Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 19, 2022 3:11 AM
|
Un article paru dans le magazine The Conversation et immédiatement repris par Scientific American le 22 janvier 2020 rapportait : « Les serpents – le krait chinois et le cobra chinois – pourraient être la source d'origine du coronavirus récemment découvert qui a déclenché une épidémie d'une...

|
Rescooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
from Veille Coronavirus - Covid-19
November 16, 2021 3:12 AM
|
Since the first case of COVID-19 was identified in the USA in January, 2020, over
46 million people in the country have tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Several
COVID-19 vaccines have received emergency use authorisations from the US Food and
Drug Administration, with the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine receiving full approval on Aug
23, 2021. When paired with masking, physical distancing, and ventilation, COVID-19
vaccines are the best intervention to sustainably control the pandemic. However, surveys
have consistently found that a sizeable minority of US residents do not plan to get
a COVID-19 vaccine.
Via HAS-veille

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 26, 2021 6:33 AM
|
The development of COVID-19 vaccines is occurring at unprecedented speeds, but require high coverage rates to be successful. This research examines in…

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
June 26, 2021 11:33 AM
|
A systematic review of the spread of information during pandemics: A case of the 2020 COVID-19 virus Buy Article: $14.00 + tax (Refund Policy) Pressing the buy now button more than once may result in multiple purchases Author: Shobowale, Oluwakemi Source: Journal of African Media Studies, Volume 13, Number 2, 1 June 2021, pp. 221-234(14) Publisher: Intellect DOI: https://doi.org/10.1386/jams_00045_1 < previous article| view table of contents|next article > The 2020 COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic represents a severe threat to the continent of Africa ‐ to its people, its fauna (as COVID-19 can spread to non-human creatures and human respiratory diseases are often deadly to other primates) and its economy. The context of Africa is unique in its relation to COVID-19 in that Africa has recently suffered from ‐ and still suffers from ‐ severe viral epidemics of HIV and Ebola virus, which creates both more significant vulnerabilities and relevant experience combatting viruses. Within the pandemic, there is a secondary ‘infodemic’ of misinformation which has served to complicate and worsen the effects of COVID-19 itself by undermining the public health measures necessary to prevent the spread of the virus. The purpose of this strategic review of recently published and relevant literature was to assess initial response to pandemics on the continent of Africa, in order to identify how the conspiracy theories, misinformation and disinformation related to COVID-19 may be identified and mitigated throughout the coming months and years and suggest a research agenda for better informing these issues. The study took the form of a systematic review of the literature relating to COVID-19 misinformation in Africa, especially as it relates to prior viral epidemics of HIV/AIDS and Ebola virus. This research is significant as it sheds light on potential means of mitigating the spread of disinformation, and therefore saving lives as we move through this ongoing pandemic. Keywords: Africa; COVID-19; coronavirus; fake news; infodemic; information; misinformation Document Type: Research Article Affiliations: 0000000404092862Swinburne University of Technology Publication date: June 1, 2021
Willingness to get vaccinated against Covid-19 and attitudes toward vaccination in genera
Via HAS-veille

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 28, 2021 1:48 PM
|
One cannot spend >5 min on social media at the moment without finding a link to some conspiracy theory or other regarding the origin of SARS-CoV2, the coronavirus responsible for the COVID-19 pande...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 15, 2021 6:35 AM
|
160 Research Papers Supporting the Vaccine/Autism Link - Free download as Open Office file (.odt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Media reports have claimed that there is no scientific evidence supporting the link between vaccines and autism.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 12, 2021 1:29 PM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 12, 2021 12:48 PM
|
The 1998 Lancet paper by Wakefield et al., despite subsequent retraction and evidence indicating no causal link between vaccinations and autism, triggered significant parental concern. The aim of this study was to analyze the online information available on this topic. Using localized versions of Google, we searched “autism vaccine” in English, French, Italian, Portuguese, Mandarin, and Arabic and analyzed 200 websites for each search engine result page (SERP). A common feature was the newsworthiness of the topic, with news outlets representing 25–50% of the SERP, followed by unaffiliated websites (blogs, social media) that represented 27–41% and included most of the vaccine-negative websites. Between 12 and 24% of websites had a negative stance on vaccines, while most websites were pro-vaccine (43–70%). However, their ranking by Google varied. While in Google.com, the first vaccine-negative website was the 43rd in the SERP, there was one vaccine-negative webpage in the top 10 websites in both the British and Australian localized versions and in French and two in Italian, Portuguese, and Mandarin, suggesting that the information quality algorithm used by Google may work better in English. Many webpages mentioned celebrities in the context of the link between vaccines and autism, with Donald Trump most frequently. Few websites (1–5%) promoted complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) but 50–100% of these were also vaccine-negative suggesting that CAM users are mor

|
Rescooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
from Veille Coronavirus - Covid-19
December 22, 2020 11:05 AM
|
Journal of Medical Internet Research - International Scientific Journal for Medical Research, Information and Communication on the Internet
Via HAS-veille
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 14, 2022 12:03 PM
|
2 articles importants publiés le 10/03 dans Nature Portfolio qui permettent une meilleure compréhension de la désinformation médicale et des théorie

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 2, 2021 3:03 AM
|
Identifying and understanding COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy within distinct populations may aid future public health messaging. Using nationally representative data from the general adult populations of Ireland (N = 1041) and the United Kingdom (UK; N = 2025), we found that vaccine hesitancy/resistance was evident for 35% and 31% of these populations respectively. Vaccine hesitant/resistant respondents in Ireland and the UK differed on a number of sociodemographic and health-related variables but were similar across a broad array of psychological constructs. In both populations, those resistant to a COVID-19 vaccine were less likely to obtain information about the pandemic from traditional and authoritative sources and had similar levels of mistrust in these sources compared to vaccine accepting respondents. Given the geographical proximity and socio-economic similarity of the populations studied, it is not possible to generalize findings to other populations, however, the methodology employed here may be useful to those wishing to understand COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy elsewhere. Hesitancy and resistance towards vaccination is a challenge for public health. Here the authors determine psychological characteristics associated with COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy or resistance attitudes in the UK and Ireland.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 3, 2021 8:20 AM
|
The journal retracts the article, The Safety of COVID-19 Vaccinations—We Should Rethink the Policy [...]
Vaccination programs against COVID-19 are being scaled up. We aimed to assess the effects of vaccine characteristics on vaccine hesitancy among healthcare workers in a multi-center survey conducted within French healthcare facilities from 1 December 2020 to 26 March 2021. We invited any healthcare workers naïve of COVID-19 vaccination to complete an online self-questionnaire. They reported on their socio-demographic characteristics, as well as their perception and beliefs towards vaccination. We measured their willingness to get vaccinated in eight scenarios for candidates’ vaccines presented sequentially (1 to 4-point scale). Candidates’ vaccines varied for efficacy (25%, 50%, 100%), length of immunization (1 year or lifetime), frequency (<1/100, <1/10,000), and severity (none, moderate, severe) of adverse events. We analyzed 4349 healthcare workers’ responses with interpretable questionnaires. The crude willingness to get vaccinated was 53.2% and increased over time. We clustered the trajectories of responses using an unsupervised classification algorithm (k-means) and identified four groups of healthcare workers: those willing to get vaccinated in any scenario (18%), those not willing to get vaccinated at all (22%), and those hesitating but more likely to accept (32%) or reject (28%) the vaccination depending on the scenario. In these last two subgroups, vaccine acceptance was growing with age, educational background and was higher among men with condition. Compared to an ideal vaccine candidate, a 50% reduced efficacy resulted in an average drop in acceptance by 0.8 (SD ± 0.8, −23.5%), while it was ranging from 1.4 (SD ± 1.0, −38.4%) to 2.1 (SD ± 1.0, −58.4%) in case of severe but rare adverse event. The acceptance of a mandatory immunization program was 29.6% overall and was positively correlated to the willingness to get vaccinated, ranging from 2.4% to 60.0%. Even if healthcare workers represent a heterogeneous population, most (80%) could accept the vaccination against COVID-19. Their willingness to get the vaccine increased over time and as immunization programs became available. Among hesitant professionals, the fear of adverse events was the main concern. Targeted information campaigns reassuring about adverse events may increase vaccine coverage, in a population with a strong opinion about mandatory immunization programs.
Via HAS-veille

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 18, 2021 9:01 AM
|
Being a grand challenge of global scale, the COVID‐19 pandemic requires collective and collaborative efforts from a variety of actors to enable the expected scientific advancement and technological...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 12, 2021 1:39 PM
|
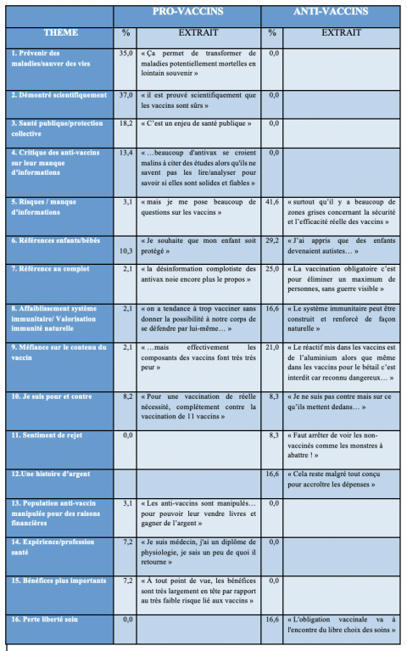
Le combat mené par les instances médicales afin de promouvoir la vaccination et de sensibiliser la population mondiale à ses bienfaits est loin d’être gagné. Afin de mieux comprendre cette situation, les auteurs ont mené une étude en psychologie sur la représentation sociale du vaccin en France à l’aide d’un questionnaire basé sur une méthodologie mixte et composé de trois parties. Le questionnaire a été publié sur le réseau social Facebook de mars à juin 2019, plus particulièrement sur le site des groupes de personnes se déclarant comme « anti-vaccins » et sur le site des groupes dits « neutres ».

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 12, 2021 12:52 PM
|
One of the challenges today is to face fake news (false information) in health due to its potential impact on people’s lives. This article contributes to a new application of social impact in social media (SISM) methodology. This study focuses on the social impact of the research to identify what type of health information is false and what type of information is evidence of the social impact shared in social media. The analysis of social media includes Reddit, Facebook, and Twitter. This analysis contributes to identifying how interactions in these forms of social media depend on the type of information shared. The results indicate that messages focused on fake health information are mostly aggressive, those based on evidence of social impact are respectful and transformative, and finally, deliberation contexts promoted in social media overcome false information about health. These results contribute to advancing knowledge in overcoming fake health-related news shared in social media.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
February 12, 2021 11:45 AM
|
Fake news: misinformation and falsehood of health news in social media constitute a potential threat to the public health, but the scope of this issue…

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 15, 2020 3:47 AM
|
In recent years, mass media and social networks have played an important role in disseminating information regarding public health. During the COVID-19 epidemic, misinformation and fake news have represented an important issue generating confusion and ...

|
Suggested by
Société Francaise d'Immunologie
May 25, 2019 2:25 PM
|
The scientists who published a study a decade ago that linked a gene variant to 'adverse events' in response to smallpox shots say the study, used by anti-vaxxers, is invalid.
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...