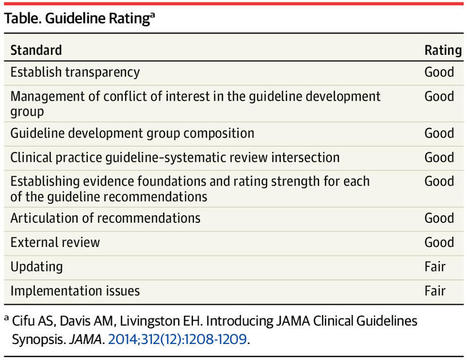
Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA) is a multidimensional interdisciplinary diagnostic process focused on determining an older person's medical, psychological and functional capability in order to develop a co‐ordinated and integrated care plan. CGA is not limited simply to assessment, but also directs a holistic management plan for older people, which leads to tangible interventions.
While there is established evidence that CGA reduces the likelihood of death and disability in acutely unwell older people, the effectiveness of CGA for community‐dwelling, frail, older people at risk of poor health outcomes is less clear.
CGA had no impact on death or nursing home admission.
There is low‐certainty evidence that community‐dwelling, frail, older people who undergo CGA may have a reduced risk of unplanned hospital admission.
Further studies examining the effect of CGA on emergency department visits and change in function and quality of life using standardised assessments are required.






 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...

















Necesidad de profundizar en el conocimiento sobre la efectividad de la intervención. Las variables resultado estudiadas…
Primary outcomes: Death, Nursing home admission, Unplanned hospital admission, Emergency department visits, Serious adverse events.
Secondary outcomes: Change in function, Quality of life (QoL), Resource use.
A considerar nuevas variables resultado (PROMs y PREMs).