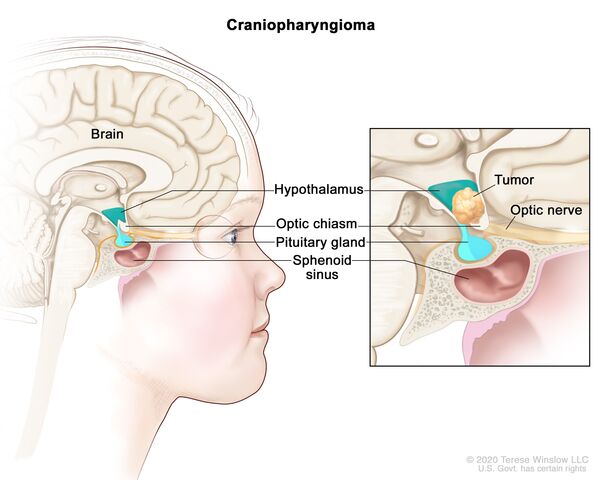
New immunotherapy targets for glioblastoma identified by mapping cell interactions
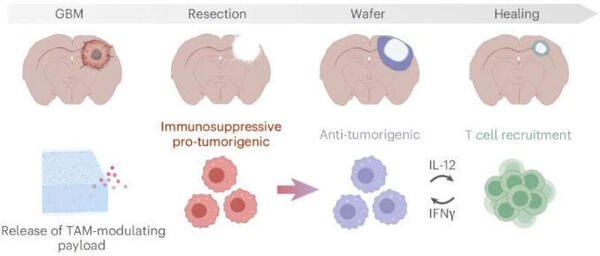
Glioblastoma is unusually resistant to attack by T cells, rendering immune checkpoint inhibitors ineffective. The culprit is a different immune cell, macrophages, which have been recruited to tumors, where they support tumor growth while suppressing the ability of T cells to infiltrate and attack tumors. A team of researchers led by Forest White at the MIT Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research used sophisticated immune profiling tools to map out how macrophages evolve from a first-line defense against cancer and other pathogens into a shield that protects the glioblastoma tumor—as well as how the tumor cells themselves are transformed by the encounter.
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...