 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Can understanding the mechanics of the throwing motion help to understand why it may cause shoulder pain, the symptoms of a shoulder problem, the diagnosis, and the treatment options available? Throwing a Ball and Shoulder Pain The throwing motion is a complex shoulder movement that requires the mechanics of muscles, tendons, joints, ligaments, and bones. They all must move in a synchronized and stable pattern to move the shoulder joint. When these mechanics are interrupted or altered, inflammation can result in pain symptoms. (Wardell M., Creighton D., & Kovalcik C., 2022) Throwing Motion Distinct phases characterize the throwing motion: - The wind up
- Cocking
- Acceleration
- Follow-through
- Deceleration
- The rotator cuff and shoulder muscles sequentially guide the movements for effective throwing mechanics. (Wardell M., Creighton D., & Kovalcik C., 2022)
- The labrum stabilizes the ball in the socket of the shoulder.
- The shoulder blade rotation coordinates with the arm to ensure mobility. (Itoigawa Y. et al., 2023)
The throwing motion generates high torque and acceleration forces acting on the shoulder joint and the surrounding muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Causes of Pain Pain when throwing can come from the: - Shoulder blade
- Shoulder joint - cartilage and labrum
- Rotator cuff muscles and tendons
- Nerves that control the muscles' function
The shoulder blade is attached to the upper back by ligaments, muscles, and tendons. The various muscles and tendons that control the movement of the shoulder blade impact movements. Abnormalities of any area can lead to shoulder dysfunction and pain when throwing. (Wardell M., Creighton D., & Kovalcik C., 2022) The most common is the tightness of the posterior shoulder capsule, causing a loss of normal internal rotation of the shoulder. If this is causing pain, individuals may notice that they can't reach up as high on the side with the painful shoulder when reaching behind their back. Symptoms Whether an athlete or playing catch in the backyard, shoulder function abnormalities can cause significant pain. Some symptoms include. Aching Pain - Often deep in the shoulder or extending down the upper arm.
Dead Arm - Lack of strength in the throwing motion.
Pain at Night - Pain can awaken you from sleep.
Diagnosis Finding a healthcare provider familiar with sports injuries can be helpful. They can best determine if a structural abnormality needs to be addressed. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2021) Treatment Most can improve with nonsurgical treatments. The earliest phase of treatment is resting the joint and reducing inflammation. Treatments can include: - Ice
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Cortisone injection
Once the inflammation has subsided, the source of the discomfort can be addressed. Physical Therapy Therapy can include: - A structured shoulder stretching and strengthening program will help.
- The physical therapist will focus on scapular mobility when managing shoulder joint problems.
Exercises may include: (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2024) - Stretching to improve internal rotation or any other lost motion can help allow a more normal throwing motion.
- Strength exercises are often aimed at the rotator cuff, as these muscles initiate proper shoulder movements and stabilize the shoulder joint.
- Maintaining flexibility and strength of the periscapular muscles (muscles that attach to the scapula bone) is important to ensure that the scapular movements are coordinated with the throwing motion.
If improvements are not made within three months of therapy, or individuals can't return to competitive sports within six months. In that case, the individual may need to return to their healthcare provider or see an orthopedic specialist who may recommend surgery. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2024) Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic As a Family Practice Nurse Practitioner, Dr. Jimenez combines advanced medical expertise with chiropractic care to address various conditions. -
Wellness & Nutrition: Personalized plans to optimize health and prevent disease. -
Chronic Pain Management: Non-invasive solutions for fibromyalgia, sciatica, and low back pain. -
Personal Injury & Auto Accident Care: Tailored rehabilitation for whiplash, soft tissue injuries, and more. -
Sports Injuries & Orthopedic Care: Treatment for sprains, strains, and complex injuries. -
Functional Medicine: Root-cause analysis for chronic disorders, incorporating nutrition, lifestyle, and environmental factors. -
Neuromusculoskeletal Health: Care for neck pain, migraines, herniated discs, and scoliosis. Our clinic integrates Functional Medicine, Acupuncture, Electro-Acupuncture, and Sports Medicine to create customized care plans that promote natural healing, mobility, and long-term wellness. By focusing on flexibility, agility, and strength, we empower patients to thrive, regardless of age or health challenges. At El Paso’s Chiropractic Rehabilitation Clinic & Integrated Medicine Center, we passionately focus on treating patients after frustrating injuries and chronic pain syndromes. We focus on improving your ability through flexibility, mobility, and agility programs tailored for all age groups and disabilities. We use in-person and virtual health coaching and comprehensive care plans to ensure every patient’s personalized care and wellness outcomes. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, and physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice. Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol. To discuss the subject matter above further, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or us at 915-50-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Wardell, M., Creighton, D., & Kovalcik, C. (2022). Glenohumeral Instability and Arm Pain in Overhead Throwing Athletes: A Correlational Study. International journal of sports physical therapy, 17(7), 1351–1357. https://doi.org/10.26603/001c.39800 Itoigawa, Y., Koga, A., Morikawa, D., Kubota, A., Uehara, H., Maruyama, Y., Takazawa, Y., & Ishijima, M. (2023). Posterior shoulder stiffness was associated with shoulder pain during throwing in college baseball players: assessment of shear wave elastography. European journal of orthopaedic surgery & traumatology: orthopedie traumatologie, 33(4), 1237–1244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-022-03286-z American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2021). Shoulder Injuries in the Throwing Athlete. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/shoulder-injuries-in-the-throwing-athlete/ American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2024). Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/shoulder-impingementrotator-cuff-tendinitis
Finger pulley injuries are unique digital injuries distinct from sprains or dislocations. They occur specifically in rock climbers and occasionally in baseball pitchers. What are the symptoms, diagnoses, and treatments available? Finger Pulley Injury A finger pulley injury, common in activities like climbing, involves damage to the fibrous bands (pulleys) that hold tendons against bones. This causes pain, swelling, and potentially bowstringing of the tendons. - Finger pulleys are structures that hold tendons against the bones of the fingers.
- Injury symptoms include pain, swelling, and a popping sound heard at the time of the injury.
- Finger pulley injuries, or ruptures of the digital pulley, are seen almost exclusively in rock climbers. (Miro P. H. et al., 2021)
This activity stresses the digits when maneuvering along uneven surfaces while supporting the entire body's weight. The injuries result from the mechanics of the finger tendons and joints and the position the fingers hold while rock climbing. Rock climbing has grown in popularity. The only other sport in which this injury has been described is baseball, in pitchers. The forces acting on the finger are very different in these activities, but both place high stress on the finger pulleys. Digital Pulleys Everyone has structures in their fingers called digital pulleys. These pulleys hold the tendons against the bones of the fingers. Each finger has eight pulleys, but only two are considered critical to prevent the finger tendons' bowstringing (when one pulley gives out or ruptures). This can result in various injury outcomes, from a simple strain of the pulley to ruptures of multiple pulleys in a single digit. Pain, stiffness, and an inability to fully flex the finger can occur. (Carruthers K. H., Skie M., & Jain M. 2016) In severe situations, when the tendons are bowstringing, the tendon may lift away from the finger when making a fist. Symptoms Pain and Tenderness - Localized pain and tenderness at the finger's base, particularly when gripping or bending. Pain on the palm side of finger and tenderness with pressure
Swelling - Swelling and bruising around the affected finger joint, especially on the palm side.
Popping Sound Stiffness and Difficulty Bending - Stiffness and pain when bending the fingers or difficulty gripping. Difficulty forming a fist
Bowstringing - Visible displacement of the tendon from its normal position, causing a bulge at the finger's base.
Most commonly, the middle or index digit is the injured finger. The two critical pulleys in the finger are designated the A2 and A4. (Carruthers K. H., Skie M., & Jain M. 2016) Individuals may see swelling, redness, and inflammation at the base of the finger (A2) and/or in the space between the two finger joints closest to the tip of the finger (A4). In rock climbers, either or both of those pulleys may be injured. In baseball pitchers, the injury is typically isolated to the A4 pulley. Causes - Overuse and Repetitive Strain: Frequent or intense gripping or crimping, common in rock climbing and other activities, can cause pulley injuries.
- Dynamic or Sudden Movements: Desperate or dynamic moves or poor technique can lead to injury.
- Excessive Force: Pulleys can rupture when the force exerted on them is too great.
- Mechanism of injury: The A2 pulley is the most commonly injured, followed by the A4 pulley.
Diagnosis Emergency treatment is generally unnecessary. However, it is important to have suspected digital pulley injuries examined by a specialist within several days to a week after the injury. The most important aspect of an evaluation is determining whether the injury has caused the bowstringing of the tendons. Imaging tests may be performed to help with the diagnosis and plan treatment. An ultrasound is recommended as the initial imaging technique. (Miro P. H. et al., 2021) If an ultrasound is inconclusive, an MRI may be advised. Sometimes, an MRI is performed with the finger held straight and then bent to see if the tendons are bowstringing. An X-ray can also help exclude other causes of finger pain, including sprains and fractures. Treatment Conservative Care - Immobilization, physical therapy, and pulley-protective measures, such as splints or taped fingers, are often used.
Surgery - Surgery may be necessary for severe grade IV injuries where conservative care fails.
- Only in situations where there are multiple pulley ruptures or if there is delayed treatment should surgery be necessary.
Rehabilitation - Focuses on regaining flexibility, strength, and grip function through exercises and physical therapy.
If the tendons do not bowstring, treatment usually protects the injured finger until swelling and pain subside. If there is bowstringing of the tendons, more careful management of the injury is needed. Individuals who suspect a pulley injury rest or splint the finger and use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as necessary for pain until they can get a medical evaluation. (Carruthers K. H., Skie M., & Jain M. 2016) Physical therapy, along with immobilization, the H-tape method, and a protective pulley splint, are recommended for most injuries. (Miro P. H. et al., 2021) Specialized splints and therapy techniques can allow the pulleys to heal properly. Returning to activity varies significantly with the severity of the injury. With mild pulley strains, full activity can be resumed as soon as swelling and pain have subsided. Treatment for full ruptures that are treated non-surgically typically lasts between one and three months. For individuals requiring surgical reconstruction of a pulley injury, restrictions may apply up to a year after the surgery. Injury Medical Chiropractic & Functional Medicine Clinic To prevent complications, a healthcare provider should evaluate pulley injuries immediately. Treatment most often consists of physical therapy, but surgery may be necessary. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice. Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol. To discuss the subject matter above further, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or us at 915-50-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Miro, P. H., vanSonnenberg, E., Sabb, D. M., & Schöffl, V. (2021). Finger Flexor Pulley Injuries in Rock Climbers. Wilderness & environmental medicine, 32(2), 247–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wem.2021.01.011 Carruthers, K. H., Skie, M., & Jain, M. (2016). Jam Injuries of the Finger: Diagnosis and Management of Injuries to the Interphalangeal Joints Across Multiple Sports and Levels of Experience. Sports Health, 8(5), 469–478. https://doi.org/10.1177/1941738116658643
Could incorporating standing lumbar flexion exercise into a daily routine help decrease pain and improve overall spinal mobility for individuals with low back pain? Standing Lower Back Flexion Exercise A chiropractic physical therapy team visit can help determine which exercises are best for an individual's injury or condition and teach them what to stop doing if they have low back pain. Exercise and proper posture can decrease discomfort and improve mobility for individuals with low back pain. (Suh, J. H. et al., 2019) Sometimes, exercises that bend backward are recommended, while other times, flexion or forward bending movements are the best way to manage lower back pain. Many find the standing Williams lumbar flexion exercises maneuver helpful for low back pain. (Amila A, Syapitri H, Sembiring E. 2021) Benefits Individuals with certain diagnoses may benefit from spinal flexion. These diagnoses include: Be sure to speak with a healthcare provider to understand the diagnosis and low back symptoms, and work with a physical therapist to be sure that forward flexion of the spine is the correct exercise for your back. When To Avoid Lumbar Flexion Some should avoid excessive forward bending, which could cause further damage or injury to the spine. Reasons to avoid flexion include: Before starting this or any other exercise program for your spine, check with a healthcare provider or physical therapist. How to Perform Gradually progressing with other gentle lumbar flexion exercises before full-standing lumbar flexion is recommended. These include performing a week or two of lumbar flexion lying down, followed by a couple weeks of lumbar flexion seated. Once these exercises are easy to perform and pain-free, progress with lumbar flexion standing postures.To perform, follow these steps: - Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Slowly bend forward by sliding your hands down the front of your thighs.
- Reach down as far as possible and let your lower back bend forward.
- Grab your ankles and gently pull into more forward flexion to increase the backstretch.
- Hold the end position for a second or two, then slowly return to the starting position.
As you exercise, be sure to monitor changes in symptoms. Pain worsening in the back or traveling down your leg indicates that you should stop the exercise (Spine-health, 2017). If the pain decreases in your leg or centralizes to your back, continue the exercise. Standing lumbar flexion can be repeated for 10 repetitions a couple of times daily. It can help decrease low back or leg pain symptoms and stretch tight hamstrings and back muscles. (Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center, 2003) Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic Exercise can also prevent future lower back problems. Standing back flexion, postural correction, regular physical activity, and exercise are tools for keeping the spine healthy. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to build optimal health and wellness solutions. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, prevent injury, and help mitigate issues through adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal problems. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Suh, J. H., Kim, H., Jung, G. P., Ko, J. Y., & Ryu, J. S. (2019). The effect of lumbar stabilization and walking exercises on chronic low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine, 98(26), e16173. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000016173 Amila A, Syapitri H, Sembiring E. (2021). The effect of William Flexion Exercise on reducing pain intensity for elderly with low back pain. Int J Nurs Health Serv., 4(1), 28-36. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.35654/ijnhs.v4i1.374 Lurie, J., & Tomkins-Lane, C. (2016). Management of lumbar spinal stenosis. BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 352, h6234. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.h6234 Sfeir, J. G., Drake, M. T., Sonawane, V. J., & Sinaki, M. (2018). Vertebral compression fractures associated with yoga: a case series. European journal of physical and rehabilitation medicine, 54(6), 947–951. https://doi.org/10.23736/S1973-9087.18.05034-7 Howell E. R. (2012). Conservative management of a 31 year old male with left sided low back and leg pain: a case report. The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association, 56(3), 225–232. Spine-health. (2017). Exercise with lower back pain: Should you work through the pain? Spine-health
Knowledge from Veritas. https://www.spine-health.com/blog/exercising-lower-back-pain-should-you-work-through-pain Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center. Center, M. P. O. a. S. (2003). Low Back Strain. https://www.cham.org/File%20Library/Global%20Navigation/Expertise%20And%20Programs/Pediatric%20Expertise/Orthopedics/Monte-LOW-BACK-STRAIN-WITH-EXERCISES.pdf
Can incorporating an exercise program like the Alfredson Protocol help athletes and individuals who have hurt their Achilles tendon find pain relief and healing so they can return to regular physical activities? Exercise Protocol Achilles Tendonitis Achilles tendonitis occurs when the tendon at the back of the ankle gets injured. It is common in runners. For individuals who have Achilles tendonitis, walking and running can be painful. You might have to stop engaging in exercise and physical activities like sports. Depending on your job, having the condition may make working harder. Here are a few of the signs and symptoms of the condition: - Pain in the back of the lower leg, just above the heel.
- Pain with running, jumping, or pointing the toes.
- A small lump on the Achilles tendon just above the heel.
The first line of treatment is to rest and ice the tendon. Anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce pain. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022) Physical therapy can include strengthening exercises, ultrasound heat therapy, and deep massage. Exercises stretching the nearby muscles will help gradually increase the stress the tendon can handle, eventually reducing inflammation and swelling. Stretching and flexibility exercises will help an Achilles tendon heal. (University of Michigan, 2023) The only way to determine if an individual has injured their Achilles tendon is to see a doctor. If the injury is Achilles tendonitis, a physical therapist may be recommended. A physical therapist can train individuals on the Alfredson protocol, an exercise protocol program for those with Achilles tendonitis (tendinopathy) that research has shown is helpful for those with the condition. The therapist will train on how to exercise to strengthen the tendon. The exercises stretch the Achilles tendon to help it handle forces and stress, known as eccentric loading. (Stevens M., & Tan C. W. 2014) Inflammation Tendonitis is inflammation of a tendon. However, studies have shown that the tendon might not be inflamed in those with the condition. When an area of the body is inflamed, inflammatory cells are present. Individuals usually feel pain in the inflamed area. For those with Achilles tendonitis, the tendon will present with pain, but not necessarily because the tendon is inflamed. Under a microscope, researchers examined tissue from the tendons of those with Achilles tendonitis. They did not find inflammatory cells in the tissue. (Stevens M., & Tan C. W. 2014) This means that although individuals felt pain, they were not inflamed. If there are no inflammatory cells in the tendon, this could explain why those with Achilles tendonitis often do not find relief from the anti-inflammatory treatment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Studies have shown that gentle exercise protocols for the tendon are more helpful. However, researchers are not sure why these exercises are so beneficial. (O'Neill S., Watson P. J., & Barry S. 2015) Eccentric Exercise A chiropractic physical therapy team can help individuals heal the injury with eccentric loading exercises. Eccentric loading exercises work the muscles and tendons to help them get stronger. Once healing has begun, they can help strengthen the tendon. Individuals start slowly with easy exercises and then work up to harder ones. They will have the patient lengthen or stretch out the muscle. As the patient moves, the muscles and tendons contract or shorten. The Alfredson protocol consists of eccentric loading exercises for the Achilles and the muscles that support it. Alfredson Protocol Before exercising, talk to a doctor or physical therapist to know if it's safe. How to do the Alfredson protocol: - First, stand on a small step or curb.
- Stand with the balls of your feet on the edge.
- Your heels should hang over the edge.
- Hold onto something for balance.
- Keep the knees straight.
- This will load a muscle part of the Achilles tendon called the gastrocnemius.
- Using both feet, lift the heels and rise onto the balls of the feet.
- Keep the foot with the painful Achilles tendon on the step.
- Lift the non-injured foot off the step.
- Slowly lower down using the injured ankle.
- The heel should move towards the floor.
- The ball of the foot should remain in contact with the edge of the step.
- Return the non-injured foot to the step.
- Repeat the exercise.
Do three sets of 15 reps with the knees straight. Then, do the Alfredson protocol again with the knees slightly bent. This will work a muscle called the soleus, which connects to the gastrocnemius. Perform three sets of 15 repetitions. Perform both exercises twice a day. This could be in the morning and the evening. The Alfredson protocol is most beneficial when done for about 12 weeks. (Stevens M., & Tan C. W. 2014) Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic The Alfredson exercise protocol can be done at home with a step or raised platform to put the feet on safely. Individuals should consider working with a personal trainer to ensure safety and get the most out of the workouts. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to build optimal health and wellness solutions. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, prevent injury, and help mitigate issues through adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal problems. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. OrthoInfo. (2022). Achilles Tendinitis. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/achilles-tendinitis/ University of Michigan. (2023). Achilles Tendon Injury: Physical Therapy and Rehab. https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/tr2261 Stevens, M., & Tan, C. W. (2014). Effectiveness of the Alfredson protocol compared with a lower repetition-volume protocol for midportion Achilles tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial. The Journal of orthopaedic and sports physical therapy, 44(2), 59–67. https://doi.org/10.2519/jospt.2014.4720 O'Neill, S., Watson, P. J., & Barry, S. (2015). WHY ARE ECCENTRIC EXERCISES EFFECTIVE FOR ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY?. International journal of sports physical therapy, 10(4), 552–562.
Can understanding what knee tests are used help a healthcare provider diagnose the cause of individuals experiencing knee pain? Knee Pain Tests A knee examination is the first step in determining the cause of knee pain. Different knee tests may be performed during the exam to help the healthcare provider find the cause and develop an optimal treatment plan. These tests evaluate knee function and range of motion and look for conditions and injuries such as arthritis, meniscus tears, ACL tears, other ligament injuries, and kneecap issues. Checking If There is Fluid in the Knee Many individuals know if their knee is swollen, as they can see or feel the swelling. However, if there is excess fluid in the knee joint, the healthcare provider may compress the joint to feel for excess fluid. Fluid is often visible above the kneecap and can be compressed in this area. Fluid may also be detected in the back of the knee, referred to as a Baker's cyst if the fluid has collected into a cluster. (Frush T. J., & Noyes F. R. 2015) Arthritis Tests Certain characteristic findings can detect knee arthritis: Crepitus - Crepitus is the sensation when rough cartilage or exposed bone is rubbing when the knee is bent. (Lo G. H. et al., 2018)
- The examiner will feel and listen for grinding as the knee is bent back and forth.
Deformity - As knee cartilage wears away, the knees can become progressively knock-kneed or bow-legged.
Limited Motion - If arthritis, bone spurs, and swelling prevent normal mobility, the knee's range of motion often becomes limited.
Torn Meniscus Tests Tests used to determine if there is a meniscus tear include: Joint Line Tenderness - Joint line tenderness is a non-specific test in which the area of the meniscus is felt. It is considered a positive test when there is pain in this area.
McMurray's test - This test is performed with the patient lying flat. The examiner bends the knee and rotates the shin bone.
- A click can be felt over the tear as the knee is brought from full flexion to full extension. (Gupta Y., Mahara D., & Lamichhane A. 2016)
Ege's Test - This test is performed with the patient squatting.
- The test is performed with the leg fully externally rotated or internally rotated, depending on whether the lateral or medial meniscus is being tested.
- A click is heard or felt over the area of the tear.
ACL Tear Tests These knee pain tests are for an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear: Lachman Test - The Lachman test is one of the most reliable to diagnose an ACL tear.
- With the knee slightly bent, the examiner stabilizes the thigh while pulling the shin forward.
- The shin shifts too far forward with a torn ACL.
Anterior Drawer Test - This test is performed with the patient lying flat.
- The knee is bent 90 degrees, and then the shin is pulled forward to check the stability of the ACL.
Pivot Shift Test - The pivot shift test can be difficult, especially if the patient is experiencing discomfort and cannot relax the knee.
- This test places stress on the knee joint and assesses the rotational stability of the ACL.
Other Ligament Injuries For a suspected injury to other ligaments, including the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and lateral collateral ligament (LCL), the following tests may be used: Posterior Drawer Test - The posterior drawer is performed similarly to the anterior drawer test, in which the patient lies flat.
- The knee is bent 90 degrees; the shin is pushed backward to check stability and function and detect if the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) has been injured.
Collateral Ligament Stability - Side-to-side stability of the knee detects problems with the MCL and LCL.
- The shin is shifted to each side, with the patient lying flat and the knee slightly bent.
- The LCL or MCL damage causes the knee to open up too much, a condition known as varus (LCL) or valgus (MCL) instability. (Ohori T. et al., 2017)
Kneecap Tests Tests for kneecap issues include: Patellar Grind - In this test, also called Clarke's sign, the patient lies on their back with the leg extended.
- The examiner pushes the kneecap down to reproduce the knee pain while the patient flexes the thigh muscles.
- Damaged cartilage can cause a grinding sensation/crepitus.
Patellar Tenderness - The examiner can slightly lift the kneecap and place direct pressure on parts of the underside.
- The examiner looks for regions of sensitivity or pain.
Patellar Apprehension - This test indicates an unstable kneecap.
- The examiner places pressure on the kneecap in a certain direction, and the patient may feel like the kneecap is going to pop out.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic Knee pain tests typically check the range of motion, discomfort symptoms, and sounds that could indicate a specific type of knee injury. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Frush, T. J., & Noyes, F. R. (2015). Baker's Cyst: Diagnostic and Surgical Considerations. Sports health, 7(4), 359–365. https://doi.org/10.1177/1941738113520130 Lo, G. H., Strayhorn, M. T., Driban, J. B., Price, L. L., Eaton, C. B., & Mcalindon, T. E. (2018). Subjective Crepitus as a Risk Factor for Incident Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis: Data From the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Arthritis care & research, 70(1), 53–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.23246 Gupta, Y., Mahara, D., & Lamichhane, A. (2016). McMurray's Test and Joint Line Tenderness for Medial Meniscus Tear: Are They Accurate?. Ethiopian journal of health sciences, 26(6), 567–572. https://doi.org/10.4314/ejhs.v26i6.10 Ohori, T., Mae, T., Shino, K., Tachibana, Y., Fujie, H., Yoshikawa, H., & Nakata, K. (2017). Varus-valgus instability in the anterior cruciate ligament-deficient knee: effect of posterior tibial load. Journal of experimental orthopaedics, 4(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40634-017-0087-3
What type of concussion tests are there to help establish the extent of head injuries and help assess improvement during recovery? Concussion Tests A concussion is a temporary change in brain function that occurs from a traumatic brain injury or TBI. It can cause problems with thinking and mood and can take weeks to years to heal. Concussion tests are done after a suspected head injury and are also used after diagnosis to assess healing progress. They are noninvasive tests that measure brain functions. Several tests vary in how they are given and what they measure. Tests A mild or moderate traumatic brain injury can cause damage to the brain that is not detectable with brain imaging tests. However, the damage can cause serious symptoms, including headaches, emotional changes, difficulty concentrating, and memory problems. (Haider M. N. et al., 2021) The effects of a concussion can be hard to describe, but concussion testing can help identify and quantify these changes. For individuals who don't have time to heal or experience further brain injuries while recovering, the effects can be prolonged and worsen. This is one reason why concussion testing is vital to get a diagnosis and follow medical recommendations to avoid further injury to the brain. Diagnosis can help set goals, adjust, and assess how the effects improve over time. With improvement, individuals can participate in rehabilitation and follow their doctor's instructions for gradually returning to work, school, and other activities. Measurements Concussion tests can measure subtle aspects of brain function, like visual or auditory perception and response speed (Joyce A. S. et al., 2015). The damage sustained can impair these abilities, like slow decision-making. A traumatic brain injury can be associated with serious injuries, like a skull fracture, swelling, bruise, or bleeding in the brain. These injuries can be detected with imaging tests and often require surgery or other interventions. Brain damage from bleeding or swelling would cause focal neurological symptoms and signs, including partial vision loss, numbness, and weakness. Individuals can have a concussion along with detectable brain injuries or in the absence of detectable brain injuries. Types of Tests There are several types of concussion tests. Individuals may have one or more of these, depending on the standard test that is used in their school, sports league, or by their doctor. These can include: Online Checklists - Several different online checklists are available for concussion screening.
- These tests may include questions about symptoms and are often used as self-tests but are not intended to replace an evaluation by a medical professional.
Baseline and Post-Injury Tests - Many schools and sports leagues conduct preseason skill measurements, including memory tests or tests of speed and accuracy, either in an interview form or with computer testing.
- Individuals might be asked to retake the test that is used as a comparison if they have experienced a traumatic brain injury.
Standardized Assessment of Concussion - SAC - This five-minute test can be done on the sidelines after a sports injury or later.
- It evaluates orientation, immediate memory, neurologic function, concentration, and delayed recall. (Kaufman M. W. et al., 2021)
King-Devick Concussion Test - This two-minute test can be performed on the sidelines after a sports injury or later to assess language, eye movement, and attention. (Krause D. A. et al., 2022)
Post-Concussion Symptom Scale - This test includes 22 questions involving neurocognitive factors, including difficulty concentrating or remembering, physical symptoms like headaches and dizziness, and emotional symptoms like sadness or irritability. (Langevin P. et al., 2022)
Sport Concussion Assessment Tool - SCAT - This test includes an on-field assessment noting concussion symptoms, memory assessment using Maddocks questions (a short list of specific questions), Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), and cervical spine assessment.
- An off-field assessment involves the evaluation of cognitive, neurological, balance, and delayed recall. (Kaufman M. W. et al., 2021)
Buffalo Concussion Physical Examination - BCPE - A modified physical examination that assesses neck tenderness and range of motion, head, jaw, and face abnormalities, eye movements examination, and coordination. (Haider M. N. et al., 2021)
- After a concussion, individuals will also have a physical examination, including a full neurological examination, in a doctor’s office.
Results A doctor will diagnose based on symptoms, physical examination, and concussion test results. For example, for individuals who have broken several bones and are taking powerful pain medications, concussion test results can be abnormal even if they did not experience a concussion. The results of concussion testing can be compared with results before the head injury. Often, baseline testing is required for participation in certain sports leagues at professional and amateur levels. A low score can indicate that head injury has impaired brain function. Sometimes, testing can be done within a few hours of the head trauma and then again a few days later. Responses of individuals who did not have measurements taken before a head injury can be compared with the average results of people their age. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Haider, M. N., Cunningham, A., Darling, S., Suffoletto, H. N., Freitas, M. S., Jain, R. K., Willer, B., & Leddy, J. J. (2021). Derivation of the Buffalo Concussion Physical Examination risk of delayed recovery (RDR) score to identify children at risk for persistent postconcussive symptoms. British journal of sports medicine, 55(24), 1427–1433. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2020-103690 Joyce, A. S., Labella, C. R., Carl, R. L., Lai, J. S., & Zelko, F. A. (2015). The Postconcussion Symptom Scale: utility of a three-factor structure. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 47(6), 1119–1123. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000000534 Kaufman, M. W., Su, C. A., Trivedi, N. N., Lee, M. K., Nelson, G. B., Cupp, S. A., & Voos, J. E. (2021). The Current Status of Concussion Assessment Scales: A Critical Analysis Review. JBJS reviews, 9(6), e20.00108. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.RVW.20.00108 Krause, D. A., Hollman, J. H., Breuer, L. T., & Stuart, M. J. (2022). Validity Indices of the King-Devick Concussion Test in Hockey Players. Clinical journal of sport medicine: official journal of the Canadian Academy of Sport Medicine, 32(3), e313–e315. https://doi.org/10.1097/JSM.0000000000000938 Langevin, P., Frémont, P., Fait, P., & Roy, J. S. (2022). Responsiveness of the Post-Concussion Symptom Scale to Monitor Clinical Recovery After Concussion or Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Orthopaedic journal of sports medicine, 10(10), 23259671221127049. https://doi.org/10.1177/23259671221127049
For individuals and athletes with a gluteal contusion with severe bruising, can a healthcare provider determine if there are any other injuries to underlying structures, including muscle or tendon tears? Gluteal Contusion A gluteal contusion is an injury, in this case, a bruise to the buttocks' gluteal muscles caused by damage to muscle fibers and blood vessels. A buttock bruise is caused by direct bodily impact, typically from falls, automobile collisions, accidents, bumping into something, or being struck by an object or person. Like all bruises, a gluteal bruise most often results in pain and visible discoloration of the skin at the injury site, varying in severity from grade I to grade III, with higher-graded bruises requiring more time to heal. Most butt bruises can heal on their own with time and rest, but if bruising is severe, individuals may require physical therapy to restore full muscle function. Symptoms A contusion is a muscle injury that can affect the body's skeletal muscles. A gluteal contusion can be painful, with a black and blue mark that changes color over time. Other symptoms may include: (Mount Sinai, 2024) - Tenderness to touch over the injury site
- Increased pain with contraction of the glutes
- Swelling
- Discomfort with sitting
Causes A contusion occurs from direct trauma and forceful impact on the gluteal muscles, causing damage to underlying blood vessels, muscle fibers, and sometimes bone, resulting in bleeding under the skin. (MedlinePlus, 2016) Direct impacts to the gluteal muscles that can cause a contusion include: - Falls
- Car accidents
- Direct hits to the buttocks from a piece of sports equipment or person.
- Bumping into furniture, a door, or a counter.
- Intramuscular injections into the gluteal muscles.
- Individuals who take blood thinners or anticoagulant medication have an increased risk of bruising from direct contact injuries.
Diagnosis A gluteal contusion is usually diagnosed through a physical examination and is generally straightforward to diagnose based on physical appearance, symptoms, and type of injury. Contusions can be graded based on the severity according to the following criteria (Fernandes, T. L. et al., 2015) Grade I - An injury that affects only a small amount of muscle fibers, resulting in minimal pain, tenderness, and possible swelling.
- Causes minimal or no loss of strength in the affected muscle or range of motion limitations.
- Muscle use is typically unaffected.
Grade II - An injury that causes significant damage to muscle fibers, resulting in increased pain and impaired muscle contraction.
- A small muscle defect can be felt to the touch.
- Discoloration increases over the first few days after injury.
Grade III - An injury that involves extensive muscle fiber damage and bleeding across an entire area of a muscle that results in severe, and sometimes total, loss of muscle function.
- Causes severe pain and significant discoloration of the skin.
- When contusions are larger, deeper, and involve significant blood pooling and swelling, they are called hematomas.
- If the bruising is severe, a diagnostic ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be used to determine whether any underlying structures are damaged.
Treatment Contusions are generally mild injuries. Treatment typically involves rest to allow the muscles to heal from the bleeding and the bruising to dissipate. - Applying ice to the injury site can help relieve pain and inflammation.
- If the bruising is severe, significant physical activity like sports, dancing, running, jumping, and weight lifting should be avoided until the muscles heal. (Mount Sinai, 2024)
- With more severe bruising, contraction and stretching of the glutes are painful and can require longer healing and recovery time.
- Physical therapy rehabilitation may be needed for more significant injuries to restore muscle function.
Prognosis A mild injury usually heals on its own with time and rest. More significant injuries take longer to heal and may require physical therapy to build strength and range of motion if muscle function is affected. Healing Time and Recovery Healing and recovery times for gluteal contusions vary depending on the severity of the injury (Fernandes T. L. et al., 2015) Grade I - Minor injuries that cause minimal discomfort typically heal fully in five days to two weeks.
Grade II - During the first two to three days, contusions develop, increasing discoloration under the skin, and complete healing can take two to three weeks.
- Return to sport is typically resumed after a month.
Grade III - Contusions can take up to four to six weeks to heal, often requiring rehabilitation to restore muscle strength and range of motion.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic At Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic, we passionately focus on treating patients’ injuries and chronic pain syndromes. We focus on improving ability through flexibility, mobility, and agility programs tailored to the individual. We use in-person and virtual health coaching and comprehensive care plans to ensure every patient’s personalized care and wellness outcomes. Our providers use an integrated approach to create personalized care plans that include Functional Medicine, Acupuncture, Electro-Acupuncture, and Sports Medicine principles. Our goal is to relieve pain naturally by restoring health and function to the body. If he feels the individual needs other treatment, they will be referred to a clinic or physician best suited for them as Dr. Jimenez has teamed up with the top surgeons, clinical specialists, medical researchers, and premier rehabilitation providers to provide our community with the best clinical treatments. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Mount Sinai. (2024). Bruise. https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/injury/bruise MedlinePlus. (2016). Bruises. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/bruises.html Fernandes, T. L., Pedrinelli, A., & Hernandez, A. J. (2015). MUSCLE INJURY - PHYSIOPATHOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT AND CLINICAL PRESENTATION. Revista brasileira de ortopedia, 46(3), 247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2255-4971(15)30190-7
Competitive swimmers, recreational, and swimming enthusiasts who experience pinching and sharp shoulder pain while swimming may suffer from shoulder impingement. Can understanding symptoms can help healthcare providers develop an effective treatment program? Swimmer's Shoulder Swimmer's shoulder, medically known as rotator cuff impingement syndrome, is a common injury among swimmers. It can limit swimming ability and normal arm use for functional tasks. It is caused by persistent and abnormal rubbing and pinching of the structures in the shoulder, causing pain and irritation of the shoulder's rotator cuff tendons and the bursa. The injury affects 40% to 90% of swimmers at some point. (Wanivenhaus F. et al., 2012) Self-care treatment involves rest, anti-inflammatory medication, and exercise to restore normal shoulder mobility. Most cases resolve within a few months, but physical therapy may be needed along with continued exercises and stretches to maintain pain relief. Anatomy The shoulder is a complex joint with extreme mobility. It is comprised of three bones: - The scapula or shoulder blade.
- The clavicle or collar bone.
- The humerus or upper arm bone.
These three bones combine at various places to make up the joint. Several muscles attach to and move the joint. (Kadi R. et al., 2017) The rotator cuff is one group of four muscles deep in the shoulder surrounding the joint. When lifting the arm, these muscles contract to hold the ball in the joint's socket, allowing the arm to be raised in a fluid and smooth motion. Several ligaments hold the shoulder joint together and connect the various bones of the shoulder, giving the joint stability when moving. (Kadi R. et al., 2017) Symptoms Common symptoms include: (Wanivenhaus F. et al., 2012) - Swelling in the front or top of the shoulder
- Difficulty reaching up overhead
- Shoulder pain
- Shoulder pain when bearing weight through the arm.
- Symptoms tend to be worse during or immediately after swimming.
This is due to the position of the arms and upper extremities while swimming. (Wanivenhaus F. et al., 2012) Reaching overhead and turning the hand inward can cause the rotator cuff tendons or shoulder bursa to become pinched underneath the acromion process of the shoulder blade, similar to the motion that occurs during the crawl or freestyle stroke. When pinching/impingement occurs, the tendons or bursa can become inflamed, leading to pain and difficulty with normal arm use. (Struyf F. et al., 2017) The condition may also occur due to the laxity of the shoulder ligaments. (Wanivenhaus F. et al., 2012) It is theorized that the ligaments in swimmers become stretched and lax, leading to shoulder joint instability. This can cause the shoulder joint to become loose and compress the shoulder structures. Diagnosis A clinical examination can diagnose cases of swimmer's shoulder. (Wanivenhaus F. et al., 2012) The exam can include: - Palpation
- Strength test
- Specialized tests
One shoulder test that is often used is called Neer's test. A physician elevates the arm overhead to the maximum degree during this examination. If this results in pain, the rotator cuff tendons may be compressed, and the test is positive. Individuals may begin treatment after the examination, but a doctor may also refer them for diagnostic testing. An X-ray may be taken to examine the bone structures, and an MRI may be used to examine the soft tissue structures, such as the rotator cuff tendons and the bursa. Treatment Appropriate treatment of swimmer's shoulder involves managing pain and inflammation in your shoulder and improving the way your shoulder moves so you avoid pinching structures inside the joint. (Wanivenhaus F. et al., 2012) There are various treatments available and can include: - Rest
- Physical therapy
- Acupuncture
- Non-surgical decompression
- Targeted exercises and stretches
- Medications
- Injections
- Surgery for serious cases
Physical Therapy A physical therapist can treat shoulder impingement. They can assess the condition and prescribe treatments and exercises to improve mobility and strength. (Cleveland Clinic, 2023) They may use various treatment modalities to decrease pain and improve circulation to facilitate and expedite healing. Physical therapy treatments can include: - Ice
- Heat
- Trigger point release
- Joint mobilizations
- Stabilization
- Stretching
- Exercise
- Electrical stimulation
- Ultrasound
- Taping
Medication Medication may include over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medicine to help decrease pain and inflammation. A physician may prescribe stronger medication to manage inflammation if the condition is severe. While taking medication, the shoulder will need rest, so avoiding swimming or other shoulder movements for a week or two may be necessary. Injections Cortisone is a powerful anti-inflammatory medicine. Individuals may benefit from cortisone injections into their shoulders. (Wanivenhaus F. et al., 2012) When injected, cortisone decreases pain, reduces swelling in the rotator cuff and bursa, and improves shoulder mobility. Surgery If symptoms are persistent and fail to be alleviated with conservative treatments, surgery may be recommended. An arthroscopic procedure called subacromial decompression may be performed. (Cleveland Clinic, 2023) This type of surgery is done with small incisions, inserting a camera, and tiny tools. During this procedure, inflamed tissue and bone spurs are removed from the underside of the acromion process of the shoulder blade, allowing more space to the shoulder joint. Post-surgery, individuals can gradually return to swimming and all other activities in about eight weeks. Recovery Most episodes last about eight to ten weeks, and severe cases last up to three months. (Struyf F. et al., 2017) Often, the symptoms slowly resolve with rest and gentle stretching. As symptoms improve, individuals can slowly return to normal activity and swimming. However, performing prescribed exercises two to three times a week may be necessary to maintain shoulder strength and mobility and help prevent future episodes of shoulder impingement. Individuals experiencing any of these symptoms should visit their physician for an accurate diagnosis of their condition to begin proper treatment. Discuss goals with a healthcare professional and physical therapist. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Wanivenhaus, F., Fox, A. J., Chaudhury, S., & Rodeo, S. A. (2012). Epidemiology of injuries and prevention strategies in competitive swimmers. Sports Health, 4(3), 246–251. https://doi.org/10.1177/1941738112442132 Kadi, R., Milants, A., & Shahabpour, M. (2017). Shoulder Anatomy and Normal Variants. Journal of the Belgian Society of Radiology, 101(Suppl 2), 3. https://doi.org/10.5334/jbr-btr.1467 Struyf, F., Tate, A., Kuppens, K., Feijen, S., & Michener, L. A. (2017). Musculoskeletal dysfunctions associated with swimmers' shoulders. British journal of sports medicine, 51(10), 775–780. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2016-096847 Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Swimmer's shoulder. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17535-swimmers-shoulder
For wrestling athletes or those thinking about getting into the sport, can knowing about common injuries help in rehabilitation and prevention? Wrestling Injuries Wrestling is an intense and demanding sport. Studies have found that football and wrestling are the two high school sports with the highest risk of serious injury to athletes (Center for Injury Research and Policy, 2009). The injury rate for college wrestlers is 9 injuries per 1,000 athlete exposures. (Kroshus, E. et al., 2018) While most wrestling injuries include strains and sprains, there can also be serious traumatic and unusual injuries. Using proper safety gear and learning correct techniques can significantly reduce the risk of injuries. The majority occur during competition. Common The most common wrestling injuries are similar to those in other sports and include: Muscle Soreness - Muscle soreness that is experienced 12 to 48 hours after an intense workout or competition.
- Resting is often all that is needed to recover.
Bruises and Contusions - Sparring, take-downs, and hard landings can result in various bruises and contusions.
Sprains and Strains - Rest, ice, compression, and elevation are recommended to treat sprains and strains immediately.
Ankle Sprains - Ankle sprains occur when surrounding ligaments stretch and tear around the joint.
Wrist Sprains - Typically, it occurs when stretching or tearing the ligaments.
- Falling or landing on the hands is a common cause.
Overtraining Syndrome - Frequently occurs in athletes who train beyond the body's ability to recover.
Dehydration - When trying to make weight, dehydration can be a serious health problem that many wrestlers experience.
Other Injuries Other injuries common in wrestling: - Wrist tendinitis
- Finger fractures
- Iliotibial band syndrome
- Meniscus tears
- Groin pull
- Hamstring pull or tear
- Pulled calf muscle
- Achilles tendonitis
- Achilles tendon rupture
- Clavicle/Collarbone fracture
- Concussion
Serious The forcing of a joint beyond its normal range of motion is the most common cause of serious injuries. The most serious wrestling injuries affect the neck, shoulder, elbow, and knee and include: Neck - The cervical vertebrae are often forced into vulnerable positions during various techniques and movements, which can result in a neck injury. Common types include:
- Neck Strain
- Whiplash
- Cervical Fracture
Shoulder - A combination of leverage and twisting causes most upper body and shoulder injuries during competition. Types of shoulder injuries include:
- Rotator cuff injury
- Shoulder separation
- Shoulder dislocation
Elbow Dislocation - Elbows are under tremendous strain when maneuvering.
- Dislocations of the radial head are often related to the athlete bracing for a fall on an outstretched arm during take-downs.
Knee - Most knee injuries occur to the ligaments of the knee joint.
- These include anterior and posterior cruciate ligament or ACL/PCL injuries.
Safety Wrestling requires flexibility, strength, and proper technique to prevent injury, combined with thorough instruction and coaching and following basic safety precautions. Some tips include. Safety Gear - Wear appropriate headgear and mouthguards during practices, meets, and tournaments.
Improving Joint Flexibility - Wrestlers with a high degree of shoulder flexibility have fewer injuries.
- The flexibility of the lower back, hamstrings, elbows, and cervical spine should also be worked on.
Gain or Lose Weight Safely - Avoid dramatic weight loss and weight-gaining strategies by maintaining healthy nutrition and hydration during the season.
Avoiding Dangerous Holds and Slam Moves - Safe wrestling techniques need to be followed as these can generate severe injuries.
Regardless of how common or seemingly not serious an injury or medical condition is, it's important to rest and recover and tell a coach and health care professional, as some injuries and conditions can become serious if left untreated. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic focuses on and treats injuries and chronic pain syndromes through personalized care plans that improve ability through flexibility, mobility, and agility programs to relieve pain. Our providers use an integrated approach to create personalized care plans for each patient, including Functional Medicine, Acupuncture, Electro-Acupuncture, and Sports Medicine principles. Our goal is to relieve pain naturally by restoring health and function to the body. If other treatment is needed, Dr. Jimenez has teamed up with top surgeons, clinical specialists, medical researchers, and rehabilitation providers to provide the most effective treatments. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Nationwide Children’s Hospital. (2024). Center for Injury Research and Policy. https://www.nationwidechildrens.org/research/areas-of-research/center-for-injury-research-and-policy Kroshus, E., Utter, A. C., Pierpoint, L. A., Currie, D. W., Knowles, S. B., Wasserman, E. B., Dompier, T. P., Marshall, S. W., Comstock, R. D., & Kerr, Z. Y. (2018). The First Decade of Web-Based Sports Injury Surveillance: Descriptive Epidemiology of Injuries in US High School Boys' Wrestling (2005-2006 Through 2013-2014) and National Collegiate Athletic Association Men's Wrestling (2004-2005 Through 2013-2014). Journal of athletic training, 53(12), 1143–1155. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-154-17
For individuals who lift weights, are there ways to protect the wrists and prevent injuries when lifting weights? Wrist Protection The wrists are complex joints. The wrists significantly contribute to stability and mobility when performing tasks or lifting weights. They provide mobility for movements using the hands and stability to carry and lift objects securely and safely (National Library of Medicine, 2024). Lifting weights is commonly performed to strengthen and stabilize the wrists; however, these movements can cause wrist pain and lead to injuries if not performed correctly. Wrist protection can keep wrists strong and healthy and is key to avoiding strains and injuries. Wrist Strength The wrist joints are set between the hand and forearm bones. Wrists are aligned in two rows of eight or nine total small bones/carpal bones and are connected to the arm and hand bones by ligaments, while tendons connect the surrounding muscles to the bones. Wrist joints are condyloid or modified ball and socket joints that assist with flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction movements. (National Library of Medicine. 2024) This means the wrists can move in all planes of motion: - Side to side
- Up and down
- Rotate
This provides a wide range of motion but can also cause excessive wear and tear and increase the risk of strain and injury. The muscles in the forearm and hand control finger movement necessary for gripping. These muscles and the tendons and ligaments involved run through the wrist. Strengthening the wrists will keep them mobile, help prevent injuries, and increase and maintain grip strength. In a review on weightlifters and powerlifters that examined the types of injuries they sustain, wrist injuries were common, with muscle and tendon injuries being the most common among weightlifters. (Ulrika Aasa et al., 2017) Protecting the Wrists Wrist protection can use a multi-approach, which includes consistently increasing strength, mobility, and flexibility to improve health and prevent injuries. Before lifting or engaging in any new exercise, individuals should consult their primary healthcare provider, physical therapist, trainer, medical specialist, or sports chiropractor to see which exercises are safe and provide benefits based on injury history and current level of health. Increase Mobility Mobility allows the wrists to have a full range of motion while retaining the stability necessary for strength and durability. Lack of mobility in the wrist joint can cause stiffness and pain. Flexibility is connected to mobility, but being overly flexible and lacking stability can lead to injuries. To increase wrist mobility, perform exercises at least two to three times a week to improve range of motion with control and stability. Also, taking regular breaks throughout the day to rotate and circle the wrists and gently pull back on the fingers to stretch them will help relieve tension and stiffness that can cause mobility problems. Warm-Up Before working out, warm up the wrists and the rest of the body before working out. Start with light cardiovascular to get the synovial fluid in the joints circulating to lubricate the joints, allowing for smoother movement. For example, individuals can make fists, rotate their wrists, perform mobility exercises, flex and extend the wrists, and use one hand to pull back the fingers gently. Around 25% of sports injuries involve the hand or wrist. These include hyperextension injury, ligament tears, front-inside or thumb-side wrist pain from overuse injuries, extensor injuries, and others. (Daniel M. Avery 3rd et al., 2016) Strengthening Exercises Strong wrists are more stable, and strengthening them can provide wrist protection. Exercises that improve wrist strength include pull-ups, deadlifts, loaded carries, and Zottman curls. Grip strength is vital for performing daily tasks, healthy aging, and continued success with weightlifting. (Richard W. Bohannon 2019) For example, individuals who have difficulty increasing the weight on their deadlifts because the bar slips from their hands could have insufficient wrist and grip strength. Wraps Wrist wraps or grip-assisting products are worth considering for those with wrist issues or concerns. They can provide added external stability while lifting, reducing grip fatigue and strain on the ligaments and tendons. However, it is recommended not to rely on wraps as a cure-all measure and to focus on improving individual strength, mobility, and stability. A study on athletes with wrist injuries revealed that the injuries still occurred despite wraps being worn 34% of the time prior to the injury. Because most injured athletes did not use wraps, this pointed to potential preventative measures, but the experts agreed more research is needed. (Amr Tawfik et al., 2021) Preventing Overuse Injuries When an area of the body undergoes too many repetitive motions without proper rest, it becomes worn, strained, or inflamed faster, causing overuse injury. The reasons for overuse injuries are varied but include not varying workouts enough to rest the muscles and prevent strain. A research review on the prevalence of injuries in weightlifters found that 25% were due to overuse tendon injuries. (Ulrika Aasa et al., 2017) Preventing overuse can help avoid potential wrist problems. Proper Form Knowing how to perform movements correctly and using proper form during each workout/training session is essential for preventing injuries. A personal trainer, sports physiotherapist, or physical therapist can teach how to adjust grip or maintain correct form. Be sure to see your provider for clearance before lifting or starting an exercise program. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic can advise on training and prehabilitation or make a referral if one is needed. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Erwin, J., & Varacallo, M. (2024). Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Wrist Joint. In StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30521200 Aasa, U., Svartholm, I., Andersson, F., & Berglund, L. (2017). Injuries among weightlifters and powerlifters: a systematic review. British journal of sports medicine, 51(4), 211–219. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2016-096037 Avery, D. M., 3rd, Rodner, C. M., & Edgar, C. M. (2016). Sports-related wrist and hand injuries: a review. Journal of orthopaedic surgery and research, 11(1), 99. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-016-0432-8 Bohannon R. W. (2019). Grip Strength: An Indispensable Biomarker For Older Adults. Clinical interventions in aging, 14, 1681–1691. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S194543 Tawfik, A., Katt, B. M., Sirch, F., Simon, M. E., Padua, F., Fletcher, D., Beredjiklian, P., & Nakashian, M. (2021). A Study on the Incidence of Hand or Wrist Injuries in CrossFit Athletes. Cureus, 13(3), e13818. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.13818
For individuals experiencing eye problems, can acupuncture treatment help and benefit overall eye health? Acupuncture For Eye Health Acupuncture is an alternative medical practice that involves inserting thin needles at specific points on the body. The objective is to restore balance and health by restoring and balancing energy circulation through pathways throughout the body. These pathways, known as meridians, are separate from nerve and blood pathways. - Studies have shown that the insertion of needles manipulates local accumulations of certain neurotransmitters by nearby nerves, which causes beneficial health effects of acupuncture. (Heming Zhu 2014)
- Scientists are not sure exactly how acupuncture works, but it has been shown to provide pain relief and alleviation of cancer treatment nausea. (Weidong Lu, David S. Rosenthal 2013)
- Studies have shown that acupuncture can help treat eye conditions like dry eye syndrome. (Tae-Hun Kim et al., 2012)
Eye Problems For some individuals, a body imbalance can be caused by eye problems or disease. With acupuncture, imbalance-causing symptoms are addressed. Acupuncture promotes the circulation of energy and blood around the eyes. - Acupuncture has been used as an alternative treatment for chronic dry eye syndrome. (Tae-Hun Kim et al., 2012)
- Studies have shown acupuncture helps reduce the eye surface's temperature to reduce the evaporation of tears.
- The procedure is also sometimes used to treat glaucoma.
- Glaucoma is an optic nerve disease usually caused by above-normal eye pressure levels.
- One study found eye pressure significantly decreased after acupuncture. (Simon K. Law, Tianjing Li 2013)
- Another study showed successful reduced allergic and inflammatory eye disease symptoms. (Justine R. Smith et al., 2004)
Eye Acupoints The following acupoints are for eye health. Jingming - Jingming - UB-1 is located in the inner corner of the eye.
- This point is thought to increase energy and blood and to help with problems such as blurry vision, cataracts, glaucoma, night blindness, and conjunctivitis. (Tilo Blechschmidt et al., 2017)
Zanzhu - The Zanzhu point - UB-2 is in the crease at the inner end of the eyebrow.
- This acupoint is used when individuals complain of headaches, blurred vision, pain, tearing, redness, twitching, and glaucoma. (Gerhard Litscher 2012)
Yuyao - Yuyao is in the middle of the eyebrow, above the pupil.
- This point is used for treating eye strain, eyelid twitching, ptosis, or when the upper eyelid droops over, cloudiness of the cornea, redness, and swelling. (Xiao-yan Tao et al., 2008)
Sizhukong - The Sizhukog - SJ 23 area is in the hollow area outside the eyebrow.
- It is thought to be a point where acupuncture can help with eye and facial pain, including headaches, redness, pain, blurred vision, toothache, and facial paralysis. (Hongjie Ma et al., 2018)
Tongzilia - The Tongzilia - GB 1 is located on the outside corner of the eye.
- The point helps brighten the eyes.
- Acupuncture also helps treat headaches, redness, eye pain, light sensitivity, dry eyes, cataracts, and conjunctivitis. (GladGirl 2013)
Early studies with acupuncture have shown promise for improving eye health. Individuals considering acupuncture are recommended to consult their primary healthcare provider to see if it can be an option for those who have not found a resolution by traditional means. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Zhu H. (2014). Acupoints Initiate the Healing Process. Medical acupuncture, 26(5), 264–270. https://doi.org/10.1089/acu.2014.1057 Lu, W., & Rosenthal, D. S. (2013). Acupuncture for cancer pain and related symptoms. Current pain and headache reports, 17(3), 321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-013-0321-3 Kim, T. H., Kang, J. W., Kim, K. H., Kang, K. W., Shin, M. S., Jung, S. Y., Kim, A. R., Jung, H. J., Choi, J. B., Hong, K. E., Lee, S. D., & Choi, S. M. (2012). Acupuncture for the treatment of dry eye: a multicenter randomised controlled trial with active comparison intervention (artificial teardrops). PloS one, 7(5), e36638. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036638 Law, S. K., & Li, T. (2013). Acupuncture for glaucoma. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 5(5), CD006030. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006030.pub3 Smith, J. R., Spurrier, N. J., Martin, J. T., & Rosenbaum, J. T. (2004). Prevalent use of complementary and alternative medicine by patients with inflammatory eye disease. Ocular immunology and inflammation, 12(3), 203–214. https://doi.org/10.1080/092739490500200 Blechschmidt, T., Krumsiek, M., & Todorova, M. G. (2017). The Effect of Acupuncture on Visual Function in Patients with Congenital and Acquired Nystagmus. Medicines (Basel, Switzerland), 4(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines4020033 Litscher G. (2012). Integrative laser medicine and high-tech acupuncture at the medical university of graz, austria, europe. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2012, 103109. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/103109 Tao, X. Y., Sun, C. X., Yang, J. L., Mao, M., Liao, C. C., Meng, J. G., Fan, W. B., Zhang, Y. F., Ren, X. R., & Yu, H. F. (2008). Zhongguo zhen jiu = Chinese acupuncture & moxibustion, 28(3), 191–193. Ma, H., Feng, L., Wang, J., & Yang, Z. (2018). Zhongguo zhen jiu = Chinese acupuncture & moxibustion, 38(3), 273–276. https://doi.org/10.13703/j.0255-2930.2018.03.011 GladGirl The Lash & Brow Expert Blog. Acupuncture for Eye Health. (2013). https://www.gladgirl.com/blogs/lash-brow-expert/acupuncture-for-eye-health
Individuals who participate in physical and sports activities could suffer an Achilles tendon tear. Can understanding the symptoms and risks help in treatment and return the individual back to their sports activity sooner? Achilles Tendon This is a common injury that occurs when the tendon attaching the calf muscle to the heel gets torn. About the Tendon - The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body.
- In sports and physical activities, intense explosive movements like running, sprinting, quickly shifting positions, and jumping are exerted on the Achilles.
- Males are more likely to tear their Achilles and sustain a tendon rupture. (G. Thevendran et al., 2013)
- The injury often occurs without any contact or collision but rather the running, starting, stopping, and pulling actions placed on the feet.
- Certain antibiotics and cortisone shots can increase the likelihood of Achilles tear injuries.
- A specific antibiotic, fluoroquinolones, has been shown to increase the risk of Achilles tendon problems.
- Cortisone shots are also associated with Achilles tears, which is why many healthcare providers don't recommend cortisone for Achilles tendonitis. (Anne L. Stephenson et al., 2013)
Symptoms - A tendon tear or rupture causes sudden pain behind the ankle.
- Individuals may hear a pop or a snap and often report the feeling as being kicked in the calf or heel.
- Individuals have difficulty pointing their toes downward.
- Individuals may have swelling and bruising around the tendon.
- A healthcare provider will examine the ankle for continuity of the tendon.
- Squeezing the calf muscle is supposed to cause the foot to point downwards, but in individuals with a tear, the foot will not move, resulting in positive results on the Thompson test.
- A defect in the tendon can usually be felt after a tear.
- X-rays may be used to rule out other conditions, including ankle fracture or ankle arthritis.
Risk Factors - Achilles tendon ruptures are most seen in men around 30 or 40. (David Pedowitz, Greg Kirwan. 2013)
- Many individuals have symptoms of tendonitis prior to sustaining a tear.
- The majority of individuals have no history of previous Achilles tendon problems.
- The majority of Achilles tendon tears are associated with ball sports. (Youichi Yasui et al., 2017)
Other risk factors include: - Gout
- Cortisone injections into the Achilles tendon
- Fluoroquinolone antibiotic use
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics are commonly used for the treatment of respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, and bacterial infections. These antibiotics are associated with Achilles tendon rupture, but further research is needed to determine how they affect the Achilles tendon. Individuals taking these medications are advised to consider an alternative medication if Achilles tendon problems begin to develop. (Anne L. Stephenson et al., 2013) Treatment Depending on the severity of the injury, treatment can consist of non-surgical techniques or surgery. - The benefit of surgery is there is usually less immobilization.
- Individuals can often return to sports activities sooner, and there is less chance of re-rupturing the tendon.
- Non-surgical treatment avoids the potential surgical risks, and the long-term functional results are similar. (David Pedowitz, Greg Kirwan. 2013)
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Thevendran, G., Sarraf, K. M., Patel, N. K., Sadri, A., & Rosenfeld, P. (2013). The ruptured Achilles tendon: a current overview from biology of rupture to treatment. Musculoskeletal surgery, 97(1), 9–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-013-0251-6
Stephenson, A. L., Wu, W., Cortes, D., & Rochon, P. A. (2013). Tendon Injury and Fluoroquinolone Use: A Systematic Review. Drug safety, 36(9), 709–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-013-0089-8
Pedowitz, D., & Kirwan, G. (2013). Achilles tendon ruptures. Current reviews in musculoskeletal medicine, 6(4), 285–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-013-9185-8 Yasui, Y., Tonogai, I., Rosenbaum, A. J., Shimozono, Y., Kawano, H., & Kennedy, J. G. (2017). The Risk of Achilles Tendon Rupture in the Patients with Achilles Tendinopathy: Healthcare Database Analysis in the United States. BioMed research international, 2017, 7021862. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7021862
For individuals experiencing a turf toe injury, can knowing the symptoms help athletes and non-athletes with treatment, recovery time, and returning to activities? Turf Toe Injury A turf toe injury affects the soft tissue ligaments and tendons at the base of the big toe under the foot. This condition usually occurs when the toe is hyperextended/forced upward, such as when the ball of the foot is on the ground and the heel is lifted. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2021) The injury is common among athletes who play sports on artificial turf, which is how the injury got its name. However, it can also affect non-athletes, like individuals working on their feet all day. - Recovery time after turf toe injury depends on the severity and the type of activities the individual plans to return to.
- Returning to high-level sports activities after a severe injury can take six months.
- These injuries vary in severity but usually improve with conservative treatment. In severe cases, surgery could be required.
- Pain is the primary issue that stops physical activities after a grade 1 injury, while grades 2 and 3 can take weeks to months to heal completely.
Meaning A turf toe injury refers to a metatarsophalangeal joint strain. This joint comprises ligaments that connect the bone on the sole of the foot, below the big toe/proximal phalanx, to the bones that connect the toes to the larger bones in the feet/metatarsals. The injury is usually caused by hyperextension that often results from a pushing-off motion, like running or jumping. Grading Turf toe injuries can range from mild to severe and are graded as follows: (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2021) - Grade 1 - The soft tissue is stretched, causing pain and swelling.
- Grade 2 - The soft tissue is partially torn. Pain is more pronounced, with significant swelling and bruising, and it is difficult to move the toe.
- Grade 3 - Soft tissue is completely torn, and symptoms are severe.
Is This What's Causing My Foot Pain? Turf toe can be an: - Overuse injury - caused by repeating the same motion repeatedly for an extended period, that causes symptoms to worsen.
- Acute injury - that occurs suddenly, causing immediate pain.
Symptoms can include the following: (Mass General Brigham. 2023) - Limited range-of-motion.
- Tenderness in the big toe and surrounding area.
- Swelling.
- Pain in the big toe and surrounding area.
- Bruising.
- Loose joints can indicate there is a dislocation.
Diagnosis If experiencing turf toe symptoms, see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis so they can develop a personalized treatment plan. They will perform a physical exam to assess pain, swelling, and range of motion. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2021) If the healthcare provider suspects tissue damage, they may recommend imaging with X-rays and (MRI) to grade the injury and determine the proper course of action. Treatment A healthcare provider will determine the best treatment based on the severity of the injury. All turf toe injuries can benefit from the RICE protocol: (American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons. Foot Health Facts. 2023) - Rest - Avoid activities that worsen symptoms. This can include using an assistive device like a walking boot or crutches to reduce pressure.
- Ice - Apply ice for 20 minutes, then wait 40 minutes before reapplying.
- Compression - Wrap the toe and foot with an elastic bandage to support and reduce swelling.
- Elevation - Prop the foot above the level of the heart to help decrease swelling.
Grade 1 Grade 1 turf toe is classified by stretched soft tissue, pain, and swelling. Treatments can include: (Ali-Asgar Najefi et al., 2018) - Taping to support the toe.
- Wearing shoes with a rigid sole.
- Orthotic support, like a turf toe plate.
Grades 2 and 3 Grades 2 and 3 come with partial or complete tissue tearing, severe pain, and swelling. Treatments for more severe turf toe can include: (Ali-Asgar Najefi et al., 2018) - Limited weight bearing
- Using assistive devices like crutches, a walking boot, or a cast.
Other Treatment - Less than 2% of these injuries require surgery. It is usually recommended if there is instability in the joint or when conservative treatments are unsuccessful. (Ali-Asgar Najefi et al., 2018) (Zachariah W. Pinter et al., 2020)
- Physical therapy is beneficial for decreasing pain and improving the range of motion and strength after injury. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2021)
- Physical therapy also includes proprioception and agility training exercises, orthotics, and wearing recommended shoes for specific physical activities. (Lisa Chinn, Jay Hertel. 2010)
- A physical therapist can also help ensure that the individual does not return to physical activities before the injury is fully healed and prevent the risk of re-injury.
Recovery Time Recovery depends on injury severity. (Ali-Asgar Najefi et al., 2018) - Grade 1 - Subjective as it varies depending on the individual's pain tolerance.
- Grade 2 - Four to six weeks of immobilization.
- Grade 3 - Eight weeks minimum of immobilization.
- It can take up to six months to return to normal function.
Returning To Normal Activities After a grade 1 turf toe injury, individuals can return to normal activities once the pain is under control. Grades 2 and 3 take longer to heal. Returning to sports activities after a grade 2 injury can take around two or three months, while grade 3 injuries and cases that require surgery can take up to six months. (Ali-Asgar Najefi et al., 2018) General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2021). Turf toe. Mass General Brigham. (2023). Turf toe. American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons. Foot Health Facts. (2023). RICE protocol. Najefi, A. A., Jeyaseelan, L., & Welck, M. (2018). Turf toe: A clinical update. EFORT open reviews, 3(9), 501–506. https://doi.org/10.1302/2058-5241.3.180012 Pinter, Z. W., Farnell, C. G., Huntley, S., Patel, H. A., Peng, J., McMurtrie, J., Ray, J. L., Naranje, S., & Shah, A. B. (2020). Outcomes of Chronic Turf Toe Repair in Non-athlete Population: A Retrospective Study. Indian journal of orthopaedics, 54(1), 43–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-019-00010-8 Chinn, L., & Hertel, J. (2010). Rehabilitation of ankle and foot injuries in athletes. Clinics in sports medicine, 29(1), 157–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csm.2009.09.006
|
What are some leg-strengthening exercises that will expedite recovery for athletes and physically active individuals who have undergone leg surgery? Post Surgery Leg Strengthening Leg muscles may weaken after hip, knee, ankle, or foot surgery. This happens because those muscles are not used as much during recovery. Gaining back strength and muscle endurance after an injury or surgery is an important step in recovery. Leg exercises can help regain mobility and prevent complications like blood clots and pressure sores after surgery or an injury, which is why engaging in post-surgery leg strengthening is important once the doctor gives the ok. Benefits Post-surgery leg strengthening exercises have several benefits, including - Rebuilds strength and confidence
- Retraining for optimal mobility and flexibility
- Prevents pressure sores
- Prevents blood clots
When the leg muscles are contracted, they move blood like a pump, maintaining proper circulation. Moving in a bed after surgery also helps prevent pressure sores from forming and blood clots. A physical therapy team will determine the right leg exercises for each individual and their injury/condition. This is an important step when moving forward after surgery. (Hoogeboom T. J. et al., 2014) Starting Out The first exercises should target all the major muscles of the leg. (Madara K. C. et al., 2019) Gluteal Sets This isometric exercise means the muscles contract while no motion occurs at the hip joints. To perform: - Lie on your back and tighten your buttock muscles.
- Hold the muscles tight for 5 seconds, then relax.
- Repeat 10 or 15 times.
- Gluteal sets can be done several times per day.
Heel Slide Heel slides can help regain strength in the major muscles of the leg. To perform: - Lie on your back.
- Bend the knee of the surgical leg and slowly slide the heel toward your butt.
- Slide as far as possible and hold for 5 seconds.
- Slowly return to the starting position and repeat.
Short Arc Quad The short arc quad, or SAQ, is a simple way to get the quadricep muscles working. To perform: - Lie on your back with a towel roll, small ball, or something similar under the knee.
- Slowly straighten the knee.
- Tighten the quad muscle on the top of the thigh.
- Hold for 3 seconds, then relax.
- Repeat 10 to 15 times.
Quad Set This exercise helps get the quad muscles working. It also helps control the position of the kneecap. To perform: - Lie on your back.
- Place a small towel roll under the knee.
- Try to press the back of the knee flat against the floor.
- Hold for 10 seconds and release.
- Repeat 10 to 15 times.
Individuals can complete quad sets bilaterally or with both knees simultaneously. This makes the stronger leg help strengthen the weaker side. Straight Leg Raise To perform: - Lie on your back.
- Lift your leg straight off the floor until it is at the height of the opposite bent knee.
- Hold for 10 seconds and slowly lower.
- Repeat 10 to 15 times.
Be sure to keep the knee straight for the entire exercise. Keep the opposite knee bent for comfort. To ensure the knee is straight, individuals can complete a quad set first and then the straight leg raise. The exercise can be more challenging by increasing repetitions or adding a 2- to 3-pound ankle weight on the thigh. For even more challenge, add the ankle weight to the ankle. Hamstring Strengthening Working out the hamstrings after injury or surgery is important. The hamstring muscles bend the knee and extend the hip backward. To perform: - Lie on your stomach.
- Bend one knee to raise the lower limb straight in the air.
- Hold for 5 seconds and lower slowly.
- Repeat 10 to 15 times.
Once the exercise is easy to do, increase the repetitions to 30. Individuals can also add a 2- to 3-pound ankle weight. Physical therapy can help individuals regain mobility after injury or surgery. A therapist may prescribe exercises as part of an at-home exercise program. Over time, progress will go from simple exercises to more challenging ones to improve balance and mobility. (Madara K. C. et al., 2019) Injury Medical Chiropractic & Functional Medicine Clinic Before starting this or any other exercise program, consult a doctor and a physical therapist to find the right exercises for your situation. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, and physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice. Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol. To discuss the subject matter above further, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or us at 915-50-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Hoogeboom, T. J., Dronkers, J. J., Hulzebos, E. H., & van Meeteren, N. L. (2014). Merits of exercise therapy before and after major surgery. Current opinion in anaesthesiology, 27(2), 161–166. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0000000000000062 Madara, K. C., Marmon, A., Aljehani, M., Hunter-Giordano, A., Zeni, J., Jr., & Raisis, L. (2019). PROGRESSIVE REHABILITATION AFTER TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: A PILOT AND FEASIBILITY STUDY. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy, 14(4), 564–581.
In females, hernia symptoms are often smaller and deeper without a noticeable lump and can mimic gynecological issues, with misdiagnoses being common. Can knowing the risk factors and how female hernias are treated help women get relief? Female Hernia A hernia occurs when an internal structure pushes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall, the muscles, and the tissue covering the front of the torso. The more common include: - Groin hernia, known as an inguinal hernia.
- Upper thigh or femoral hernia.
However, a hernia can develop anywhere from the ribcage to the upper thigh. Hernias are less common in women, have different symptoms than in men, and are often misdiagnosed. Lower abdominal and pelvic hernias present differently in women than men, who typically have a visible bulge. Instead, female hernias tend to be smaller, deeper, and less noticeable. They can also cause chronic pelvic pressure or pain that can be mistaken for gynecological problems. Hernia Symptoms For a Woman Hernias in women tend to be smaller and deeper than male hernias, with no lump showing. Instead, female hernias can cause chronic, deep pelvic pain and occasional sharp, stabbing pain that comes on fast and lingers. (Köckerling F., Koch A., & Lorenz R. 2019) Hernia pain worsens with exercise, laughing, coughing, or straining to evacuate the bowels. The pain is often described as: - Dull
- Aching
- Pinching
- Sharp
- Shooting
- Burning
Inguinal hernia pain is usually felt at or above the groin and may radiate to the hip, lower back, vulva, or thigh. Many women find the pain increases during their menstrual cycle. The pain can also be exacerbated by any activity that generates extra pressure on the pelvic floor, including: - Prolonged sitting or standing.
- Bending
- Getting in or out of bed.
- Getting in or out of a car.
- Sexual intercourse
Emergency Hernias in the pelvic area are at risk of becoming incarcerated hernias. An incarcerated hernia occurs when a portion of the intestine or other abdominal tissue becomes trapped in the hernial sac, making it impossible to push it back into place. If this gets trapped or strangulated, it can cause tissue death. Strangulated hernias are a medical emergency. Symptoms include: - Deep red or purple tissues.
- The hernia bulge does not shrink when you lie down.
Other symptoms that warrant immediate medical attention include: (Johns Hopkins Medicine, 2025) - Worsening pain
- Bloating
- Difficulty with bowel movements
- Nausea
- Fever
- A fast, racing heartbeat.
Contact a healthcare provider or the emergency room if experiencing any of the above symptoms. Types Hernias can occur anywhere on the abdominal wall. They may be caused by: - Internal pressure, such as during pregnancy.
- A sports injury
- Tissue weakness
Hernias in the lower abdomen or groin are typically indirect inguinal hernias. The inguinal canal comprises multiple layers of muscles and fascia that the thin round ligament threads through. Other groin and pelvic hernias include: - A direct inguinal hernia
- A femoral hernia at the top of the inner thigh.
- An obturator hernia in the front upper thigh, although this type is rare.
Other common hernias in women are: - Incisional hernia - at the site of a surgical incision
- Umbilical hernia - around the belly button
- Ventral hernia - abdominal midline
Less common hernias include: - Hiatal hernia - diaphragm
- Perineal hernia - pelvic floor
Risk Factors Risk factors for developing a hernia include: (Johns Hopkins Medicine, 2025) - Obesity
- Frequent constipation
- Abdominal or pelvic surgery.
- Allergies with chronic sneezing.
- A chronic cough.
- Collagen defects or connective tissue disorders.
Pregnancy and repeated pregnancies are linked to an increased risk of hernia. Types that are more common in pregnancy include: - Umbilical hernia
- Ventral hernia
- Inguinal hernia
Umbilical hernias are the most common. However, only a small percentage of pregnant individuals get them. (Kulacoglu H. 2018) Diagnosis A hernia diagnosis is made with a physical examination and, if needed, imaging studies. Patients are asked to describe their symptoms precisely, where the pain is located, and any activities that exacerbate it. To check for a hernia, the healthcare provider will palpate for a hernia while the patient sits, stands, or coughs. Imaging tests can include: - Ultrasound
- CT scan
- Endoscopy - a camera is used to see inside the esophagus and stomach.
Misdiagnoses Female hernia symptoms can be vague, which often points healthcare providers in the wrong direction. Female hernias are commonly misdiagnosed as: (Köckerling F., Koch A., & Lorenz R. 2019) - Cysts in the reproductive organs
- Endometriosis
- Fibroid tumors
Treatment A small hernia that does not cause problems or pain may be treated with a wait-and-evaluate protocol. A hernia often worsens over time and could eventually require surgery. (University of Michigan Health, 2024) Self-care treatments include: Medical treatments usually start with conservative measures, including physical therapy, stretching, exercise, and rest. Physical therapists often use myofascial release techniques to relieve muscle spasms. Surgery may be needed to repair the weak area of the abdominal wall to relieve symptoms. (University of Michigan Health, 2024) Hernia repair surgery is typically performed as a laparoscopic surgery. (Köckerling F., Koch A., & Lorenz R. 2019) Most patients heal quickly from the surgery and can return to regular activities in a week or two. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Köckerling, F., Koch, A., & Lorenz, R. (2019). Groin Hernias in Women-A Review of the Literature. Frontiers in surgery, 6, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2019.00004 Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2025). How to tell if you have a hernia. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/how-to-tell-if-you-have-a-hernia Kulacoglu H. (2018). Umbilical Hernia Repair and Pregnancy: Before, during, after…. Frontiers in surgery, 5, 1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2018.00001 University of Michigan Health. (2024). Inguinal hernia: Should I have surgery now, or should I wait? https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/za1162 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2022). Sports hernia. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/sports-hernia-athletic-pubalgia/ Northeast Georgia Health System. (2022). Living with a hernia. Northeast Georgia Health System Improving the health of our community in all we do. https://www.nghs.com/2022/02/15/living-with-a-hernia
Can a knee brace relieve discomfort, provide support, and expedite recovery for individuals recovering from an injury or surgery? Knee Brace A knee brace is a medical device that supports and stabilizes the knee joint to help with pain and recovery after an injury or surgery. Many knee braces are made of various materials and offer a range of support levels. A healthcare provider or physical therapist can recommend the appropriate one for your condition and suggest the best one. Ask a healthcare provider if you're unsure, as wearing a knee brace correctly and for the recommended time is important for healing. They are generally safe. However, individuals with health conditions such as poor circulation should be cautious when using them and consult their healthcare provider. What They Do The knee joint comprises bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. A knee brace stabilizes these structures, preventing them from moving too much or too fast. Some braces redistribute the knee joint's weight, decreasing the force the knee absorbs. (American Academy of Family Physicians, 2020) Conditions A knee brace is used after surgery to aid in healing and following an injury. This can be: - Sprain
- Ligament injury
- Patellar/kneecap dislocation
They are also used to support the knee and relieve pain from some chronic conditions including: (Sprouse R. A., McLaughlin A. M., & Harris G. D. 2018) - Tendonitis
- Patellar tendinopathy
- Chondromalacia patellae
- Patellofemoral stress syndrome
- Medial knee osteoarthritis
Types Knee braces differ in function and support level. Some stabilize the knee, while others completely immobilize the joint. A healthcare provider and/or physical therapist will explain what support is needed and how to use it. They can also check the brace's fit and determine if adjustments or a different size are required. Most Commonly Used Prophylactic Brace Unloader - This brace helps rebalance the weight and shift the pressure on the knee joint to other parts of the leg, reducing pain. (American Academy of Family Physicians, 2020)
- A knee unloader is typically used to control discomfort due to inflammatory conditions like tendonitis and osteoarthritis.
Functional - This brace limits motion in the joint after an injury or prevents dislocation.
Bledsoe Brace - This brace has straps to wrap around the thigh and shin and support brackets on the inside and outside of the knee joint.
- A small mechanism locks the knee into full extension or allows the knee to bend a specific amount.
Knee Immobilizer - A knee immobilizer keeps the knee in one position.
- It is a long cloth brace that runs the length of the shin and thigh.
Knee Brace vs Knee Support A knee support or sleeve is usually a tight-fitting fabric garment. It provides compression to help reduce swelling and discomfort. A knee brace offers more support and can also be set to limit mobility. Wearing The Brace Individuals may need to wear a knee brace all day or only when performing specific tasks and operations. It depends on the individual and the condition the brace is being used for. Some may only need a knee brace during certain activities or a flare-up of pain. (Mayo Clinic, 2022) Wearing a brace for unnecessarily long periods can cause skin abrasion, joint stiffness, and muscle atrophy. (American Academy of Family Physicians, 2020) Conversely, neglecting to wear it can cause more susceptibility to injury or extend and or impair healing time. Ask a healthcare provider when you should and should not wear the brace. This could be when: - Sitting
- Walking
- Driving
- Sleeping
- Stretching
Contraindications Some medical conditions can make an individual susceptible to injury and adverse effects from wearing a knee brace. These include: (Holden, M. A. et al., 2021) - Poor circulation
- Superficial wounds on the knee
- Psoriasis
- Eczema
- Arterial insufficiency
- Severe varicose veins
- A history of thrombophlebitis
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic If you have one of these conditions, a healthcare provider will decide if a knee brace is safe. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to build optimal health and wellness solutions. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, prevent injury, and help mitigate issues through adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal problems. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References American Academy of Family Physicians. (2020). Knee Bracing: What Works? https://familydoctor.org/knee-bracing-what-works/ Sprouse, R. A., McLaughlin, A. M., & Harris, G. D. (2018). Braces and Splints for Common Musculoskeletal Conditions. American Family Physician, 98(10), 570–576. American Academy of Pediatrics. (2019). Knee pain: how to choose the right knee brace for your child. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/health-issues/injuries-emergencies/sports-injuries/Pages/Knee-Pain-and-braces.aspx Mayo Clinic. (2022). To brace or not to brace: What's the best answer? https://www.mayoclinichealthsystem.org/hometown-health/speaking-of-health/to-brace-or-not-to-brace#:~:text=If%20you%20have%20early%20onset%2C%20mild%20arthritis,below%20the%20knee%20for%20compression%20and%20comfort. Holden, M. A., Callaghan, M., Felson, D., Birrell, F., Nicholls, E., Jowett, S., Kigozi, J., McBeth, J., Borrelli, B., Jinks, C., Foster, N. E., Dziedzic, K., Mallen, C., Ingram, C., Sutton, A., Lawton, S., Halliday, N., Hartshorne, L., Williams, H., Browell, R., … Peat, G. (2021). Clinical and cost-effectiveness of bracing in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis management: protocol for a multicentre, primary care, randomised, parallel-group, superiority trial. BMJ open, 11(3), e048196. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-048196
Athletic individuals must train regularly, eat healthy, and rest properly to recover and perform their best. Is sleep different for athletes? Athletes and Sleep Physical activity is an important component of a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise increases longevity and can also reduce the risk of anxiety and depression and improve sleep (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024). When one area is lacking for athletes, overall performance can suffer. Evidence shows that more or extended sleep can benefit athletes and their recovery and performance. (Bird, Stephen P. 2013) Recommendations for athletes range between seven and nine hours nightly, and elite athletes are encouraged to get at least nine hours of sleep nightly and to treat sleep as much as athletic training and diet. Sleep is essential for overall health and well-being for both athletes and non-athletes. Everyone needs sleep to feel restored and function their best daily. (Richard J. Schwab, 2024) Other physical benefits include: Cardiovascular Recovery This allows the heart to rest and cells and tissue to be repaired. (MedlinePlus, 2017) This can help the body recover after physical exertion. As an individual progresses through the stages of sleep, the changes in heart rate and breathing throughout the night promote cardiovascular health (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, 2011) Illness Prevention The proper amount of sleep helps the body recover from illness. During sleep, the body produces cytokines/hormones that help the immune system fight off infections. These therapeutic effects are important for an athlete’s recovery and performance. Lack of Sleep Affects Performance Poor quality and quantity of sleep can lead to several negative effects. Sleep deprivation reduces the ability to react quickly and think clearly. A lack of sleep also increases irritability and risk for anxiety and depression. Sleep-deprived individuals are more likely to make poor decisions and take unnecessary risks. From a physical standpoint, a lack of sleep increases the risk for medical concerns, including type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, kidney disease, and stroke. When athletes do not receive adequate sleep, it can: Inhibit Ability - In a study of sleep-deprived male team athletes, average and total sprint times decreased. (Skein, M. et al., 2011)
Decrease Accuracy - In a study, male and female sleep-deprived tennis players had decreased serve accuracy by up to 53% compared to performance after normal sleep. (Reyner L. A. & Horne J. A. 2013)
Cause Quicker Exhaustion - A study of male runners and volleyball players found that both athletes exhausted faster after sleep deprivation. (Azboy O. & Kaygisiz Z. 2009)
Decrease Reaction Time Difficulty Learning and Decision Making - A lack of sleep negatively impacts cognitive skills and functions.
- Athletes can become distracted, and decisions like passing the ball or going for the smash can be difficult or made too late.
Increases Risk of Injury - Research on middle—and high-school athletes showed that chronic lack of sleep was associated with increased rates of injury. (Milewski M. D. et al., 2014)
Increases The Risk of Illness or Immunosuppression Athletic Sleep Hygiene Common components to sleep well include: Avoid alcohol and Caffeine - Before bedtime, these can interrupt sleep or lead to more disturbed sleep.
Have a Wind-Down Routine - Activities such as reading, bathing, or meditating can help the body relax and get ready for sleep.
Reduce Stressors - Not only do mental stressors affect sleep quality, but they also impact performance overall.
Create an Optimal Sleep Environment - A sleeping space should be dark and cool with little to no noise.
- The environment should be used only for sleep and sex.
No Electronics Before Bed - This includes TVs, cell phones, and computers.
- The blue light that these devices emit can affect circadian rhythm.
Don't Stay Awake In Bed - If you can’t fall asleep after 20 minutes of trying, get out of bed.
- Do a quiet activity in another space until you feel sleepy.
Avoid Overtraining - Keep a consistent training schedule so as not to overexert yourself.
Quick Naps - Keep naps brief. Naps should be longer than an hour and not after 3 p.m.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic The right bed and mattress contribute to overall health and can improve one's quality of life. Doctor Alexander Jimenez, DC, at Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic, says a healthy mattress can improve sleep, reduce pain, increase energy levels, and elevate mood. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, prevent injury, and help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). Benefits of Physical Activity. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/physical-activity-basics/benefits/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/physicalactivity/basics/pa-health/index.htm Bird, Stephen P. PhD. (2013). Sleep, Recovery, and Athletic Performance: A Brief Review and Recommendations. Strength and Conditioning Journal, 35(5), 43-47. https://doi.org/DOI: 10.1519/SSC.0b013e3182a62e2f Schwab, R. J. (2024). Overview of Sleep. Merck Manual Consumer Version. https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/brain-spinal-cord-and-nerve-disorders/sleep-disorders/overview-of-sleep National Library of Medicine. MedlinePlus. (2017). Healthy Sleep Also called: Sleep Hygeine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/healthysleep.html National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2011). Your guide to healthy sleep. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/resources/your-guide-healthy-sleep Skein, M., Duffield, R., Edge, J., Short, M. J., & Mündel, T. (2011). Intermittent-sprint performance and muscle glycogen after 30 h of sleep deprivation. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 43(7), 1301–1311. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31820abc5a Reyner, L. A., & Horne, J. A. (2013). Sleep restriction and serving accuracy in performance tennis players, and effects of caffeine. Physiology & behavior, 120, 93–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2013.07.002 Azboy, O., & Kaygisiz, Z. (2009). Effects of sleep deprivation on cardiorespiratory functions of the runners and volleyball players during rest and exercise. Acta physiologica Hungarica, 96(1), 29–36. https://doi.org/10.1556/APhysiol.96.2009.1.3 Taheri, M., & Arabameri, E. (2012). The effect of sleep deprivation on choice reaction time and anaerobic power of college student athletes. Asian journal of sports medicine, 3(1), 15–20. https://doi.org/10.5812/asjsm.34719 Milewski, M. D., Skaggs, D. L., Bishop, G. A., Pace, J. L., Ibrahim, D. A., Wren, T. A., & Barzdukas, A. (2014). Chronic lack of sleep is associated with increased sports injuries in adolescent athletes. Journal of pediatric orthopedics, 34(2), 129–133. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000151 Prather, A. A., Janicki-Deverts, D., Hall, M. H., & Cohen, S. (2015). Behaviorally Assessed Sleep and Susceptibility to the Common Cold. Sleep, 38(9), 1353–1359. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.4968
Yips are involuntary wrist muscle spasms that affect athletes. They are often associated with golf, baseball, and sports that involve swinging and throwing motions, such as bowling, darts, cricket, and others. Can understanding the information and causes help diagnose and find the right therapy or training? Yips Yips are involuntary wrist spasms that athletes experience. The term is also used to refer to performance anxiety without physical spasms. Researchers believe they are caused by muscle overuse that leads to dystonia (a condition that causes muscles to contract involuntarily), and combined with psychological factors like performance anxiety and overthinking, can make them worse. (Beacon Health Systems, 2024) Types Researchers have identified three types of yips that affect athletes (Clarke P. Sheffield D. and Akehurst S., 2020) Type I - Muscle spasms
- Freezing up/choking
Type II - Performance anxiety
- Psychological symptoms
Type III - Muscle spasms
- Performance anxiety
A study of over a hundred experienced athletes found that nearly 68% of archers and 40% of golfers experienced yips. (Clarke P., Sheffield D. and Akehurst S. 2020) Symptoms The most common symptom is muscle spasms, often in the hands and wrists. That’s why it is the most common among athletes who play sports that require precision hand and wrist movements. Yips affect fine motor skills. (Aoyama, T. et al., 2021) In addition to muscle spasms, symptoms can also include: (Beacon Health Systems, 2024) - Twitching
- Tremors
- Freezing up
- Psychological distress
Causes Healthcare providers, trainers, coaches, and researchers know that psychological and physical factors cause yips. Underlying physical causes include overusing wrist muscles, which leads to dystonia or involuntary muscle movements. Also known as task-specific dystonia, it can also affect individuals who engage in repetitive muscle movements, like factory and assembly line workers, store check-out clerks, musicians, etc. (Clarke P., Sheffield D., and Akehurst S. 2020). Performance anxiety and psychological stress can worsen dystonia. (Aoyama, T. et al., 2021) Athletes can become so focused on their movements that they overthink their actions and perform worse. Individuals who have anxiety, self-consciousness, or stress about a game or performance often find that their involuntary wrist spasms are worse. (Clarke P., Sheffield D. and Akehurst S. 2020) Increased Risk Yips are most common in athletes who use their hands and wrists for their sport and are likely to impact more experienced, competing, and older athletes. (Beacon Health Systems, 2024) They are more common in athletes focused on smaller movements or shorter distances. For example, golfers commonly experience involuntary wrist spasms when putting, and baseball players are likelier to experience them when throwing less than 20 meters. (Clarke P., Sheffield D. and Akehurst S. 2020) Diagnosis There is no official diagnosis for yips. However, a coach, athletic trainer, sports doctors, and others can observe the pattern of symptoms and behavior and provide an informed diagnosis. Treatment Identifying triggers is important as yips can be triggered by: (Aoyama, T. et al., 2021) - Psychological distress - anxiety and/or fear
- Abnormal sensations
- Symptoms of discomfort and pain
- Mechanical movement/motion adjustments or changes
Once trigger/s are identified, they can be addressed. Treatments that can help include: (Beacon Health Systems, 2024) Alternate Hand Positions - This can provide relief from dystonia and overthinking.
Using Different Equipment or Stabilizers - This allows the immobilization of certain muscles and the activation of different muscles.
Mindfulness - Reducing anxiety and distress can help relax the body.
- Practicing mindfulness before games or tournaments can help reduce psychological triggers.
Botox Injections - Botox injections can treat certain types of dystonia.
Sports Psychology - A sports psychologist is a healthcare provider who studies individual athletes' sports performance and how it affects their minds and skills.
- A sports psychologist can help individuals create a program that reduces stress or anxiety around games and performance.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic Yips are common among athletes. It is important to address the physical and psychological components to treat the condition. Talking with a coach or a sports psychologist, other athletes, and supporting staff like trainers can help you find a solution. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop an optimal health and wellness solution. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent injury. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Beacon Health Systems. (2024). Yips. https://www.beaconhealthsystem.org/library/diseases-and-conditions/yips/ Clarke, P., Sheffield, D., & Akehurst, S. (2020). Personality Predictors of Yips and Choking Susceptibility. Frontiers in psychology, 10, 2784. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02784 Aoyama, T., Ae, K., Souma, H., Miyata, K., Kajita, K., Kawamura, T., & Iwai, K. (2021). Difference in Personality Traits and Symptom Intensity According to the Trigger-Based Classification of Throwing Yips in Baseball Players. Frontiers in sports and active living, 3, 652792. https://doi.org/10.3389/fspor.2021.652792
For individuals dealing with finger injuries, which can occur from various causes, including overuse, jobs, sports, and more, can knowing the cause of finger pain help healthcare providers determine what steps to take for treatment? Finger Injuries Finger injuries are common and can range from minor to serious. (van Veenendaal L. M. et al., 2014) Symptoms can result from an acute injury, including broken fingers and sprains, or chronic conditions like arthritis. Fractures Finger fractures can vary and can be serious and lead to permanent damage, deformity, and loss of function if not treated properly. What is important is that fractures are appropriately diagnosed so the proper treatment plan can be initiated. Most finger fractures can be addressed with simple treatments, while others may require surgery. (Oetgen M. E., and Dodds S. D. 2008) Sprain and Dislocation Sprains and dislocations are common finger injuries. (Prucz R. B. and Friedrich J. B. 2015) Both damage the ligaments that support the finger joints. In more severe injuries, a dislocation can occur, necessitating the finger to be put back into place or reduced. Individuals with a sprain or dislocation often notice finger swelling or stiffness for months after the injury. Ligament Damage Some call this injury skier's or gamekeeper's thumb, which results from a specific type of thumb dislocation. Here, the ulnar collateral ligament of the thumb is damaged. This ligament helps keep the thumb stable and supports grip and hand strength. However, this type of ligament injury often requires surgery. (Christensen T. et al., 2016) Arthritis Arthritis causes damage to normal joint surfaces where two bones come together. Fingers are one of the most common locations where arthritis occurs. (Spies C. K. et al., 2018) Two types of arthritis commonly affect the fingers: osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis of The Thumb Arthritis of the thumb usually occurs at the joint where the thumb meets the wrist. This joint called the carpometacarpal/CMC joint, helps with gripping and pinching. Thumb arthritis is more common in women than men and increases in frequency over 40. (Deveza L. A. et al., 2017) Trigger Finger Trigger finger or stenosing tenosynovitis, is a common injury that causes pain and snapping of the fingers' tendons, resulting in a sensation of locking or catching when bending and straightening the digits. (Makkouk A. H. et al., 2008) Other symptoms include pain and stiffness in the fingers and thumb. Treatments can vary from observation, rest, splinting, injections, and surgery. Tendon Injuries Mallet finger A mallet finger is an injury to the tip of the finger. Usually, it occurs when the end of a straightened finger or thumb is hit, jamming the finger. After the injury, the individual may notice that they cannot fully straighten the tip of the finger. Treatment almost always uses a splint that has to stay on for about six weeks without removal. (Alla, S. R., Deal, N. D., and Dempsey, I. J. 2014) Very rarely is a surgical procedure necessary. Jersey Finger This is an injury to the finger flexor tendon. The flexor tendon pulls the finger into the palm when contracting the forearm flexor muscles. The injury occurs at the tip of the finger; typically, the tendon snaps back to the finger's base or into the palm. Ring Injuries Injuries to the finger while wearing wedding bands or other finger jewelry can lead to serious complications. Even minor injuries can have devastating complications if the severity of the injury is not recognized and addressed. If an injury occurs while wearing the jewelry and there is soft tissue damage, including blood circulation being cut off, immediate medical attention is necessary. Other Injuries Bruises The most common finger injury is caused by direct trauma to the skin and muscles. Symptoms include pain, swelling, tenderness, and discoloration of the skin. Cuts and Scrapes These can range from minor to more serious, such as injuries that cut through blood vessels, nerves, and tendons. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic After the initial inflammation and swelling have subsided, a doctor will recommend a treatment plan that usually involves physical therapy, self-performed physical rehabilitation, or supervision by a physical therapist or team. At Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic, our areas of practice include Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Wellness & Nutrition, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols. We focus on what works for you to relieve pain and restore function. If other treatment is needed, individuals will be referred to a clinic or physician best suited to their injury, condition, and/or ailment. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References van Veenendaal, L. M., de Klerk, G., & van der Velde, D. (2014). A painful finger as first sign of a malignancy. Geriatric orthopaedic surgery & rehabilitation, 5(1), 18–20. https://doi.org/10.1177/2151458514522125 Oetgen, M. E., & Dodds, S. D. (2008). Non-operative treatment of common finger injuries. Current reviews in musculoskeletal medicine, 1(2), 97–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-007-9014-z
Prucz, R. B., & Friedrich, J. B. (2015). Finger joint injuries. Clinics in sports medicine, 34(1), 99–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csm.2014.09.002
Christensen, T., Sarfani, S., Shin, A. Y., & Kakar, S. (2016). Long-Term Outcomes of Primary Repair of Chronic Thumb Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries. Hand (New York, N.Y.), 11(3), 303–309. https://doi.org/10.1177/1558944716628482 Spies, C. K., Langer, M., Hahn, P., Müller, L. P., & Unglaub, F. (2018). The Treatment of Primary Arthritis of the Finger and Thumb Joint. Deutsches Arzteblatt international, 115(16), 269–275. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2018.0269 Deveza, L. A., Hunter, D. J., Wajon, A., Bennell, K. L., Vicenzino, B., Hodges, P., Eyles, J. P., Jongs, R., Riordan, E. A., Duong, V., Min Oo, W., O'Connell, R., & Meneses, S. R. (2017). Efficacy of combined conservative therapies on clinical outcomes in patients with thumb base osteoarthritis: protocol for a randomised, controlled trial (COMBO). BMJ open, 7(1), e014498. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014498 Makkouk, A. H., Oetgen, M. E., Swigart, C. R., & Dodds, S. D. (2008). Trigger finger: etiology, evaluation, and treatment. Current reviews in musculoskeletal medicine, 1(2), 92–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-007-9012-1 Alla, S. R., Deal, N. D., & Dempsey, I. J. (2014). Current concepts: mallet finger. Hand (New York, N.Y.), 9(2), 138–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11552-014-9609-y
Individuals who engage in sports and physical activities that involve lunging forward while running or jumping can sustain a plantaris muscle injury. Can understanding the anatomy of the back of the leg and the symptoms help diagnose and treat plantar muscle injuries? Plantaris Muscle The plantaris muscle is a long, narrow muscle in the calf that runs along the back of the leg. It's part of the Triceps Surae, a group of muscles in the calf that, along with the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, makes up the bulk of the back of the leg. It is located in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg. Strains or tears of the plantaris muscle at the back of the leg can cause pain and swelling, similar to a calf strain or Achilles tendon tear. Individuals may feel immediate pain, cramping, and other symptoms. Anatomy The gastrocnemius and soleus muscles are the major muscles, with the soleus located deeper in the leg. Together, they form the Achilles tendon, which blends into a tendon in the back of the heel and attaches to the heel bone/calcaneus. When the calf muscles contract, they point the foot downward, propelling the body forward when walking, running, and sprinting. The plantaris muscle and tendon sit more or less in the center of the calf, between the two heads of the gastrocnemius. Around 7% to 20% of the population are born without plantaris muscles. There are variations, such as having a double- or triple-headed plantaris muscle. (Olewnik Ł. et al., 2020) However, individuals that do not have the muscle or have a variation have not been shown to affect long-term or short-term mobility. Symptoms Plantaris muscle ruptures are the most common injury and occur often during running or jumping. (Spang C. et al., 2016) Many who sustain this injury are athletes who have to lunge forward. Common symptoms include: - Sudden onset pain behind the calf.
- Swelling of the calf muscle.
- Muscle knots or myofascial trigger points of the calf muscle.
- Swelling and bruising in the back of the calf area.
- Cramping in the calf muscle.
- Spasm sensations of the calf muscle.
- Symptoms of a plantaris muscle strain are less severe, with the common signs being tightness and pain during and after physical activity.
Diagnosis Plantaris muscle tears differ from Achilles tendon tears because the foot can be pointed downward following the rupture, whereas an Achilles tear cannot. Plantaris ruptures can also be confused with a blood clot in the large veins of the calf, called deep vein thrombosis/DVT. (Rohilla S. et al., 2013) Tests like MRI or ultrasound can be performed to confirm or exclude a plantaris rupture. Both can be useful for verifying whether the injury is a strain or tear and identifying other possible causes of calf pain. Treatment Treatment is typically non-surgical. While the injuries can cause pain and disability, the symptoms almost always resolve with conservative treatments and therapies. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation are the first line used and may be all that is needed for a muscle strain. Short-term use of NSAIDs may be recommended for a strain or tear to reduce pain and inflammation. (Morelli K. M. et al., 2018) If the pain is profound or there is a tear, patients may require short-term immobilization or the use of a crutch for the pain to subside. With the assistance of a physical therapist, sports chiropractor, and athletic trainer, gradual increases in mobility and strength can be obtained. Symptoms usually gradually resolve over several weeks. Full recovery may take up to eight weeks, depending on the severity of the injury. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop customized treatment programs through an integrated approach to treating injuries and chronic pain syndromes, improving flexibility, mobility, and agility, relieving pain, and helping individuals return to normal activities. If other treatments are needed, Dr. Jimenez has teamed up with top surgeons, clinical specialists, medical researchers, and rehabilitation providers to provide the most effective treatments. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, don't hesitate to contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Olewnik, Ł., Zielinska, N., Karauda, P., Tubbs, R. S., & Polguj, M. (2020). A three-headed plantaris muscle: evidence that the plantaris is not a vestigial muscle? Surgical and radiologic anatomy: SRA, 42(10), 1189–1193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02478-8 Spang, C., Alfredson, H., Docking, S. I., Masci, L., & Andersson, G. (2016). The plantaris tendon: a narrative review focusing on anatomical features and clinical importance. The bone & joint journal, 98-B(10), 1312–1319. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.98B10.37939 Rohilla, S., Jain, N., & Yadav, R. (2013). Plantaris rupture: why is it important? BMJ case reports 2013, bcr2012007840. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2012-007840 Morelli, K. M., Brown, L. B., & Warren, G. L. (2018). Effect of NSAIDs on Recovery From Acute Skeletal Muscle Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. The American journal of sports medicine, 46(1), 224–233. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546517697957
Can athletic individuals with ACL injuries find relief through non-surgical treatments to restore knee mobility? Introduction The body’s lower extremities help the individuals to be mobile but also help stabilize the body’s upper weight. From the hips to the feet, many people are on their feet and using every muscle group to allow functionality. Athletic individuals use their lower extremities to do various physical activities and are susceptible to injuries. An ACL injury is one of the most common and feared injuries that can impact an athletic person’s performance. These types of injuries affect the knees of the individual and can make a person feel miserable. However, numerous surgical and non-surgical treatments can help the recovery process of an ACL injury while helping the individual restore their motion to their lower extremities. Today’s article looks at what an ACL injury is, how it affects the knees, and how non-surgical treatments can help restore knee mobility from ACL injuries. We discuss with certified associated medical providers who consolidate our patients’ information to assess ACL injuries affecting their mobility. We also inform and guide patients while asking their associated medical provider intricate questions to integrate and provide them with numerous non-surgical treatments to be incorporated into their personalized treatment plan. Dr. Jimenez, D.C., includes this information as an academic service. Disclaimer. What Is An ACL Injury? Do you feel aches or pains around your knees after a long exercise regime? Do you feel or hear a loud popping sensation in your knees? Or do you experience pain and swelling affecting your ability to be mobile? Many of these pain-like scenarios are correlated with ACL injuries, that is amongst the most common and feared injuries for athletic individuals and non-athletic individuals. However, we must look at the ACL itself to better understand ACL injuries. The ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) plays an important role as it helps with knee joint stabilization, prevents excessive forward movements from the tibia (shin bone), and limits rotational knee movements. (Yoo & Marappa-Ganeshan, 2024) This ligament is one of the most injured structures affecting athletic performance. ACL injuries and tears can lead to many individuals having knee instability and an increased risk of future knee osteoarthritis. (Atik, 2024) This is because ACL injuries typically occur during physical activities involving sudden stops, jumps, or directional impacts to the knees. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
What are the healing times of common sports injuries for athletes and individuals who engage in recreational sports activities? Healing Times for Sports Injuries Healing time from sports injuries depends on various factors, such as the location and extent of the injury and the health of the skin, joints, tendons, muscles, and bones. It is also important to take the time to recuperate or not rush back into physical sports activities before the bones or tissues have fully healed. To prevent re-injury, ensure the doctor clears health before returning to sports or strenuous physical activity. According to CDC research, an average of 8.6 million sports and recreation-related injuries occur annually. (Sheu, Y., Chen, L. H., and Hedegaard, H. 2016) However, most sports injuries are superficial or caused by low-grade strains or sprains; at least 20% of injuries result from bone fractures or more serious injuries. Bone fractures take longer than sprains or strains, and complete tendon or muscle ruptures can take months before one can fully return to activities. Individuals in decent physical shape with no underlying illness or impairment, here is what they can expect when recovering from the following sports injuries: Bone Fractures In sports, the highest rate of bone fractures occurs with football and contact sports. Most are centered around the lower extremities but can involve the neck and shoulder blades, arms, and ribs. Simple Fractures - Depends on the individual's age, health, type, and location.
- Generally, takes at least six weeks to heal.
Compound Fractures - In this case, a bone is broken in several places.
- It may require surgery to stabilize the bone.
- Healing time can take up to eight months.
Fractured Clavicle/Collarbone - It may require the immobilization of the shoulder and upper arm.
- It can take five to ten weeks to heal fully.
- Fractured fingers or toes can heal in three to five weeks.
Fractured Ribs - Part of the treatment plan includes breathing exercises.
- Painkillers may be needed short term.
- Usually, it takes around six weeks to heal.
Neck Fractures - It may involve any one of the seven neck vertebrae.
- A neck brace or a halo device that is screwed into the skull for stability may be used.
- It can take up to six weeks to heal.
Sprains and Strains According to the CDC report, sprains and strains account for 41.4% of all sports injuries. (Sheu, Y., Chen, L. H., and Hedegaard, H. 2016) - A sprain is the stretching or tearing of ligaments or the tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect two bones at a joint.
- A strain is the overstretching or tearing of muscles or tendons.
Sprained Ankles - It can heal in five days if there are no complications.
- Severe sprains involving torn or ruptured tendons can take three to six weeks to heal.
Calf Strains - Classified as grade 1 - a mild strain can heal in two weeks.
- A grade 3 - severe strain may require three months or more to heal completely.
- The use of calf suppression sleeves can expedite the recovery of strains and sprains in the lower leg.
Acute Neck Strain - A tackle, impact, fall, quick shifting, or whipping motion can cause a whiplash injury.
- Healing time can take a couple of weeks to six weeks.
Other Injuries ACL Tears - Involving the anterior cruciate ligament.
- Usually, it requires months of recuperation and rehabilitation, depending on several factors, including the type of sports activity.
- Full recovery from surgery takes six to 12 months.
- Without surgery, there is no specific timeline for rehabilitation.
Achilles Tendon Ruptures - It is a serious injury.
- These occur when the tendon is either partially or completely torn.
- Individuals will more than likely require surgery.
- Recovery time is four to six months.
Cuts and Lacerations - Depends on the depth and location of the injury.
- It can take anywhere from a week to a month to heal.
- If there are no accompanying injuries, stitches can be removed within two to three weeks.
- If a deep cut requires stitches, more time is necessary.
Mild Contusions/Bruises - Are caused by a trauma to the skin, causing blood vessels to break.
- In most cases, a contusion will take five to seven days to heal.
Shoulder Separations - When treated properly, it usually takes around two weeks of rest and recovery before the patient returns to activity.
Multidisciplinary Treatment After the initial inflammation and swelling have subsided, a doctor will recommend a treatment plan that usually involves physical therapy, self-performed physical rehabilitation, or supervision by a physical therapist or team. Fortunately, athletes and individuals who regularly exercise tend to have a faster healing time because they are in top physical shape, and their cardiovascular system provides a stronger blood supply that speeds up the healing process. At El Paso’s Chiropractic Rehabilitation Clinic & Integrated Medicine Center, we passionately focus on treating patients' injuries and chronic pain syndromes. We focus on improving ability through flexibility, mobility, and agility programs tailored to the individual. We use in-person and virtual health coaching and comprehensive care plans to ensure every patient’s personalized care and wellness outcomes. Our providers use an integrated approach to create personalized care plans that include Functional Medicine, Acupuncture, Electro-Acupuncture, and Sports Medicine principles. Our goal is to relieve pain naturally by restoring health and function to the body. If the chiropractor feels the individual needs other treatment, they will be referred to a clinic or physician best suited for them. Dr. Jimenez has teamed up with the top surgeons, clinical specialists, medical researchers, and premier rehabilitation providers to provide the top clinical treatments for our community. Providing highly noninvasive protocols is our priority, and our personalized patient-based clinical insight is what we provide. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Sheu, Y., Chen, L. H., & Hedegaard, H. (2016). Sports- and Recreation-related Injury Episodes in the United States, 2011-2014. National Health Statistics Reports, (99), 1–12.
For athletes and sports enthusiasts, a torn triceps can be a serious injury. Can knowing their symptoms, causes, risk factors, and potential complications help healthcare providers develop an effective treatment plan? Torn Triceps Injury The triceps is the muscle on the back of the upper arm that allows the elbow to straighten. Fortunately, triceps tears are uncommon, but they can be serious. The injury affects men more often than women and usually occurs from trauma, sports, and/or exercise activities. Depending on the extent and severity of the injury, a torn triceps injury can require splinting, physical therapy, and possibly surgery to regain movement and strength. Recovery after a triceps tear typically lasts around six months. (The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. 2021) Anatomy The triceps brachii muscle, or triceps, runs along the back of the upper arm. It is named tri- because it has three heads - the long, medial, and lateral head. (Sendic G. 2023) The triceps originates at the shoulder and attaches to the shoulder blade/scapula and upper arm bone/humerus. At the bottom, it attaches to the point of the elbow. This is the bone on the pinky side of the forearm, known as the ulna. The triceps cause movement at the shoulder and the elbow joint. At the shoulder, it performs extension or backward movement of the arm and adduction or moving the arm toward the body. The main function of this muscle is at the elbow, where it performs extension or straightening of the elbow. The triceps work the opposite of the biceps muscle on the front of the upper arm, which conducts flexion or bending of the elbow. Triceps Tear Tears can occur anywhere along the length of a muscle or tendon, which is the structure that attaches the muscle to the bones. Triceps tears commonly occur in the tendon connecting the triceps to the back of the elbow. Muscle and tendon tears are graded from 1 to 3 based on severity. (Alberto Grassi et al., 2016) Grade 1 Mild - These small tears cause pain that worsens with movement.
- There is some swelling, bruising, and minimal loss of function.
Grade 2 Moderate - These tears are larger and have moderate swelling and bruising.
- The fibers are partially torn and stretched.
- Up to 50% loss of function.
Grade 3 Severe - This is the worst type of tear, where the muscle or tendon is completely torn.
- These injuries cause severe pain and disability.
Symptoms Triceps tears cause immediate pain in the back of the elbow and upper arm that worsens when trying to move the elbow. Individuals might also feel and/or hear a popping or tearing sensation. There will be swelling, and the skin will likely be red and/or bruised. With a partial tear, the arm will feel weak. If there is a complete tear, there will be significant weakness when straightening the elbow. Individuals may also notice a lump on the back of their arm where the muscles have contracted and knotted together. Causes Triceps tears usually occur during trauma, when the muscle is contracted and an external force pushes the elbow into a bent position. (Kyle Casadei et al., 2020) One of the most common causes is by falling on an outstretched arm. Triceps tears also occur during sports activities like: - Throwing a baseball
- Blocking in a football game
- Gymnastics
- Boxing
- When a player falls and lands on their arm.
- Tears can also happen when using heavy weights during triceps-targeted exercises, such as the bench press.
- Tears can also occur from direct trauma to the muscle, like a motor vehicle accident, but are less common.
Long-Term Triceps tears can develop over time as a result of tendonitis. This condition usually occurs from repetitive use of the triceps muscle during activities like manual labor or exercise. Triceps tendonitis is sometimes referred to as weightlifter's elbow. (Orthopedic & Spine Center. N.D.) The strain on tendons causes tiny tears that the body typically heals. However, if more strain is placed on the tendon than it can keep up with, the small tears can begin to grow. Risk Factors Risk factors can increase the risk of a triceps tear. Underlying medical conditions can weaken tendons, increasing the risk of injury, and can include: (Tony Mangano et al., 2015) - Diabetes
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Lupus
- Xanthoma - fatty deposits of cholesterol under the skin.
- Hemangioendothelioma - cancerous or noncancerous tumors caused by abnormal growth of blood vessel cells.
- Chronic kidney failure
- Chronic tendonitis or bursitis in the elbow.
- Individuals who have had cortisone shots in the tendon.
- Individuals using anabolic steroids.
Triceps tears tend to occur more commonly in males between 30 and 50. (Ortho Bullets. 2022) This comes from participating in activities like football, weightlifting, bodybuilding, and manual labor, which also increases the risk of injury. Treatment Treatment depends on which part of the triceps is affected and the extent of the damage. It may only need resting for a few weeks, physical therapy, or require surgery. Nonsurgical Partial tears in the triceps that involve less than 50% of the tendon can often be treated without surgery. (Mehmet Demirhan, Ali Ersen 2016) Initial treatment includes: - Splinting the elbow with a slight bend for four to six weeks allows the injured tissue to heal. (Ortho Bullets. 2022)
- During this time, ice can be applied to the area for 15 to 20 minutes several times daily to help decrease pain and swelling.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications/NSAIDs - Aleve, Advil, and Bayer can help reduce inflammation.
- Other over-the-counter medications like Tylenol can help decrease the pain.
- Once the splint is removed, physical therapy will help restore movement and strength in the elbow.
- Full movement is expected to return within 12 weeks, but full strength will not return until six to nine months after the injury. (Mehmet Demirhan, Ali Ersen 2016)
Surgery Triceps tendon tears that involve more than 50% of the tendon require surgery. In some cases, however, surgery may still be recommended for tears smaller than 50% if the individual has a physically demanding job or plans to resume playing sports at a high level. Tears in the muscle belly or area where the muscle and tendon join are typically sewn back together. If the tendon is no longer attached to the bone, it is screwed back on. Recovery and physical therapy after surgery depend on the specific surgeon's protocols. In general, individuals will spend a couple of weeks in a brace. Around four weeks after surgery, individuals will be able to start moving the elbow again. However, they won't be able to start doing heavy lifting for four to six months. (Ortho Bullets. 2022) (Mehmet Demirhan, Ali Ersen 2016) Complications Complications can occur after triceps repair, whether there was surgery or not. For example, individuals may have problems regaining full elbow extension or straightening. They are also at a higher risk of re-rupture if they try to use the arm before it's fully healed. (Mehmet Demirhan, Ali Ersen 2016) General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies that are available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. (2021). Distal triceps repair: clinical care guideline. (Medicine, Issue. https://medicine.osu.edu/-/media/files/medicine/departments/sports-medicine/medical-professionals/shoulder-and-elbow/distaltricepsrepair.pdf? Sendic G. Kenhub. (2023). Triceps brachii muscle Kenhub. https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/triceps-brachii-muscle Grassi, A., Quaglia, A., Canata, G. L., & Zaffagnini, S. (2016). An update on the grading of muscle injuries: a narrative review from clinical to comprehensive systems. Joints, 4(1), 39–46. https://doi.org/10.11138/jts/2016.4.1.039 Casadei, K., Kiel, J., & Freidl, M. (2020). Triceps Tendon Injuries. Current sports medicine reports, 19(9), 367–372. https://doi.org/10.1249/JSR.0000000000000749 Orthopedic & Spine Center. (N.D.). Triceps tendonitis or weightlifter's elbow. Resource Center. https://www.osc-ortho.com/resources/elbow-pain/triceps-tendonitis-or-weightlifters-elbow/ Mangano, T., Cerruti, P., Repetto, I., Trentini, R., Giovale, M., & Franchin, F. (2015). Chronic Tendonopathy as a Unique Cause of Non Traumatic Triceps Tendon Rupture in a (Risk Factors Free) Bodybuilder: A Case Report. Journal of orthopaedic case reports, 5(1), 58–61. https://doi.org/10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.257 Ortho Bullets. (2022). Triceps rupture https://www.orthobullets.com/shoulder-and-elbow/3071/triceps-rupture Demirhan, M., & Ersen, A. (2017). Distal triceps ruptures. EFORT open reviews, 1(6), 255–259. https://doi.org/10.1302/2058-5241.1.000038
Knee injuries can present in physically active individuals that lift weights. Can understanding the types of weightlifting knee injuries help in prevention? Weightlifting Knee Injuries Weight training is very safe for the knees as regular weight training can improve knee strength and prevent injury as long as the correct form is followed. For Individuals with knee injuries from other activities, incorrect weight-training exercises could worsen the injury. (Ulrika Aasa et al., 2017) As well as, sudden twisting movements, poor alignment, and pre-existing injuries can increase the risk of worsening or creating further injuries. (Hagen Hartmann et al, 2013) The body and the knees are designed to support vertical forces on the joints. Common Injuries Weightlifting knee injuries occur as the knee joints endure a wide range of stresses and strains. In weight training, the ligaments that attach to the complex bone system of the knee joint can be damaged by incorrect movements, overloading the weight, and increasing the weight too soon. These injuries can result in pain, swelling, and immobility that can range from minor to severe, from a sprain or a slight tear to a complete tear in serious cases. Anterior Cruciate Ligament - ACL - Injury This ligament attaches the thigh's femur bone to the lower leg's shin bone/tibia and controls excessive rotation or extension of the knee joint. (American Academy of Family Physicians. 2024) - Anterior means front.
- ACL injuries are seen mostly in athletes but can happen to anybody.
- Severe damage to the ACL usually means surgical reconstruction and up to 12 months of rehabilitation.
- When weightlifting, try to avoid twisting knee movements, intentionally or accidentally, under excessive load.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament - PCL - Injury - The PCL connects the femur and tibia at different points to the ACL.
- It controls any backward motion of the tibia at the joint.
- Injuries occur most with high-impact forces as a result of accidents and sometimes in activities where forceful trauma to the knee occurs.
Medial Collateral Ligament - MCL - Injury - This ligament maintains the knee from bending too far to the inside/medially.
- Injuries mostly occur from impact to the outside of the knee or from accidental bodyweight force on the leg that bends at an unusual angle.
Lateral Collateral Ligament - LCL - Injury - This ligament connects the smaller bone of the lower leg/fibula to the femur.
- It is opposite to the MCL.
- It maintains excessive outward movement.
- LCL injuries occur when a force pushes the knee out.
Cartilage Injury - Cartilage prevents bones from rubbing together and cushions impact forces.
- Knee menisci are cartilage that cushions the knee joints inside and outside.
- Other types of cartilage protect the thigh and shin bones.
- When cartilage gets torn or damaged, surgery may be required.
Tendonitis - Aggravated and overused knee tendons can lead to weightlifting knee injuries.
- A related injury known as iliotibial band syndrome/ITB causes pain to the outside of the knee, usually in runners, but it can occur from overuse.
- Rest, stretching, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medication are a common treatment plan.
- Individuals should consult a physical therapist for pain lasting longer than two weeks. (Simeon Mellinger, Grace Anne Neurohr 2019)
Osteoarthritis - As the body ages, normal wear and tear can cause the development of osteoarthritis of the knee joints. (Jeffrey B. Driban et al., 2017)
- The condition causes the cartilage to deteriorate and bones to rub together, resulting in pain and stiffness.
Prevention - Individuals can minimize their risk of weightlifting knee injuries and pain by following their doctor's and personal trainers' recommendations.
- Individuals with an existing knee injury should follow their doctor's or physical therapist's recommendations.
- A knee sleeve can keep the muscles and joints secure, providing protection and support.
- Stretching the leg and knee muscles can maintain joint flexibility.
- Avoid sudden lateral movements.
- Possible recommendations can include:
Avoiding Certain Exercises - Isolation exercises like leg curls, standing, or on a bench, as well as using the leg extension machine, can stress the knee.
Deep Squat Training Research shows that the deep squat can protect against lower leg injury if the knee is healthy. However, this is when done with proper technique, under expert supervision, and with a gradual progressive load. (Hagen Hartmann et al, 2013) Individuals should talk to their doctor before beginning a new exercise routine. A personal trainer can provide training in learning the proper technique and weightlifting form. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Aasa, U., Svartholm, I., Andersson, F., & Berglund, L. (2017). Injuries among weightlifters and powerlifters: a systematic review. British journal of sports medicine, 51(4), 211–219. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2016-096037 Hartmann, H., Wirth, K., & Klusemann, M. (2013). Analysis of the load on the knee joint and vertebral column with changes in squatting depth and weight load. Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.), 43(10), 993–1008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-013-0073-6 American Academy of Family Physicians. ACL injury. (2024). ACL injury (Diseases and Conditions, Issue. https://familydoctor.org/condition/acl-injuries/ Mellinger, S., & Neurohr, G. A. (2019). Evidence based treatment options for common knee injuries in runners. Annals of translational medicine, 7(Suppl 7), S249. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.04.08 Driban, J. B., Hootman, J. M., Sitler, M. R., Harris, K. P., & Cattano, N. M. (2017). Is Participation in Certain Sports Associated With Knee Osteoarthritis? A Systematic Review. Journal of athletic training, 52(6), 497–506. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-50.2.08
For individuals into sports, fitness enthusiasts, and those that engage in physical activities, musculoskeletal injuries are common. Can using ice tape help during the initial or acute phase of injury decrease inflammation and swelling to expedite recovery and return to activities sooner? Ice Tape After a musculoskeletal injury, individuals are recommended to follow the R.I.C.E. method to help reduce swelling and inflammation. R.I.C.E. is the acronym for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. (Michigan Medicine. University of Michigan. 2023) The cold helps to decrease pain, lower tissue temperature, and decrease swelling around the site of the injury. By controlling the inflammation with ice and compression early after injury, individuals can maintain the appropriate range of motion and mobility around the injured body part. (Jon E. Block. 2010) There are different ways to apply ice to an injury. - Store-bought ice bags and cold packs.
- Soaking the injured body part in a cold whirlpool or tub.
- Making reusable ice packs.
- A compression bandage can be used together with the ice.
Ice Tape is a compression bandage that provides cold therapy all at once. After an injury, applying it can help decrease the pain and swelling during the acute inflammatory phase of healing. (Matthew J. Kraeutler et al., 2015) How The Tape Works The tape is a flexible bandage that is infused with therapeutic cooling gel. When applied to an injured body part and exposed to air, the gel activates, generating a cold sensation around the area. The therapeutic medicinal effect can last five to six hours. Combined with a flexible bandage, it provides ice therapy and compression. The ice tape can be used straight out of the package but can also be stored in the refrigerator to increase the cold effect. Depending on the maker's instructions, the tape should not be stored in the freezer as this can make it too hard to wrap around the injured area. Advantages The benefits include the following: Easy to Use - The product is easy to use.
- Take out the tape, and start wrapping it around the injured body part.
Fasteners Not Required - The wrap sticks to itself, so the tape stays in place without using clips or fasteners.
Easy to Cut - The standard roll is 48 inches long by 2 inches wide.
- Most injuries require enough to wrap around the injured area.
- Scissors cut the exact amount needed, and store the rest in the resealable bag.
Reusable - After 15 to 20 minutes of application, the product can be easily removed, rolled up, stored in the bag, and used again.
- The tape can be used multiple times.
- The tape begins to lose its cooling quality after several uses.
Portable - The tape does not need to be placed in a cooler when traveling.
- It is easily portable and perfect for a quick ice and compression application immediately after an injury.
- It can decrease pain and inflammation and kept at the workplace.
Disadvantages A few disadvantages include the following: Chemical Odor - The gel on the flexible wrap can have a medicine odor.
- It is not quite as powerful smelling as pain creams, but the chemical odor could bother some individuals.
Might Not Be Cold Enough - The tape works for immediate pain relief and inflammation, but it may not get cold enough for the user when applied right from the package at room temperature.
- However, it can be placed in a refrigerator to increase the coldness and may provide a more therapeutic cooling effect, especially for those dealing with tendinitis or bursitis.
Stickiness Could Be Distracting - The tape could be a bit sticky for some.
- This sticky factor can be a minor annoyance.
- However, it just feels sticky when being applied.
- A couple of flecks of the gel may get left behind when removed.
- The ice tape can also stick to clothing.
For individuals looking for a quick, on-the-go cooling therapy for injured or aching body parts, ice tape may be an option. It could be good to have on hand to provide cooling compression if a minor injury occurs while participating in athletics or physical activities and relief for overuse or repetitive strain injuries. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research studies or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Michigan Medicine. University of Michigan. Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE). Block J. E. (2010). Cold and compression in the management of musculoskeletal injuries and orthopedic operative procedures: a narrative review. Open access journal of sports medicine, 1, 105–113. https://doi.org/10.2147/oajsm.s11102 Kraeutler, M. J., Reynolds, K. A., Long, C., & McCarty, E. C. (2015). Compressive cryotherapy versus ice-a prospective, randomized study on postoperative pain in patients undergoing arthroscopic rotator cuff repair or subacromial decompression. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery, 24(6), 854–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2015.02.004
|



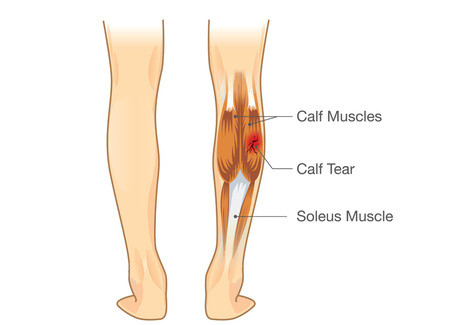


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...



























The slender plantaris is the topic of this case study, outlining a debilitating injury known as "plantaris tendon rupture." For Answers to any questions you may have please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900