Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
?
Today, 1:48 AM
|
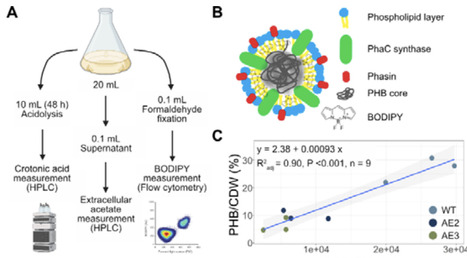
Acetate can be a sustainable and renewable carbon source which holds significant promise for biotechnological production but is underutilized industrially due to limited microbial efficiency. Vibrio natriegens, recognized for exceptionally fast growth rates, represents a compelling host for developing efficient acetate-based bioprocesses. In this study, adaptive laboratory evolution significantly enhanced V. natriegens′ ability to grow on acetate as the sole carbon source, achieving an 89% increase in growth rate. Genetic and transcriptomic analyses revealed key adaptations improving acetate uptake and metabolism via increased salt tolerance, boosted Pta/AckA pathway activity, and rewired quorum sensing. Further metabolic engineering and bioprocess optimization enabled the evolved strain to reach high cell densities and efficiently convert acetate into the bioplastic poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), with productivities up to 0.27 g/L/h and PHB accumulation reaching 45.66% of cell biomass. These advances position V. natriegens as a highly promising microbial platform for sustainable, scalable, and cost-effective biomanufacturing using acetate as green feedstock.

|
Scooped by
?
Today, 1:35 AM
|
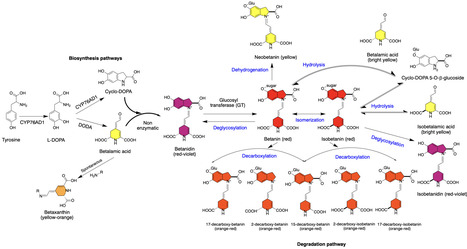
Genetically encoded enzymatic and fluorescence-based reporters have become powerful tools to monitor and visualize diverse cellular processes. Despite their vast utility, some of these reporters require invasive analysis, while others need costly equipment and/or exogenous substrates. Recently, a new class of visual reporters have been developed based on the synthesis of betalains, which are either red or yellow pigments that produce outputs visible to the naked eye without the need for exogenous substrates. Since 2020, the betalain-based RUBY reporter has been used to visually track various cellular processes. Here, we explore the applications of RUBY in basic research and agriculture, discuss its limitations, and highlight its potential as an educational tool for teaching fundamental concepts in cell and molecular biology.

|
Scooped by
?
Today, 1:26 AM
|
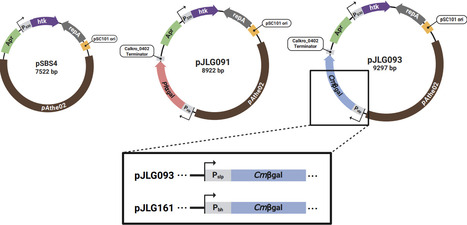
Thermophilic anaerobic organisms, particularly species that can naturally degrade lignocellulosic biomass, show great promise for next generation bioprocessing. This has led to the development of nascent genetic systems to metabolically engineer these non-model organisms. However, a major challenge remains a lack of reliable reporter systems compatible with the combination of thermophilic and anaerobic growth conditions. Additionally, native glycoside hydrolases in these organisms limit the usefulness of traditional glycosidic enzyme reporters (e.g. LacZ) because of the native background activity present on para-nitrophenyl glucoside substrates. Here we describe the development of a straightforward and robust enzymatic reporter system that overcomes these challenges in Anaerocellum (f. Caldicellulosiruptor) bescii, an anaerobic, extremely thermophilic (Topt ~78 °C), lignocellulolytic bacterium. Our method is based on heterologous expression of hyperthermophilic archaeal galactosidases: an α-galactosidase from Pyroccous furiosus (Pfαgal), and a β-galactosidase from Caldivirga maquilingensis (Cmβgal). We show that these reporters produce strong, orthogonal signals on colorimetric substrates at high temperatures (≥90 °C) that eliminate background activity from endogenous galactosidases. We then demonstrate the capability of Cmβgal, the stronger of the two reporters, to distinguish differences in levels of expression between A. bescii promoter sequences, which we verify through qRT-PCR. With its high signal to noise ratio and ease of use, this reporter system offers a reliable method for assessing protein expression in anaerobic thermophilic organisms, opening doors to improved genetic tools and metabolic engineering applications for industrial biotechnology.

|
Scooped by
?
Today, 1:16 AM
|
The consistency of the associations between the breast microbiome and breast cancer (BC) across various studies remains uncertain. Publicly accessible data sets from five BC studies, comprising 16S rRNA gene sequencing data from 161 BC tissues (BC_tissue), 195 BC adjacent non-cancerous tissues (BC_adjacent), and 451 normal breast tissues (normal_tissue), were retrieved from the European Nucleotide Archive. Overall, the microbial composition across the three breast tissue statuses was predominantly characterized by the phyla Proteobacteria and Firmicutes, a distribution likely attributable to the fatty acid-rich environment of the breast tissue. Comparative analysis revealed that the relative abundances of the genera Cutibacterium and Burkholderia were significantly increased in both BC_adjacent and normal_tissue compared to BC_tissue. This observation suggested a potential anticancer effect associated with these genera. Our analysis revealed a significant reduction in the abundance of Cutibacterium and Cutibacterium acnes in BC tissues, which served as specific diagnostic features for BC. This finding was corroborated by our in-house data set (n = 28), which yielded similar conclusions. Subsequent in vitro and in vivo experiments verified the potential anti-tumor effects of C. acnes supernatant in BC. In conclusion, our study highlighted the predictive capacity of microbial biomarkers in the onset of BC. Notably, specific bacterial species within the breast microbiome, such as Cutibacterium and C. acnes, exhibited potential as diagnostic markers for BC and may contribute significantly to antitumor activity. Nevertheless, the molecular mechanisms governing their interactions with cancer cells are not yet fully understood, necessitating further research to investigate their viability as targets for tumor prevention.

|
Scooped by
?
Today, 1:01 AM
|
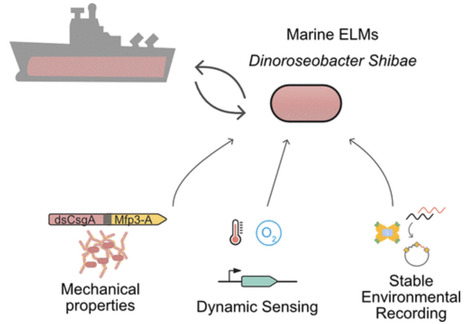
Marine bacteria offer a promising alternative for developing Engineered Living Materials (ELMs) tailored to marine applications. We engineered Dinoroseobacter shibae to increase its surface-associated growth and develop biosensors for ocean environment monitoring. By fusing the endogenous extracellular matrix amyloidogenic protein CsgA with mussel foot proteins, we significantly increased D. shibae biofilm formation. Additionally, D. shibae was engineered to express the tyrosinase enzyme to further enhance microbial attachment through post-translational modifications of tyrosine residues. By exploiting D. shibae‘s natural genetic resources, two environmental biosensors were created to detect temperature and oxygen. These biosensors were coupled with a CRISPR-based recording system to store transient gene expression in stable DNA arrays, enabling long-term environmental monitoring. These engineered strains highlight D. shibae‘s potential in advancing marine microbiome engineering for innovative biofilm applications, including the development of natural, self-renewing biological adhesives, environmental sensors, and “sentinel” cells equipped with CRISPR-recording technology to capture and store environmental signals.

|
Scooped by
?
Today, 12:06 AM
|
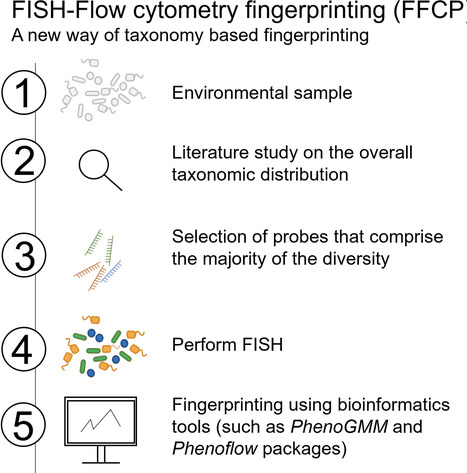
Flow cytometry is a powerful tool to monitor microbial communities, as it allows tracking both changes in the subpopulations and cell numbers at high throughput and a low sample cost. This information can be combined in a phenotypic fingerprint that can be leveraged for diversity analysis. However, as isogenic individuals can manifest phenotypic diversity, for example, due to differing physiological state and phenotypic plasticity, combining the phenotypic information with taxonomic information adds an extra dimension for describing the dynamics of a microbial community. In this research, taxonomic information was incorporated in the microbial fingerprint through fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) at a single-cell level. To validate this concept and explore its versatility, two ecosystems with different micro-biodiversity were considered. In the first environment, marine bacteria were monitored for plastic biodegradation in a trickling filter, and in the second, an in vitro simulated human gut microbiome was followed over time. Samples were prepared using different (staining) methods, including FISH, and beta diversity analysis was used to evaluate the level of distinction between differently treated groups in both environments. As a reference to correlate increased distinction with the incorporation of taxonomic information, 16S rRNA gene sequencing was used. Finally, a predictive algorithm was trained to correctly classify samples in the differently treated groups. The results showed that the implementation of FISH in flow cytometry provides more information on a single-cell level to answer specific scientific questions, like distinguishing between phenotypically similar communities or following a specific taxonomic group over time.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 11:35 PM
|
Numerous important environments harbor low levels of microbial biomass, including certain human tissues, the atmosphere, plant seeds, treated drinking water, hyper-arid soils and the deep subsurface, with some environments lacking resident microbes altogether. These low microbial biomass environments pose unique challenges for standard DNA-based sequencing approaches, as the inevitability of contamination from external sources becomes a critical concern when working near the limits of detection. Likewise, lower-biomass samples can be disproportionately impacted by cross-contamination and practices suitable for handling higher-biomass samples may produce misleading results when applied to lower microbial biomass samples. This Consensus Statement outlines strategies to reduce contamination and cross-contamination, focusing on marker gene and metagenomic analyses. We also provide minimal standards for reporting contamination information and removal workflows. Considerations must be made at every study stage, from sample collection and handling through data analysis and reporting to reduce and identify contaminants. We urge researchers to adopt these recommendations when designing, implementing and reporting microbiome studies, especially those conducted in low-biomass systems. In this Consensus Statement, the authors outline strategies for processing, analysing and interpreting low-biomass microbiome samples, and provide recommendations to minimize contaminants.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 1:10 PM
|
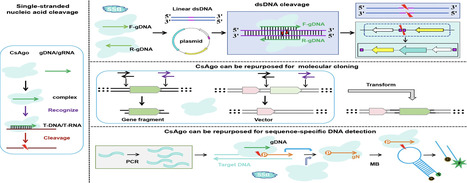
Eukaryotic Argonautes (eAgos) have traditionally been characterized by their ability to utilize RNA guides to identify RNA targets, thereby engaging in post-transcriptional gene silencing pathways. While some eAgos have been demonstrated to use DNA guides for RNA cleavage, the ability of eAgos to cleave DNA targets remains unclear. In this study, we characterized CsAgo, an eAgo protein derived from thermophilic eukaryote Chaetomiumsp. MPI-CAGE-AT-0009, demonstrating a novel ability to cleave both DNA and RNA targets in vitro. Guided by short single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or RNA, CsAgo exhibits robust RNA cleavage activity at 20–90°C in vitro. CsAgo can effectively cleave ssDNA guided by RNA guides at 20–50°C in vitro. Notably, CsAgo can utilize DNA guides to effectively cleave ssDNA, plasmid double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), and linear dsDNA at ≥80°C in vitro. Based on its ability to cleave dsDNA at high temperatures, CsAgo demonstrates versatility and efficacy in simplifying routine cloning workflows. Additionally, we have developed a CsAgo-based nucleic acid detection method based on a Pyrococcus furiosus Ago-mediated nucleic acid detection method, which exhibits a high sensitivity of six copies/reaction. These results suggest that eAgos include that, in theory, can be utilized for potential DNA-targeting applications. This not only enhances our understanding of eAgos but also expands the toolkit for DNA manipulation.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 12:48 PM
|
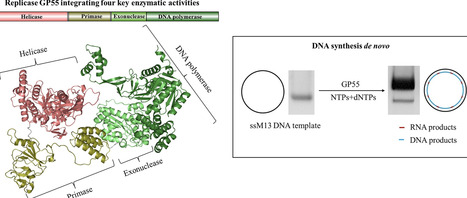
DNA replication is a fundamental process in all living organisms. As the most diverse and abundant biological entities on Earth, bacteriophages may utilize unconventional methods for genome replication. In this study, we identified a novel DNA replicase, GP55, from lactococcal phage 1706. GP55 comprises a helicase domain, a distinctive archaeo-eukaryotic primase domain, and a family B DNA polymerase domain, collectively exhibiting helicase, primase, and DNA polymerase activities, along with intrinsic 3′–5′ exonuclease activity. Notably, the helicase activity of GP55 is UTP/dTTP-dependent rather than ATP-dependent and facilitates strand displacement during DNA synthesis. GP55 exhibits a unique primase activity, recognizing specific but less stringent DNA sequences and preferring GTP for the initiation of RNA primer synthesis. Additionally, a newly identified α-helix domain, composed of two pairs of parallel α-helices, was found to be essential for its primase activity. The multiple activities enable GP55 to efficiently synthesize DNA de novo in the presence of dNTPs and NTPs. This study reveals a concise strategy employed by bacteriophages for genome replication using multifunctional replicases.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 11:30 AM
|
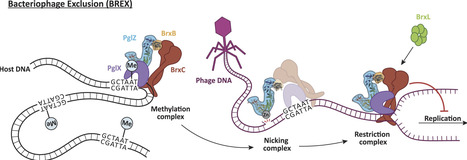
BREX (Bacteriophage Exclusion) systems, identified through shared identity with Pgl (Phage Growth Limitation) systems, are a widespread, highly diverse group of phage defence systems found throughout bacteria and archaea. The varied BREX Types harbor multiple protein subunits (between four and eight) and all encode a conserved putative phosphatase, PglZ, and an equally conserved, putative ATPase, BrxC. Almost all BREX systems also contain a site-specific methyltransferase, PglX. Despite having determined the structure and fundamental biophysical and biochemical behaviours of several BREX factors (including the PglX methyltransferase, the BrxL effector, the BrxA DNA-binding protein, and a commonly-associated transcriptional regulator, BrxR), the mechanism by which BREX impedes phage replication remains largely undetermined. In this study, we identified a stable BREX sub-complex of PglZ:BrxB, generated and validated a structural model of that protein complex, and assessed the biochemical activity of PglZ from BREX, revealing it to be a metal-dependent nuclease. PglZ can cleave cyclic oligonucleotides, linear oligonucleotides, plasmid DNA and both non-modified and modified linear phage genomes. PglZ nuclease activity has no obvious role in BREX-dependent methylation, but does contribute to BREX phage defence. BrxB binding does not impact PglZ nuclease activity. These data contribute to our growing understanding of BREX phage defence.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 11:12 AM
|
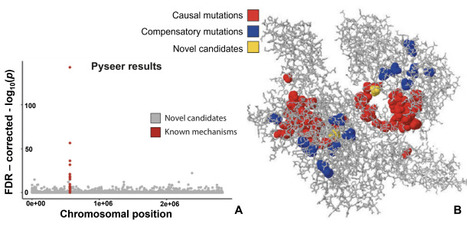
How can we identify causal genetic mechanisms governing bacterial traits? Initial efforts entrusting machine learning models to handle the task of predicting phenotype from genotype yield high accuracy scores. However, attempts to extract meaningful interpretations from the predictive models are found to be corrupted by falsely identified “causal” features. Relying solely on pattern recognition and correlations is unreliable, significantly so in bacterial genomics settings where high-dimensionality and spurious associations are the norm. Though it is not yet clear whether we can overcome this hurdle, significant efforts are being made towards discovering potential high-risk bacterial genetic variants. In view of this, we set up open problems surrounding phenotype prediction from bacterial whole-genome datasets and extending those approaches to learning causal effects, and discuss challenges that impact the reliability of a machine’s decision-making when faced with datasets of this nature. We identify major sources of non-injectivity in the formulation of the genotype-to-phenotype mapping function—linkage-disequilibrium, limited sampling, information loss in representations, unmeasured confounders and observational noise—and analyse their implications for machine learning applications. Using a collection of 4,140 Staphylococcus aureus isolates, we illustrate challenges surrounding the defined open problems.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 11:01 AM
|
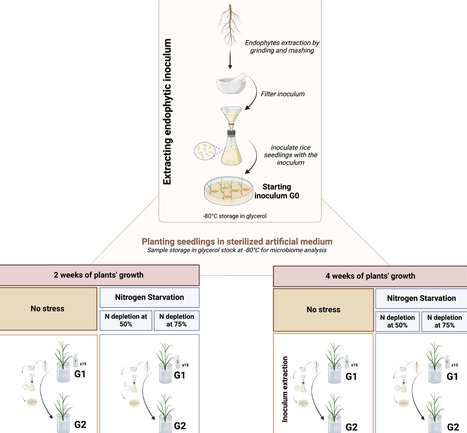
Microorganisms live in close association with plants, forming ecological interaction webs and providing beneficial traits such as nutrition, growth, and tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses. Via the rhizosphere, plants recruit bacteria which colonize internal plant tissues, creating a spatial gradient between the rhizosphere and the endosphere. This study presents a high throughput in planta endophyte enrichment scheme designed for the identification of 'super'-endophytic bacteria which can serially colonise the rice root endosphere. Oryza sativa (rice) plants were grown in bulk soil, and endophytes were then recovered from roots. The recovered endophyte mixture was used as inoculum for the first generation of rice plantlets, which were then grown under no stress or nitrogen (N) depletion. The total endophytic community was then purified and used as a second inoculum for a new set of plants; this procedure was repeated for four generations. Enrichment patterns of root bacterial endophytes were observed, such as Kosakonia in the non-stressed plants and Ferrovibrio in plants grown under nitrogen starvation. This enrichment method proved to be suitable for the identification of endophytes which can efficiently colonise the root endosphere.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 10:50 AM
|
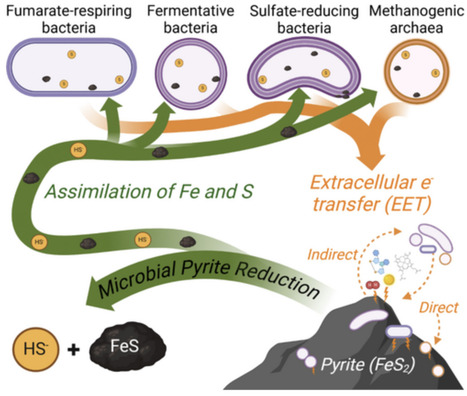
Pyrite, the most abundant iron sulfide mineral in the Earth's crust, has traditionally been considered as a sink for iron and sulfur in the absence of oxygen. Recent research, however, has shown that anaerobic methanogenic archaea can reductively dissolve pyrite and assimilate its products as sources of iron and sulfur. This study explores whether other anaerobic bacteria, including fermentative, nitrate-, iron oxide-, fumarate-, and sulfate-respiring bacteria, can also reduce pyrite and use its dissolution products as sources of iron and sulfur. Results indicate that heterotrophic bacteria respiring fumarate or sulfate, or fermenting organic carbon, can reduce pyrite and assimilate released iron and sulfur. In contrast, nitrate- or iron oxide-respiring cells did not reduce pyrite, suggesting that microbial pyrite reduction is metabolism-specific. All strains capable of reducing pyrite could also use mackinawite as an iron and sulfur source. With the exception of fermentative Bacteroides, strains did not require direct contact with pyrite to reduce the mineral, indicating extracellular electron transfer via electron shuttles. These findings expand the known diversity of microbial groups capable of pyrite reduction and highlight the mineral's lability in various anaerobic environments, with potential implications for the biogeochemical cycles of iron, sulfur, carbon, and oxygen.
|

|
Scooped by
?
Today, 1:44 AM
|
Biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) provides half of global new nitrogen annually and plays an important role in biodiversity patterns and global biological carbon uptake processes. BNF rates accelerate with warming, with known implications for ecological functioning, yet the strength of this temperature sensitivity and its context dependence are not well understood. Here we synthesize 70 controlled experimental tests of the acute temperature dependence of nitrogen fixation rates and demonstrate that BNF rates accelerate with temperature in a remarkably consistent manner across biological systems. BNF temperature dependence is also consistent across levels of biological organization from enzyme to community, mirroring scaling of metabolic temperature dependence across levels of organization for respiration, photosynthesis and methane production. This analysis provides the first evidence of general, scalable effects of temperature on nitrogen fixation rates, which can be used to better predict shifts in coupled carbon-nitrogen systems with global change.

|
Scooped by
?
Today, 1:28 AM
|
The gut microbiota serves as a critical interface between lifestyle factors and host physiology. Despite extensive research on individual domains including diet, sleep, and exercise, an integrated understanding of their synergistic effects on microbial communities remains incomplete. This knowledge gap limits our ability to develop targeted microbiome-based interventions for metabolic and immune-related disorders. To address this gap, we conducted a comprehensive evaluation of peer-reviewed literature from 2000 to present, identified through systematic searches of PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus using key terms related to gut microbiota and lifestyle interventions. Our analysis focused on studies incorporating microbiome profiling techniques, controlled lifestyle interventions, and multi-omics data integration. The review prioritized mechanistic insights from both clinical and preclinical investigations while critically assessing methodological approaches across the field. High-fiber dietary patterns consistently promoted the abundance of beneficial, short-chain fatty acid-producing bacteria, though with notable inter-individual variation. Circadian rhythm disruption was associated with reduced microbial diversity and expansion of pro-inflammatory bacterial taxa, paralleling increases in systemic inflammation markers. Athletic populations demonstrated unique microbial signatures characterized by enhanced metabolic potential, with distinct taxonomic profiles emerging across different sport disciplines. This work synthesizes current evidence into a novel framework for understanding lifestyle-microbiota interactions, while identifying key challenges in study design and data interpretation. We propose standardized methodological approaches for future investigations and outline translational strategies for personalized microbiota modulation. These insights advance the potential for targeted microbial interventions to optimize metabolic and immune health outcomes.

|
Scooped by
?
Today, 1:22 AM
|
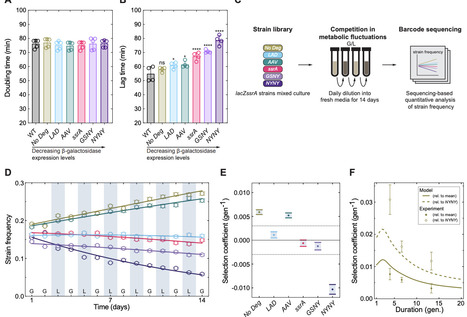
Gene regulatory networks enable bacteria to sense and respond in fluctuating environments and to control gene expression levels in constant conditions. Despite substantial advances in understanding their molecular biology, the evolutionary conditions that select for and maintain gene regulatory networks have remained elusive. Here, we investigate the evolutionary costs and benefits of gene regulation under metabolic fluctuations, and identify distinct fluctuating environments that select for or against gene regulation. Using barcode sequencing to track strain frequencies over time, we compete strains with perturbed expression dynamics to assess the strength of selection on gene expression levels. We reveal that expression levels can be shaped to enhance phenotypic memory of past environmental states, reducing the impact of lag phases on long-term population growth. By independently perturbing the ability to sense the environment and the control of expression levels, we discover sign epistasis between sensing and control in a gene regulatory network, and identify its molecular underpinnings. Due to this epistatic interaction, maintenance of sensing in gene regulation enhances the ability of evolution to tune gene expression in a fluctuating environment. Our work establishes a new basis for understanding how gene regulatory networks evolve in fluctuating environments.

|
Scooped by
?
Today, 1:12 AM
|
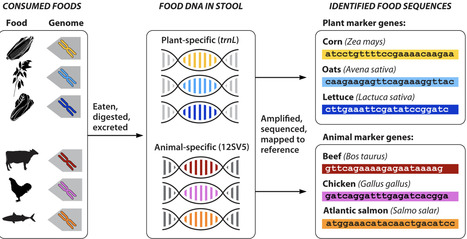
Diet plays a pivotal role in human health and disease. Yet, nutrition studies have long relied on self-report methods for collecting dietary intake data despite known limitations. Although new technologies for dietary intake assessment and biomarker identification are in development, the integration of genomics has been limited. DNA metabarcoding, a method that identifies many taxa at once using a short region of DNA, has recently been adapted for use in stool samples from free-living humans. This process, called FoodSeq, provides an objective way to determine the foods people eat. FoodSeq has numerous advantages over self-report methods, is a necessary complement to other methodological innovations in dietary intake assessment, and holds considerable promise for application on an epidemiologic scale, enabling more robust analysis of global dietary patterns.

|
Scooped by
?
Today, 12:12 AM
|
Nature has evolved an exquisite yet limited set of chemical reactions that underpin the function of all living organisms. By contrast, the field of synthetic organic chemistry can access reactivity not observed in nature, and integration of these abiotic reactions within living systems offers an elegant solution to the sustainable synthesis of many industrial chemicals from renewable feedstocks. Here we report a biocompatible Lossen rearrangement that is catalysed by phosphate in the bacterium Escherichia coli for the transformation of activated acyl hydroxamates to primary amine-containing metabolites in living cells. Through auxotroph rescue, we demonstrate how this new-to-nature reaction can be used to control microbial growth and chemistry by generating the essential metabolite para-aminobenzoic acid. The Lossen rearrangement substrate can also be synthesized from polyethylene terephthalate and applied to whole-cell biocatalytic reactions and fermentations generating industrial small molecules (including the drug paracetamol), paving the way for a general strategy to bioremediate and upcycle plastic waste in native and engineered biological systems. Biocompatible chemistry merges chemo-catalytic reactions with cellular metabolism for sustainable small-molecule synthesis. Now a biocompatible Lossen rearrangement has been demonstrated to control bacterial cell growth and chemistry and applied to the remediation and upcycling of polyethylene terephthalate plastic waste in whole-cell reactions and fermentations to produce valuable industrial chemicals, including the drug paracetamol.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 11:51 PM
|
Plant synthetic biology holds great promise for engineering plants to meet future demands. Genetic circuits are being designed, built, and tested in plants to demonstrate proof of concept. However, developing these components in monocots, which the world relies on for grain, lags behind dicot models, such as Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana. Here, we show the successful adaptation of a ligand-inducible sensor to activate an endogenous anthocyanin pathway in the C4 monocot model Setaria viridis. We identify two transcription factors sufficient to induce endogenous anthocyanin production in S. viridis protoplasts and whole plants in a constitutive or ligand-inducible manner. We also test multiple ligands to overcome physical barriers to ligand uptake, identifying triamcinolone acetonide (TA) as a highly potent inducer of this system. Using hyperspectral imaging and a discriminative target characterization method in a near-remote configuration, we can non-destructively detect anthocyanin production in leaves in response to ligands. This work demonstrates the use of inducible expression systems in monocots to manipulate endogenous pathways, stimulating plants to overproduce secondary metabolites with value to human health. Applying inducible pigmentation coupled with sensitive detection algorithms could enable crop plants to report on the status of field contamination or detect undesirable chemicals impacting agriculture, ushering in an era of agriculture-based sensor systems.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 11:08 PM
|
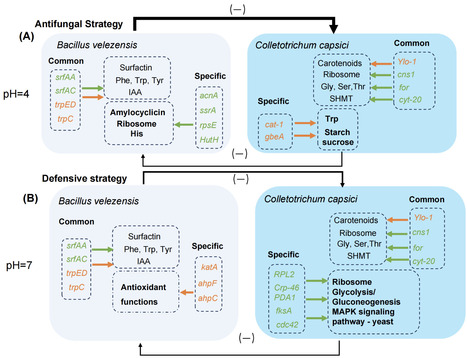
Colletotrichum capsici is the etiological agent of Capsicum anthracnose. Bacillus velezensis has traditionally been recognized as an effective biocontrol agent; however, its efficacy decreases due to soil acidification. In this study, we domesticated Bacillus velezensis XY40-1 along an acid resistance gradient, resulting in a strain capable of growth at pH 4, and might adapt to acidic environments by regulating genes related to spore formation. Notably, the domesticated Bacillus velezensis XY40-1 exhibits significant antagonistic activity against Colletotrichum capsici in acidic dual cultures and effectively reduces the disease index in Capsicum. The domesticated strain employs a direct antifungal strategy under acidic conditions, with the production of amylocyclicin, regulated by acnA, potentially serving as a primary mechanism through which Bacillus velezensis combats Colletotrichum capsici. Conversely, under neutral conditions, domesticated Bacillus velezensis focuses on bolstering its defense mechanisms by increasing the expression of katA, ahpF, and ahpC genes to detoxify peroxides. In addition, a dual RNA-Seq analysis comprehensively investigated the acid tolerance mechanisms and defensive responses of B. velezensis and the pathogenic mechanisms of C. capsici, providing a foundation for the practical application of B. velezensis as a biocontrol agent. These findings offer important insights into the impact of soil acidification on plant disease suppression and contribute to the development of sustainable agricultural practices.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 1:02 PM
|
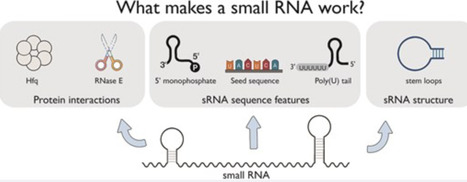
Bacterial small RNAs (sRNA) are key regulators of gene expression, interacting with target messenger RNAs (mRNAs) through imperfect base pairing. Unlike other non-coding RNAs such as microRNAs and PIWI-interacting RNAs, bacterial sRNAs exhibit significant sequence and structural diversity, complicating functional predictions. Recent high-throughput profiling of the sRNA interactome has accentuated this problem by revealing a highly complex network of sRNA interactions. It is clear that there is an incredible diversity of sRNA interactions with different RNA classes in vivo, including different interaction modes with mRNAs. In this review, we attempt to summarize the known sequence and structural features that contribute to sRNA function in bacteria. As many of these features drive recruitment of protein partners, we necessarily focus on interactions with chaperones and ribonucleases, the best studied being Hfq and RNase E. Where possible, we have included examples outside this well-studied system as diversity and rule breaking appear to be central themes of sRNA biology. Understanding the sequences and structures that drive sRNA function will enhance our ability to predict regulatory outcomes, and this may inform the development of effective RNA therapeutics that are inspired by bacterial sRNA mechanisms.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 11:36 AM
|
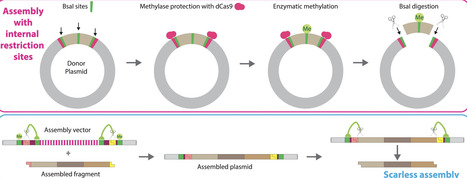
Type IIS restriction enzyme-mediated DNA assembly is efficient but has sequence constraints and can result in unwanted sequence scars. To overcome these drawbacks, we developed UniClo, a type IIS restriction enzyme-mediated method for universal and flexible DNA assembly. This is achieved through a combination of vector engineering, DNA methylation using recombinant methylases, and steric blockade using CRISPR–dCas9 technology to regulate this methylation. Type IIS restriction enzyme sites within fragments to be assembled are methylated using recombinant methylases, while the fragment-flanking outer sites are protected from methylation by a recombinant dCas9–sgRNA complex. During the subsequent assembly reaction, only the protected flanking sites are cut as only they are unmethylated. Fragments are correctly assembled, despite containing internal sites for the single type IIS restriction enzyme used for the one-pot assembly. The assembled plasmid can be used as a donor plasmid in a subsequent assembly round with the same type IIS restriction enzyme and the assembly vector engineering ensures removal of potential scars by a trimming process. This simplifies assembly design and only three vectors are required for any multi-round assembly. These vectors all use the same pair of overhangs. UniClo provides a simple scarless approach for hierarchical assembly of any sequence and has wide potential application.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 11:20 AM
|
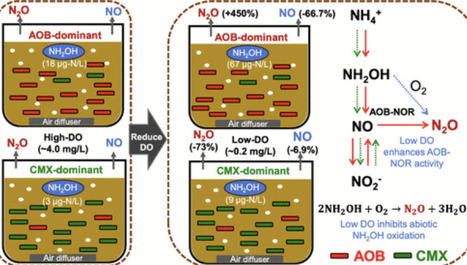
Nitrification significantly contributes to N2O emissions in wastewater treatment, typically enhanced at low dissolved oxygen (DO). The present study revealed that low DO (∼0.2 mg/L) enhanced the N2O emission factor (EF) from nitrification by 4.5 times in canonical ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB)-dominated sludge, while it reduced N2O EF by 73% in comammox Nitrospira-dominated sludge. During nitrification, the accumulation of intermediate NH2OH in AOB-dominant sludge was much higher and increased more significantly by low DO (from 0.018 to 0.067 mg-N/L) compared to comammox Nitrospira-dominant sludge (from 0.004 to 0.009 mg-N/L). In AOB-dominant sludge, the increased NH2OH and upregulated AOB-NOR gene at low DO promoted NO reduction, thus increasing N2O EF while simultaneously decreasing NO emission. In the comammox Nitrospira-dominant sludge, N2O was primarily produced via abiotic pathways. Further investigation found that N2O production decreased significantly under low DO in inactivated sludge and pure water with the sole addition of NH2OH, suggesting that low DO inhibited N2O formation via abiotic NH2OH oxidation. Therefore, in comammox Nitrospira-dominant sludge, low DO decreased N2O production primarily due to the inhibition of low DO to N2O formation via abiotic NH2OH oxidation and the low NH2OH accumulation. These results imply that enriching comammox Nitrospira in the wastewater treatment process can ensure stably low N2O emissions regardless of the variations in DO.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 11:09 AM
|
Recombinant proteins play a crucial role in both fundamental research and biotechnology. In the laboratory, recombinant proteins are used in a myriad of ways, including to label cells, localize proteins and isolate complexes. In the clinic, antibody-based therapeutics can dramatically increase cancer survival rates, while virus-like particles (VLPs) are being developed as next-generation vaccines. These innovations have escalated demands for biopharmaceutical recombinant proteins. However, in traditional systems (e.g. mammalian and microbial) the expression of recombinant proteins can be prohibitively expensive. One sustainable, low-cost solution is to use a microalgal-based expression system, such as Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Phaeodactylum tricornutum, Chlorella sp., Haematococcus pluvialis or Nannochloropsis gaditana. Tools for microalgal protein expression are developing rapidly. Yet our understanding of recombinant protein expression and purification in microalgal systems lags that of traditional systems. Here, we review the impact of commonly used affinity and epitope tags (e.g. Polyhistidine-tag, Strep-tag II, HA-tag and FLAG-tag) on recombinant protein detection, purification and biofunctionality in microalgae. Additionally, we review fluorescent protein tags (such as GFP, mVenus, DsRed and mCherry) and protease cleavage sites, including ‘self-cleaving’ 2A peptides. Finally, we provide guidance on experimental design to enhance the likelihood of successfully expressing recombinant proteins in microalgae.

|
Scooped by
?
June 23, 10:55 AM
|
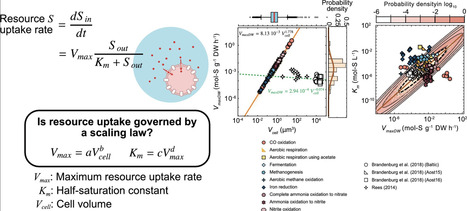
Microbial growth is often described in terms of resource uptake rates, making the understanding and parameterisation of these rate-limiting processes critical for microbial modelling. In phototrophic plankton, theoretical studies suggest that nutrient uptake is limited by mechanistic processes involving membrane transporters, and it has been observed that the cell-specific maximum resource uptake rate (Vmax) follows a power-law relationship with cell size, as well as a trade-off between Vmax and the half-saturation constant (Km). These constraints may also apply to chemotrophic microorganisms; however, many datasets lack direct cell-size measurements. We therefore leveraged the assumption that prokaryotic cell sizes, Vmax, and Km each follow log-normal distributions, drawing parallels with established phytoplankton scaling laws. Our analysis suggests that chemotrophic organisms generally exhibit higher maximum uptake rate per dry weight (VmaxDW) and Km values than phototrophs, and that VmaxDW and Km are not strongly correlated when all chemotroph data are combined. Furthermore, the Bayesian-derived exponents for VmaxDW and Km exceeded those expected from allometric scaling relationships based on the membrane-transport capacity observed for phototrophs, implying that a range of additional factors likely affect observed kinetic parameters.
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...