Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 19, 2024 7:02 AM
|
Do you know Arthur?
ARTHUR is a robot developed by ROPCA, an Odense-based startup founded in 2019 by a specialist in rheumatology and a professor in robotics…

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 8, 2024 4:06 AM
|
This eLearning course has been designed to educate healthcare professionals (HCPs) on the management of rheumatoid arthritis with interleukin-6 receptor inhibition therapy, with a specific focus on tocilizumab and its biosimilars.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 28, 2024 1:07 PM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 9, 2024 4:33 AM
|
A newly approved drug blocks two cytokines...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 2, 2024 6:29 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 11, 2024 3:37 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 9, 2024 11:14 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 31, 2024 9:47 AM
|
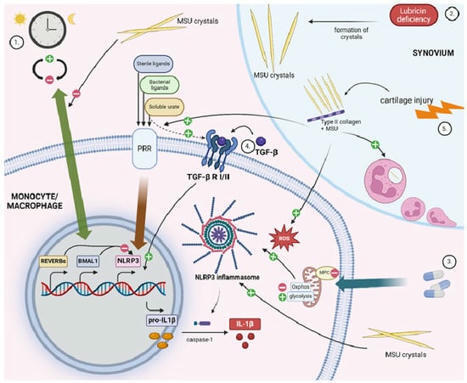
Gout is a prevalent form of inflammatory arthritis caused by the crystallization of uric acid in the joints and soft tissues, leading to acute, painful attacks. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in mononuclear cells, along with inflammasome-independent pathways, is responsible for the inflammatory phenotype in gout. Research into the different aspects of gout pathophysiology and potential treatment options is ongoing. This review highlights some of the basic research published in the 12 months following the 2022 Gout, Hyperuricemia, and Crystal-Associated Disease Network (G-CAN) conference and focuses on mechanisms of inflammation, encompassing pro- and anti-inflammatory pathways, as well as the exploration of various biological systems, such as single-cell transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and microbiome analyses.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 11, 2024 3:35 AM
|
Research has unveiled the intricate cellular landscape of healthy human hamstring tendons, shedding new light on this vital yet often overlooked component of our musculoskeletal system.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
June 8, 2024 1:56 AM
|
A EULAR consensus group has established classification criteria for overall hand osteoarthritis (OA) and its subtypes (interphalangeal OA and thumb base OA).The criteria require two mandatory criteria to be met:must have symptoms (pain, aching and/or stiffness) in at least one target joint on most days of the previous 6 weeks.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 24, 2024 4:44 AM
|
The Stanford Medicine researcher was known for his groundbreaking work and his generous spirit as a mentor and colleague.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 1, 2024 5:07 AM
|
<em>Arthritis Care & Research</em> is a rheumatology journal from the American College of Rheumatology and the Association of Rheumatology Health Professionals.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 15, 2024 3:52 PM
|
Les 29 entreprises de la Prosthesis Valley entre Chaumont et Nogent en Haute-Marne, un ancien territoire spécialisé dans la coutellerie, sont devenues en quelques années des leaders mondiaux sur le marché médical.
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 17, 2024 7:34 AM
|
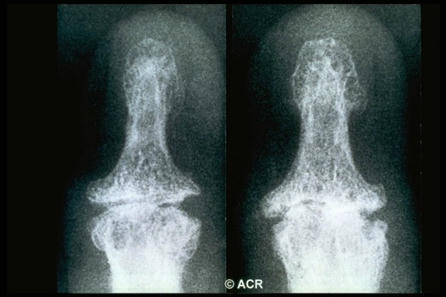
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) disease is a crystalline arthritis that was described more than 60 years ago, yet our knowledge about this condition greatly lags behind other forms of arthritis. This is an exciting era for CPPD disease as a robust framework for CPPD clinical research has been established. The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and EULAR co-sponsored the development of the first-ever classification criteria for CPPD. The Outcomes Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) CPPD Ultrasound Subtask Force developed and validated definitions for ultrasonographic findings of CPPD, and the OMERACT CPPD Working Group is establishing a core outcome domain set for this crystalline arthritis. This review focuses on key elements of the 2023 ACR/EULAR CPPD disease classification criteria and considerations for measuring outcomes in CPPD disease.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
December 4, 2024 1:57 PM
|
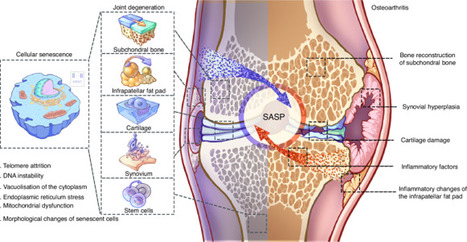
Osteoarthritis (OA) poses a significant challenge in orthopedics. Inflammatory pathways are regarded as central mechanisms in the onset and progression of OA. Growing evidence suggests that senescence acts as a mediator in inflammation-induced OA.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 18, 2024 6:10 AM
|
Les annonces et les contenus non personnalisés dépendent, par exemple, du contenu du site que vous consultez et de votre position (la diffusion d'annonces est basée sur votre position approximative). Les annonces et les contenus personnalisés peuvent aussi inclure, par exemple, des recommandations...

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
November 7, 2024 10:30 AM
|
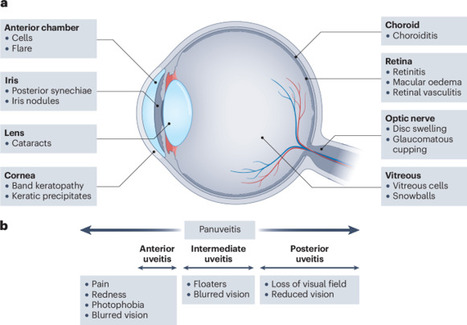
Uveitis encompasses multiple different conditions that are all characterized by intra-ocular inflammation. Uveitis occurs in the context of many different rheumatological conditions and carries a substantial risk to vision. Uveitis can develop both at the early stages of rheumatic diseases, sometimes even preceding other clinical features, and at later stages of disease. Uveitis can also occur as either a direct or an indirect complication of therapies used to treat patients with rheumatic disease. Conversely, patients with uveitis of non-rheumatic aetiology sometimes require immunosuppression, a treatment option that is not readily accessible to ophthalmologists. Thus, collaborative working between rheumatologists and ophthalmologists is critical for optimal management of patients with uveitis. This Review is written with rheumatologists in mind, to assist in the care of patients with uveitis. We collate and summarize the latest evidence and best practice in the diagnosis, management and prognostication of uveitis, including future trends and research priorities. This Review provides an overview of the pathogenesis, classification and diagnosis of and treatment strategies for adult and paediatric rheumatology patients with uveitis. The authors highlight the importance of collaborations between ophthalmologists and rheumatologists to provide optimal treatment of uveitis, improve patient care and enhance future research.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
September 10, 2024 11:22 AM
|
Periarticular calcifications are a common condition for rheumatologists. They are characterized by deposition of carbonated apatite in tendons or connective tissues around joints. It most commonly affects patients between 30 and 60, and the main location is the shoulder (rotator cuff tendons), followed by the hip. Although the disease is frequent, factors associated with the appearance of the deposits or their spontaneous resorption remain unclear. In this review, we will summarize the available data about mechanisms underlying the constitution of the deposits and their resorption and describe the various affected sites and the associated symptoms. In the last part, we will discuss current treatment options.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 10, 2024 4:46 AM
|
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a highly prevalent joint disease that causes substantial disability, yet effective approaches to disease prevention or to the delay of OA progression are lacking. Emerging evidence has pinpointed ion channels as pivotal mediators in OA pathogenesis and as promising targets for disease-modifying treatments. Preclinical studies have assessed the potential of a variety of ion channel modulators to modify disease pathways involved in cartilage degeneration, synovial inflammation, bone hyperplasia and pain, and to provide symptomatic relief in models of OA. Some of these modulators are currently being evaluated in clinical trials. This review explores the structures and functions of ion channels, including transient receptor potential channels, Piezo channels, voltage-gated sodium channels, voltage-dependent calcium channels, potassium channels, acid-sensing ion channels, chloride channels and the ATP-dependent P2XR channels in the osteoarthritic joint. The discussion spans channel-targeting drug discovery and potential clinical applications, emphasizing opportunities for further research, and underscoring the growing clinical impact of ion channel biology in OA. Ion channels have key functions in chondrocytes, bone cells, immune cells and neurons. Liu and colleagues discuss how these functions might contribute to cartilage degeneration, bone formation inflammation and pain in osteoarthritis, and highlight the therapeutic potential of ion channel modulators.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
August 2, 2024 4:24 AM
|
Lancet Rheumatology has published a review of Calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) disease - a chronic inflammatory and degenerative crystal arthropathy that increases with aging.While the inflammatory response to calcium pyrophosphate (CPP) crystals may cause an acute or chronic inflammatory arthritis, over time CPPD is associated with cartilage degradation and osteoarthritis, but its unclear which is primary or if this evolution is bidirectional. The following are highlight or excerpts from the review article by Pascart et al:

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
July 23, 2024 3:30 AM
|
Background The increased availability of myositis autoantibodies represents new possibilities and challenges in clinical practice (Lundberg IE, Tjärnlund A, Bottai M, Werth VP, Pilkington C, de Visser M, et al. 2017 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and their major subgroups. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:1955–64. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211468 .). The aim of this study was to perform a retrospective data analysis of patient cases with positive myositis autoantibodies to analyse their significance in routine rheumatology practice. Methods A monocentric analysis of all the orders used to determine myositis autoantibodies from July 2019 to May 2022 in the Department of Rheumatology, Krankenhaus Porz am Rhein, Cologne, Germany, was carried out. Results In the defined time interval, a total of 71,597 laboratory values for the antibodies mentioned above were obtained. A total of 238 different positive autoantibodies were detected in 209 patients. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy was diagnosed in 37 patients (18%), and inflammatory rheumatic diseases other than idiopathic inflammatory myopathy were diagnosed in 90 patients (43%). No inflammatory rheumatic disease was diagnosed in 82 patients (39%). General clusters of clinical manifestations were observed. Conclusions In our cohort, we were able to show that a relevant proportion of patients with positive myositis antibodies did not have idiopathic inflammatory myopathies or inflammatory rheumatic diseases. This finding indicates the importance of myositis autoantibodies in this group of patients. However, further studies on the course of symptoms and examination results in patients without inflammatory rheumatic diseases and with positive myositis antibodies are necessary.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
June 10, 2024 9:08 AM
|
Exercising and stretching can help relieve lower back pain. Learn the best exercises for your lower back, where to start, and how to prevent future pain.

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 30, 2024 11:26 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
April 7, 2024 5:02 AM
|
Breaking Barriers Through Multi-Disciplinary Osteoarthritis (OA) Research - the OARSI - Osteoarthritis Research Society International World Congress in Vienna,…

|
Scooped by
Gilbert C FAURE
March 17, 2024 6:20 AM
|
Today I want to highlight the paper of Marta Favero, Roberta Ramonda and team on erosive hand osteoarthritis.
This disease is most common in women and…
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...