Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
December 20, 2021 4:44 AM
|
Chloé Quignot receives the GGMM 2021 award
Chloé Quignot was awarded "Prix 2021 du Groupe Graphisme et Modélisation Moléculaire (GGMM)" for her PhD thesis in the group "Molecular Assemblies and Genome Integrity". Chloé Quignot received the GGMM prize for her thesis entitled "Modelling Protein interfaces using evolutionary information", carried out at the I2BC, B3S department, in the Molecular Assemblies and Genome Integrity team and co-supervised by Jessica Andreani and Raphael Guerois. Chloé presented her thesis work at the GGMM-SFCi conference held in Lille in October 2021.
The Graphical and Molecular Modeling Group (GGMM) is a learned society that brings together a large part of the French community whose activity is dedicated to, or involves, the use of molecular modeling. The GGMM prize is awarded every two years for original work in molecular modeling, bioinformatics, chemoinformatics and numerical simulation in the field of structural biology and pharmacology. Congratulations, Chloé! more information here.

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
December 20, 2021 4:32 AM
|
New arrivals on I2BC PIM facility
We are very pleased to announce that Magali Noiray arrived this summer to work on the PIM platform.This arrival coincides with the commissioning of BLI, a new machine dedicated to the study of macromolecular interactions. Magali Noiray has a solid expertise in the field of the study of macromolecular interactions (SPR, ITC, DSC...) and worked for 10 years on the interaction platform of Chatenay Malabry (Pharmacy Faculty) specialized in nanomedicines and small molecules. She joined the PIM platform this summer to strengthen the team and to work with Magali Aumont. In parallel, thanks to funding obtained last year from the Ile de France region , we have obtained and put into operation a new device to replace the SPR. Based on Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI), the fluidics-free ForteBio’s Octet® RED96 system is a multi-functional, label-free, real-time analysis instrument. It is ideal for rapidly screening protein-protein, protein-nucleic acids and protein-small molecule interactions. The Octet RED96 system can be used for a wide range of analyses. System provides up to 8-channel quantitation and kinetic measurements of molecules greater than 150 Da, compatibility with 96-well plates and cooling for temperature control down to 15°C. Team Protein Interaction

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
December 20, 2021 4:03 AM
|
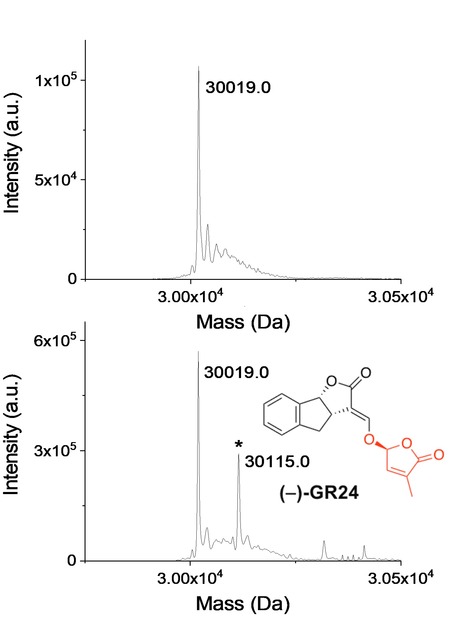
The Physcomitrium (Physcomitrella) patens PpKAI2L receptors for strigolactones and related compounds function via MAX2-dependent and independent pathways
Mass spectrometry was used to investigate the role of PpKAI2L protein in the moss Physicomitrium patens as receptor of a class of phytohormones , striptolactones, in the moss Physcomitrium patens and to compare this processes with the more known vascular plants. Results on Physcomitrium highlight surprising evolutive innovations from vascular plant. Abstract from The Plant Clell article: Strigolactones (SL) make up a novel class of phytohormones that are found across the whole land plant lineage. In vascular plants, the main hormonal role of SL is the repression of shoot axillary branching. However, SL are also a major symbiotic signal, granting the plant increased access to the nutrients and water contained in the rhizosphere. These two functions of SL led to the hypothesis that these molecules have been instrumental at the time of land colonization by plants, approximately 450 million years ago. Studying SL biosynthesis and signaling in the bryophyte Physcomitrium patens (P. patens, a non-vascular plant), and comparing these processes with the available knowledge in vascular plants, enables to investigate the evolution of SL cellular pathways in land plants. In angiosperms, the perception of SLs relies on a receptor called D14 (encoded by the same gene family as KAI2) along with the F-box protein MAX2. In moss, Max2 is not required for the SL response although it possesses 13 KAI2-like genes (PpKAI2L). An unusual aspect of SL perception is that the D14 protein is both a receptor and an enzyme that cleaves its substrate (and covalently binds part of the SL) in a signaling mechanism that is still under debate. To further investigate whether PpKAI2L proteins play roles as receptors of SLs and related compounds, we examined the covalent attachment of the artificial SL GR24 isomers to the PpKAI2L proteins by mass spectrometry (MS). Analyses revealed 96 Da increments (corresponding to the D ring mass) when AtKAI2 and PpKAI2L were incubated with GR24 isomers indicating that moss PpKAI2L proteins, like vascular plant receptors, covalently link GR24 enantiomers. As SL signaling is not conserved in P. patens, it appears that the known SL signaling pathway results from a vascular plants specific innovation. Likewise, SL response in P. patens would be the product of a convergent evolution. Therefore, the question as to how P. patens transduces the SL signal, downstream of perception by specific PpKAI2L proteins, remains open. This work was conducted by a team of INRAE (Sandrine Bonhomme) in collaboration with other teams of french institute (ICSN) and laboratory (LBPV). Mass spectrometry analyses were performed at the I2BC proteomics platform. More information here. Contact person: David Cornu

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
December 20, 2021 3:44 AM
|
Intergenic ORFs as elementary structural modules of de novo gene birth and protein evolution
Intergenic ORFs of S. cerevisiae encode the elementary building bricks of protein structures and can provide the raw material for de novo gene birth and protein evolution. The noncoding genome plays an important role in de novo gene birth and in the emergence of genetic novelty. Nevertheless, how noncoding sequences’ properties could promote the birth of novel genes and shape the evolution and the structural diversity of proteins remains unclear. In this work, in collaboration with Namy's team, IMPMC and DSIMB lab, we show that the Intergenic ORFs (Open Reading Frames) of S. cerevisiae encode the elementary building bricks of protein structures and can provide the raw material for de novo gene birth and protein evolution. In particular, we show that the noncoding genome contain a vast amount of Intergenic ORFs encoding foldable peptides. The latter can serve as starting points for de novo gene emergence or be integrated into pre-existing proteins, thus contributing to protein modularity and participating in protein evolution. Then, we investigated the early stages of de novo gene birth by reconstructing the ancestral sequences of 70 yeast de novo genes and characterized the sequence and structural properties of intergenic ORFs with a strong translation signal. This enabled us to highlight sequence and structural factors determining de novo gene emergence. In particular, we showed that ancestral intergenic ORFs and highly translated intergenic ORFs are enriched in ORFs encoding peptides with a strong folding potential, thereby giving a central role to protein foldability in the emergence of new genes. Finally, we showed a strong correlation between the fold potential of de novo proteins and one of their ancestral amino acid sequences, reflecting the intimate relationship between the noncoding genome and the protein structure universe.

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
November 16, 2021 11:38 AM
|
BSI 2021 is presenting special sessions: "Science & Société : La parole scientifique dans l'espace public": Many questions have raised by the period we have just passed through concerning the place of scientific speech in public debate, the role of experts (or so-called), interactions between researchers/experts, the media, politicians and the public. This roundtable will seek to shed light on what could/should be the contribution of researchers to public debates and the conditions for this contribution to be effective. "Session étudiants": UPSaclay students are invited to attend the morning sessions and meet up with researchers. Free but registration required HERE. "Satellite event - Alpha Fold": With the advent of AlphaFold, the BSI welcomes you to a round table meeting to discuss the impact and opportunity offered by this revolutionary tool. Free but registration required HERE. Further information and details on how to access the conference location can be found on the BSI 2021 website.

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
November 10, 2021 8:44 AM
|
The Physcomitrium (Physcomitrella) patens PpKAI2L receptors for strigolactones and related compounds function via MAX2-dependent and independent pathways
Mass spectrometry was used to allow the characterization of the biosynthesis of a novel class of phytohormones, striptolactones, in the bryophyte Physcomitrium patens and to compare this processes with the more known vascular plants. Results on Physcomitrium highlight surprising evolutive innovations from vascular plant. Strigolactones (SL) make up a novel class of phytohormones that are found across the whole land plant lineage. In vascular plants, the main hormonal role of SL is the repression of shoot axillary branching. However, SL are also a major symbiotic signal, granting the plant increased access to the nutrients and water contained in the rhizosphere. These two functions of SL led to the hypothesis that these molecules have been instrumental at the time of land colonization by plants, approximately 450 million years ago. Studying SL biosynthesis and signaling in the bryophyte Physcomitrium patens (P. patens, a non-vascular plant), and comparing these processes with the available knowledge in vascular plants, enables to investigate the evolution of SL cellular pathways in land plants. In angiosperms, the perception of SLs relies on a receptor called D14 (encoded by the same gene family as KAI2) along with the F-box protein MAX2. In moss, Max2 is not required for the SL response although it possesses 13 KAI2-like genes (PpKAI2L). An unusual aspect of SL perception is that the D14 protein is both a receptor and an enzyme that cleaves its substrate (and covalently binds part of the SL) in a signaling mechanism that is still under debate. To further investigate whether PpKAI2L proteins play roles as receptors of SLs and related compounds, we examined the covalent attachment of the artificial SL GR24 isomers to the PpKAI2L proteins by mass spectrometry (MS). Analyses revealed 96 Da increments (corresponding to the D ring mass) when AtKAI2 and PpKAI2L were incubated with GR24 isomers indicating that moss PpKAI2L proteins, like vascular plant receptors, covalently link GR24 enantiomers. As SL signaling is not conserved in P. patens, it appears that the known SL signaling pathway results from a vascular plants specific innovation. Likewise, SL response in P. patens would be the product of a convergent evolution. Therefore, the question as to how P. patens transduces the SL signal, downstream of perception by specific PpKAI2L proteins, remains open. More details here Contact person: David Cornu

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
November 10, 2021 8:31 AM
|
Agrobacterium tumefaciens fitness genes involved in the colonization of plant tumors and roots
High throughput analysis of fitness genes in a bacterial pathogen: towards the discovery of new targets to develop treatments. The pathogenic bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens provokes crown-gall disease on a wide diversity of host plants. It colonizes the galls it causes on host plants, poplar and tomato plant for instance. This pathogen also colonizes the roots of host plants and non-host plants, such as maize. We used a genome-wide approach (transposon sequencing) to discover Agrobacterium tumefaciens genes involved in reproductive success on tomato and poplar galls and tomato and maize roots. We used this knowledge to develop plant protection approaches against this pathogen. This wok was supported by the I2BC sequencing platform. More information here Contact person: Denis Faure

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
October 14, 2021 3:09 AM
|
Un portail commun pour les appels à projets de l'ADEME, de l' ANR, de l'ANRS, de l'ANSES, de l'institut National du Cancer et de l'INSERM.
Appelsprojetsrecherche.fr est un portail à destination des acteurs de la recherche. Inscrit dans le cadre de la Loi de Programmation de la Recherche, il est porté aujourd’hui par six partenaires : l’Ademe, l’ANR, l’ANRS, l’ANSES, l’INCa et l’Inserm. Il offre ainsi un accès unifié aux appels à projets ou à candidatures à venir et en cours, pour une plus grande visibilité de l’offre de financement. Après la date de clôture, les appels restent publiés encore quelques mois.

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
October 14, 2021 2:59 AM
|
BitQT: a graph-based approach to the quality threshold clustering of molecular dynamics
A fast and yet accurate QT clustering method: BitQT, example of application to MD trajectories The term clustering designates a comprehensive family of unsupervised learning methods, allowing to group similar elements into sets called clusters. The Quality Threshold (QT) clustering algorithm stands out as an ideal option whenever highly correlated elements are needed to be returned as clusters. QT guarantees that all cluster members will maintain a collective similarity established by a user-defined threshold. Unfortunately, the high computational cost of this algorithm for processing big data limits its application domain. In this work, we proposed a methodological parallel between QT clustering and another well-known algorithm in Graph Theory, the Maximum Clique Problem. We targeted Molecular Dynamics (MD) trajectories as an object of study, by representing molecular conformations as nodes of a graph whose edges imply a mutual similarity between conformations. Using a binary-encoded similarity matrix coupled to the exploitation of bitwise operations to extract clusters significantly contributed to reaching a very affordable algorithm compared to the few implementations of QT for MD available in the literature. Our alternative provides results in good agreement with the exact one, while strictly preserving the collective similarity of clusters. We believe methodological parallels discussed here may be translated to other areas where the QT hallmarks are helpful (e.g. transcriptomics). More details here Contact person: Fabrice Leclerc Follow the team

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
October 14, 2021 2:45 AM
|
Characterization of the Radiation Desiccation Response Regulon of the Radioresistant Bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans by Integrative Genomic Analyses
Characterization of the Radiation Desiccation Response
Regulon of the Radioresistant Bacterium Deinococcus
radiodurans by Integrative Genomic Analyses Numerous genes are overexpressed in the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans after exposure to radiation or prolonged desiccation. It was shown that the DdrO and IrrE proteins play a major role in regulating the expression of approximately twenty genes. At present, many questions remain, such as the number of genes regulated by the DdrO regulator. Here, we present the first ChIP-seq analysis performed at the genome level in Deinococcus species coupled with RNA-seq, which was achieved in the presence or not of DdrO. We also resequenced our laboratory stock strain of D. radiodurans R1 ATCC 13939 to obtain an accurate reference for read alignments and gene expression quantifications. We highlighted genes that are directly under the control of this transcriptional repressor and showed that the DdrO regulon in D. radiodurans includes numerous other genes than those previously described, including DNA and RNA metabolism proteins. These results thus pave the way to better understand the radioresistance pathways encoded by this bacterium and to compare the stress-induced responses mediated by this pair of proteins in diverse bacteria. More details here Contact person: Fabrice Confalonieri Follow the team

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
September 29, 2021 5:49 AM
|
Biogenesis of a gadget-free long tail bacteriophage.
Uncovering the complete building plan and assembly pathway of a viral DNA delivery device Siphoviruses are the major killers of bacteria. A long non-contractile tail is the key device of these bacteriophages to recognize specifically the host cell and to deliver their viral dsDNA to the bacterial cytoplasm. Furthermore, bacteria use nanotubes homologous to phage long tails to attack other cells. Although structures of these megadalton protein complexes are available, significantly less is known on the molecular mechanisms leading to their assembly. In a study published in J Mol Biol, I2BC researchers and their collaborators have undertaken a comprehensive analysis of the complete molecular organization of the siphovirus SPP1 tail, which infects Bacillus subtilis, and its biogenesis mechanisms. During tail assembly, the association of proteins follows a strict order. This implies that the third component of a complex does not bind until the first two proteins interact together and so on. Characterization of assembly intermediates from mutants deficient in each of the tail components revealed the sequential program of interactions leading to the construction of the SPP1 tail (~6.8 MDa). All proteins engaged, with the probable exception of one (gp22), are required for assembly. They likely represent the minimal protein set required to construct functional long tails. Bioinformatics analysis highlighted the structural plasticity of these tail components, a source of variability and innovation for the functional diversification of this type of nanotube. More details here Contact: Isabelle.Auzat or Paulo Tavares Follow the team

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
September 20, 2021 5:42 AM
|
Demonstration of a BioRad bench-top cell sorter
Bio-rad is organizing a demonstration of its S3e sorter with the I2BC Cytometry facility (Mr. Mickaël BOURGE). BioRad will organize a videoconference on Monday, October 18 at 2 p.m. (45-minute slot). Andrea Tradori will present the technical characteristics of the S3e as well as the associated benefits.
This videoconference will be carried out in Teams format, I have attached the link below to participate.
Click here to join the meeting Hope to see many of you on this occasion. Contact person : Mickael Bourge

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
September 16, 2021 6:16 AM
|
Clostridioides difficile CRISPR-Cas system PAM specificity for interference and adaptation
First experimental evidence for type I-B CRISPR-Cas system adaptation in the emerging human enteropathogen C. difficile and a functional link between the adaptation and interference CRISPR machineries sharing similar tri-nucleotide PAM motif for recognition of foreign nucleic acid sequences. CRISPR-Cas systems provide prokaryotes with adaptive immunity for defense against foreign nucleic acid invaders, such as viruses or phages and plasmids. The CRISPR-Cas systems are highly diverse, and detailed studies of individual CRISPR-Cas subtypes are important for our understanding of various aspects of microbial adaptation strategies and for the potential applications. The significance of this collaborative work of French, Russian and US labs from I2BC, Skoltech and Waksman Institute of Microbiology is in providing the first experimental evidence for type I-B CRISPR-Cas system adaptation in the emerging human enteropathogen Clostridioides difficile. This bacterium needs to survive in phage-rich gut communities, and its active CRISPR-Cas system might provide efficient antiphage defense by acquiring new spacers within CRISPR arrays that constitute memory for further invader elimination. This study also reveals a functional link between the adaptation and interference CRISPR machineries. The definition of all possible functional trinucleotide motifs upstream protospacers within foreign nucleic acid sequences is important for CRISPR-based genome editing in this pathogen and for developing new drugs against C. difficile infections. More details here Contact person: Olga Soutourina Follow the team
|

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
December 20, 2021 4:37 AM
|
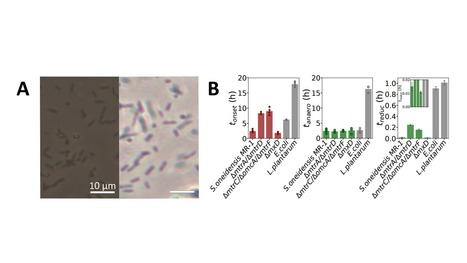
Modifying solid surfaces, the daily life of bacteria
Unveiling how bacteria modify the surface of solid walls in their close environment at the nanoscale is an important step in nanotechnology and bioengineering as well as in geomicrobiology and fundamental surface chemistry/physics. Bacteria have evolved on earth for billions of years and have managed to colonize all ecological niches. Their metabolic diversity is so vast that they play a major role in the biogeochemical cycles of our planet. Understanding the mechanisms by which bacteria interact with the first interfacial layers of the solid matter that surrounds them is an important issue with many perspectives in both fundamental and applied science. Thin iron films, with a surface area of centimeters and a thickness of nanometers, have been produced. The nanofilm’s opacity being related to its thickness, it is then possible to measure both the nanofilm’s degradation and to localize and quantify the bacteria dynamics in situ and in real time by simple optical means (backgroud of the picture). This experimental work published in the journal ACS Central Science indicates a homogeneous corrosion of iron nanofilms triggered suddenly by bacteria. Experiments reveal in particular rapid motions of Shewanella oneidensis MR1 bacteria during iron dissolution. Mutants of S. oneidensis as well as other bacterial species such as E. coli and L. plantarum are also able to induce corrosion (figure). All the experiments highlight more generally the role of electroactive respiratory proteins and soluble secreted molecules in the modification of the surface properties of nanofilms. More information here. Contact person: Christophe Regeard

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
December 20, 2021 4:10 AM
|
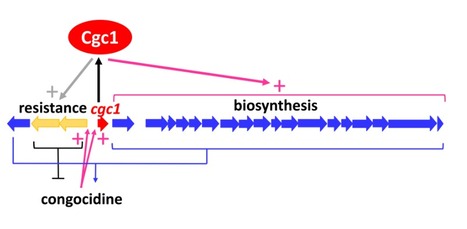
Transcriptional Regulation of Congocidine (Netropsin) Biosynthesis and Resistance
The transcriptional regulation of the biosynthesis and resistance to netropsin is not only controlled by a transcriptional regulator, Cgc1, but also by netropsin itself, which induces the expression of the resistance genes and of cgc1 by a new type of feedforward induction mechanism. Understanding the mechanisms of regulation of specialized metabolite production can have important implications both at the level of specialized metabolism study (expression of silent gene clusters) and at the biotechnological level (increase of the production of a metabolite of interest). We report here the first study on the regulation of the biosynthesis of a metabolite from the pyrrolamide family, congocidine (netropsin). Most pyrrolamides bind into the minor groove of DNA, specifically in A/T-rich regions, which gives them numerous biological activities, such as antimicrobial and antitumoral activities. We demonstrate that Cgc1, a cluster-situated, atypical orphan response regulator, controls congocidine biosynthesis and resistance. In addition, we show that congocidine induces the expression of the operon containing the resistance genes, offering protection against congocidine to cells that are not yet producing it. Finally, our results reveal that congocidine induces its own biosynthesis through the induction of the transcription of cgc1, in a new type of feed-forward induction mechanism. More information here. Contact person: Sylvie Lautru

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
December 20, 2021 3:57 AM
|
I2BC comes forward at Declics event on 18 November 2021
Several I2BC members participated in the Declics outreach event at French high school Lycée Sainte-Marie (Antony) on 18 Nov 2021. Declics is a half-day outreach event organized by Cercle FSER, in which scientists (researchers, engineers, technicians, with a permanent or short-term position) visit a high school to talk about science, research jobs and the process of building up knowledge. On 18 November, a team of 7 scientists met 38 high school students and 2 high school teachers of Lycée Sainte-Marie (Antony). The team included 5 scientists from I2BC: Jessica Andreani (team captain, B3S department), Adriana Alberti (Genome Biology department), Audrey Esclatine (Virology department), Vicky Lioy (Genome Biology department) and Nathalie Scrima (Virology department). After an overall presentation by the team captain, almost two hours of speed-meetings in small groups. A very positive experience! More information here. Contact person: Jessica Andreani

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
November 26, 2021 5:16 AM
|
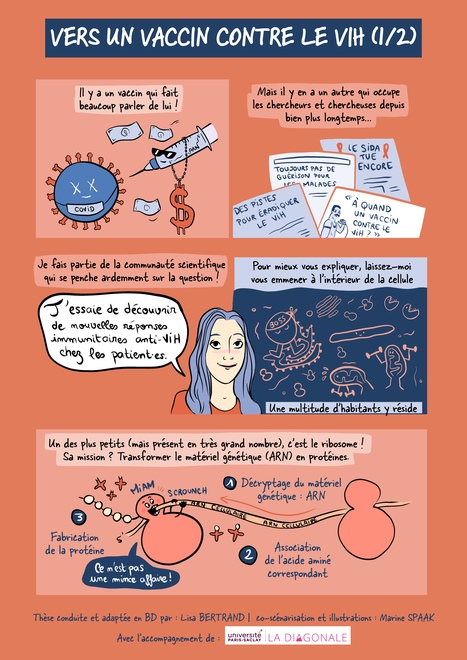
The research out of its bubble
A PhD student (Université Paris-Saclay) unveils her comic strip, illustrated by Marine Spaak, and invites you to dive into the heart of scientific research on HIV ! Like the book "Sciences en bulles", presented at the "Fête de la Science", the "Diagonale Paris-Saclay" challenged our doctoral student, Lisa Bertrand, to explain and share her thesis in a fun way in the form of a comic strip. His topic? Defining the translatome of HIV-1 in order to identify new antigens recognized by T-cells.
She followed several introductory sessions that taught her how to synthesize her ideas, turn them into a playful script, choose illustrations to complete her remarks, until she got a first storyboard. The illustrator Marine Spaak accompanied her throughout this process and then took it upon herself to shape all these ideas! Discover their image and immerse yourself in the world of the ribosome, a small cellular constituent responsible for protein production.You will find there that the AIDS virus hijacks ribosomes for its own benefit to make its own viral proteins. And how French research explores this phenomenon, in order to develop therapies. In addition to therapeutic research, the study of viruses is an excellent tool for understanding the functioning of the cell.
The comic on :
http://www.sciencesociete.universite-paris-saclay.fr/decouvrir/la-recherche-sort-de-sa-bulle/#section_3

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
November 16, 2021 4:22 AM
|
A Gold medal and the Best Inclusivity Prize for the iGEM GO Paris-Saclay team 2021 supported by I2BC!
The GO Paris-Saclay 2021 team won a gold medal and the "Best Inclusivity" prize at the iGEM 2021 international synthetic biology competition on Sunday, November 14. The team's project "EndoSeek" aims to develop a new diagnostic tool for endometriosis, which is a painful and poorly understood pathology caused by the proliferation of uterine cells outside the uterus. Worldwide, this disease affects about 10% of women and can take up to 7 years to diagnose. Based on preliminary studies using small patient cohorts, certain blood microRNAs (miRNAs) may be biomarkers of the disease.
The team has developed a machine learning program that will allow identification of new endometriosis biomarkers with future cohorts. In experiments conducted this summer at I2BC, students exploited Cas13a and Cas14a1 nucleases for miRNA detection. They created a video game to educate adults and children over the age of 10 about endometriosis and synthetic biology. Finally, following their dialogue with patients and physicians, they questioned the ethical implications of diagnostics.
The team was awarded the Best Inclusivity Award for outstanding efforts to include people with diverse identities. The students thought about the position of LGBT+ people in their project and created a multi-language, voice-assisted website with color customization.
This project was supported by the I2BC, the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Paris-Saclay, La Diagonale Paris-Saclay, EUGLOH (European University Alliance for Global Health), the Graduate School Life Sciences and Health, IDT and Promega. Team 2021 supervisors included Téo Hébra (ICSN) and 5 members of the I2BC: Philippe Bouloc, Stéphanie Bury-Moné, Emma Piattelli, Ombeline Rossier and Charlène Valadon.
For more information, see the wiki https://2021.igem.org/Team:GO_Paris-Saclay and the video https://video.igem.org/w/ihqYR3UfveimEtZVv7x6jE.

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
November 10, 2021 8:39 AM
|
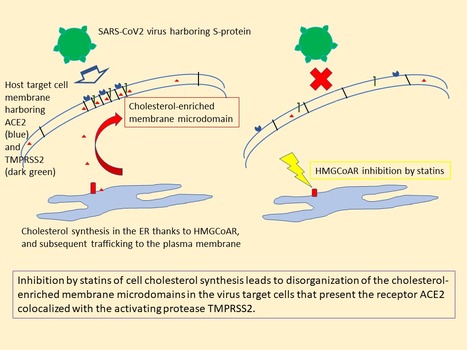
Coronaviruses, cholesterol and statins : proposal for a repurposing against Covid-19
Thanks to the similarity of in-vitro and in-vivo disorganizing effect of statins on cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains, which constitute the cell entry platforms of the various coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2, this host-directed therapeutic approach can be proposed to fight against Covid-19. The entry of SARS-CoV-2, as well as the other coronaviruses, into its target cells is mediated by cholesterol-rich plasma membrane microdomains, whatever the followed pathway. These «lipid rafts» can be destructured in-vitro by the inhibiting action of statins on the key enzyme of cell cholesterol biosynthesis. As a consequence, raft-dependent signaling platforms are disorganized, leading to various cellular effects. In clinics, beyond the classical hypocholesterolemic effect of statins, these drugs can induce various «pleiotropic effects» (anti-inflammatory, immunomodulation, vascular protection...) that are mediated by such signaling platforms. This indicates that statins, administered under clinical situations, are able to in-vivo perturb cholesterol-rich membrane domains, which should include those involved in various pathogenic agents, including SARS-CoV-2, entry platforms. We thus propose statins as a new repurposing strategy against Covid-19, taking into account they are well-known, widely-used safe drugs (used for long-term prevention for high-risk cardio-vascular patients), administered per os, cheap, and overall avoiding any risk of encountering treatment resistances due to viral mutations because it is a «host-directed» therapeutic approach [Orlowski et al, Biochimie 189, 51 (2021)]. It remains to test experimentally this hypothesis. Contact person: Stephane Orlowski

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
October 18, 2021 8:12 AM
|
Macromolecular interactions in vitro, comparing classical and novel approaches
In a study published in European Biophysics Journal, two teams of the B3S department (INTGEN and MIP) with the PIM platform, in collaboration with national and international experts on molecular scale biophysics compare six approches to measure macromolecular interactions in vitro. The results were obtained in the context of a Training School (ARBRE-MOBIEU COST Action) organized in 2019 in our institute. Biophysical quantification of protein interactions is central to unveil molecular mechanisms of cellular processes. Researchers can choose from a wide panel of biophysical methods, including classical and more novel ones. A real-life proof-of-concept was carried out during an ARBRE-MOBIEU training school held in June 2019 in Gif-sur-Yvette, France (https://mosbio.sciencesconf.org/). Twenty European students benefited from a one-week training with lessons and practical sessions on six complementary approaches: (i) Analytical UltraCentrifugation with or without a Fluorescence Detector System (AUC-FDS), (ii) Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC), (iii) Size Exclusion Chromatography coupled to Multi-Angle Light Scattering (SEC-MALS), (iv) Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI), (v) MicroScale Thermophoresis (MST) and, (vi) switchSENSE. They implemented all these methods on two examples of macromolecular interactions: firstly, a protein-protein interaction between an artificial alphaRep binder, and its target protein, also an alphaRep; secondly, a protein-DNA interactionbetween a DNA repair complex, Ku70/Ku80 (hereafter called Ku), and its cognate DNA ligand. The students acknowledged that the workshop provided them with a clearer understanding of the advantages and limitations of the different techniques and will help them in the future to choose the approaches that are most relevant or informative for their projects. More details here Contact person: Paloma Fernandez Varela

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
October 14, 2021 3:05 AM
|
Presence of 2-hydroxymyristate on endotoxins is associated with death in neonates with Enterobacter cloacae complex septic shock
This is the first published evidence linking lipopolysaccharide structural moiety to neonatal sepsis outcome and opens the possibility of using the 2-hydroxymyristate marker as a detection tool for high-risk patients, which could help reduce their mortality. Enterobacter cloacae complex species are involved in infections among critically ill patients. After a recent E.cloacae outbreak of fulminant neonatal septic shock, we conducted a study to determine whether septic shock severity and its lethal consequence are related to structural features of the endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide [LPS]) of the strains isolated from hospitalized infants and more specifically its lipid A region. It appeared that the LPSs are very heterogeneous, carrying fifteen different molecular species of lipid A. The virulence was correlated with a structural feature identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry and gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry: the presence of 2-hydroxymyristic acid as a secondary substituent in lipid A. This is the first published evidence linking LPS structural moiety to neonatal sepsis outcome and opens the possibility of using this fatty acid marker as a detection tool for high-risk patients, which could help reduce their mortality. More details here Contact person: Pierre Tissières Follow the team

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
October 14, 2021 2:54 AM
|
The Environmental and Agronomical Genomics 2021 symposium is jointly organised by France Génomique and the GDR Génomique Environnementale.
Last call for registration at the Environmental and Agronomical Genomics 2021 Symposium until 13th October. The Environmental and Agronomical Genomics 2021 symposium will be the opportunity to have an update on most recent environmental genomics research, as well as an overview of high scientific impact projects carried out in collaboration with France Genomique platforms. This year we are also celebrating the 10th anniversary of the GDR Génomique environnementale. Contact person: Denis Faure

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
October 14, 2021 2:36 AM
|
Role of polycomb in the control of transposable elements
This opinion piece reviews for the first time the evidences across kingdoms that Polycomb (PcG) Repressive Complex 2, thought to be dedicated to the epigenetic silencing of protein-coding genes, can also target, and even silence, transposable elements: could an ancestral role of PcG proteins be to silence transposable elements? It is generally considered that Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 deposits the histone mark H3K27me3 on silent protein coding genes, while transposable elements are repressed by DNA and/or H3K9 methylation. Yet, there is increasing evidence that the Polycomb repressive complexes also target and even silence transposable elements in representatives of several distantly related eukaryotic lineages. In plants and animals, H3K27me3 is present on transposable elements in mutants and specific cell types devoid of DNA methylation. In this opinion, we summarize the experimental evidence for this phenomenon across the eukaryotic kingdom, and discuss its functional and evolutionary significance. We hypothesize that an ancestral role of Polycomb group proteins was to silence transposable elements. More details here Contact person: Angélique Déléris Follow the team
La plateforme de protéomique de Gif-sur-Yvette, créée en 2007 sous le nom de SICaPS (Service d’Identification des Protéines par Spectrométrie de masse), récemment rebaptisée Protéomique-Gif, fait partie intégrante de l’Institut de Biologie Intégrative de la cellule (I2BC, Gif-sur-Yvette) depuis 2015. Elle couvre différents aspects de la protéomique et des analyses de protéines par spectrométrie de masse : du contrôle qualité de protéines à l’analyse en profondeur des interactomes, des protéomes et de leurs modifications. Protéomique-Gif offre un ensemble de spectromètres de masse, de stratégies et de méthodes de préparation des échantillons nécessaires pour identifier et quantifier des protéines et leurs modifications chimiques, co- et post-traductionnelles. L’un des spectromètres de masse, le timsTOF Pro de Bruker (obtenu grâce à des financements SESAME Santé IdF 2017, Plan Cancer 2018, IBiSA, Université Paris-Saclay et CNRS) permet désormais d’identifier plusieurs milliers de protéines à partir de 50 à 200 ng de protéines. Mais que sont des analyses protéomiques ? Des analyses protéomiques consistent à étudier l’ensemble des protéines d’un compartiment cellulaire, d’une cellule, d’un tissu, d’un organisme ou d’un fluide biologique. Cet ensemble de protéines, nommé protéome, résulte de la combinatoire de l’expression des gènes et des modifications post-transcriptionnelles, co- et post-traductionnelles parfois complexes. Des stratégies analytiques dédiées, mettant en jeu des digestions de protéines, des enrichissements de peptides, des séparations chromatographiques et des analyses par spectrométrie de masse, ainsi que des analyses bio-informatiques et statistiques des données générées, permettent d’identifier, quantifier et caractériser finement les protéines d’un échantillon biologique à un instant donné. Elles permettent d’étudier les changements d’expression des protéines, leurs modifications et les interactions qu’elles établissent avec des partenaires protéiques qui contribuent à réguler les fonctions normales et pathologiques des protéines. Un exemple d’application de ces approches et expertises ? Regard sur un interactome choisi ! L’agrégation des protéines Tau et la propagation de ces agrégats dans le cerveau sont liées à la progression de la maladie d’Alzheimer. Les agrégats de Tau se propagent d’une cellule neuronale à une autre en se liant aux membranes des cellules, avant d’être internalisés et amplifiés dans la cellule réceptrice. L’étape clé dans la propagation de ces agrégats pathogéniques est la fixation d’agrégats provenant de cellules neuronales affectées aux membranes de cellules indemnes. Par une approche protéomique de pêche des partenaires des agrégats de protéines Tau fibrillaire, l’équipe de Ronald Melki (MIRCen, CNRS/CEA/Université Paris-Saclay, Laboratoire des Maladies Neurodégénératives, Fontenay-aux-Roses), en collaboration avec l’équipe d’Antoine Triller (Ecole Normale Supérieure, Sorbonne Université et l’Inserm) et la plateforme Protéomique-Gif, a identifié l’interactome membranaire de neurones de souris des agrégats de Tau pathogéniques, et a ainsi pu identifier les cibles de ces agrégats. Ce travail a permis de documenter les conséquences fonctionnelles de l’interaction des agrégats de Tau avec notamment la pompe sodium/potassium et des récepteurs du glutamate, des protéines essentielles à la survie des neurones. En savoir plus ? Shrivastava A et al., EMBO J. 2019. Cette étude illustre l’intérêt et le potentiel des approches de protéomique et le savoir-faire de la plateforme Protéomique-Gif. L’accès au timsTOF Pro et a ses nouvelles performances a récemment permis d’accéder à une profondeur d’analyse des protéomes plus grande encore. Et de nouvelles sensibilités pourraient encore être atteintes dans le futur… Les analyses d’interactomes, de protéomes complexes ou des caractérisations fines de protéines vous intéressent, n’hésitez pas à nous contacter et à nous soumettre vos demandes. Nous élaborerons ensemble la stratégie la plus adaptée à la réalisation de votre projet. Contact : Virginie Redeker (virginie.redeker@cnrs.fr) Plug In Labs Université Paris-Saclay : cliquer ici La plateforme Protéomique-Gif (SICaPS), labellisée IBiSA, est ouverte à l'ensemble de la communauté scientifique. La plateforme propose des méthodologies de protéomique et des technologies de spectrométrie de masse de pointe pour identifier, caractériser et quantifier les protéines et certaines de leurs modifications à partir d'échantillons plus ou moins complexe. Une technologie de dernière génération permet l'identification et la quantification relative de protéines peu abondantes dans des échantillons protéiques très complexes. Des méthodes analytiques adaptées permettent de caractériser des modifications co-, post-traductionnelles ou chimiques des protéines (phosphorylations, lipides, pontages covalents …). La plateforme dispose d'une solide expertise dans la préparation d'échantillons protéiques de nature variée, leur analyse par spectrométrie de masse et le traitement des données. Elle optimise et développe des méthodes analytiques en réponse aux besoins des utilisateurs. La plateforme propose une variété de services sous forme de prestations : i) standards : préparations d'échantillons, mesures de masse exacte, identification de protéines, contrôle-qualités de protéines recombinantes ou ii) collaboratives : quantification relative des protéines, comparaisons approfondies de protéomes, interactomes, caractérisation de déterminants structuraux et de modifications des protéines.
Via Life Sciences UPSaclay

|
Scooped by
I2BC Paris-Saclay
September 20, 2021 4:48 AM
|
Confocal microscopy workshop
Interested in confocal microscopy ?
Come to the Imagerie-Gif Confocal Workshop to acquire and reinforce the theoretical basis of photonic microscopy and master the practical use of a full field and confocal microscope !
As well you will be able to integrate the principles and possibilities of new applications and developments in photonic microscopy and understand the complementarities of techniques from conventional microscopy to super-resolution ! Lecture (40% of the time)
- Reminder of conventional microscopy, videomicroscopy
- Introduction to confocal microscopy (instrument physics, acquisition, digitization, sampling, multiple labeling)
- Fast confocal microscope with Nipkow disk (Spinning-Disk)
- Understanding and using fluorochromes in confocal microscopy, proteins and fluorescent probes
- Preparation of live and fixed biological samples
- Processing and use of 2D and 3D images applied to microscopy
- Specific applications in confocal microscopy, FLIM, FRET, etc.
- Increased resolution and super-resolution (PALM, STORM, STED, SIM)
- Application seminars
Practical work (60% of the time)
A cycle of ten practical works over twenty hours will allow to reinforce the link between theory and applications, to recognize the elements implemented, to acquire images, to process them and to analyze them with ImageJ in particular.
One day will also be dedicated to the discovery of advanced techniques such as biphotonic excitation, light sheet microscopy, F-techniques (FRAP, photoactivation) and deconvolution. More details here Contact : Mébarek TEMAGOULT
|




 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...