 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
November 7, 2019 3:47 AM
|
Event chain methodology is a network analysis technique that is focused on identifying and managing events and relationship between them (event chains) that affect project schedules. It is an uncertainty modeling schedule technique. Event chain methodology is an extension of quantitative project risk analysis with Monte Carlo simulations.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
November 7, 2019 3:41 AM
|
Information technology risk, IT risk, IT-related risk, or cyber risk is any risk related to information technology. While information has long been appreciated as a valuable and important asset, the rise of the knowledge economy and the Digital Revolution has led to organizations becoming increasingly dependent on information, information processing and especially IT.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
November 7, 2019 3:26 AM
|
IT risk management is the application of risk management methods to information technology in order to manage IT risk, i.e.: The business risk associated with the use, ownership, operation, involvement, influence and adoption of IT within an enterprise or organization Different methodologies have been proposed to manage IT risks, each of them divided into processes and steps.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
November 4, 2019 6:20 AM
|
The article then explains how uncertainty is treated during these 25 years: model and propagate uncertainty, manage and analyze the uncertain data, decide in an uncertain context. The article concludes with the different actions that should be involved in the near future.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
September 18, 2019 3:28 AM
|
This post comes after a series of three posts where I exposed my thoughts about development of software medical devices with agile methods. These posts were focussed on software

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
August 20, 2019 4:20 AM
|
In Scrum, the risk management activities are divided among various roles with some responsibility resting with everyone in the Scrum Team and the Scrum Master facilitating the process. Risk management is integral to ensuring value creation; therefore, risk management activities are performed throughout the project lifecycle and not just during project initiation.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
July 10, 2019 8:42 AM
|
Une approche complexe
Cette dernière approche, qui est celle que je propose, se base sur le constat de l’imprédictibilité des crises et de la dimension d’improvisation nécessaire venant compléter la préparation de l’organisation.
« crisis is an unexpected, undesirable, unpredictable and unthinkable, which most of the time produces uncertainty and disbelief« (Milasinovic et al., 2010 ; Heat et al., 2009)
Cette approche met en évidence la nature complexe de l’organisation impactée et la non-proportionalité (ou non-linéarité) de l’événement. L’organisation et les acteurs sont confrontés à une situation totalement inattendue, imprévisible et dans une incertitude omniprésente dans laquelle il devient fondamental de s’adapter aux moyens disponibles, voire d’improviser, afin de limiter au mieux les conséquences.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
March 18, 2019 5:46 AM
|
Antifragile : le dernier élément de la triade : fragile – robuste – antifragile. Ce qui est fragile se casse avec le temps (et donc le hasard), ce qui est robuste résiste, ce qui est antifragile se renforce.
Heuristique : une heuristique est une hypothèse pratique que l’on formule sous forme de règle et qui est validé par la pratique sans que l’on sache nécessairement expliquer pourquoi. Pour Taleb plus les heuristiques sont anciennes plus elles sont « sûres ».
#skininthegame : seules les personnes qui payent les conséquences de leurs décisions doivent en prendre. C’est sa position que j’adapte en disant que ceux qui sont #skininthegame sont ceux qui « savent », c’est-à-dire qu’ils choisissent les conseils qu’on leur donne et que si ils refusent le conseil donné, c’est eux qui ont raison, même si ils sont incapables de vous expliquer pourquoi.
Conséquences : pour étudier une décision risquée (et donc difficile) il vaut mieux se fier à l’analyse des conséquences (négatives et positives) qu’aux probabilités.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
October 5, 2018 1:27 AM
|
Comment définir le risque et le gérer dans le cadre d'un projet Agile ? • quel type de risque ? • priorisation et risque • quels outils et techniques ?

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
September 26, 2018 10:45 AM
|
Agile methods incorporate many mechanisms for dealing with late breaking changes (an easily reprioritized backlog, short iterations, frequent inspection, and re-planning, etc.) that also lend themselves to proactively responding to risks. We can insert risk avoidance and risk reduction actions into the backlog to proactively attack the risks before they have an impact on the project. This paper describes a set of collaborative team games used to engage the whole team in opportunity and risk management activities. It outlines an approach that overcomes many of the "correct-but-not-sufficient" aspects of risk management seen too often on projects: poor engagement; done once; not revisited enough; not integrated into the project life cycle; and not engaging, poor visibility. The paper begins with an explanation of the risk management strategies implicit in the agile life cycle, and then describes a series of team games to explicitly tackle risk and opportunity management.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
August 9, 2018 4:55 AM
|
La fiche action risque liste les actions spécifiques qui vont être menées pour traiter les risques identifiés. Elle est élaborée par le responsable du risque, avec l'aval du chef de projet pour l'obtention des ressources associées. Les actions décidées sont intégrées dans l'organigramme des tâches, le planning et le budget du projet. Des budgets leur sont alloués. L'avancement de ces actions est maîtrisé et les résultats produits sont reportés dans cette fiche. Il est alors possible de décider de continuer les actions ou de les arrêter.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
August 17, 2017 2:26 AM
|
Manage 3 common ERP Risk factors - including cost, time, complexity. Proper planning and building a solid foundation to your ERP project is key.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
April 28, 2017 10:16 AM
|
Une SIF a pour objectif de réduire un risque. Pour définir le niveau de SIL à allouer (SIL requis) à une SIF, il est nécessaire de mener une démarche rigoureuse. Pour déterminer le SIL requis d’une SIF, la norme IEC 61511 introduit trois méthodes qui sont de ce fait les plus répandues dans le secteur des industries de procédés : - graphe de risque ;
- matrice de criticité ;
- LOPA.
Dans la pratique, ces trois méthodes ont des étapes communes, qui peuvent, suivant la méthode, être explicites ou implicites : - estimation de la criticité du risque « initial » (c’est-à-dire sans prendre en compte la SIF dont on cherche à déterminer le SIL requis) ;
- confrontation de la criticité du risque à des critères d’acceptabilité, qui permettent de déterminer le facteur de réduction du risque (FRR) que la SIF doit introduire pour rendre le risque acceptable ;
- estimation du niveau de SIL requis à partir du FRR.
Étapes :
|

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
November 7, 2019 3:43 AM
|
Risk analysis is the science of risks and their probability and evaluation. Probabilistic risk assessment is one analysis strategy usually employed in science and engineering. Risk analysis should be performed as part of the risk management process for each project.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
November 7, 2019 3:32 AM
|
MEHARI ( MEthod for Harmonized Analysis of RIsk) is a free, open-source information risk analysis assessment and risk management method, for the use of information security professionals. MEHARI enables business managers, information security/risk management professionals and other stakeholders to evaluate and manage the organization's risks relating to information, information systems and information processes (not just IT).

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
November 4, 2019 6:22 AM
|
L'exposé présentera quelques-unes des méthodes utilisées à l'heure actuelle pour résoudre ce problème. Ces dernières s'appuient principalement sur les connaissances disponibles issues du retour d'expérience (données historiques, données mesurées), de l'expertise et de modèles de comportement fiabiliste ou physique.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
October 23, 2019 7:54 AM
|
1. PRINCIPE DE LA MÉTHODOLOGIE « BOWTIE » OU « NOEUD PAPILLON » Le « Bowtie » est une approche probabiliste d’évaluation du risque. Elle résulte de la combinaison d’un arbre de défaillances et d’un arbre d’événements, centré sur un même événement redouté. L’application de cette méthode dans le milieu industriel est de plus en plus répandue. La méthode de « Bowtie » présente l’avantage d’apporter un modèle pour la Maîtrise des Risques. Le mode de représentation sous forme de nœud papillon a donné son nom à la méthodologie. 2. OBJECTIFS DE LA MÉTHODOLOGIE « BOWTIE » OU « NOEUD PAPILLON« Concrètement cette approche permet de : - représenter les relations entre les dangers leurs causes et leurs effets ;
- évaluer la contribution de chaque cause et la gravité de chaque risque ;
- positionner des barrières de prévention et de protection ;
- évaluer les facteurs aggravants diminuant l’efficacité des barrières ;
- évaluer la robustesse et la contribution des barrières à l’atténuation des risques ;
- évaluer l’impact de ces barrières sur la cotation générale du risque.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
September 17, 2019 10:55 AM
|
If my PACS viewer can't read 100% DICOM compliant data, it's a defect.
If my PACS viewer can't read corrupted data, it's a software failure.
You can see in this case that, this software failure doesn't mean that the software is guilty. Data were corrupted through the network, when burning the CDROM ... not by the PACS viewer.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
August 6, 2019 8:24 AM
|
Les prévisions sont en général à peu près justes, mais lorsqu’elles s’avèrent inexactes, les effets peuvent être spectaculaires. Cela arrive rarement, et parce que la probabilité de tels évènements est faible, nous pensons que nous pouvons nous en tirer à bon compte. Cependant, comme l’a observé Nassim Taleb en formulant l’expression « Cygne noir », des évènements de faible probabilité peuvent cependant avoir un très fort impact. En fait, on peut même avancer que nos efforts pour réduire la survenance de tels évènements, c’est à dire réduire la volatilité dans le langage de Ben Bernanke, ne font que contribuer à augmenter leur impact quand ils surviennent, car ils finissent toujours par survenir (leur probabilité n’est jamais nulle, seulement faible). En substance, moins un évènement est probable, plus sa survenance est coûteuse.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
May 8, 2019 8:25 AM
|
La méthode EBIOS (Expression des Besoins et Identification des Objectifs de Sécurité) est un outil complet de gestion des risques SSI conforme au RGS et aux dernières normes ISO 27001, 27005 et 31000.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
March 13, 2019 1:05 PM
|
In my previous post, I discussed the five risk areas found on most projects and how Agilemanaging risk in scrum agile addresses them.
Managing risk is prevalent in Scrum on a daily basis. Discovery, analysis, and mitigation for risk happens organically in Agile, and particularly in Scrum. Let’s compare risk management practices between traditional/”waterfall” project management and Scrum.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
September 26, 2018 10:47 AM
|
To help provide current and aspiring Agile professionals with additional information and guides for Scrum, we have compiled a list of member-written articles from a wide variety of experts. We have articles that cover a wide range of topics to help you learn everything you need to know.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
August 13, 2018 12:20 PM
|
Le registre des risques permet d'agréger en un document unique la totalité des risques identifiés pour un projet. Il facilite par ailleurs la mise en commun des risques d'un portefeuille de projets de l'entreprise. Il comprend les données descriptives essentielles de chacun des risques. Il est mis à jour au fur et à mesure de l'avancement du projet. Un registre des risques peut contenir des risques de maturité différente : certains risques ont été identifiés depuis le début du projet et ont déjà fait l'objet d'actions de réduction. Les risques les plus récemment identifiés n'ont pas forcément été traités.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
January 23, 2018 2:13 AM
|
Why RiskStorming? Beren van Daele and Andreas Faes were chosen to give a workshop at the Agile & Automation days in Krakau.

|
Scooped by
Mickael Ruau
April 28, 2017 10:18 AM
|
Une analyse des risques permet de déterminer comment la sûreté de fonctionnement permettra d’assurer une protection adéquate contre chacun des risques qui peuvent survenir. Ces dangers sont donc traités de manière appropriée pendant la phase de conception pour que le système final soit exempt de défaut.
En effet, les fonctions de sécurité sont la résultante des systèmes électriques, électroniques ou électroniques programmables qui sont habituellement complexes, ce qui a pour conséquence de rendre très difficile la détermination des défaillances. L’objectif est donc de concevoir le système d’une manière qui évite un maximum de pannes et qui les contrôle si elles apparaissent Les pannes peuvent provenir de nombreux facteurs différents :
> Erreurs sur le logiciel,
> Erreur humaine,
> Influence de l’environnement,
> Panne matérielle aléatoire des mécanismes,
> Etc… Ainsi, la sécurité de fonctionnement dépend du bon fonctionnement d’un système global ou d’un équipement en réponse à ses entrées.
C’est pourquoi la norme IEC 61508 (CEI 61508 en français) fut créée.
|




 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...


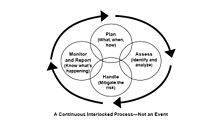







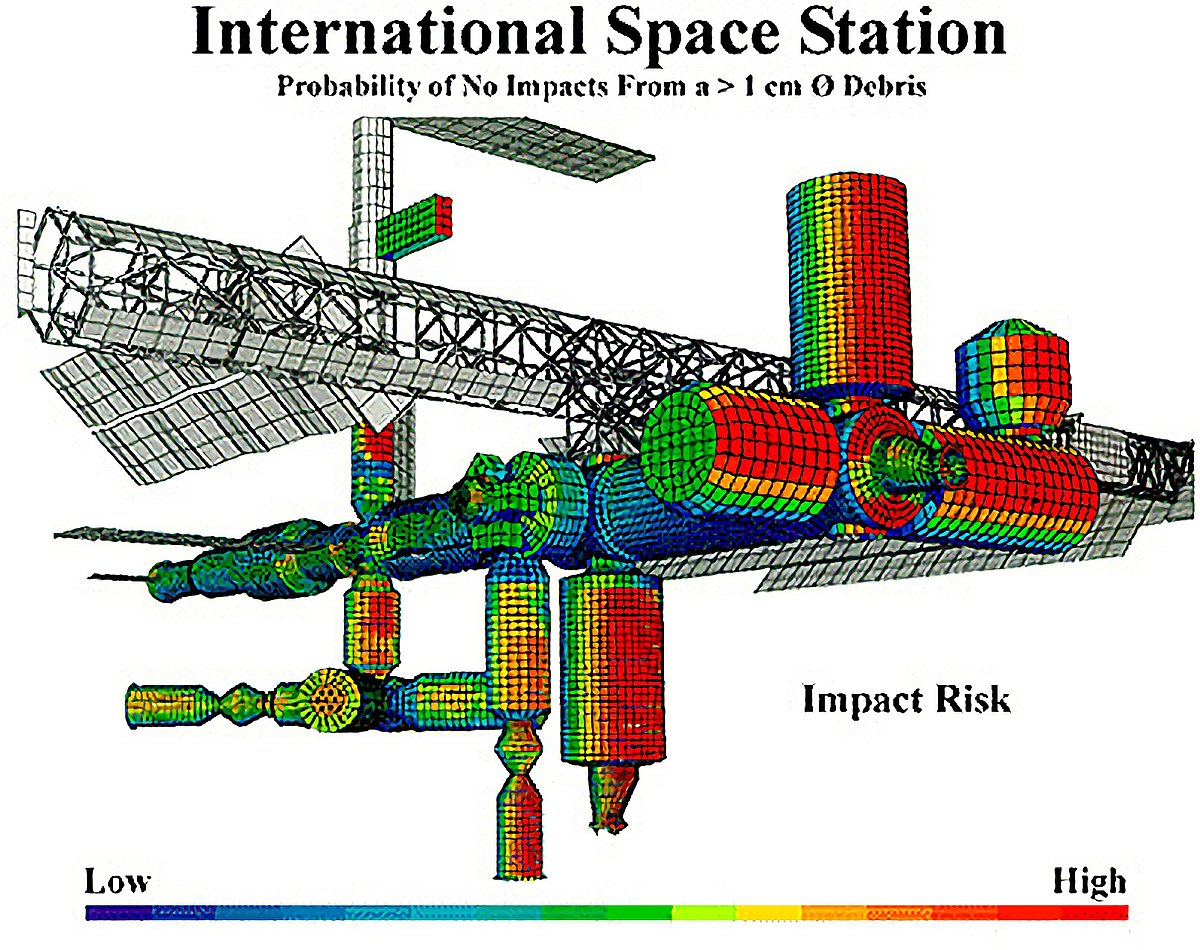
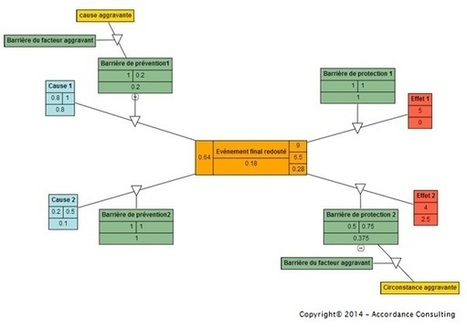











Event chain methodology helps to mitigate the effect of motivational and cognitive biases in estimating and scheduling.[2][3] It improves accuracy of risk assessment and helps to generate more realistic risk adjusted project schedules.[4]