Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Rescooped by
Judie Haynes
from Immigrant children & trauma
February 6, 2019 10:10 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
December 31, 2016 9:26 PM
|
“We are asking students to change a belief system without changing the situation around them.”

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
December 3, 2016 3:28 PM
|
Use these five best practices to help your students build a valuable 21st-century skill.

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
August 18, 2016 11:02 AM
|
Two teachers' research and ELA unit explored students' own family immigrant stories while creating a storytelling experience as a vehicle for empathy, community, and great writing.

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
August 14, 2016 4:54 PM
|
Economic disadvantage is often gauged by student eligibility for subsidized lunch, but this standard measure substantially understates the achievement gap.

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
August 7, 2016 1:25 PM
|
Developing an English language learner's sense of agency can feel like a challenge when so many variables are at stake. Teachers Larry Ferlazzo and Katie Hull

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
July 26, 2016 5:56 PM
|
Dual Language Learner, English Learner, multilingualism, bilingualism, achievement gap

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
July 25, 2016 11:49 AM
|
To help a student who's experienced trauma, ground yourself emotionally, determine your own role, and address that student's emotional truth from a place of informed support.

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
July 15, 2016 11:27 AM
|
Developing an English language learner's sense of agency can feel like a challenge when so many variables are at stake. Teachers Larry Ferlazzo and Katie Hull

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
June 29, 2016 3:59 PM
|
When 3,100 teachers were surveyed by the Gates Foundation in November 2015 about the biggest barriers to using digital resources, the most common response was “My students do not have access to technology outside of the classroom.”The lack of access to high-speed internet and its impact on learning

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
June 17, 2016 5:11 PM
|
High-poverty schools can meet student, professional, and system learning agendas by strengthening instructional framework, targeted interventions, reading proficiency, reflective practice, and data-based inquiry.

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
June 11, 2016 10:27 AM
|

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
May 29, 2016 9:03 PM
|
What Undocumented Students Bring to the Classroom is the headline of an article at The Atlantic today. Thought I frequent talk and write about the assets that English Language Learners bring to the...
|

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
April 27, 2018 10:23 PM
|

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
December 21, 2016 4:27 PM
|
. Establish Positive Teacher-Student Relationships
High-quality teacher-student relationships are another critical factor in determining student engagement, especially in the case of difficult students and those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds (Fredricks, 2014). When students form close and caring relationships with their teachers, they are fulfilling their developmental need for a connection with others and a sense of belonging in society (Scales, 1991). Teacher-student relationships can be facilitated by:
Caring about students' social and emotional needs
Displaying positive attitudes and enthusiasm
Increasing one-on-one time with students
Treating students fairly
Avoiding deception or promise-breaking
6. Promote Mastery Orientations
Finally, students' perspective of learning activities also determines their level of engagement. When students pursue an activity because they want to learn and understand (i.e. mastery orientations), rather than merely obtain a good grade, look smart, please their parents, or outperform peers (i.e. performance orientations), their engagement is more likely to be full and thorough (Anderman & Patrick, 2012). To encourage this mastery orientation mindset, consider various approaches, such as framing success in terms of learning (e.g. criterion-referenced) rather than performing (e.g. obtaining a good grade). You can also place the emphasis on individual progress by reducing social comparison (e.g. making grades private) and recognizing student improvement and effort.
Do you generally consider any of the above facilitators of engagement when designing and implementing learning activities? If so, which ones? If not, which are new to you?
Research
Ames, C. (1992). Achievement goals and the classroom motivational climate. In D. Schunk & J. Meece (Eds.), Student perceptions in the classroom (pp. 327-348). Hillsdale, N.J: L. Erlbaum.
Anderman, E. M., & Patrick, H. (2012). Achievement goal theory, conceptualization of ability/intelligence, and classroom climate. In S. Christenson, A. Reschly, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of Research on Student Engagement (pp. 173-191). New York, NY: Springer.
Assor, A., Kaplan, H., & Roth, G. (2002). Choice is good, but relevance is excellent: Autonomy-enhancing and suppressing teacher behaviours predicting students' engagement in schoolwork. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 72(2), 261-278.
Baker, J. A., Grant, S., & Morlock, L. (2008). The teacher-student relationship as a developmental context for children with internalizing or externalizing behavior problems. School Psychology Quarterly, 23(1), 3-15.
Bandura, A., & Schunk, D. H. (1981). Cultivating competence, self-efficacy, and intrinsic interest through proximal self-motivation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 41(3), 586-598.
Belland, B. R., Kim, C., & Hannafin, M. J. (2013). A framework for designing scaffolds that improve motivation and cognition. Educational Psychologist, 48(4), 243-270.
Black, P., Harrison, C., Lee, C., & Marshall, B. (2003). Assessment for learning: Putting it into practice. Maidenhead: Open University Press.
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2000). The "what" and "why" of goal pursuits: Human needs and the self-determination of behavior. Psychological Inquiry, 11(4), 227–268.
Driscoll, K. C., & Pianta, R. C. (2010). Banking time in head start: Early efficacy of an intervention designed to promote supportive teacher-child relationships. Early Education and Development, 21(1), 38-64.
Fredricks, J. A. (2014). Eight Myths of Student Disengagement: Creating Classrooms of Deep Learning. Los Angeles: Corwin.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research, 74(1), 59-109.
Gillies, R. M., & Ashman, A. F. (1998). Behavior and interactions of children in cooperative groups in lower and middle elementary grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90(4), 746-757.
Gregory, A., & Weinstein, R. S. (2004). Connection and regulation at home and in school: Predicting growth in achievement for adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Research, 19(4), 405-427.
Johnson, D. W., Johnson, R. T., & Holubec, E. (1994). The new circles of learning: Cooperation in the classroom and school. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.
Kidd, C., Palmeri, H., & Aslin, R. N. (2013). Rational snacking: Young children's decision making on the marshmallow task is moderated by beliefs about environmental reliability. Cognition, 126(1), 109-114.
Linnenbrink, E. A., & Pintrich, P. R. (2003). The role of self-efficacy beliefs in student engagement and learning in the classroom. Reading & Writing Quarterly, 19(2), 119-137.
Middleton, M. J., & Midgley, C. (2002). Beyond motivation: Middle school students' perceptions of press for understanding in math. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 27(3), 373-391.
Newmann, F., Wehlage, G., & Lamborn, D. (1992). The significance and sources of student engagement. In Student Engagement and Achievement in American Secondary Schools (pp. 11-39). ERIC.
Noels, K. A., Clement, R., & Pelletier, L. G. (1999). Perceptions of teachers' communicative style and students' intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. The Modern Language Journal, 83(1), 23-34.
Peter, F., & Dalbert, C. (2010). Do my teachers treat me justly? Implications of students' justice experience for class climate experience. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 35(4), 297-305.
Reeve, J. (1998). Autonomy support as an interpersonal motivating style: Is it teachable? Contemporary Educational Psychology, 23(3), 312-330.
Reeve, J., & Jang, H. (2006). What teachers say and do to support students' autonomy during a learning activity. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98(1), 209-218.
Reeve, J., Jang, H., Carrell, D., Jeon, S., & Barch, J. (2004). Enhancing students' engagement by increasing teachers' autonomy support. Motivation and Emotion, 28(2), 147-169.
Scales, P. C. (1991). Creating a developmental framework: The positive possibilities of young adolescents. In A portrait of young adolescents in the 1990s: Implications for promoting healthy growth and development. ERIC.
Schunk, D., & Swartz, C. (1993). Goals and progress feedback: Effects on self-efficacy and writing achievement. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 18, 337-354.
Schunk, D. H., & Mullen, C. A. (2012). Self-Efficacy as an engaged learner. In S. Christenson, A. Reschly, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of research on student engagement (pp. 219-235). Boston, MA: Springer US.
Schunk, D. H. (2003). Self-efficacy for reading and writing: influence of modeling, goal setting, and self-evaluation. Reading & Writing Quarterly, 19(2), 159–172.
Shernoff, D. J., Csikszentmihalyi, M., Shneider, B., & Shernoff, E. S. (2003). Student engagement in high school classrooms from the perspective of flow theory. School Psychology Quarterly, 18(2), 158-176.
Slavin, R. E. (1996). Cooperative learning in middle and secondary schools. The Clearing House, 69(4), 200-204.
Turner, J. C., Midgley, C., Meyer, D. K., Gheen, M., Anderman, E. M., Kang, Y., & Patrick, H. (2002). The classroom environment and students' reports of avoidance strategies in mathematics: A multimethod study. Journal of Educational Psychology, 94(1), 88-106.
Tyler, J. M., Feldman, R. S., & Reichert, A. (2006). The price of deceptive behavior: Disliking and lying to people who lie to us. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 42(1), 69-77.
Webb, N. M., Nemer, K. M., & Ing, M. (2009). Small-Group reflections: Parallels between teacher discourse and student behavior in peer-directed groups. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 15(1), 63–119.
Wentzel, K. R. (2009). Peers and academic functioning at school. In K. Rubin, W. Bukowski, & B. Laursen (Eds.), Handbook of peer interactions, relationships, and groups. Social, emotional, and personality development in context (pp. 531-547). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Willingham, D. T. (2009). Why don't students like school?: A cognitive scientist answers questions about how the mind works and what it means for the classroom. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Nicolás Pino James, PhD's Profile
Was this useful? Sign in to vote! (4)
Learn More About Student Engagement
Good Time: 4 Ways to Reawaken Student Engagement
How to Engage Underperforming Students
How to Engage Underperforming Students
photograph of a teacher at a table working with a group of students
3 Types of Unintentional Learning (And How to Make Them Intentional)
young boy in school working alone
Where Do Introverts Fit Into Group Work?
Nicolás Pino James, PhD
Educational Researcher
follow:
https://twitter.com/npinojames
https://uk.linkedin.com/in/npinojames
Related Tags:
Student Engagement
Collaborative Learning
Social and Emotional Learning
Teaching Strategies
All Grades

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
November 18, 2016 9:45 PM
|
Teachers can create a calm classroom atmosphere that helps troubled students be more receptive to learning.

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
August 17, 2016 4:39 PM
|
Harley Center shares how relationships, humor, choice, and displaying his work engaged him, plus his three-minute video highlighting student work and personalized learning.

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
August 7, 2016 9:49 PM
|
By Daun Kauffman. Trauma during development, or childhood trauma, changes brain architecture and ability to learn and social behavior. It impacts two out of three children at some level, but I didn’t even know what it was… Childhood Trauma, or adverse childhood experiences(ACEs)can be defined as a response of overwhelming, helpless fear to a painful or shocking event. ACEs include physical, emotional and sexual abuse, physical and emotional neglect, a missing parent (due to separation, divorce, incarceration, death), witnessing household substance abuse, violence, or mental illness and more. The children are not sick or “bad”. Childhood trauma is an injury. …

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
August 4, 2016 10:14 AM
|
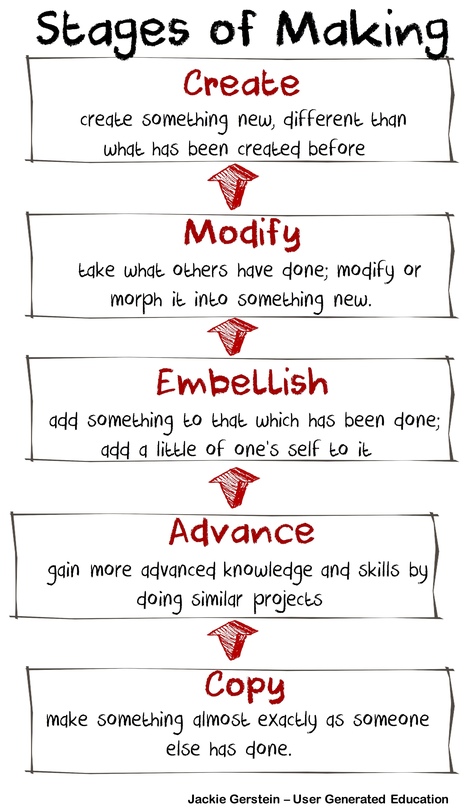
So what is making? I've proposed that the heart of making is creating new and unique things. I also realize that in order for this type of making to occur, there needs to be some scaffolding so that maker learners can develop a foundation of knowledge and skills. The end result, though should be maker…

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
July 25, 2016 11:57 AM
|
The Long Read: When Kate Clanchy began teaching the children of refugees, she sought out those silenced by trauma and loss. Their weekly sessions released a torrent of untold stories

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
July 17, 2016 8:32 PM
|
In many high-poverty urban neighborhoods, it’s nearly impossible for a poor child to find something to read in the summer.

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
July 6, 2016 2:14 PM
|
Carol Dweck, who parsed the difference between a "fixed" and a "growth" mindset, clarifies her theories of intelligence.

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
June 17, 2016 9:04 PM
|
Great article for schools on how to register the names of children from other countries.

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
June 11, 2016 10:47 AM
|
Judit Moschkovich offers teachers recommendations for supporting English learners in mathematics classrooms Developing mathematics instruction for English Language Learners (ELLs) that is aligned with the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) can be achieved through research-based teaching practices that often run counter to commonsense notions of language and mathematics. This article outlines recommendations that are motivated …

|
Scooped by
Judie Haynes
June 10, 2016 6:21 PM
|
There is a considerable body of research linking physical activity to academic learning. For example, one action research study found that recess breaks before or after academic lessons led to students being more on task (Fagerstrom & Mahoney, 2006). Students with ADHD experience reduced symptoms when they engage in physical exercise (Pontifex et al., 2012) -- ironic given that students with ADHD are probably among the most likely to have their recess taken away. There are alternatives to taking away recess that are much more effective and don't run the risk of reducing students' attention to important literacy instruction (Cassetta & Sawyer, 2013).
|






 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...














![Nowhere to Hide: “The Elephant in the [Class]room” - Living in Dialogue | Immigrant children & trauma | Scoop.it](https://img.scoop.it/b4AqFt-5EC4ejXF-PRXUhDl72eJkfbmt4t8yenImKBVvK0kTmF0xjctABnaLJIm9)