Your new post is loading...
Au cœur du site classé au Patrimoine mondial de l’Unesco en 1981, la Société des mines de fer de Guinée s’apprête à lancer la première phase d’un chantier d’exploitation qui menace des écosystèmes d’une exceptionnelle rareté. Le gouvernement guinéen doit encore donner son accord.
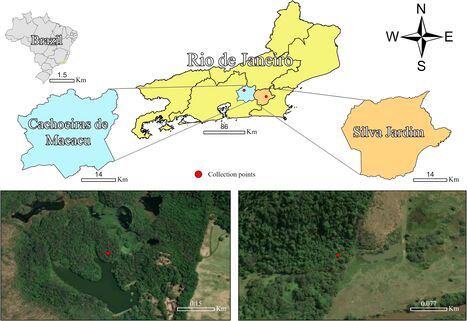
Dans l’Etat de Rio, la déforestation massive et la disparition des animaux vertébrés poussent les moustiques à s’aventurer à l’extérieur de la forêt, augmentant les risques de propagation de virus, révèle une étude publiée ce jeudi.
Via Bernadette Cassel, DocBiodiv
Yokohama, 14 January 2026 — A sustainable tropical timber s...A sustainable tropical timber sector can be achieved through the combined and cumulative impact of many related advances rather than a single dramatic leap. This edition of Tropical Forest Update explores how stakeholders across the sector are taking essential steps—sometimes under difficult circumstances—to ensure that tropical forests continue to thrive, provide livelihoods and environmental benefits for generations to come.
Tropical forests are critical for maintaining the global carbon balance and mitigating climate change, yet their exchange of greenhouse gases with the atmosphere remains understudied, particularly for methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O). This study reports on continuous measurements of CH4 and N2O fluxes at the ecosystem and soil levels, respectively through eddy covariance and an automated chamber technique, in a wet tropical forest in French Guiana over a period of 26 months. We studied ...
Forests are dynamic repositories of carbon, biodiversity and ecological resilience, offering numerous additional ecosystem services beyond their commonly known advantages. The land use, land-use change and forestry (LULUCF) sector plays a dual role in global emissions, acting as both a source and a sink for greenhouse gases.The Enhanced Transparency Framework of the Paris Agreement establishes standardized reporting requirements for all countries, ensuring comprehensive, consistent and comparable reporting. The Biennial Transparency Reports (BTRs) emerged out of this framework as a new approach to international climate reporting to track the progress of national determined contributions.The Global Forest Resources Assessment (FRA) of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) is the global reference of data on forest resources of 236 countries and territories....
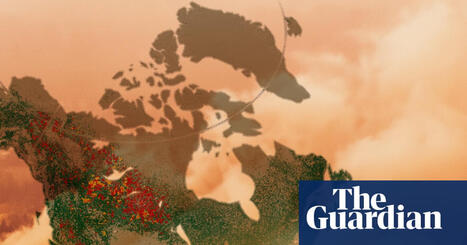
Wildfires now destroy twice as much tree cover per year as two decades ago – a crisis fuelled by climate change...
En Polynésie, scientifiques et pêcheurs travaillent ensemble pour lutter contre le déclin de certaines espèces de poissons dans le lagon.
Un rapport international coordonné par la DEAL Guadeloupe dresse un constat préoccupant sur l’état des récifs coralliens caribéens. Publié le 9 décembre 2025, il met en évidence une dégradation rapide de ces écosystèmes essentiels et appelle à une mobilisation collective pour les préserver.
Les premiers résultats de recherches menées par l’université des Antilles permettent de mieux cerner l’impact des algues brunes sur la faune et la flore de plusieurs écosystèmes cruciaux.
Il était à l'initiative du Radeau des cimes, une série de missions scientifiques visant à explorer la canopée et sa biodiversité.
Disponible en libre accès, ce nouveau fascicule analyse la diversité des impacts d’un projet de recherche co-porté par l’IRD sur une agriculture amérindienne en Amazonie du nord-ouest.
La récente COP Climat au Brésil était aussi une « COP des forêts ». Quatre participants à la caravane Iaraçu et à la COP témoigneront du déroulé et des retombées.
Certaines plantes produisent de la chaleur pour faciliter leur reproduction. Une nouvelle étude parue dans Science révèle que, chez les cycadées, ce signal thermique suffit à attirer et orienter les pollinisateurs, suggérant une forme très ancienne de communication entre plantes et insectes.
|
En Côte d’Ivoire, la forêt disparaît à grande vitesse. En réponse, de nombreux acteurs de la filière cacao promeuvent l’agroforesterie, c’est-à-dire la culture du cacao associée à des arbres. Mais les modèles actuels, souvent basés sur des plantations d’arbres standardisées, montrent des résultats limités. Une équipe franco-ivoirienne propose aujourd’hui une autre approche : plutôt que planter toujours plus d’arbres, il faut d’abord mieux gérer ceux qui sont déjà là. Retrouvez un résumé des travaux dans ce nouveau numéro de Perspective.
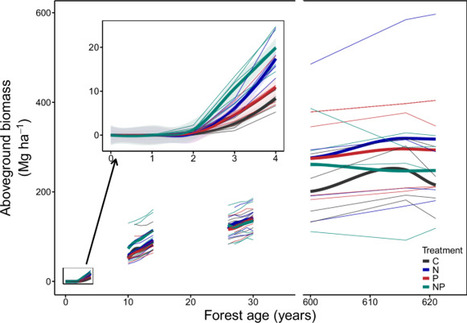
Understanding forest carbon sequestration is crucial for predicting and managing the carbon cycle, yet we lack evidence for whether, when and how the carbon sink in tropical forests recovering from land use change is nutrient limited. Here we show how the tropical forest recovery rate responds to experimental nutrient manipulation over a secondary succession gradient in a naturally recovering Central American landscape. Nutrient limitation of aboveground biomass accumulation shifts from strong nitrogen limitation in young forests to no evidence of nitrogen or phosphorus limitation in older secondary or mature forests. Nitrogen addition increases aboveground biomass accumulation by 95% in recently abandoned pasture and 48% in 10-year-old forests. Conversely, we observe no influence of nitrogen on older forests and no evidence of phosphorus limitation at any stage. If our findings of nitrogen limitation extend to young tropical forests globally, nitrogen could prevent the sequestration of 0.69 (0.47-0.84) Gt CO2 each year. Tropical forests regulate Earth’s carbon cycle, but what governs carbon sequestration following land use remains unclear. Here Tang et al find a shift from strong nitrogen limitation to no nutrient limitation over tropical forest secondary succession.
Le droit de l’environnement applicable dans les outre-mer relève, dans certains territoires, du droit commun et, dans d’autres, d’un droit propre. Confronté à des contraintes et à des problématiques spécifiques, il se révèle d’une grande richesse. La présente chronique, qui couvre la période allant de janvier 2024 à juin 2025, le montre encore.
Au Brésil, deux tiers des entreprises, dont les géants internationaux Cargill et Louis Dreyfus, se retirent du moratoire sur le soja. Ce pacte, conclu il y a vingt ans, interdisait à ses signataires de commercialiser tout soja issu de surfaces de la forêt amazonienne déboisées après 2008. C'était l'un des outils efficaces pour freiner la déforestation en Amazonie.
Premiers résultats de l’exploration scientifique « La Planète Revisitée des Îles de Guadeloupe » Une mission scientifique d’envergure au service de la biod
Dans les forêts tropicales, les exploitations de moins de deux hectares représentent près de 90% des émissions de carbone dues aux déforestations. Un constat qui impose d’agir sur les conditions de vie de millions de petits agriculteurs des pays du Sud.
Conservation, sustainable use and development of forest genetic resources are of vital importance to the management and utilization of the world’s forests and other wooded lands, including agroforestry systems. These resources, i.e. the heritable materials maintained within and among tree and other woody plant species, underpin the resilience, adaptability and productivity of forests and other tree-based systems, and contribute in many ways to sustainable development.At its Twentieth Regular Session in March 2025, the Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture agreed upon the revised Global Plan of Action for the Conservation, Sustainable Use and Development of Forest Genetic Resources based on the findings of The Second Report on the State of the World’s Forest Genetic Resources and the recommendations of the Intergovernmental Technical Working Group on Forest Genetic Resources.
Le chlordécone est un insecticide organochloré utilisé dans le monde entier depuis les années 1960. En raison de sa forte toxicité, de sa bioamplification et de sa persistance à long terme dans l'environnement, il a été interdit en France en 1990, sauf aux Antilles françaises où il a été autorisé en application sur les sols pour lutter contre le charançon du bananier jusqu'en 1993. Au cours de plus de deux décennies d'utilisation, ce pesticide a lourdement contaminé les écosystèmes, entraînant des conséquences délétères pour l'environnement et la santé. Depuis la fin des années 90, la présence et les effets du chlordécone font l'objet de recherches approfondies. La surveillance exercée a révélé de fortes concentrations de chlordécone dans les ressources en eau, ainsi que sa présence continue dans les sols. On estime qu'en raison de sa persistance, il est probable que la contamination environnementale causée par le chlordécone dure des siècles. Des études épidémiologiques ont montré que la population des Antilles françaises est fortement exposée au chlordécone, notamment au travers de la consommation de produits alimentaires. Les premiers résultats des projets lauréats de l’appel Chlordécone I (1er appel à projets conjoint Chlordécone) suggèrent la nécessité de prolonger l’effort de recherche par un nouvel appel à projets Chlordécone II : « Sociétés et multi-expositions ». Il donnera une place certaine aux sciences humaines et sociales et aux multi-expositions tout en s’inscrivant dans la continuité du travail déjà engagé et en consolidant les coopérations entre les équipes de recherche et les acteurs des territoires ultramarins.
Comment analyser sans tarder des milliers de photographies issues de caméras piège capturées sur le terrain en forêts tropicales pour l’identification d’espèces animales ? DeepForestVision est l’outil adapté et facile d’utilisation pour y remédier.
Surnommée « l’île de la Paix » car préservée de la guerre qui ravage la République démocratique du Congo, Idjwi souffre de l'exploitation de son sable et de son bois. Loin de Kinshasa, la population tente de réhabiliter son île.
Publié dans le cadre de la COP30 avec la contribution de l'IRD, le rapport 2025 du panel scientifique pour l’Amazonie “Connectivity of the Amazon for a Living Planet”, rassemble les connaissances scientifiques relatives à la connectivité écologique et socioculturelle, considérée comme une stratégie essentielle pour préserver les écosystèmes amazoniens, promouvoir un développement durable et renforcer le bien-être humain et environnemental.
Principale source de caoutchouc naturel, l’hévéaculture est indispensable pour de nombreux secteurs industriels, notamment celui des pneumatiques qui utilise 70 % de la production mondiale. Le Cirad consacre d’importants travaux de recherche à cette filière et lance une feuille de route avec quatre ambitions principales pour la soutenir dans la décennie à venir. Confrontée à de multiples défis sociaux, économiques et environnementaux, l’hévéaculture doit accélérer sa transition vers plus de durabilité.
|




 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...