Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 20, 2023 8:13 AM
|
Aim: The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to identify, evaluate, and synthesize the evidence from studies that have investigated the treatment effect via telemedicin

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 15, 2023 8:48 AM
|
Background: Owing to the increasing number of people with palliative care needs and the current shortage of health care professionals (HCPs), providing quality palliative care has become challenging. Telehealth could enable patients to spend as much time as possible at home. However, no previous systematic mixed studies reviews have synthesized evidence on patients’ experiences of the advantages and challenges of telehealth in home-based palliative care.
Objective: In this systematic mixed studies review, we aimed to critically appraise and synthesize the findings from studies that investigated patients’ use of telehealth in home-based palliative care, focusing on the advantages and challenges experienced by patients.
Conclusions: The advantages of telehealth were that patients experience a potential support system that could enable them to remain at home, and the visual features of telehealth enable them to build interpersonal relationships with HCPs over time. Self-reporting provides HCPs with information about symptoms and circumstances that facilitates tailoring care to specific patients. Challenges with the use of telehealth were related to barriers to technology use and inflexible reporting of complex and fluctuating symptoms and circumstances using electronic questionnaires. Few studies have included the self-reporting of existential or spiritual concerns, emotions, and well-being. Some patients perceived telehealth as intrusive and a threat to their privacy at home. To optimize the advantages and minimize the challenges with the use of telehealth in home-based palliative care, future research should include users in the design and development process.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 15, 2023 5:36 AM
|
Background: In 2021 alone, diabetes mellitus, a metabolic disorder primarily characterized by abnormally high blood glucose (BG) levels, affected 537 million people globally, and over 6 million deaths were reported. The use of noninvasive technologies, such as wearable devices (WDs), to regulate and monitor BG in people with diabetes is a relatively new concept and yet in its infancy. Noninvasive WDs coupled with machine learning (ML) techniques have the potential to understand and conclude meaningful information from the gathered data and provide clinically meaningful advanced analytics for the purpose of forecasting or prediction.
Objective: The purpose of this study is to provide a systematic review complete with a quality assessment looking at diabetes effectiveness of using artificial intelligence (AI) in WDs for forecasting or predicting BG levels.
Conclusions: This review has provided the most extensive work to date summarizing WDs that use ML for diabetic-related BG level forecasting or prediction. Although current studies are few, this study suggests that the general quality of the studies was considered high, as revealed by the QUADAS-2 assessment tool. Further validation is needed for commercially available devices, but we envisage that WDs in general have the potential to remove the need for invasive devices completely for glucose monitoring in the not-too-distant future.
Trial Registration: PROSPERO CRD42022303175; https://tinyurl.com/3n9jaayc

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 9, 2023 3:47 AM
|
IntroductionVideoconferencing circumvents various physical and financial barriers associated with in-person care. Given this technology's potential benefits and timely nature, we conducted

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 7, 2023 3:55 AM
|
Le Think Tank Téléophtalmologie a le plaisir de vous partager ses nouveaux travaux : un rapport d'analyse sur les pratiques et organisations de téléophtalmologie en France, complété par un recueil de cas d'usages présentant des initiatives variées en réponse aux besoins de la population. Ce rapport a été présenté à des représentants de la DGOS, de la Direction de la Sécurité Sociale et de la CNAM lors d'une restitution des travaux organisée le 20 janvier 2023...

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 1, 2023 9:24 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 10:20 AM
|
Background The rising incidence of chronic diseases among the population, further exacerbated by the phenomenon of aging, is a primary concern and a serious challenge for the healthcare systems worldwide. Among the wide realm of health digital technologies, the rise of Digital Therapeutics (DTx), which are medical devices able to deliver evidence-based treatments to manage and treat diseases, opens new opportunities. However, their diffusion and usage are still fragmented among countries. As the diffusion results from the adoption of technology from a social system and individual acceptance, this study aims to design and test a theoretical model that investigates the intention to use DTx, with a particular focus on the treatment of obesity, as a widespread and burdensome chronic condition. Methods This research is built on 336 answers coming from a survey to test the proposed model, which consists of a combination of organizational mechanisms, derived from Institutional Theory, and rational factors, derived from the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). The survey has been delivered to patients and former patients of Istituto Auxologico Italiano, a hospital with several locations in northern Italy, recognized as a center of excellence for the treatment of obesity. Results The analyses of the answers, performed through the Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) technique, confirmed the influence of the Perceived Usefulness on Intention To Use, and of the Perceived Ease Of Use on the Perceived Usefulness, confirming the validity of the assumptions derived from the TAM. On the other hand, institutional factors were introduced as antecedents of the Perceived Usefulness, and the Perceived Ease Of Use. Results show that the Regulative Pillar influences both the TAM constructs, the Normative Pillar (peer influence) has a positive effect only on the Perceived Usefulness, and finally, the Cultural Pillar impacts the Perceived Ease Of Use. Conclusion This study allows filling the knowledge gap regarding the usage of the Institutional as a means to predict individuals’ intentions. Moreover, managerial contributions are available as the results have been operationalized into practical advice to managers and healthcare professionals to foster the adoption, and thus the diffusion, of Digital Therapeutics.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 7:38 AM
|
Stakeholder preferences for attributes of digital health technologies to consider in health service funding - Volume 39 Issue 1

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 27, 2023 11:18 AM
|
L’acteur de télésanté Medaviz dévoile pour la troisième année consécutive son étude annuelle sur la…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 9, 2023 3:08 AM
|
Timely detection of congenital anomalies using ultrasound improves neonatal care. As specialist sonographers are often geographically dispersed, they are sometimes requested to provide a secon

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 7, 2023 9:22 AM
|
This special issue on telehealth in Behavior Modification features 10 studies related to developing and delivering behavioral interventions through telehealth. The studies in this issue cover

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 6, 2023 9:34 AM
|
Clinicians and researchers have historically deprioritized incorporating technology solutions into mental health care, leaving a void that's being filled by non-experts. The real experts need to get on board.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 3, 2023 1:52 AM
|
This nonrandomized controlled trial assesses the concordance between measurements from a telemedicine physical examination using a mobile medical device and measurements from a conventional in-person physical examination among pediatric patients.
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 16, 2023 5:51 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 15, 2023 5:36 AM
|
Background: Hypertension and diabetes are becoming increasingly prevalent worldwide. Telemedicine is an accessible and cost-effective means of supporting hypertension and diabetes management, especially as the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of technological solutions for care. However, to date, no review has examined the contextual factors that influence the implementation of telemedicine interventions for hypertension or diabetes worldwide.
Objective: We adopted a comprehensive implementation research perspective to synthesize the barriers to and facilitators of implementing telemedicine interventions for the management of hypertension, diabetes, or both.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that the successful implementation of telemedicine interventions for hypertension and diabetes requires comprehensive efforts at the planning, execution, engagement, and reflection and evaluation stages of intervention implementation to address challenges at the individual, interpersonal, organizational, and environmental levels.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 13, 2023 8:11 AM
|
La pratique de la télémédecine est susceptible de soulever des problèmes éthiques et juridiques qui affectent la relation médecin/patient. De ce fait, le respect des principes éthiques s’avère nécessaire. C’est également le cas de l’implication du législateur. Ce dernier doit édicter des instruments spécifiques, capables de cerner toutes les problématiques induites par la télémédecine et de contribuer à une certaine humanisation de la relation médecin/patient.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 8, 2023 3:47 AM
|
Explore the latest in national and global health policy, including health care pricing, delivery, access, quality, safety, equity, and reform.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
March 3, 2023 9:29 AM
|
Thieme E-Books & E-Journals

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 10:58 AM
|
Background: Telemedicine is increasingly viewed as a tool to provide a wide range of health services. This article presents policy lessons drawn from the evaluation of telemedicine experiments conducted in the Paris region. Methods: We used a mixed method design to study telemedicine projects commissioned by the Paris Regional Health Agency between 2013 and 2017. We combined data analysis of the telemedicine projects, review of the protocols, and interviews with stakeholders. Results: We identified the following reasons for disappointing outcomes: the outcome measure was requested too early during the experiments because payers required information for budgetary decisions; and the learning curve, technical problems, diversion of use, insufficient number of inclusions, and a lack of adherence prevented the demonstration of successful outcomes of the projects. Conclusion: The evaluation of telemedicine should be undertaken after sufficient uptake to ensure barriers to implementation are overcome, and to obtain the sample size necessary for statistical power and reduce the average cost for one telemedicine request. Randomized controlled trials should be encouraged with appropriate funding and the follow-up period should be extended.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 28, 2023 7:52 AM
|
Aim The use of direct-to-consumer (DTC) telemedicine consultations in primary healthcare has increased rapidly, in Sweden and internationally. Such consultations may be a low-cost alternative to face-to-face visits, but there is limited evidence on their effects on overall healthcare consumption. The aim of this study was to assess the short- and intermediate-term impact of DTC telemedicine consultations on subsequent primary healthcare consumption, by comparing DTC telemedicine users to matched controls in a Swedish setting. Methods We constructed a database with individual-level data on healthcare consumption, for all residents of Region Stockholm in 2018, by linking national and regional registries. The study population included all individuals who had ≥ 1 physician consultation (telemedicine or face-to-face) during the first half of 2018. DTC telemedicine users were matched 1:2 to controls who were non-users of DTC telemedicine but who had a traditional face-to-face consultation during the study period. The matching criteria were diagnosis and demographic and socioeconomic variables. An interrupted time series analysis was performed to compare the healthcare consumption of DTC telemedicine users to that of the control group. Results DTC telemedicine users increased their healthcare consumption more than controls. The effect seemed to be mostly short term (within a month), but was also present at the intermediate term (2–6 months after the initial consultation). The results were robust across age and disease groups. Conclusion The results indicate that DTC telemedicine consultations increase the total number of physician consultations in primary healthcare. From a policy perspective, it is therefore important to further investigate for which diagnoses and treatments DTC telemedicine is suitable so that its use can be encouraged when it is most cost-efficient and limited when it is not. Given the fundamentally different models for reimbursement, there are reasons to review and possibly harmonise the incentive structures for DTC telemedicine and traditional primary healthcare.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 27, 2023 11:38 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 27, 2023 11:13 AM
|
Background: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a growing epidemic, with a heavy associated economic burden. Education, physical activity, and pulmonary rehabilitation programs are important aspects of the management of COPD. These interventions are commonly delivered remotely as part of telemedicine interventions. Several systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been conducted to assess the effectiveness of these interventions. However, these reviews often have conflicting conclusions.
Objective: We aim to conduct an umbrella review to critically appraise and summarize the available evidence on telemedicine interventions for the management of COPD.
Methods: In this umbrella review, the MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, and Cochrane databases were searched from inception to May 2022 for systematic reviews and meta-analyses relating to telemedicine interventions for the management of COPD. We compared odds ratios, measures of quality, and heterogeneity across different outcomes.
Results: We identified 7 systematic reviews that met the inclusion criteria. Telemedicine interventions used in these reviews were teletreatment, telemonitoring, and telesupport. Telesupport interventions significantly reduced the number of inpatient days and quality of life. Telemonitoring interventions were associated with significant reductions in respiratory exacerbations and hospitalization rates. Teletreatment showed significant effectiveness in reducing respiratory exacerbations, hospitalization rate, compliance (acceptance and dropout rate), and physical activity. Among studies that used integrated telemedicine interventions, there was a significant improvement in physical activity.
Conclusions: Telemedicine interventions showed noninferiority or superiority over the standard of care for the management of COPD. Telemedicine interventions should be considered as a supplement to usual methods of care for the outpatient management of COPD, with the aim of reducing the burden on health care systems.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 8, 2023 5:25 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 7, 2023 8:58 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
February 6, 2023 8:00 AM
|
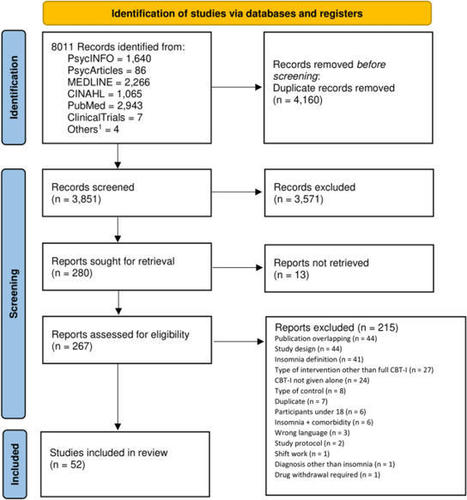
Given the limited availability and accessibility of onsite cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), other CBT-I settings, such as internet-delivered CBT-I (iCBT-I), have been proposed. The primary aim of the study was to compare the efficacy of available CBT-I settings on insomnia severity. A systematic review and frequentist network meta-analysis of available CBT-I settings was performed. PsycINFO, PsycARTICLES, MEDLINE, PubMed, and CINAHL were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating any CBT-I settings in adults with insomnia disorder. The systematic literature search (3851 references) resulted in 52 RCTs. For the primary outcome insomnia severity, all examined CBT-I settings except smartphone-delivered CBT-I yielded significant effects when compared to WL. Large standardized mean differences were found for individual onsite CBT-I (− 1.27;95%CI − 1.70, − 0.84), group-delivered CBT-I (− 1.00;95%CI − 1.42. − 0.59), telehealth (− 1.28;95%CI − 2.06, − 0.50), and guided bibliotherapy (− 0.99;95%CI − 1.67, − 0.32). Both guided iCBT-I (− 0.71;95%CI − 1.18, − 0.24) and unguided iCBT-I (− 0.78;95%CI − 1.18, − 0.38) yielded medium effect sizes. The results underline that health care systems should intensify their efforts to provide synchronously-delivered CBT-I (individual onsite, group-delivered, and telehealth), and particularly individual onsite CBT-I, given its solid evidence base. Medium to large effect sizes for iCBT-I and guided bibliotherapy indicate that self-help settings may be a viable alternative when synchronously-delivered CBT-I is not available.
|

 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...