Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 2:29 PM
|
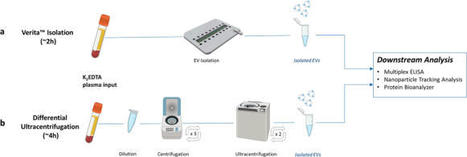
Detecting cancer at early stages significantly increases patient survival rates. Because lethal solid tumors often produce few symptoms before progressing to advanced, metastatic disease, diagnosis frequently occurs when surgical resection is no longer curative. One promising approach to detect early-stage, curable cancers uses biomarkers present in circulating extracellular vesicles (EVs). To explore the feasibility of this approach, we developed an EV-based blood biomarker classifier from EV protein profiles to detect stages I and II pancreatic, ovarian, and bladder cancer.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 2:24 PM
|
There has been growing interest in the development of exosomes as vehicles to deliver therapeutic substances to brain tissues and alter CNS functions. Being natural delivery vehicles for genetic material, several proof-of-concept studies have concluded that exosomes derived from the CNS and circulating in the blood have a BBB permeability similar to liposomes. But unlike liposomes, they accumulate in endothelial cells. Ultimately, the fulfillment of exosomal therapy may hinge on the development of suitable strategies for exosome production, characterization, targeting, and loading.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 2:13 PM
|
Researchers discover how some microRNA gets picked to travel inside tiny sacs to other organs and regulate metabolism at a distance. The finding could improve early cancer diagnosis and help treat diabetes and high cholesterol

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 2:11 PM
|
Exosomes are nanosized (50–150 nm) extracellular vesicles released by all types of cells in the body. They transport various biological molecules, such as DNAs, RNAs, proteins, and lipids from parent cells to recipient cells for intercellular communication. Exosomes, especially those from tumor cells, are actively involved in caner development, metastasis, and drug resistance. Recently, many studies have shown that exosomal proteins are promising biomarkers for cancer screening, early detection and prognosis. Among many detection techniques, surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is a highly sensitive, label-free, and real-time optical detection method. Commercial prism-based wavelength/angular-modulated SPR sensors afford high sensitivity and resolution, but their large footprint and high cost limit their adaptability for clinical settings.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 2:08 PM
|
Scientists are finding that microscopic membranous bubbles called extracellular vesicles transmit messages from cells and do big jobs in many areas of biology — plus they might be useful for therapies. Call it the body’s postal system. Cells package goodies into little envelopes made of membranes. Then these packages cruise the bloodstream — billions of them in every milliliter of blood — to recipient cells far and near, delivering freight such as genetic material and proteins.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 1:51 PM
|
Exosomes are nano-size extracellular vesicles secreted by all cells, they are classified as nanoparticle based on size and they transport proteins and genetic information between cells. These exosomes hold promise to become powerful tools for targeted drug-delivery approaches.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 1:40 PM
|
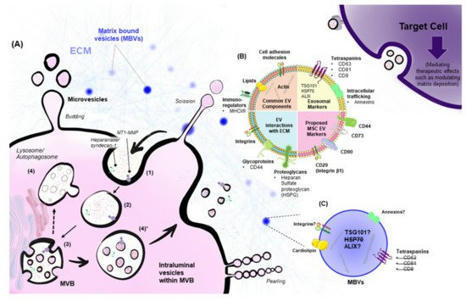
The extracellular matrix (ECM) contains signaling and structural molecules that are central to tissue maintenance and repair. Recently, a subset of EVs residing within the extracellular matrix has been identified. Although some roles have been proposed for matrix-bound vesicles, their role as signaling molecules within the ECM is yet to be explored. Given the close association of EVs and the ECM, it is not surprising that EVs partly mediate repair and regeneration by modulating matrix deposition and degradation through their cellular targets. This review addresses unique EV features that allow them to interact with and navigate through the ECM, describes how their release and content is influenced by the ECM, and emphasizes the emerging role of stem-cell derived EVs in tissue repair and regeneration through their matrix-modulating properties.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 1:35 PM
|
Exosome production comprises intraluminal vesicles from endosomal compartments called multivesicular bodies, which are released into the extracellular compartment when the late endosomes fuse with the cell membrane.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 1:32 PM
|
Exogenus Therapeutics is an early-stage R&D company dedicated to the development of innovative products using naturally derived extracellular vesicles. Its lead product Exo-101 is recognized as a major advancement in the field of exosome-based therapeutics, and as a reference for an alternative clinical use for umbilical cord blood. Leveraging on its experience, Exogenus Therapeutics’ mission is to foster a new era of extracellular vesicle-based solutions to solve major healthcare challenges, through internal and collaborative R&D.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 1:24 PM
|
The Astellas Institute for Regenerative Medicine (AIRM) has signed a Master Collaborative Services Agreement (MSA) with Exopharm, through which the partners plan to carry out initial lab work, with the goal for Astellas of deciding whether exosome products can be added to its pipeline. That work will begin at Exopharm's laboratories in Melbourne, Australia, when the partners seek to purify exosomes derived from two proprietary AIRM cell line by applying Exopharm's Ligand-based Exosome Affinity Purification (LEAP™) technology platform . . .

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 4:13 AM
|
The field of extracellular vesicle (EV) research has developed rapidly over the last decade from the study of fundamental biology to a subject of significant clinical relevance. The potential of harnessing EVs in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases — including cancer and neurological and cardiovascular disorders — is now being recognized. Accordingly, the applications of EVs as therapeutic targets, biomarkers, novel drug delivery agents and standalone therapeutics are being actively explored. This Review provides a brief overview of the characteristics and physiological functions of the various classes of EV, focusing on their association with disease and emerging strategies for their therapeutic exploitation.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 4:12 AM
|
Ciloa will develop this new generation of vaccines, which will eventually target several major viruses that have no effective treatment to date (SARS-CoV-2, HIV, Chikungunya, Zika, Dengue, etc.) until the end of the regulatory preclinical phases. The preclinical phases of some of these vaccine candidates will be conducted in collaboration with the Institut Pasteur, with the objective of confirming the safety of the vaccine candidates as well as their ability to protect effectively against the virus.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 4:10 AM
|
Exosomes have been characterized using various techniques, including biophysical, molecular, and microfluidic methods. The exosomal size range is characterized using biophysical techniques.
|

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 2:27 PM
|
Myocardial infarction (MI) represents a severe cardiovascular disease with limited therapeutic agents. This study was aimed to elucidate the role of the exosomes derived from human placental mesenchymal stem cells (PMSCs-Exos) in MI.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 2:23 PM
|
We observed that depending on the concentration and physicochemical characteristics, specific NMs promote a significant increase in EV secretion as well as changes in their cargo, especially regarding the expression of proteins and miRNAs, which, in turn, were involved in biological processes that included cell communication, angiogenesis, and activation of the immune response, etc. Although further studies are necessary, this work suggests that molecular investigations on EVs induced by NM exposure may become a potential tool for toxicological studies since they are widely accessible biomarkers that may form a bridge between NM exposure and the cellular response and pathological outcome.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 2:12 PM
|
As a large, high-resolution instrument, cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) can be used to study subcellular structures in addition to protein structural analysis. Cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) is for subcellular studies, such as the structure of organelles, the distribution of protein molecules, and the composition of cytoskeletons. Extracellular research includes exosomes, biomacromolecules and a series of nano-scale biomaterials. Combined with ultra-low temperature sample manipulation, cryo-EM can provide high-resolution information that connects molecular and cellular level knowledge in order to understand cellular function.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 2:11 PM
|
Expansion of clinical programs to investigate hMSC-EVs, including exosomes, requires maximizing EV/exosome productivity in a scalable manufacturing platform. EV productivity is determined during the upstream process by the number of cells and the number of EVs/exosomes produced per cell. Rapid and efficient cell expansion facilitates a greater yield of consistent and scalable hMSC-EV/exosome production. Improvements in EV/exosome productivity will be driven by bioreactor-based processes to amplify cell number and by media development to increase EVs produced per cell.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 2:08 PM
|
The exosome is considered a useful biomarker for the early diagnosis of cancer. However, pretreatment of samples used in diagnosis is time-consuming. Researchers at Kwangwoon University have fabricated a capacitance-based electrical biosensor that requires no pretreatment of the sample; it is composed of a DNA aptamer/molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) heterolayer on an interdigitated micro-gap electrode (IDMGE)/printed circuit board (PCB) system for detecting exosomes in an undiluted serum sample. The DNA aptamer detects the CD63 protein on the exosome as the biomarker, while the MoS2 nanoparticle enhances electrical sensitivity.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 1:48 PM
|
The most abundant biomarker found in a liquid biopsy sample are exosomes. Exosomes are a type of extracellular vesicle around 100 nm in diameter that derive from any and every cell in the body. During their formation, a diverse array of information from the parent cell is packed into the exosome, making for an excellent representation of the parent cell ex situ. For instance, the DNA contained in exosomes is representative of the entire genome and the mutational profile specific to the tumour cell from which it derives, offering the advantage over analysis of ctDNA, for example, which is fragmented and mostly derived from dying cells1. Exosomes, therefore, give a more current overview of the tumour landscape; something that is extremely important in such a rapidly mutating disease.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 1:38 PM
|
In silico functional analysis showed that the ESCs-Exo microRNAs‒target genes were primarily involved in homeostatic processes and cell differentiation and highlighted regulatory control of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/protein kinase B and TGFβ signaling pathways. This was also validated in vitro. Collectively, our results indicate that epidermal stem cells and ESCs-Exo are equally effective in promoting impaired diabetic wound healing and that ESCs-Exo treatment may be a promising and technically advantageous alternative to stem cell therapies.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 1:34 PM
|
HELA-Exos exhibit potent antitumor activity in both a mouse model and human breast cancer organoids by promoting the activation of cDC1s in situ and thus improving the subsequent tumor-reactive CD8+ T cell responses. The strategy proposed here is promising for generating an in situ DC-primed vaccine and can be extended to various types of cancers.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 1:27 PM
|
A new study using blood samples taken from astronauts before and after various space shuttle missions from 1998 to 2001 revealed potential biomarkers which could be used to predict the health risks posed by space travel. In a recently published paper, an international group of researchers detail how they analyzed exosomes, vesicles which transmit information between cells, isolated from the blood plasma of three astronauts.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 4:14 AM
|
Stem cell and other cell-based therapies have proven to be strong therapeutic candidates for many regenerative and tissue restorative applications. However, complications with post transplantation viability, clinical reproducibility, and large-scale development have stalled these products in the path to drug approval. In an effort to enhance and build from the lessons learned in cell-based research and clinical trials, researchers have begun to shift focus to cell-to-cell secreted factors such as extracellular vesicles. Extracellular vesicles, secreted from the cell membrane or the cell’s internal recycling pathways, carry many of the same molecular messengers and factors found to be therapeutic in cell therapies.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 4:12 AM
|
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles (EVs) of endosomal origin that range in size between 30 and 150 nanometers. Exosomes are secreted by a wide range of cells, since virtually all living cells utilize exosome-mediated communication. Exosomes carry cell-specific cargos of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids that are selectively taken up by recipient cells.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
April 10, 2022 4:11 AM
|
Exosomes include plasma-transported vesicles that are secreted by human tissues and reflect metabolic status. The profile of exosomes (particularly microRNA content) is altered in metabolic disease. In type 2 diabetes mellitus, exosomes circulating in plasma induce transcriptional changes related to tumour progression and pro-metastatic phenotypes in target cancer cells, potentially linking obesity to cancer progression and metastasis.
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...