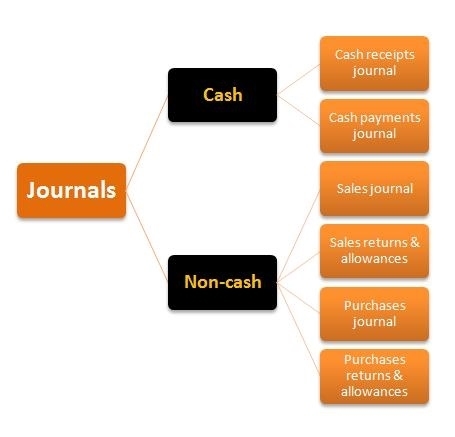
Journals in accounting were traditionally called the 'day book'. This is due to the term's derivation from the French word "jour", which means 'day', and the fact that it was expected that journals would record all of the financial transactions that occurred on each particular day. Journals recorded these original transactions in a date and time order as the transaction occured or as soon as possible thereafter.
Journal also became known as the 'books of original entry' because it is the entry point for financial information to get into the accounting information system. This system manages this financial data as it is entered into the journal, transferred to the general ledger, summarized in the trial balance and finally presented for stakeholders in the form of financial reports.





 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...














