 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Abstract Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are complex molecules composed of monoclonal antibodies conjugated to potent cytotoxic agents through chemical linkers. Because of this complexity, sponsors have used different approaches for the design of nonclinical studies to support the safety evaluation of ADCs and first-in-human (FIH) dose selection. We analyzed this data with the goal of describing the relationship between nonclinical study results and Phase 1 study outcomes. We summarized the following data from investigational new drug applications (INDs) for ADCs: plasma stability, animal study designs and toxicities, and algorithms used for FIH dose selection. Our review found that selecting a FIH dose that is 1/6th the highest non-severely toxic dose (HNSTD) in cynomolgus monkeys or 1/10th the STD10 in rodents scaled according to body surface area (BSA) generally resulted in the acceptable balance of safety and efficient dose-escalation in a Phase 1 trial. Other approaches may also be acceptable, e.g. 1/10th the HNSTD in monkeys using BSA or 1/10th the NOAEL in monkeys or rodents using body weight for scaling. While the animal data for the vc-MMAE platform yielded variable range of HNSTDs in cynomolgus monkeys, MTDs were in a narrow range in patients, suggesting that for ADCs sharing the same small molecule drug, linker and drug:antibody ratio, prior clinical data can inform the design of a Phase 1 clinical trial.
Via Krishan Maggon
The list of ADCs in the clinic continues to grow, bolstered by the success of first two marketed ADCs: ADCETRIS® and Kadcyla®. Currently, there are 40 ADCs in various phases of clinical development. However, only 34 of these have published their structures. Of the 34 disclosed structures, 24 of them use a linkage to the thiol of cysteines on the monoclonal antibody. The remaining 10 candidates utilize chemistry to surface lysines of the antibody. Due to the inherent heterogeneity of conjugation to the multiple lysines or cysteines found in mAbs, significant research efforts are now being directed toward the production of discrete, homogeneous ADC products, via site-specific conjugation. These site-specific conjugations may involve genetic engineering of the mAb to introduce discrete, available cysteines or non-natural amino acids with an orthogonally-reactive functional group handle such as an aldehyde, ketone, azido, or alkynyl tag. These site-specific approaches not only increase the homogeneity of ADCs but also enable novel bio-orthogonal chemistries that utilize reactive moieties other than thiol or amine. This broadens the diversity of linkers that can be utilized which will lead to better linker design in future generations of ADCs.
Via Dominique Blanchard
WOONSOCKET, R.I., March 12, 2015 /PRNewswire/ -- MultiCell Immunotherapeutics, Inc. (MCIT), a majority owned...
SynAffix BV a biotechnology company exclusively focused on the development of industry-leading antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) technology platforms today announced that it will present the new and underlying technologies used to generate enhanced ADCs...
Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1045:1-27. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-541-5_1. Review
Abstract Antibody-based therapy of various human malignancies has shown efficacy in the past 30 years and is now one of the most successful and leading strategies for targeted treatment of patients harboring hematological malignancies and solid tumors. Antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) aim to take advantage of the affinity and specificity of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to selectively deliver potent cytotoxic drugs to antigen-expressing tumor cells. Key parameters for ADC include choosing the optimal components of the ADC (the antibody, the linker and the cytotoxic drug) and selecting the suitable cell-surface target antigen. Building on the success of recent FDA approval of brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris®) and ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla®), ADCs are currently a class of drugs with a robust pipeline with clinical applications that are rapidly expanding. The more ADCs are being evaluated in preclinical models and clinical trials, the clearer are becoming the parameters and the challenges required for their therapeutic success. This rapidly growing knowledge and clinical experience are revealing novel modalities and mechanisms of resistance to ADCs, hence offering plausible solutions to such challenges. Here, we review the key parameters for designing a powerful ADC, focusing on how ADCs are addressing the challenge of multiple drug resistance (MDR) and its rational overcoming.
Via Krishan Maggon
A biotherapeutic company that fully powers the antibody-drug conjugate development spectrum from a patient-based approach to target and functional antibody discovery to ADC creation and manufacturing, accelerating development and the delivery of effective therapies to patients. In recent years, ADCs have become an important tool in fighting cancer. Our rigorous approach to target discovery and antibody development considers patient profile, tissue expression, tumor environment and antibody function as primary factors. Our target discovery platform, sTAg, systematically profiles proteins found on the cell surface of primary tumors to identify antibody-accessible antigens as candidate targets. Tumor-specific surface proteins are identified and quantified by applying advanced mass spectrometry analysis. To identify functional antibodies that are specific to target candidates, we have developed a platform, iTAb, that screens Ab candidates in vivo, to select antibodies with the most potent anti-tumor response.
Via Krishan Maggon
The cancer drug market in 2013 was over $90 billion and increasing as the number of elderly and cancer patients increases all over the world.
Via Krishan Maggon
Immunomedics Presents Clinical Data on Novel Antibody-Drug Conjugates for ...
CNNMoney
In his lecture, Dr. Goldenberg differentiated the Company's antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) platform technology from other technologies.
AB SCIEX, Dalton Pharma partner to advance antibody-drug conjugate analysis Pharmaceutical Business Review Determining where the drug attaches to a particular antibody early in its development and the number of drug molecules on the antibody are...
August 15, 2014 | Lutz Nuhn, PhD | Institute of Organic Chemistry, Johannes Gutenberg-University, Duesbergweg 10-14, D-55099 Mainz (Germany)… The comparison of antibody-polymer conjugates of different topologies (“cross-linked” versus “star-like”) demonstrated that the well-defined constructs derived from maleimide-endgroup modified HPMA copolymers prevent non-specific interaction with immune cells and guarantee antibody-mediated active delivery to the target cell type. By using aDEC205 as antibody the delivery of multifunctionalizable HPMA carrier polymers to CD8+ dendritic cells is possible enabling novel application especially for immontherapeutic purposes. [5] Considering the numerous possibilities of equipping the HPMA carriers with further tumor relevant antigens and immunostimulants, as recently shown by ligation of selective MUC1-derived glycopeptides antigens to HPMA block copolymers, [3] a combination with aDEC205 mediated delivery would guarantee antigen cross-presentation to CD8+ T cells and differentiation into specific cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) for selective antitumor response on a cellular level. As a result, such well-defined multifunctional HPMA-aDEC205 polymer conjugates can be considered as novel vaccine delivery platform towards antitumor immunity.
Via Krishan Maggon
Results from a preclinical trial shows that IMGN779, a novel, DNA-alkylating, anticancer therapeutics based on ImmunoGen, Inc, antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) t… (Data presented at the European Hematology Meeting in Milan, Italy....
While a host of cancer immunotherapies angle for attention at Chicago's American Society of Clinical Oncology meeting, AbbVie is touting early data on an antibody-drug conjugate with promise in a tough-to-treat form of brain cancer.
|
Philochem owns five antibody libraries (ETH2-GOLD, PHILO-1, PHILO-2, PHILO-DIAMOND and PHILOtop) that contain over 30 billion different binding specificities. Philochem’s human antibody libraries (ETH2-GOLD, PHILO-1, PHILO-2 and PHILO-DIAMOND) have been used to generate high-quality binding specificities against >50 different antigens, including human monoclonal antibodies which are currently being developed in clinical trials by Philogen. Philochem’s antibody libraries contain monoclonal antibodies in scFv format. Once monoclonal antibodies which are specific to the target antigen of choice are isolated, they can be easily reformatted into other recombinant antibody formats (e.g., IgG, Fab, mini-antibody, Fc-fusion) using general vectors and well-established procedures which are available at Philochem.
Via Krishan Maggon
(2015). Macrophages are critical effectors of antibody therapies for cancer. mAbs: Vol. 7, No. 2, pp. 303-310.
Via Krishan Maggon
Targeted delivery of Lck inhibitor dasatinib to human T lymphocytes=>An Immunosuppressive Antibody–Drug Conjugate http://t.co/jcHKJZbUss
Full results from a Phase II clinical trial of PSMA ADC (Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Tarrytown, NY, USA), a fully human monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate, in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) presented at ...
Via Krishan Maggon
Engineered antibodies are key players in therapy, diagnostics and research.
Via Krishan Maggon
Antibody–drug conjugates: targeted weapons against cancer Luisa Iamele, Luca Vecchia, Claudia ScottiDepartment of Molecular Medicine, Unit of Immunology and General Pathology, University of Pavia, Pavia, PV, Italy All authors contributed equally...
Via Krishan Maggon
(2015). The therapeutic monoclonal antibody market. mAbs: Vol. 7, No. 1, pp. 9-14. doi: 10.4161/19420862.2015.989042
Via Krishan Maggon
PolyTherics has developed its range of novel ThioBridge™ linkers to efficiently conjugate drugs to antibodies to create less heterogeneous ADCs with better stability. Our proprietary technology uses site-specific conjugation to naturally occurring inter-chain disulfides avoiding the need for antibody re-engineering to create a site of attachment. We offer a range of cytotoxic payloads with different mechanisms of action which we can conjugate to your antibody using our ThioBridge™ technology. These payloads have been developed internally or are accessed through our partnerships. PolyTherics can undertake the conjugation and analytical characterisation of the ADC in its own laboratories or provide a ThioBridge™ precursor reagent to you to use in-house. In addition to producing ADCs for potential therapeutic use, we can also produce antibody-conjugates for diagnostic & imaging purposes and ADCs using standard conjugation technologies for comparative purposes. Optimisation of pharmacokineticsPolyTherics provides a range of site-specific conjugation technologies to optimise the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of therapeutic peptides and proteins, including antibody fragments and other protein scaffolds, by extending their half-life to reduce the frequency of dosing. This improves patient compliance and can reduce the cost of treatment. PolyTherics also provides a low viscosity polymer, PolyPEG™, to enable the easier injection of conjugated proteins which need to be administered at high concentration. Our proprietary PEGylation technologies enable polyethylene glycol (PEG) or other polymers to be attached to different specified sites depending on the nature of the protein. TheraPEG™ conjugates PEG at disulfide bonds, HiPEG™ conjugates PEG to poly-histidine motifs and CyPEG™ conjugates PEG to a thiol on a free cysteine. These technologies are used to conjugate both linear and branched PEG to therapeutic proteins and can be used for PolyPEG™ conjugation. The conjugation processes are efficient, helping keep the cost of manufacture down, and the conjugated products are more stable and homogeneous than can be achieved with other well-established conjugation technologies. We can PEGylate your protein or peptide in our laboratories or provide you with our conjugation reagents so you can undertake the work yourself. Our reagents are available in a range of PEG molecular weights and formats, including linear and branched PEGs.
Via Krishan Maggon
Mersana Therapeutics has announced the USPTO granted patents that strengthen protections for Mersana's internal pipeline of Fleximer antibody-drug con (Mersana Strengthens Antibody-Drug Conjugate Intellectual Property Position with Issuance of...
AbbVie has obtained orphan drug designation from the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the US FDA for its anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody drug conjugate, ABT-414, as a treatment for glioblastoma multiforme.AbbVie...
T-DM1review=> Ado-trastuzumab Emtansine (T-DM1): An Antibody–Drug Conjugate (ADC) for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer http://t.co/JQgIW8RVZc
May 30, 2014 NORTH CHICAGO, Ill., May 30, 2014 /PRNewswire/ -- AbbVie (NYSE: ABBV) released preliminary results from an ongoing Phase I study with ABT-414, an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) monoclonal antibody drug conjugate, in combination with temozolomide, which showed four objective responses, including one complete response, in patients with recurrent or unresectable glioblastoma multiforme. Specifically, one patient experienced a complete response (CR) and three patients experienced partial responses (PR) as measured with the Revised Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria. These results were presented for the first time at the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), May 30 – June 3 in Chicago. The Phase I, open-label, multicenter, international trial was designed to evaluate the toxicities, pharmacokinetics and recommended Phase II dose of ABT-414 when administered every other week in combination with temozolomide in patients with recurrent or unresectable glioblastoma. Other important assessments included adverse events, pharmacokinetic parameters, objective response and tumor tissue epidermal growth factor receptor biomarkers. About ABT-414
ABT-414 is an anti-EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) monoclonal antibody drug conjugate (ADC). As an ADC, ABT-414 is designed to be stable in the bloodstream and only release the potent cytotoxic agent once inside targeted cancer cells. Developed by AbbVie researchers with components in-licensed from Life Sciences Pharmaceuticals and Seattle Genetics, ABT-414 is currently being investigated for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme, the most common and most aggressive malignant primary brain tumor. ABT-414 is also in clinical trials for the treatment of patients with squamous cell tumors. ABT-414 is an investigational compound and its efficacy and safety have not been established by the FDA
Via Krishan Maggon
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...













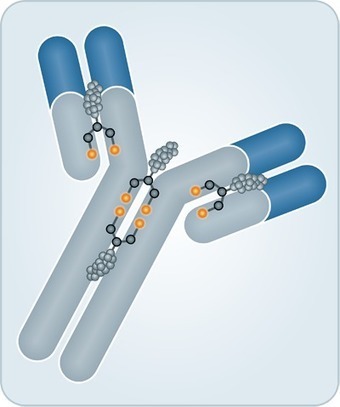








•Investigational new drug applications for antibody-drug conjugates were interrogated.
•Approaches to translating animal data to FIH dosing for ADCs are assessed.
•A comparison of rodent STD10 and monkey HNSTD to human MTD is provided.
•Toxicities associated with ADCs appear to be mainly related to the cytotoxic moiety.
•Results of in vitro plasma stability depends on the method used.