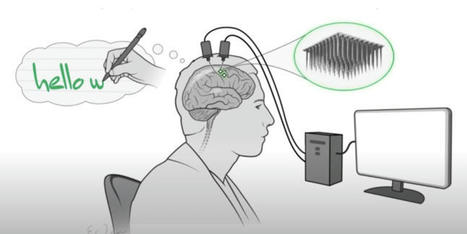
This week, the academic community provided a rather impressive example of the promise of neural implants. Using an implant, a paralyzed individual managed to type out roughly 90 characters per minute simply by imagining that he was writing those characters out by hand
Dreaming is doing
Previous attempts at providing typing capabilities to paralyzed people via implants have involved giving subjects a virtual keyboard and letting them maneuver a cursor with their mind. The process is effective but slow, and it requires the user's full attention, as the subject has to track the progress of the cursor and determine when to perform the equivalent of a key press. It also requires the user to spend the time to learn how to control the system.
But there are other possible routes to getting characters out of the brain and onto the page. Somewhere in our writing thought process, we form the intention of using a specific character, and using an implant to track this intention could potentially work. Unfortunately, the process is not especially well understood.
Downstream of that intention, a decision is transmitted to the motor cortex, where it's translated into actions. Again, there's an intent stage, where the motor cortex determines it will form the letter (by typing or writing, for example), which is then translated into the specific muscle motions required to perform the action. These processes are much better understood, and they're what the research team targeted for their new work.
Disclaimer: Not even a prototype
As the researchers themselves put it, this "is not yet a complete, clinically viable system." To begin with, it has only been used in a single individual, so we have no idea how well it might work for others. The simplified alphabet used here doesn't contain any digits, capital letters, or most forms of punctuation. And the behavior of the implants changes over time, perhaps because of minor shifts relative to the neurons they read or the build-up of scar tissue, so the system had to be recalibrated regularly—at least once per week to maintain a tolerable error rate
read the research at http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03506-2
related code : https://github.com/fwillett/handwritingBCI
read the article in its complete and unedited form at https://arstechnica.com/science/2021/05/neural-implant-lets-paralyzed-person-type-by-imagining-writing/



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...