Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 22, 2023 3:17 AM
|
Background: Mobile apps are fundamental tools in today’s society for practical and social endeavors. However, these technologies are often not usable for older users. Given the increased use of mobile apps by this group of users and the impact that certain services may have on their quality of life, such as mobile health, personal finance, or online administrative procedures, a clear set of guidelines for mobile app designers is needed. Existing recommendations for older adults focus on investigations with certain groups of older adults or have not been extracted from experimental results.
Objective: In this research work, we systematically reviewed the scientific literature that provided recommendations for the design of mobile apps based on usability testing with older adults and organized such recommendations into a meaningful set of design guidelines.
Methods: We conducted a systematic literature review of journal and conference articles from 2010 to 2021. We included articles that carried out usability tests with populations aged >60 years and presented transferable guidelines on mobile software design, resulting in a final set of 40 articles. We then carried out a thematic analysis with 3 rounds of analysis to provide meaning to an otherwise diverse set of recommendations. At this stage, we discarded recommendations that were made by just 1 article, were based on a specific mobile app and were therefore nontransferrable, were based on other authors’ literature (as opposed to recommendations based on the results of usability tests), or were not sufficiently argued. With the remaining recommendations, we identified commonalities, wrote a faithful statement for each guideline, used a common language for the entire set, and organized the guidelines into categories, thereby giving shape to an otherwise diverse set of recommendations.
Results: Among the 27 resulting guidelines, the rules Simplify and Increase the size and distance between interactive controls were transversal and of the greatest significance. The rest of the guidelines were divided into 5 categories (Help & Training, Navigation, Visual Design, Cognitive Load, and Interaction) and consequent subcategories in Visual Design (Layout, Icons, and Appearance) and Interaction (Input and Output). The recommendations were structured, explained in detail, and illustrated with applied examples extracted from the selected studies, where appropriate. We discussed the design implications of applying these guidelines, contextualized with relevant studies. We also discussed the limitations of the approach followed, stressing the need for further experimentation to gain a better understanding of how older adults use mobile apps and how to better design such apps with these users in mind.
Conclusions: The compiled guidelines support the design of mobile apps that cater to the needs of older adults because they are based on the results of actual usability tests with users aged >60 years.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 15, 2023 7:08 AM
|
Machines don’t have eyes, but you wouldn’t know that if you followed the progression of deep learning models for accurate interpretation of medical images, such as x-rays, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, patholog

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 13, 2023 10:19 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 11, 2023 7:36 AM
|
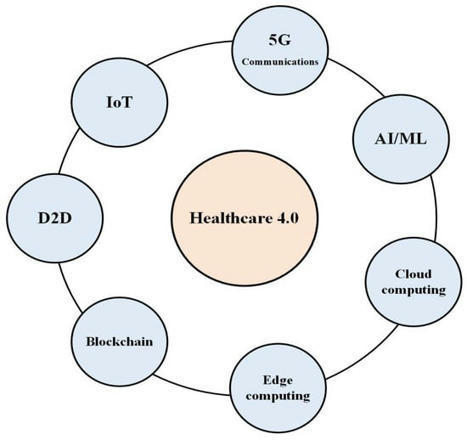
Healthcare 4.0 is a recent e-health paradigm associated with the concept of Industry 4.0. It provides approaches to achieving precision medicine that delivers healthcare services based on the patient’s characteristics. Moreover, Healthcare 4.0 enables telemedicine, including telesurgery, early predictions, and diagnosis of diseases. This represents an important paradigm for modern societies, especially with the current situation of pandemics. The release of the fifth-generation cellular system (5G), the current advances in wearable device manufacturing, and the recent technologies, e.g., artificial intelligence (AI), edge computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT), are the main drivers of evolutions of Healthcare 4.0 systems. To this end, this work considers introducing recent advances, trends, and requirements of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) and Healthcare 4.0 systems. The ultimate requirements of such networks in the era of 5G and next-generation networks are discussed. Moreover, the design challenges and current research directions of these networks. The key enabling technologies of such systems, including AI and distributed edge computing, are discussed.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 7, 2023 1:47 AM
|
The Lancet Regional Health - Europe

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 6, 2023 8:58 AM
|
AbstractObjective. Patients and families are key partners in diagnosis, but methods to routinely engage them in diagnostic safety are lacking. Policy mandating

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 6, 2023 5:53 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 31, 2023 6:21 AM
|
The objective of this study was to explore the use of natural language processing (NLP) algorithm to categorise contributing factors from patient safety event (PSE). Contributing factors are elements in the healthcare process (eg, communication failures

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 31, 2023 3:55 AM
|
Background: There is no doubt that the recent surge in artificial intelligence (AI) research will change the trajectory of next-generation health care, making it more approachable and accessible to patients. Therefore, it is critical to research patient perceptions and outcomes because this trend will allow patients to be the primary consumers of health technology and decision makers for their own health.
Objective: This study aimed to review and analyze papers on AI-based consumer health informatics (CHI) for successful future patient-centered care.
Methods: We searched for all peer-reviewed papers in PubMed published in English before July 2022. Research on an AI-based CHI tool or system that reports patient outcomes or perceptions was identified for the scoping review.
Results: We identified 20 papers that met our inclusion criteria. The eligible studies were summarized and discussed with respect to the role of the AI-based CHI system, patient outcomes, and patient perceptions. The AI-based CHI systems identified included systems in mobile health (13/20, 65%), robotics (5/20, 25%), and telemedicine (2/20, 10%). All the systems aimed to provide patients with personalized health care. Patient outcomes and perceptions across various clinical disciplines were discussed, demonstrating the potential of an AI-based CHI system to benefit patients.
Conclusions: This scoping review showed the trend in AI-based CHI systems and their impact on patient outcomes as well as patients’ perceptions of these systems. Future studies should also explore how clinicians and health care professionals perceive these consumer-based systems and integrate them into the overall workflow.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 30, 2023 6:36 AM
|
Weight loss trajectories after bariatric surgery vary widely between individuals, and predicting weight loss before the operation remains challenging.…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 28, 2023 12:05 PM
|
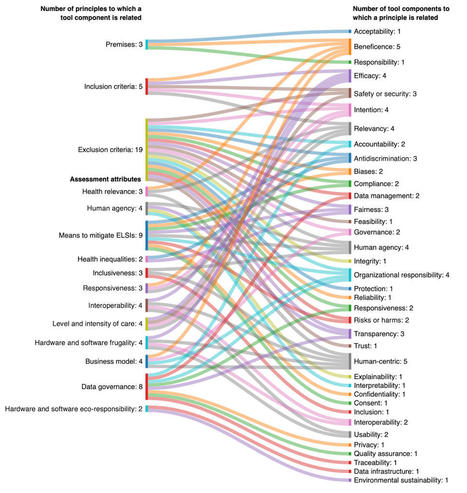
Background: Clinicians’ scope of responsibilities is being steadily transformed by digital health solutions that operate with or without artificial intelligence (DAI solutions). Most tools developed to foster ethical practices lack rigor and do not concurrently capture the health, social, economic, and environmental issues that such solutions raise.
Objective: To support clinical leadership in this field, we aimed to develop a comprehensive, valid, and reliable tool that measures the responsibility of DAI solutions by adapting the multidimensional and already validated Responsible Innovation in Health Tool.
Methods: We conducted a 3-phase mixed methods study. Relying on a scoping review of available tools, phase 1 (concept mapping) led to a preliminary version of the Responsible DAI solutions Assessment Tool. In phase 2, an international 2-round e-Delphi expert panel rated on a 5-level scale the importance, clarity, and appropriateness of the tool’s components. In phase 3, a total of 2 raters independently applied the revised tool to a sample of DAI solutions (n=25), interrater reliability was measured, and final minor changes were made to the tool.
Results: The mapping process identified a comprehensive set of responsibility premises, screening criteria, and assessment attributes specific to DAI solutions. e-Delphi experts critically assessed these new components and provided comments to increase content validity (n=293), and after round 2, consensus was reached on 85% (22/26) of the items surveyed. Interrater agreement was substantial for a subcriterion and almost perfect for all other criteria and assessment attributes.
Conclusions: The Responsible DAI solutions Assessment Tool offers a comprehensive, valid, and reliable means of assessing the degree of responsibility of DAI solutions in health. As regulation remains limited, this forward-looking tool has the potential to change practice toward more equitable as well as economically and environmentally sustainable digital health care.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 23, 2023 7:29 AM
|
The US Food and Drug Administration is clearing an increasing number of artificial
intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML)-based medical devices through the 510(k)
pathway. This pathway allows clearance if the device is substantially equivalent to
a former cleared device (ie, predicate). We analysed the predicate networks of cleared
AI/ML-based medical devices (cleared between 2019 and 2021), their underlying tasks,
and recalls. More than a third of cleared AI/ML-based medical devices originated from
non-AI/ML-based medical devices in the first generation.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 22, 2023 3:00 AM
|
INESSS, Institut national d'excellence en santé et services sociaux
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 20, 2023 4:58 AM
|
This cohort study is a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial and assesses the pedagogical value of technical competencies selected by artificial intelligence (AI) and their extended effects in surgical simulation training.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 15, 2023 3:30 AM
|
As debate rages over the abilities of modern AI systems, scientists are still struggling to effectively assess machine intelligence.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 13, 2023 6:51 AM
|
ICER-PHTI Assessment Framework for
Digital Health Technologies

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 7, 2023 5:38 AM
|
It is not known how the growth of telehealth has affected patients’ choice of visit modalities (telehealth versus in person). In 2023 we conducted a mixed-methods study that paired a nationally representative survey of 2,071 adults (including 571 who used behavioral health services) and semistructured interviews with twenty-six people with depression or bipolar disorder. We explored patients’ experiences with visit modality selection and their agency in the decision. Approximately one-third of patients receiving therapy or medication visits reported that their clinicians did not offer both modalities. Thirty-two percent reported that they did not typically receive their preferred modality, and 45 percent did not believe that their clinician considered their modality preferences. Qualitative findings revealed that some clinicians did not elicit patients’ modality preferences. Perceived lack of choice affected satisfaction and rapport with clinicians and encouraged some people to seek care elsewhere. These findings highlight trade-offs in policies to preserve patient choice and approaches that clinicians can take to identify and accommodate patients’ preferences.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 6, 2023 9:06 AM
|
We developed a machine learning-based model, which is internationally validated, for
predicting individual 5-year weight loss trajectories after three common bariatric
interventions.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 6, 2023 5:54 AM
|
Publications of the World Health Organization

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
September 4, 2023 6:51 AM
|
Telepsychiatry versus face-to-face treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials - Volume 223 Issue 3

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 31, 2023 4:56 AM
|
Informative Artifacts in AI-Assisted Health Care Medical AI tools that are trained on skewed data may exhibit bias. The authors discuss how thinking of clinical data as artifacts can identif

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 31, 2023 3:53 AM
|
Background: The adoption of virtual consultations, catalyzed by the COVID-19 pandemic, has transformed the delivery of primary care services. Owing to their rapid global proliferation, there is a need to comprehensively evaluate the impact of virtual consultations on all aspects of care quality.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the impact of virtual consultations on the quality of primary care.
Methods: A total of 6 databases were searched. Studies that evaluated the impact of virtual consultations, for any disease, were included. Title and abstract screening and full-text screening were performed by 2 pairs of investigators. Risk of bias was assessed using the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool. A narrative synthesis of the results was performed.
Results: In total, 30 studies (5,469,333 participants) were included in this review. Our findings suggest that virtual consultations are equally effective to or more effective than face-to-face care for the management of certain conditions, including mental illness, excessive smoking, and alcohol consumption. Overall, 4 studies indicated positive impacts on some aspects of patient-centeredness; however, a negative impact was noted on patients’ perceived autonomy support (ie, the degree to which people perceive those in positions of authority to be autonomy supportive). Virtual consultations may reduce waiting times, lower patient costs, and reduce rates of follow-up in secondary and tertiary care settings. Evidence for the impact on clinical safety is extremely limited. Evidence regarding equity was considerably mixed. Overall, it appears that virtual care is more likely to be used by younger, female patients, with disparities among other subgroups depending on contextual factors.
Conclusions: Our systematic review demonstrated that virtual consultations may be as effective as face-to-face care and have a potentially positive impact on the efficiency and timeliness of care; however, there is a considerable lack of evidence on the impacts on patient safety, equity, and patient-centeredness, highlighting areas where future research efforts should be devoted. Capitalizing on real-world data, as well as clinical trials, is crucial to ensure that the use of virtual consultations is tailored according to patient needs and is inclusive of the intended end users. Data collection methods that are bespoke to the primary care context and account for patient characteristics are necessary to generate a stronger evidence base to inform future virtual care policies.
Trial Registration:

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 30, 2023 4:05 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 25, 2023 4:57 AM
|
Although the use of audiovisual telemedicine has grown in recent years especially during recent COVID-19-related lockdowns, evidence shows there is still a lack of tools that can be used for th

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 23, 2023 2:36 AM
|
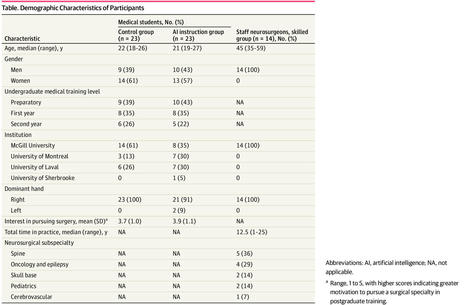
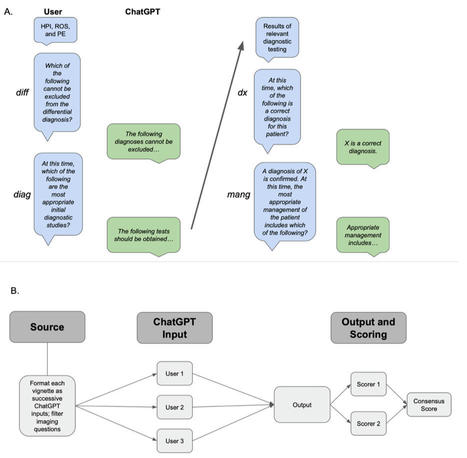
Background: Large language model (LLM)–based artificial intelligence chatbots direct the power of large training data sets toward successive, related tasks as opposed to single-ask tasks, for which artificial intelligence already achieves impressive performance. The capacity of LLMs to assist in the full scope of iterative clinical reasoning via successive prompting, in effect acting as artificial physicians, has not yet been evaluated.
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate ChatGPT’s capacity for ongoing clinical decision support via its performance on standardized clinical vignettes.
Conclusions: ChatGPT achieves impressive accuracy in clinical decision-making, with increasing strength as it gains more clinical information at its disposal. In particular, ChatGPT demonstrates the greatest accuracy in tasks of final diagnosis as compared to initial diagnosis. Limitations include possible model hallucinations and the unclear composition of ChatGPT’s training data set.
|




 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...