Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
April 11, 6:33 AM
|
In the United States, older adults aged 65 years and over make 281 million healthcare visits annually. Information exchanged in these visits forms the bedr

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
February 17, 2024 4:49 AM
|
AbstractBackground. A substantial number of Emergency Department (ED) attendances by care home residents are potentially avoidable. Health Call Digital Care Hom

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
December 29, 2023 11:22 AM
|
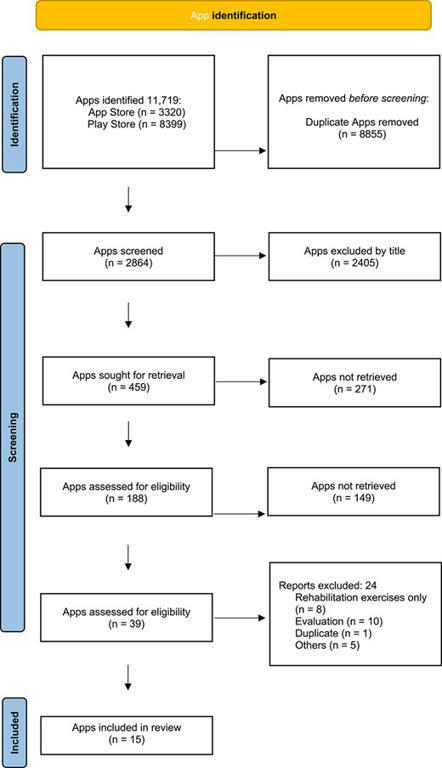
AbstractIntroduction. Different remote interventions, such as applications (apps), have been used to continue promoting healthy ageing and preventing disability

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
December 13, 2023 2:15 AM
|
Abstract. Introduction: Head-down bed rest (HDBR) has long been used as an analog to microgravity, and it also enables studying the changes occurring with aging. Exercise is the most effective countermeasure for the deleterious effects of inactivity. The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of an exercise countermeasure in healthy older participants on attenuating musculoskeletal deconditioning, cardiovascular fitness level, and muscle strength during 14 days of HDBR as part of the standard measures of the Canadian Space Agency. Methods: Twenty-three participants (12 males and 11 females), aged 55–65 years, were admitted for a 26-day inpatient stay at the McGill University Health Centre. After 5 days of baseline assessment tests, they underwent 14 days of continuous HDBR followed by 7 days of recovery with repeated tests. Participants were randomized to passive physiotherapy or an exercise countermeasure during the HDBR period consisting of 3 sessions per day of either high-intensity interval training (HIIT) or low-intensity cycling or strength exercises for the lower and upper body. Peak aerobic power (V̇O2peak) was determined using indirect calorimetry. Body composition was assessed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, and several muscle group strengths were evaluated using an adjustable chair dynamometer. A vertical jump was used to assess whole-body power output, and a tilt test was used to measure cardiovascular and orthostatic challenges. Additionally, changes in various blood parameters were measured as well as the effects of exercise countermeasure on these measurements. Results: There were no differences at baseline in main characteristics between the control and exercise groups. The exercise group maintained V̇O2peak levels similar to baseline, whereas it decreased in the control group following 14 days of HDBR. Body weight significantly decreased in both groups. Total and leg lean masses decreased in both groups. However, total body fat mass decreased only in the exercise group. Isometric and isokinetic knee extension muscle strength were significantly reduced in both groups. Peak velocity, flight height, and flight time were significantly reduced in both groups with HDBR. Conclusion: In this first Canadian HDBR study in older adults, an exercise countermeasure helped maintain aerobic fitness and lean body mass without affecting the reduction of knee extension strength. However, it was ineffective in protecting against orthostatic intolerance. These results support HIIT as a promising approach to preserve astronaut health and functioning during space missions, and to prevent deconditioning as a result of hospitalization in older adults.

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
December 13, 2023 1:55 AM
|
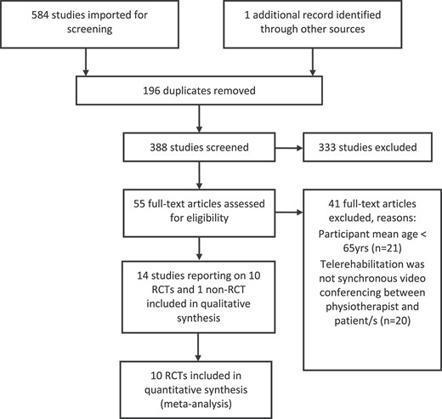
AbstractBackground. Telerehabilitation can be an appropriate alternative to face-to-face rehabilitation for adults; however, it is uncertain whether it is safe

|
Rescooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
from Content Curation World
October 21, 2023 5:29 PM
|

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
November 10, 2021 3:30 AM
|
The pandemic revealed the importance of interoperability in healthcare. Learn how the right digital foundation is essential to facilitating communication more easily and handling complex analytics to ensure better outcomes, efficacy, and equity.

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
November 9, 2021 12:37 PM
|

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
October 1, 2021 3:39 PM
|
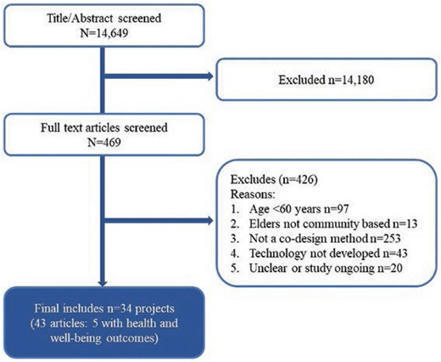
AbstractBackground and Objectives. There is a growing interest to involve older adults in the co-design of technology to maintain their well-being and independe

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
October 1, 2021 3:38 PM
|
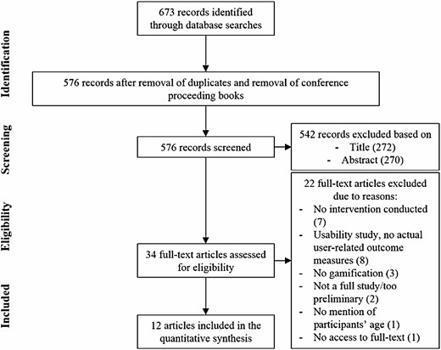
AbstractBackground and Objectives. During past years, gamification has become a major trend in technology, and promising results of its effectiveness have been

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
June 18, 2021 9:04 AM
|
Background Psychosocial issues, such as social isolation and loneliness among older adults and people with dementia, continue to pose challenges with a rapidly aging population worldwide. Social robots are a rapidly emerging field of technology, developed to help address the psychosocial needs of this population. Although studies have reported positive findings regarding their psychosocial benefits, their implementation in real-world practice remains a challenge. Nevertheless, little is known about the factors affecting their implementation. The purpose of this review is to provide a systematic overview of the barriers and facilitators affecting the implementation of social robots for older adults and people with dementia. Method The Arksey and O’Malley approach with methodological enhancement by Levac et al. was used to guide the conduct of this review. Seven electronic databases were searched. In addition, hand searching and backward citation tracing was conducted. Three independent reviewers were involved in the screening and data charting process. Findings were synthesised and categorised into the five domains outlined in the Consolidated Framework of Implementation Research (CFIR). Results A total of 53 studies were included in the final review. Most of the included studies were based in participants’ homes and in care facilities. Barriers and facilitators were mapped onto 18 constructs in the five domains of the CFIR. The most frequently cited barriers were mapped to the constructs within the domain of “Intervention characteristics”, where issues such as the complexity of using the technology and technical obstacles impeded implementation. Most facilitators were mapped onto the domain “Patient needs and resources”. Overall, existing research are disproportionately focused on the internal validity (i.e. characteristics) of social robots, and there is significantly less research investigating their external validity, such as organisational or wider contextual factors that can affect their implementation in real-world practice. Conclusion This review has identified and synthesised the breadth of evidence on the barriers and facilitators to the implementation of social robots for older adults and people with dementia. Future research should pay more attention to investigating the contextual factors, using an implementation framework, to identify barriers and facilitators to guide the implementation of social robots.

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
June 8, 2021 4:35 AM
|
The FDA recently authorized a new device that helps to reeducate muscles to improve range of motion for patients who are recovering from a stroke.Marketed as th Read the full article at: jamanetwork.com

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
April 22, 2021 2:32 PM
|
AbstractBackground. The accessibility, versatility and motivation provided by virtual reality technology (VRT) have fostered its rapid expansion as a rehabilita
|

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
February 27, 2024 3:31 AM
|
Poll results from more than 2600 respondents found that about 8% of adults aged 50 to 80 years reported using an online-only direct-to-consumer health care service. This may increase though. About one-third of the respondents expressed interest in using these services in the future, th

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
February 17, 2024 4:23 AM
|
This Viewpoint discusses the potential drawbacks of the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine, for example, the loss of certain skills due to the reliance on AI, and how physicians should consider how to take advantage of the potential benefits of AI without losing control ove

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
December 29, 2023 11:21 AM
|
Abstract. Artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare describes algorithm-based computational techniques which manage and analyse large datasets to make inferenc

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
December 13, 2023 2:13 AM
|
See the Reply by Nihal Haque in this issue.

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
December 13, 2023 1:00 AM
|
Digital Technology for Diabetes Monitors to measure glucose levels have been paired with software controlling insulin delivery. The authors examine the state of the art in digital technology t

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
October 13, 2023 5:48 AM
|
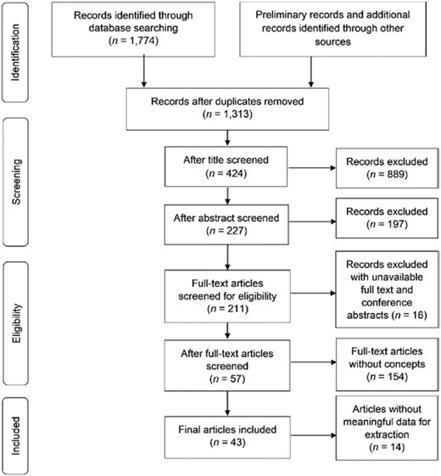
Abstract. Background and Objective: The purpose of our study was to explore the immediate and long-term effects of socially assistive robots (SARs) on neuropsychiatric symptoms (NPSs), behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD), positive emotional experiences, and social interaction in older people living with dementia. Methods: We set keywords and used Boolean operators to search the CINAHL, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, IEEE Digital Library, MEDLINE, PsycINFO, PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Chinese Electronic Periodical Service from inception to February 2022 for randomized controlled trials. The Cochrane Collaboration bias assessment tool was used to assess article quality, and RevMan 5.4.1 software was used to conduct the meta-analysis. Results: A total of 14 studies were included in the meta-analysis. SARs can help people living with dementia reduce their NPS of depression and anxiety, provide happiness from positive emotional experiences, and improve their social interaction through conversation. However, there was no significant improvement in agitation behavior, overall BPSD, or quality of life in people living with dementia. In follow-up, it was found that the effect of SRT was limited. Conclusion: SARs can reduce depression and increase positive emotions in people living with dementia. They may also reduce the burden on healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. This research was registered on PROSPERO CRD42020169340.

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
November 10, 2021 3:21 AM
|
The Covid-19 pandemic brought telehealth into its own as a viable and sometimes preferable way to deliver care. We now have the opportunity to realize its full value in improving health an

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
November 9, 2021 12:36 PM
|
If you have followed the news on digital technology and health in recent months, you will have read of a blockbuster fraud trial centred on a dubious blood-testing device, a controversial partnership between a telehealth company and a data analytics company, a social media company promising action to curb the spread of vaccine misinformation, and another addressing its role in the deteriorating mental health of young women. For proponents and critics alike, these stories encapsulate the health impact of many digital technologies, and the uncertain and often unsubstantiated position of digital technologies for health.

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
October 1, 2021 3:38 PM
|
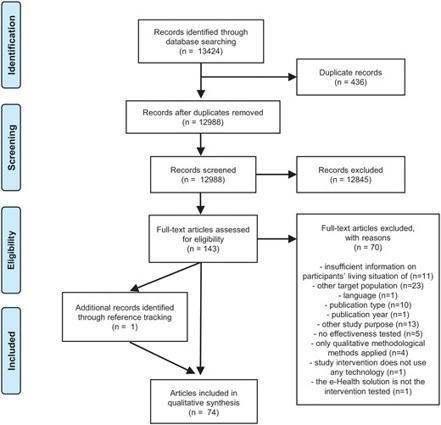
AbstractBackground and Objectives. e-Health solutions are an innovative approach to support aging with cognitive impairment. Because technology is developing at

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
October 1, 2021 3:37 PM
|
AbstractBackground and Objectives. With the emergence of healthy aging as a key societal issue in recent decades, technology has often been proposed as a soluti

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
June 8, 2021 6:35 AM
|
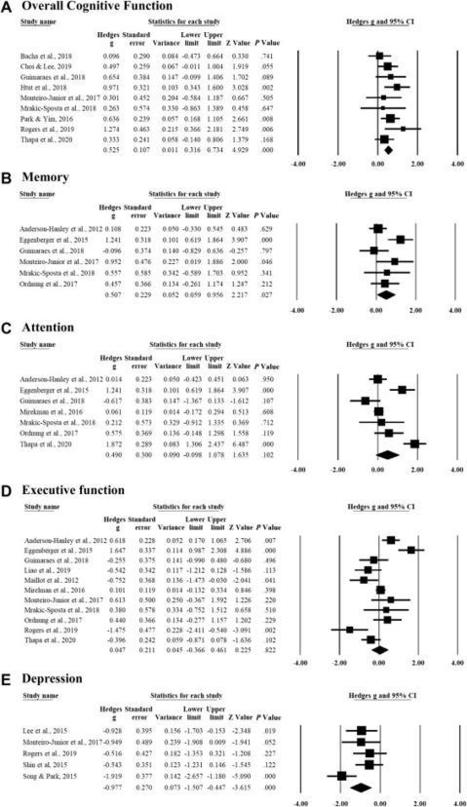
Virtual reality (VR) exergames are an innovative approach to promote older adults'
mental health. VR exergames are active video games controlled by bodily movements
in a safe surrounding with advantages of physical activity engagement and interactions.
The purpose of this study was to explore the effectiveness of VR exergames in improving
older adults’ cognition and ameliorating depressive outcome by a systematic review,
meta-analysis, subgroup analysis, and meta-regression.

|
Scooped by
Sergio Ariño Blasco
April 23, 2021 2:28 AM
|
AbstractBackground and Objectives. The relationship between frailty and disability in activities of daily living (ADLs) can be seen in different ways, with disa
|

 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...