular interest for primary prevention as they can address a broad population including people unaware of their own risk and provide information and help without the fear of stigma. Our main objective was to define the overall characteristics of an e-health tool for suicide primary prevention in the French general population by defining the characteristics of the IT features; the content of the information delivered; the best way to structure it; and how it should be relayed and by whom. The research was carried out through a literature review and a co-construction phase with stakeholders. Four types of strategies may guide the construction of e-health tools for suicide primary prevention: education and awareness, (self-)screening, accessing support, and mental health coping. They should be accessible on different devices to reach the most users, and language and content should be adapted to the target population and to the issue being addressed. Finally, the tool should be consistent with ethical and quality best practices. The e-health tool StopBlues was developed following those recommendations.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 29, 2023 4:10 AM
|
The past decade has seen a dramatic rise in consumer technologies able to monitor
a variety of cardiovascular parameters. Such devices initially recorded markers of
exercise, but now include physiological and health-care focused measurements. The
public are keen to adopt these devices in the belief that they are useful to identify
and monitor cardiovascular disease. Clinicians are therefore often presented with
health app data accompanied by a diverse range of concerns and queries. Herein, we
assess whether these devices are accurate, their outputs validated, and whether they
are suitable for professionals to make management decisions.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 29, 2023 4:07 AM
|
ChatGPT is receiving increasing attention and has a variety of application scenarios in clinical practice. In clinical decision support, ChatGPT has been used to generate accurate differential diagnosis lists, support clinical decision-making, optimize clinical decision support, and provide insights for cancer screening decisions. In addition, ChatGPT has been used for intelligent question-answering to provide reliable information about diseases and medical queries. In terms of medical documentation, ChatGPT has proven effective in generating patient clinical letters, radiology reports, medical notes, and discharge summaries, improving efficiency and accuracy for health care providers. Future research directions include real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, precision medicine and personalized treatment, the role of ChatGPT in telemedicine and remote health care, and integration with existing health care systems. Overall, ChatGPT is a valuable tool that complements the expertise of health care providers and improves clinical decision-making and patient care. However, ChatGPT is a double-edged sword. We need to carefully consider and study the benefits and potential dangers of ChatGPT. In this viewpoint, we discuss recent advances in ChatGPT research in clinical practice and suggest possible risks and challenges of using ChatGPT in clinical practice. It will help guide and support future artificial intelligence research similar to ChatGPT in health.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 26, 2023 8:28 AM
|
Virtual reality therapy - In his debut blog, Steven Parkes considers a trial exploring patient satisfaction and side effects in patients with psychosis.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 26, 2023 2:02 AM
|
Many countries around the world face a shortage of medical personnel, leading to work overload or even burnout. This calls for political and scientific solutions to relieve the medical personnel. The measurement of vital signs in hospitals is still predominately carried out manually with traditional contact-based methods, taking over a substantial share of the medical personnel’s workload. The introduction of contactless methods for vital sign monitoring (e.g., with a camera) has great potential to relieve the medical personnel. This systematic review’s objective is to analyze the state of the art in the field of contactless optical patient diagnosis. This review distinguishes itself from already existing reviews by considering studies that do not only propose the contactless measurement of vital signs but also include an automatic diagnosis of the patient’s condition. This means that the included studies incorporate the physician’s reasoning and evaluation of vital signs into their algorithms, allowing an automated patient diagnosis. The literature screening of two independent reviewers resulted in a total of five eligible studies. The highest number of studies (three) introduce methods for the risk assessment of infectious diseases, one study introduces a method for the risk assessment of cardiovascular diseases, and one study introduces a method for the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea. Overall, high heterogeneity in relevant study parameters is reported among the included studies. The low number of included studies indicates a large research gap and emphasizes the demand for further research on this emerging topic.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 23, 2023 2:15 AM
|
Author summary Though artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms were initially proposed as a means to improve healthcare and promote health equity, recent literature suggests that such algorithms are associated with bias and disparities. Therefore, we outline the various elements of potential bias in the development and implementation of AI algorithms and discuss strategies to mitigate them.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 19, 2023 2:40 AM
|
We estimate the effect of adopting a digital device for performing medical exams at home during telehealth visits. We match visits of adopters and non…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 15, 2023 12:19 PM
|
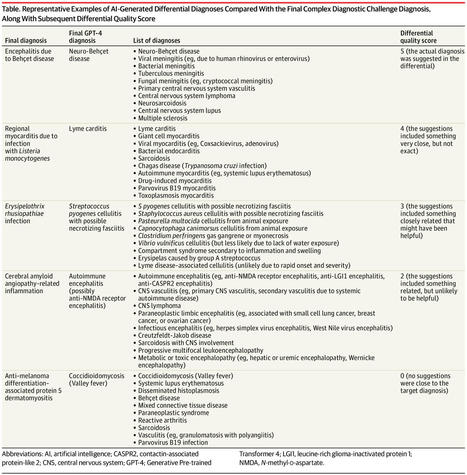
This study assesses the diagnostic accuracy of the Generative Pre-trained Transformer 4 (GPT-4) artificial intelligence (AI) model in a series of challenging cases.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 14, 2023 5:24 AM
|
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, health care providers pivoted to telehealth out of necessity. As policymakers look beyond the pandemic, concerns about telehealth's effects on health care spending and quality persist.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 12, 2023 4:07 AM
|
Computerised CBT youth anxiety depression - Jemma Baker looks at the effectiveness of cCBT for depression and anxiety in adolescents.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 12, 2023 2:52 AM
|
The FDA issued a warning to device maker iRhythm for marketing its product for “high risk” patients and changing its algorithm without permission.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 9, 2023 1:34 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 9, 2023 1:11 AM
|
Background: Digital transformation is currently one of the most influential developments. It is fundamentally changing consumers’ expectations and behaviors, challenging traditional firms, and disrupting numerous markets. Recent discussions in the health care sector tend to assess the influence of technological implications but neglect other factors needed for a holistic view on the digital transformation. This calls for a reevaluation of the current state of digital transformation in health care. Consequently, there is a need for a holistic view on the complex interdependencies of digital transformation in the health care sector.
Objective: This study aimed to examine the effects of digital transformation on the health care sector. This is accomplished by providing a conceptual model of the health care sector under digital transformation.
Conclusions: The conceptual model provides a novel and evidence-based perspective on the interrelations among actors in the health care sector, indicating that individual stakeholders need to recognize their role in the system. The model can be the basis of further evaluations of strategic actions of actors and their effects on other actors or the health care ecosystem itself.
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 29, 2023 4:33 AM
|
Digital health technologies (DHTs) can optimise healthcare costs and improve quality and efficiency of care. However, the fast-paced rate of innovatio…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 29, 2023 4:10 AM
|
Governments and medical associations across the world, including the US Food and Drug
Administration, the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency, the Royal
College of Radiologists, and the European Society of Radiology, believe the advent
of health technologies associated with artificial intelligence (AI) will be the most
radical change in how medical care is delivered in our lifetime.1,2 At a time of unprecedented
demand for medical imaging, when hospitals struggle with staffing shortages, AI tools
could provide a solution.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 29, 2023 4:06 AM
|
Background: Multimorbidity, the presence of more than one condition in a single individual, is a global health issue in primary care. Multimorbid patients tend to have a poor quality of life and suffer from a complicated care process. Clinical decision support systems (CDSSs) and telemedicine are the common information and communication technologies that have been used to reduce the complexity of patient management. However, each element of telemedicine and CDSSs is often examined separately and with great variability. Telemedicine has been used for simple patient education as well as more complex consultations and case management. For CDSSs, there is variability in data inputs, intended users, and outputs. Thus, there are several gaps in knowledge about how to integrate CDSSs into telemedicine and to what extent these integrated technological interventions can help improve patient outcomes for those with multimorbidity.
Objective: Our aims were to (1) broadly review system designs for CDSSs that have been integrated into each function of telemedicine for multimorbid patients in primary care, (2) summarize the effectiveness of the interventions, and (3) identify gaps in the literature.
Conclusions: Telemedicine and CDSSs have a role in supporting patients with multimorbidity. CDSSs can likely be integrated into telehealth services to improve the quality and accessibility of care. However, issues surrounding such interventions need to be further explored. These issues include expanding the spectrum of medical conditions examined; examining tasks of CDSSs, particularly for screening and diagnosis of multiple conditions; and exploring the role of the patient as the direct user of the CDSS.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 26, 2023 2:40 AM
|
Background Deaf signing populations face inequality in both access to health services and health outcomes. Telemedicine intervention might offer a potential solution to address these inequalities in mental health and health related services, therefore a systematic review was carried out. The review question was: “What is the efficacy and effectiveness of telemedicine intervention for Deaf signing populations in comparison to face-to-face interventions?”. Methods The PICO framework was applied to identify the components of the review question for this study. The inclusion criteria were: Deaf signing populations; any intervention that includes the delivery of telemedicine therapy and/or the delivery of assessment (e.g. psychological assessments) using telemedicine; and any evidence for the benefits, efficacy and effectiveness of telemedicine intervention with Deaf people whether in health and/or mental health services. The databases PsycINFO, PubMed, Web of Science, CINAHL, and Medline were searched up to August 2021. Results Following the search strategy, and after the duplicates were removed, 247 records were identified. Following screening, 232 were removed as they did not meet the inclusion criteria. The remaining 15 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility. Only two met the criteria to be included in the review (both concerned telemedicine and mental health interventions). However, they did not fully answer the review’s research question. Therefore, the evidence gap remains regarding the effectiveness of telemedicine intervention for Deaf people. Conclusions The review has identified a gap in the knowledge on the efficacy and effectiveness of telemedicine intervention for Deaf people when compared with face-to-face interventions.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 23, 2023 9:21 AM
|
INESSS, Institut national d'excellence en santé et services sociaux

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 20, 2023 1:59 AM
|
Objective The study aims to assess the cost-effectiveness of a personalised telehealth intervention to manage chronic disease in the long run. Method The Personalised Health Care (PHC) pilot study was a randomised trial with an economic evaluation alongside over 12 months. From a health service perspective, the primary analysis compared the costs and effectiveness of PHC telehealth monitoring with usual care. An incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was calculated based on costs and health-related quality of life. The PHC intervention was implemented in the Barwon Health region, Geelong, Australia, for patients with a diagnosis of COPD and/or diabetes who had a high likelihood of hospital readmission over 12 months. Results When compared to usual care at 12 months, the PHC intervention cost AUD$714 extra per patient (95%CI -4879; 6308) with a significant improvement of 0.09 in health-related quality of life (95%CI: 0.05; 0.14). The probability of PHC being cost-effective by 12 months was close to 65%, at willingness to pay a threshold of AUD$50,000 per quality-adjusted life year. Conclusion Benefits of PHC to patients and the health system at 12 months translated to a gain in quality-adjusted life years with a non-significant cost difference between the intervention and control groups. Given the relatively high set-up costs of the PHC intervention, the program may need to be offered to a larger population to achieve cost-effectiveness. Long-term follow-up is required to assess the real health and economic benefits over time.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 19, 2023 2:09 AM
|
Background: The development of telehealth and telemedicine, in the form of increased teleconsultation and medical telemonitoring, accelerated during the COVID-19 health crisis in France to ensure continued access to care for the population. Since these new information and communication technologies (ICTs) are diverse and likely to transform how the health care system is organized, there is a need better to understand public attitudes toward them and their relationship with peoples’ current experience of health care.
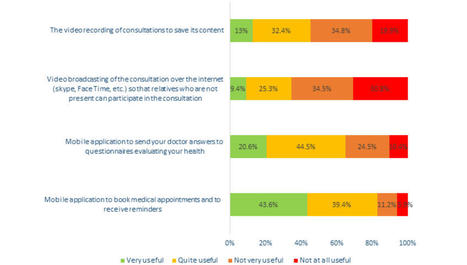
Objective: This study aimed to determine the French general population’s perception of the usefulness of video recording/broadcasting (VRB) and mobile Health (mHealth) apps for medical consultations in France during the COVID-19 health crisis and the factors associated with this perception.
Methods: Data were collected for 2003 people in 2 waves of an online survey alongside the Health Literacy Survey 2019 (1003 in May 2020 and 1000 in January 2021) based on quota sampling. The survey collected sociodemographic characteristics, health literacy levels, trust in political representatives, and perceived health status. The perceived usefulness of VRB in medical consultations was measured by combining 2 responses concerning this technology for consultations. The perceived usefulness of mHealth apps was measured by combining 2 responses concerning their usefulness for booking doctor appointments and for communicating patient-reported outcomes to doctors.
Results: The majority (1239/2003, 62%) of respondents considered the use of mHealth apps useful, while only 27.6% (551/2003) declared VRB useful. The factors associated with the perceived usefulness of both technologies were younger age (≤ 55 years), trust in political representatives (VRB: adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.68, 95% CI 1.31-2.17; mHealth apps: aOR 1.88, 95% CI 1.42-2.48), and higher (sufficient and excellent) health literacy. The period of the beginning of the COVID-19 epidemic, living in an urban area, and being limited in daily activities were also associated with perceiving VRB positively. The perceived usefulness of mHealth apps increased with the level of education. It was also higher in people who had 3 or more consultations with a medical specialist.
Conclusions: There are important differences in attitudes toward new ICTs. Perceived usefulness was lower for VRB than for mHealth apps. Moreover, it decreased after the initial months of the COVID-19 pandemic. There is also the possibility of new inequalities. Hence, despite the potential benefits of VRB and mHealth apps, people with low health literacy considered them to be of little use for their health care, possibly increasing their difficulties in accessing health care in the future. As such, health care providers and policy makers need to consider those perceptions to guarantee that new ICTs are accessible and beneficial to all.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 15, 2023 5:20 AM
|
Make sure you adopt the right digital technology for your needs .

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 12, 2023 10:50 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 12, 2023 3:59 AM
|
Artificial intelligence (AI) in the domain of healthcare is increasing in prominence. Acceptance is an indispensable prerequisite for the widespread implementation of AI. The aim of this integrative review is to explore barriers and facilitators influencing healthcare professionals’ acceptance of AI in the hospital setting. Forty-two articles met the inclusion criteria for this review. Pertinent elements to the study such as the type of AI, factors influencing acceptance, and the participants’ profession were extracted from the included studies, and the studies were appraised for their quality. The data extraction and results were presented according to the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) model. The included studies revealed a variety of facilitating and hindering factors for AI acceptance in the hospital setting. Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) were the AI form included in most studies (n = 21). Heterogeneous results with regard to the perceptions of the effects of AI on error occurrence, alert sensitivity and timely resources were reported. In contrast, fear of a loss of (professional) autonomy and difficulties in integrating AI into clinical workflows were unanimously reported to be hindering factors. On the other hand, training for the use of AI facilitated acceptance. Heterogeneous results may be explained by differences in the application and functioning of the different AI systems as well as inter-professional and interdisciplinary disparities. To conclude, in order to facilitate acceptance of AI among healthcare professionals it is advisable to integrate end-users in the early stages of AI development as well as to offer needs-adjusted training for the use of AI in healthcare and providing adequate infrastructure.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 9, 2023 2:36 AM
|
IntroductionTelecare can be an effective way to deliver healthcare to patients’ homes. Avatar or virtual agent-equipped technologies have the potential to increase user engagement and adherence t

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 9, 2023 1:28 AM
|
This JAMA Forum discusses artificial intelligence tools and the regulatory challenges for global regulatory bodies, including the US Food and Drug Administration, in creating new policies to ensure the safety and efficacy of these tools for patients.
|

 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...