 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
March 5, 4:32 AM
|
This article focuses on the implementation of interRAI instruments at a national health system level. It is based on a narrative review undertaken by the authors from several interRAI member countries. Implementation experiences from several countries and searches of PubMed and other databases, grey …

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
February 12, 4:37 AM
|
As the global population ages, the need for community-based tools to assess the functional status and care needs of older adults is increasing. This study examined the reliability, validity, and feasibility of the interRAI Check-Up Self-Reporte

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
May 10, 2025 12:19 PM
|

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
April 16, 2025 7:05 AM
|
Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is the most common chronic liver disease in the United States. It is characterized by steatosis in the liver and is potentially reversible. Risk factors include obesity, type 2 mellitus, and other metabolic disorders. Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis (MASH), a more severe form of MASLD, puts patients at risk for cirrhosis, liver decompensation, and liver cancer. Diet, exercise, and weight loss are the cornerstones of management. Although only 1 medication has been approved for treatment of MASH, other pharmacotherapies and surgeries that aid weight loss and optimize metabolic risk factors can be used. Early diagnosis and intervention are important to prevent progression to cirrhosis and its complications, including cancer.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 7:07 AM
|
MetaboHealth, not MetaboAge, was associated with cognitive functioning independent of conventional risk factors. Individual metabolites affect cognitive functioning differently in men and women, suggesting sex-specific pathophysiological pathways underlying cognitive functioning.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 7:03 AM
|
Most diabetes CPGs recommend strict HbA1c targets in healthier older adults, with more relaxed targets in
those living with frailty or medical complexity. However, significant variability exists in pharmacotherapy recommendations
and there were proportionately less recommendations forindividuals who are frail.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 7:01 AM
|
This systematic review examines and synthesises findings from relevant studies, enhancing understanding of the symptoms and implications of MBI in PD. Nine studies from five separate research institutions were identified. The conceptualisation of MBI varied considerably, affecting the reported prevalence rates of MBI in individuals with early-stage PD. Among PwP, MBI was associated higher education and impaired cognition. Affective dysregulation and impulse control disorders were primary contributors to MBI; abnormal perception was least contributor. This systematic review underscores the specific characteristics and incidence of MBI in early-stage PD. Mood and impulse control disorders are primary concerns associated with MBI. Future longitudinal studies are required to clarify the progression of these symptoms and evaluate MBI’s potential as an indicator for PD-related dementia or increased dependency.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 6:34 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 6:24 AM
|
Early DOAC initiation within 4 days after ischaemic stroke associated with atrial fibrillation was non-inferior to delayed initiation for the composite outcome of ischaemic stroke, intracranial haemorrhage, unclassifiable stroke, or systemic embolism at 90 days. Our findings do not support the current common and guideline-supported practice of delaying DOAC initiation after ischaemic stroke with atrial fibrillation.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 6:17 AM
|
In most countries, especially in low-income and middle-income countries, diabetes treatment has not increased at all or has not increased sufficiently in comparison with the rise in prevalence. The burden of diabetes and untreated diabetes is increasingly
borne by low-income and middle-income countries. The expansion of health insurance and primary health care should be accompanied with diabetes programmes that realign and resource health services to enhance the early detection and effective treatment of diabetes.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 6:15 AM
|
With the advent of the first disease-modifying, anti-amyloid β-directed passive immunotherapy
for Alzheimer's disease, questions arise who, when, and how to treat. This paper describes
shortly the pathogenic basis of and preclinical data, which have, more than two decades
ago, initiated the development of this vaccination therapy. We discuss clinical trial
results of aducanumab, lecanemab, and donanemab. We also review appropriate use recommendations
of these novel treatments on patient selection and safety monitoring.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 6:06 AM
|
In contrast to a mere 5 years ago, discussions about menopause are now more mainstream, with the 2024 Super Bowl advertisement for a drug to treat hot flashes and night sweats related to menopause being a recent example. The drug being advertised, fezolinetant, was the first novel dru

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
October 16, 2024 2:09 AM
|
This is a transformative time for patients with Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer disease is increasingly viewed as a treatable condition and managed like other major chronic diseases, such as heart disease and cancer. Management of Alzheimer disease includes early diagnosis with molecula
|

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
February 20, 12:28 PM
|
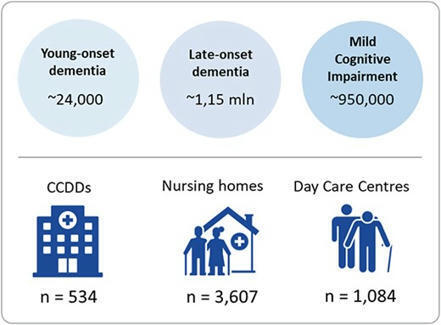
AbstractBackground. Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA), a cornerstone of geriatric care, is challenging to implement in low-resource settings due to

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
May 21, 2025 1:00 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
April 16, 2025 7:11 AM
|
This synopsis summarizes where evidence is strongest to support guidelines in crucial areas relevant to primary care physicians: transition to community (case management, psychosocial or behavioral interventions); motor therapy (task-specific practice, mirror therapy, rhythmic auditory stimulation, electrical stimulation, botulinum toxin for spasticity); dysphagia, aphasia, and cognition (chin tuck against resistance, respiratory muscle strength training); and mental health (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use, psychotherapy, mindfulness-based therapies for treatment but not prevention of depression).

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
April 16, 2025 5:32 AM
|
Abstract. Introduction: Maximizing the benefits of physical activity (PA) is important to prevent physical frailty for a measure of this public health issue. This study aimed to investigate the association of timing of PA with the conversion to physical frailty. Methods: This longitudinal observational study enrolled a total of 1,310 community-dwelling Japanese older adults who enrolled in the National Center for Geriatric and Gerontology-Study of Geriatric Syndromes remained as the examined population. A health checkup was conducted to measure baseline characteristics. Subsequently, objectively measured PA was recorded for ≥7 days (≥10 h per day) for 30 days. Daily steps and the morning (6:00–12:00), afternoon (12:00–18:00), and evening (18:00–24:00) steps were calculated. A 2-year follow-up survey was administered to determine the frailty conversion, defined by newly acquired Kihon Checklist scores of 7 or higher. A logistic regression model was constructed with timing of PA and covariates as explanatory variables and frailty conversion as the dependent variable. Results: The number of conversions to frailty was 121 (9.2%). A significant association were observed between evening steps and frailty conversion (log(OR) = −0.44; 95% confidence interval [CI] = −0.87 to 0.03; p = 0.037). No significant associations were observed in the PA of morning (log(OR) = −0.03; 95% CI = −0.51 to 0.55; p = 0.906) and afternoon (log(OR) = −0.36; 95% CI = −0.78 to 0.13; p = 0.117). Conclusions: Evening PA could be advantageous in preventing frailty conversion among community-dwelling older adults. Maximizing the impact of PA may be effective against this public health concern, physical frailty.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 7:04 AM
|
This is the first Italian guideline that makes evidence-based recommendations on the diagnosis, treatment and care for people with dementia and mild cognitive impairment and their caregivers. New Thirty-four questions were adopted or adapted from the NICE guideline NG97 and 13 new review questions were added, including 10 on the diagnosis and management of people with mild cognitive impairment. The Italian guideline also included evidence synthesis and recommendations for new disease-modifying drugs.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 7:02 AM
|
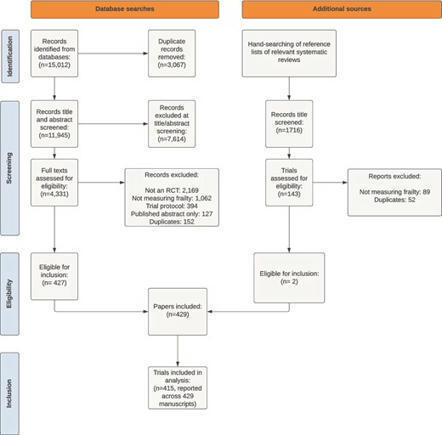
Frailty measurement in RCTs is highly variable. Understanding the properties of respective frailty measures and how these relate to frailty as encountered in clinical practice is a priority to ensure that trial findings can inform healthcare delivery for people living with frailty.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 6:35 AM
|
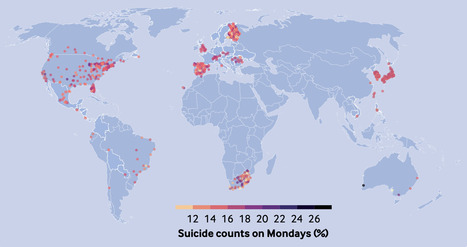
Suicide risk was highest on Mondays and increased on New Year’s day in most countries. However, the risk of suicide on weekends and Christmas varied by country and territory. The results of this study can help to better understand the short term variations in suicide risks and define suicide prevention action plans and awareness campaigns.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 6:31 AM
|
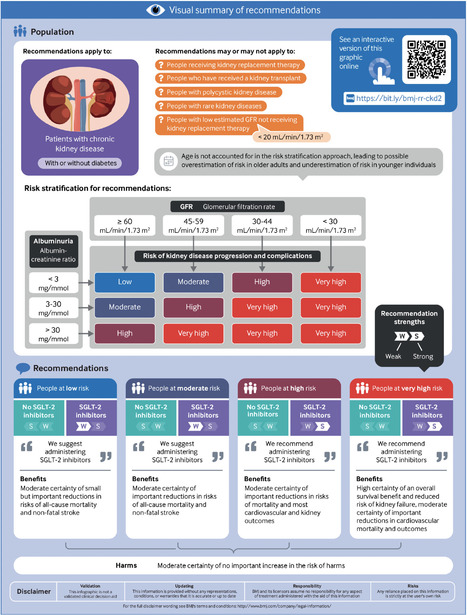
benefits and harms of SGLT-2 inhibitor therapy for adults with CKD over a five year period, along with contextual factors, and provided the following recommendations: 1. For adults at low risk of CKD progression and complications, we suggest administering SGLT-2 inhibitors (weak recommendation in favour) 2. For adults at moderate risk of CKD progression and complications, we suggest administering SGLT-2 inhibitors (weak recommendation in favour) 3. For adults at high risk of CKD progression and complications, we recommend administering SGLT-2 inhibitors (strong recommendation in favour) 4. For adults at very high risk of CKD progression and complications, we recommend administering SGLT-2 inhibitors (strong recommendation in favour). Recommendations are applicable to all adults with CKD, irrespective of type 2 diabetes status.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 6:22 AM
|
Nearly 80 years after the end of the National Socialist (Nazi) regime, its legacies persist with the continued use of anatomical atlases whose precise origins remain unknown.1 Although previous investigations on the history of anatomy during the Nazi
era have revealed unsettling evidence concerning the Pernkopf atlas and other publications of knowledge gained from the bodies of Nazi victims in life and death,2 there remains poor insight into the origins of other anatomical atlases of this period.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 6:16 AM
|
Almost 40 000 people died alone at home in Japan this year—many unnoticed for months—prompting much concern, and new policy. Megan Tatum reports.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
December 3, 2024 6:13 AM
|
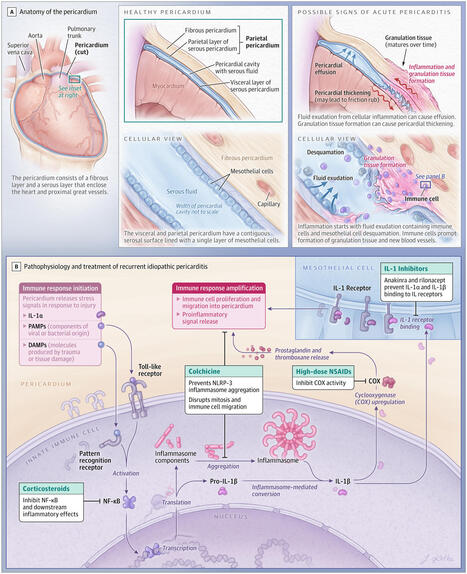
This review summarizes current evidence on recommended treatments for acute pericarditis, its prognosis, and the diagnostic evaluation of individuals with suspected initial or recurrent pericarditis.

|
Scooped by
Servicio de Geriatría
October 16, 2024 2:11 AM
|
This Review summarizes current evidence on pathogenesis, epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of community-acquired pneumonia and focuses on adults without immune-compromising conditions.
|






 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...


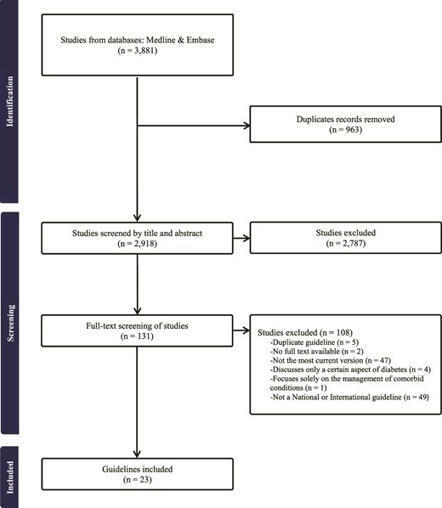
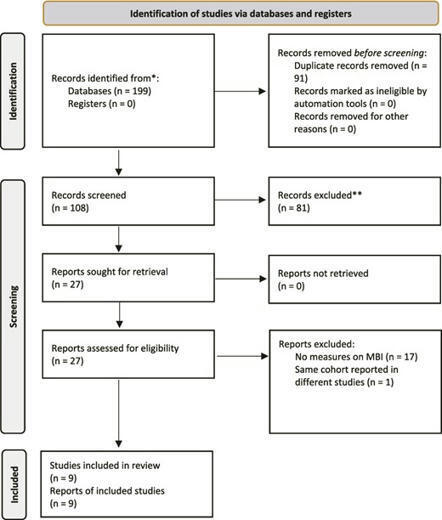














El dispositivo registraba...signos vitales, cámara para el registro de foto y video y la posibilidad de registro EKG. Reducción de hasta el 18% de las derivaciones a ucias.