Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 7, 2023 6:32 AM
|
Despite advances in the treatment and mitigation of critical illness caused by infection with SARS-CoV-2, millions of survivors have a devastating, po…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 7, 2023 4:01 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 13, 2023 8:43 AM
|
Bivalent BA.1 booster vaccines were offered to adults aged 50 years or older and clinically vulnerable people as part of the 2022 autumn COVID-19 boos…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 12, 2023 7:58 AM
|
Antiviral drugs and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), administered either separately or as combination therapy 'cocktails’, have provided a valuable tool for fighting COVID-19. Surveillance data, coupled with data on antiviral treatment susceptibility, can guide clinical decisions on selecting the best therapy for the patient.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 12, 2023 4:26 AM
|
The first genome-wide search for long-COVID risk factors could pave the way for larger studies.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 4, 2023 8:21 AM
|
Background: The performance of rapid antigen tests (Ag-RDTs) for screening asymptomatic and symptomatic persons for SARS-CoV-2 is not well established. Objective: To evaluate the performance of Ag-RDTs for detection of SARS-CoV-2 among symptomatic and asymptomatic participants. Design: This prospective cohort study enrolled participants between October 2021 and January 2022. Participants completed Ag-RDTs and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing for SARS-CoV-2 every 48 hours for 15 days. Setting: Participants were enrolled digitally throughout the mainland United States. They self-collected anterior nasal swabs for Ag-RDTs and RT-PCR testing. Nasal swabs for RT-PCR were shipped to a central laboratory, whereas Ag-RDTs were done at home. Participants: Of 7361 participants in the study, 5353 who were asymptomatic and negative for SARS-CoV-2 on study day 1 were eligible. In total, 154 participants had at least 1 positive RT-PCR result. Measurements: The sensitivity of Ag-RDTs was measured on the basis of testing once (same-day), twice (after 48 hours), and thrice (after a total of 96 hours). The analysis was repeated for different days past index PCR positivity (DPIPPs) to approximate real-world scenarios where testing initiation may not always coincide with DPIPP 0. Results were stratified by symptom status. Results: Among 154 participants who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, 97 were asymptomatic and 57 had symptoms at infection onset. Serial testing with Ag-RDTs twice 48 hours apart resulted in an aggregated sensitivity of 93.4% (95% CI, 90.4% to 95.9%) among symptomatic participants on DPIPPs 0 to 6. When singleton positive results were excluded, the aggregated sensitivity on DPIPPs 0 to 6 for 2-time serial testing among asymptomatic participants was lower at 62.7% (CI, 57.0% to 70.5%), but it improved to 79.0% (CI, 70.1% to 87.4%) with testing 3 times at 48-hour intervals. Limitation: Participants tested every 48 hours; therefore, these data cannot support conclusions about serial testing intervals shorter than 48 hours. Conclusion: The performance of Ag-RDTs was optimized when asymptomatic participants tested 3 times at 48-hour intervals and when symptomatic participants tested 2 times separated by 48 hours. Primary Funding Source: National Institutes of Health RADx Tech program.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 28, 2023 3:57 AM
|
Studies are shedding light on rates of recovery as well as the prevention and treatment of the complex condition.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 21, 2023 10:35 AM
|
COVID-19 continues to be a major health threat, particularly among at-risk groups, including individuals aged 60 years or older and people with partic…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 21, 2023 10:34 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 21, 2023 3:51 AM
|
This cohort study measures the associated long-term effects of COVID-19 that are distinct from the risks associated with hospitalization for acute illnesses in general.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 14, 2023 3:49 AM
|
The long-term health consequences of COVID-19 remain largely unclear. The aim of this study was to describe the long-term health consequences of patie…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 8, 2023 10:18 AM
|
No study has yet investigated if a severe SARS-CoV-2 infection represents a marker of an undiagnosed cancer. This population-based study, using the SNDS database, identified from 02/15/2020 to 08/31/2021, 41,302 individuals hospitalized in intensive care unit due to SARS-CoV-2 (ICU-gr) and 713,670 control individuals not hospitalized for SARS-CoV-2 (C-gr). Individuals were matched according to year of birth, sex and French department. The cancer incidence was compared in the two groups during the follow-up period (index date-12/31/2021), using Cox proportional hazards models adjusted on matching variables, socioeconomic characteristics and comorbidities. In the ICU-gr, 2.2% (n = 897) was diagnosed with a cancer in the following months, compared to 1.5% (n = 10,944) in the C-gr. The ICU-gr had a 1.31 higher risk of being diagnosed with a cancer following hospital discharge compared to the C-gr (aHR 1.31, 95% CI 1.22–1.41). A global similar trend was found when competing risk of death was taken into account (aHR 1.25, 95% CI 1.16–1.34). A significant higher risk was found concerning renal (aHR 3.16, 95% CI 2.33–4.27), hematological (aHR 2.54, 95% CI 2.07–3.12), colon (aHR 1.72, 95% CI 1.34–2.21), and lung (aHR 1.70, 95% CI 1.39–2.08) cancers. This suggests that a severe SARS-CoV-2 infection may represent a marker of an undiagnosed cancer.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 5, 2023 1:32 AM
|
An abstract is unavailable.
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 7, 2023 6:31 AM
|
Individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection can develop symptoms that persist well beyond the acute phase of COVID-19 or emerge after the acute phase, lasti…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
August 7, 2023 12:58 AM
|
Today in Nature a groundbreaking and compelling report on the genomics of why some people do not manifest symptoms of Covid. And last week 2 papers (here and here) on the genetics of Long Covid. This represents genetic probes for the extreme of the clinical spectrum—from not exhibiting symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection to developing a debilitating, chronic condition. In this edition of Ground Truths, I’ll review the 3 new studies and contextualize their importance.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 13, 2023 8:43 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 12, 2023 6:35 AM
|
Long COVID is the patient-coined term for the disease entity whereby persistent symptoms ensue in a significant proportion of those who have had COVID-19, whether asymptomatic, mild or severe. Estimated numbers vary but the assumption is that, of all those who had COVID-19 globally, at least 10% have long COVID. The disease burden spans from mild symptoms to profound disability, the scale making this a huge, new health-care challenge. Long COVID will likely be stratified into several more or less discrete entities with potentially distinct pathogenic pathways. The evolving symptom list is extensive, multi-organ, multisystem and relapsing–remitting, including fatigue, breathlessness, neurocognitive effects and dysautonomia. A range of radiological abnormalities in the olfactory bulb, brain, heart, lung and other sites have been observed in individuals with long COVID. Some body sites indicate the presence of microclots; these and other blood markers of hypercoagulation implicate a likely role of endothelial activation and clotting abnormalities. Diverse auto-antibody (AAB) specificities have been found, as yet without a clear consensus or correlation with symptom clusters. There is support for a role of persistent SARS-CoV-2 reservoirs and/or an effect of Epstein–Barr virus reactivation, and evidence from immune subset changes for broad immune perturbation. Thus, the current picture is one of convergence towards a map of an immunopathogenic aetiology of long COVID, though as yet with insufficient data for a mechanistic synthesis or to fully inform therapeutic pathways. SARS-CoV-2 infection can lead to a diverse array of chronic symptoms, collectively termed ‘long COVID’. In this Review, Altmann and colleagues explore current thinking about the pathophysiology of long COVID and discuss potential immunological mechanisms.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 6, 2023 6:25 AM
|
Global regulators confirm good safety profile of COVID-19 vaccines

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
July 3, 2023 2:36 AM
|
This systematic review and meta-analysis compares incidence rates of diabetes and diabetic ketoacidosis among children and adolescents before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 27, 2023 3:08 AM
|
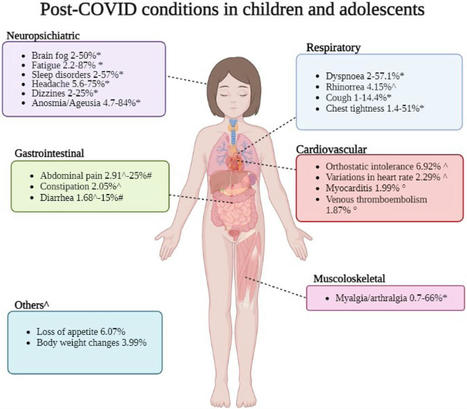
In this Personal View, we discuss current knowledge on SARS-CoV-2 RNA or antigen persistence
in children infected with SARS-CoV-2. Based on the evidence that the virus can persist
in adults, we have done a literature review and analysed studies that looked for SARS-CoV-2
RNA or antigens in children undergoing autopsy, biopsy, or surgery for either death
from COVID-19 or multisystem inflammatory syndrome, or assessments for long COVID-19
or other conditions. Our analysis suggests that in children, independent from disease
severity, SARS-CoV-2 can spread systemically and persist for weeks to months.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 21, 2023 10:34 AM
|
Aerosolised Ad5-nCoV is one of the first licensed mucosal respiratory vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in the world; however, the safety profile of this vac…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 21, 2023 4:06 AM
|

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 14, 2023 8:46 AM
|
Background: While vaccines have proved effective to prevent severe COVID-19, their impact to prevent long-term symptoms is not yet fully understood.

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 9, 2023 12:37 PM
|
Post-COVID-19 condition (also known as long COVID) is an emerging chronic illness potentially affecting millions of people. We aimed to evaluate wheth…

|
Scooped by
HAS-veille
June 6, 2023 9:37 AM
|
EMA and ECDC statement on updating COVID-19 vaccines to target new SARS-CoV-2 virus variants
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...