 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Slip and fall accidents are among the most common causes of workplace/job injuries and can happen anywhere. Work areas can have all kinds of slipping or tripping hazards, including uneven or cracked floors, equipment, furniture, cords, wet floors, and clutter from debris. Individuals involved in a slip-and-fall accident can sustain injuries that vary in severity. The key is to see a doctor or chiropractor immediately to document the slipping and falling injuries and develop a personalized treatment and rehabilitation plan. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic can help. Slipping and Falling Injuries An individual can experience the following: - Musculoskeletal injuries
- Back and/or spinal cord injuries
- Hip, knee, and ankle injuries
- Nerve injuries
- Fractured or broken bones
- Facial fractures
- Brain injuries
- Paralysis
- Permanent disability
Contributing Factors The type of injury and degree of severity depends on physical and biological factors present during the slipping and falling. These include: Physical Condition - An individual's age, size, gender, and health can influence the type of injury sustained.
Height and Location of the Fall - Slipping, tripping, stumbling, or tumbling injuries could be minimal to severe, depending on the force, height, and location.
Surface Impact - The acceleration during the fall and how the body impacts the surface play an important role in the severity of the injury.
Body Position - Protective reflexes, such as outstretched arms, to break the fall or whether or not the body hit the ground directly determine the injury and to what extent.
Symptoms - Muscle pain and tension are the most common symptoms after slipping and falling.
- The muscle fibers overstretch, causing inflammation and swelling to develop.
- The pain can often start immediately after or a few days later, known as delayed injury symptoms.
- If the nerves sustain injury or irritation, they begin to swell, and the body responds to protect the damaged areas.
- The contact inflammation and irritation can cause tightness and spasms.
- Continuing ongoing discomfort and pain.
- Stomach discomfort and pain.
- Significant bruising.
- Limitations in movement.
Chiropractic Treatment Chiropractors are experts in slip-and-fall injuries and will use adjustments and various therapy protocols to realign the body and restore function. The objective is to relieve symptoms, rehabilitate the injured area/s, and regain mobility. Physical therapy and strength-building exercises under a specialist's supervision and at home are implemented to get back the use of the injured body part. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Li, Jie, et al. “Slip and Fall Incidents at Work: A Visual Analytics Analysis of the Research Domain.” International journal of environmental research and public health vol. 16,24 4972. 6 Dec. 2019, doi:10.3390/ijerph16244972 Pant, Puspa Raj et al. “Home-related and work-related injuries in Makwanpur district, Nepal: a household survey.” Injury prevention: journal of the International Society for Child and Adolescent Injury Prevention vol. 27,5 (2021): 450-455. doi:10.1136/injuryprev-2020-043986 Shigemura, Tomonori, et al. “Characteristics of stepladder fall injuries: a retrospective study.” European journal of trauma and emergency surgery: official publication of the European Trauma Society vol. 47,6 (2021): 1867-1871. doi:10.1007/s00068-020-01339-8 Smith, Caroline K, and Jena Williams. “Work-related injuries in Washington State's Trucking Industry, by industry sector and occupation.” Accident; analysis and prevention vol. 65 (2014): 63-71. doi:10.1016/j.aap.2013.12.012 Son, Hyung Min, et al. “Occupational fall injuries presenting to the emergency department.” Emergency medicine Australasia: EMA vol. 26,2 (2014): 188-93. doi:10.1111/1742-6723.12166
It is a common scenario, whether sitting or standing, when we need to bend down or forward, and suddenly there is a sharp sting on one side of the low back. The sensation can cause the knees to buckle. So we stand up slowly to assess the condition and realize it is almost impossible to stand completely straight and even harder to bend forward. So we sit back down to try and relieve the pressure. It helps a little, but the injury has caused the back muscles to spasm and get tighter and tighter. When we try to get up, there can be one big or several mild to severe electrical shock sensations traveling through the back. A severely over-rotated vertebrae could be the cause and require chiropractic care, massage, and/or decompression therapy. Over Rotated Vertebrae The spinal column is made of 26 interconnected vertebrae. When in motion, each vertebra moves, and as the torso rotates, the spine must rotate as well. The spine can move in several ways, including: - Bending
- Rounding forward.
- Extending or arching backward.
- Twisting
- Tilting sideways uses some of the same muscles when twisting.
Although the spine can move in various directions, there are limits to how far it can and should go. For example, when bending forward to lift an object, an individual can unknowingly over-extend and over-rotate vertebrae. This is where the risk of injury increases. A rotational injury of the spine occurs when the torso turns too far, and the spinal cord can't handle it. This can stretch the ligaments in the spine to the point of snapping, causing the facet joints to dislocate. Ligament strains and facet dislocations are two of the most common rotational spine injuries. Complications An over-rotated vertebrae injury can also lead to complications that include. Chronic Pain - Spinal nerve damage can lead to chronic pain conditions.
Mobility Problems - Mobility problems are common following an injury of the spine.
- This comes from damage to the nerves that innervate the legs, causing weakness and coordination problems.
Pressure Ulcers - Numbness following a spine injury can cause individuals not to notice pressure ulcers developing.
- These can lead to infections and could require hospitalization.
Individuals accumulate tension and/or weakness in the oblique abdominal muscles and other trunk muscles that can lead to chronic tightness and weakness, affecting movement and decreasing the range of motion. Chiropractic Treatment Plan Depending on the time and severity of the injury, a personalized treatment plan may consist of the following: - Wearing a back brace.
- Non-surgical decompression.
- Muscle stimulation.
- Soft tissue massage.
- Chiropractic mobilization to release the spasms and reset the spine.
- Rest
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Janssen, Michiel M A, et al. "Pre-existent vertebral rotation in the human spine is influenced by body position." The European spine journal: official publication of the European Spine Society, the European Spinal Deformity Society, and the European Section of the Cervical Spine Research Society vol. 19,10 (2010): 1728-34. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1400-3 Kruger, Erwin A et al. "Comprehensive management of pressure ulcers in spinal cord injury: current concepts and future trends." The Journal of spinal cord medicine vol. 36,6 (2013): 572-85. doi:10.1179/2045772313Y.0000000093 Passias, Peter G et al. "Segmental lumbar rotation in patients with discogenic low back pain during functional weight-bearing activities." The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume vol. 93,1 (2011): 29-37. doi:10.2106/JBJS.I.01348 Shan, X., Ning, X., Chen, Z. et al. Low back pain development response to sustained trunk axial twisting. Eur Spine J 22, 1972–1978 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-2784-7
The ladder is one of the most utilized tools. Most individuals have a ladder or two in their homes or at work and never consider the dangers. Falling off a ladder can lead to serious injuries like muscle tears, broken bones, damage to the spinal cord, skull fractures, or traumatic brain injury. The objective is to educate homeowners and workers on being more alert, increasing awareness, and reinforcing safety protocols. Ladder Falls and Injuries According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, ladder falls account for more than 500,000 injuries and 300 deaths annually. Even professionals with experience in safety can make simple mistakes like carrying too heavy a load or not spotting signs of wearing or a defect that leads to injury. Causes Causes can arise from defects or user mistakes. These include: A Defective Ladder - Old worn-out
- Damaged or broken
- Loose or cracking rungs
- Ladders folding during use
- Using the improper type of ladder for the job or task
Incorrect Ladder Use - Carrying dangerous objects or heavy loads
- Stretching or reaching too far out
- Failing to secure the ladder properly
- Recklessness or horseplay
Injuries Common falls can cause injuries severe enough to require professional medical care. Around one in five falls, on average, cause serious injuries that include. - Muscle sprains and/or tears
- Neck and back injuries
- Herniated discs
- Hip injuries and fractures
- Broken bones
- Spinal cord injuries
- Skull fractures
- Traumatic brain injuries
Any of these injuries could cause permanent disabilities or chronic conditions. Chiropractic Care A fall can damage joints, muscles, bones, and ligaments without realizing there is a problem or injury. The back and spine are most likely to be affected. When landing flat on your back, the joints that connect the spinal column can slip, causing inflammation and joint swelling. To prevent chronic pain and alleviate acute pain, seeking medical attention and chiropractic care as soon as possible is recommended. After confirming the spine is not fractured or broken, a chiropractor can bring relief and restore mobility and function. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic are committed to helping individuals rehabilitate and recover from injuries. We develop a personalized plan to maximize the potential of recovering and returning to daily activities as soon as possible. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Cabilan, C J et al. “Impact of ladder-related falls on the emergency department and recommendations for ladder safety.” Emergency medicine Australasia: EMA vol. 30,1 (2018): 95-102. doi:10.1111/1742-6723.12854 Hicks, Cameron, et al. “Ladder Use in Older People: Type, Frequency, Tasks, and Predictors of Risk Behaviours.” International journal of environmental research and public health vol. 18,18 9799. 17 Sep. 2021, doi:10.3390/ijerph18189799 “Ladder falls.” Health news (Waltham, Mass.) vol. 4,2 (1998): 7. Muir, L, and S Kanwar. “Ladder injuries.” Injury vol. 24,7 (1993): 485-7. doi:10.1016/0020-1383(93)90156-z Partridge, R A et al. “Causes and patterns of injury from ladder falls.” Academic emergency medicine: official journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine vol. 5,1 (1998): 31-4. doi:10.1111/j.1553-2712.1998.tb02571.x
The body's musculoskeletal system consists of bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and connective tissues. These parts get pushed to the extreme with everyday wear and tear, job, school, house chores, and tasks. All the flexing and contracting cause tightness, strain, and soreness that can contribute to negative muscle behavior that holds the muscles in an unhealthy position and in a semi-flexed or tightened state. An example is an unhealthy posture that becomes the norm for an individual. A percussive massage can release tightness, maintain flexibility, relieve discomfort, alleviate stress, and improve circulation. Percussive Massage Therapy A percussive/percussion massage is a form of physical therapy that utilizes vibration through repeated pressure bursts to massage muscles. Percussive therapy offers more control over targeted muscle groups than foam rollers and other static massagers. The treatment involves using an electric massage device to relieve muscle tension. Different massage heads for various therapeutic purposes move rapidly and forcefully, applying pressure directly to the soft tissues while the vibrations help release and loosen the areas. How The Massage Works - Fascia, which wraps around the muscles and joints, can become tight and inflamed, causing soreness and pain.
- Research shows that tight fascia can limit mobility and proper range of motion.
- When a muscle group is stiff and limits the range of motion of a specific part of the body, the rest of the muscles and body will overcompensate. This increases the risk of serious injury.
- Percussive therapy loosens the tissues and increases blood circulation.
- Once the stiffness and soreness are relieved, continued percussive therapy can prevent tightness from reforming, improve the range of motion, and speed up muscle recovery.
- Massage guns can penetrate up to an inch into the soft tissue, stimulating the muscles and helping release tension.
Benefits Improved mobility - Percussive massage distributes the thickened fascia fluid to relieve pressure and tightness.
- Repeated pressure at high speed thins the fluids, making the fascia more workable so the muscles can move easily and efficiently.
Reduced Soreness - Lactic acid builds up in the muscles after working, physical activity, and exercise.
- This build-up causes soreness and pain.
- The percussion forces muscle fibers to release the lactic acid, reducing the soreness.
Decreased DOMS/Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness - It's common to experience pain and soreness 24 to 72 hours after unfamiliar physical activity, such as a new job, exercise routine, or rehabilitation after injury or surgery.
- This is known as delayed onset muscle soreness or DOMS, which results from tiny muscle fiber tears.
- Percussive therapy increases skin temperature, blood flow, and hormonal responses to reduce inflammation and pain.
Increases Relaxation - After work, school, physical activities, and working out, a percussive massage session can help the body wind down and relax.
- A percussive massage will help the muscles release and relax when the body is exhausted or overwhelmed.
How To Use A Percussive Massager - Before starting a new medical treatment, including percussion therapy, talk to your doctor, physical therapist, or chiropractor.
- Ensure you know the difference between normal muscle soreness and pain from an injury.
- Don't use a massager on an injured muscle or body part, as the aggressive motion could aggravate the injury.
- Avoid using the device on bones or joints.
- Never use a massage gun directly on the neck; perform the massage on the shoulders and upper back.
- Start with the lowest intensity level.
- The low and medium settings should provide plenty of power for most users.
- As you become more comfortable with the device, you'll understand how your body reacts then you can try out the higher settings.
- A percussive massager should be used in short bursts on small, targeted areas.
- It is recommended to perform treatments for only a few minutes.
- Seeing the muscles turning reddish during the massage signals that blood is flowing and it's time to move on to another area.
- If the massage gun makes the skin sore or sensitive, make tiny circles instead of holding the massager in one spot.
- Some massagers have pressure-sensing technology to help apply the right amount of pressure.
Combined with chiropractic and professional massage, percussive therapy can help individuals maintain a relaxed musculoskeletal system. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Cafarelli, E et al. "Vibratory massage and short-term recovery from muscular fatigue." International journal of sports medicine vol. 11,6 (1990): 474-8. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1024840 Cerciello, Simone, et al. "Clinical applications of vibration therapy in orthopedic practice." Muscles, ligaments and tendons journal vol. 6,1 147-56. 19 May. 2016, doi:10.11138/mltj/2016.6.1.147 Cheatham, Scott W et al. "Mechanical Percussion Devices: A Survey of Practice Patterns Among Healthcare Professionals." International journal of sports physical therapy vol. 16,3 766-777. 2 Jun. 2021, doi:10.26603/001c.23530 García-Sillero, Manuel et al. “Acute Effects of a Percussive Massage Treatment on Movement Velocity during Resistance Training.” International journal of environmental research and public health vol. 18,15 7726. 21 Jul. 2021, doi:10.3390/ijerph18157726 Jack Martin, "A critical evaluation of percussion muscle gun therapy as a rehabilitation tool focusing on lower limb mobility." A literature review. Department of Health and Wellbeing. The University of Winchester. https://osf.io/preprints/sportrxiv/j9ya8/ Imtiyaz, Shagufta et al. "To Compare the Effect of Vibration Therapy and Massage in Prevention of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS)." Journal of clinical and diagnostic research: JCDR vol. 8,1 (2014): 133-6. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2014/7294.3971 Konrad, Andreas et al. "The Acute Effects of a Percussive Massage Treatment with a Hypervolt Device on Plantar Flexor Muscles' Range of Motion and Performance." Journal of sports science & medicine vol. 19,4 690-694. 19 Nov. 2020
Forklifts, also known as lift trucks, are used for loading, unloading, and transporting various goods and materials in construction, shipping, and retail industries. They are heavy-duty equipment and require extensive training to operate safely. Forklifts are involved in many serious workplace accidents causing thousands of injuries annually. Chiropractors specialize in injury care and rehabilitation from vehicle accidents and collisions. They can help restore optimal musculoskeletal function and health through adjustments, massage, decompression, and traction therapies. Forklift Operation The forklift is one of the most widely used pieces of equipment to raise, lower, or remove pallets, boxes, crates, or other containers and transport and stock goods and materials. There are a variety of lift trucks that include: Operation The weight, speed, and operation difficulty increase the risk of an accident, increasing the risk of injuries. Other factors include: - They can reach up to 20 miles per hour or more.
- They have front braking systems making it harder to stop.
- The weight distribution is in the back.
- The rear wheels turn instead of the front, causing tip-overs.
- Most carry their loads in front and can obstruct an operator’s view.
- Lifting too heavy a load can destabilize a forklift and cause it to turn over.
Accident and Injury Causes Federal work safety regulations require individuals to complete a training program to operate a forklift safely. The most common causes of accidents include: - Lack of training and experience.
- Lack of safety equipment - helmets, seatbelts, grab handles, roll cages, cage guards, warning lights, and sirens.
- Lack of maintenance - bent forks, no load backrest, unbalanced wheels, etc.
- Improper loading - off center, damaged goods, loose loads.
- Lifting, moving or tilting the mast too fast.
- Riding with a raised load.
- Speeding.
- Improper backing-up techniques.
- Poor communication.
- Horseplay.
- Giving rides.
- Failing to immobilize the machine when the operator leaves.
- Failing to pay attention to the position of the forks.
- Failing to yield to pedestrians.
- Traveling up or down unsafe inclines.
- Driving off the side of a ramp.
- Design or manufacturing defects.
Common Accidents The most common type of accidents involve: - Tip-overs and Rollovers.
- Falling off the lift.
- Getting struck by falling materials or objects.
- Pedestrian injuries like getting hit by the vehicle or tripping over the forks.
- Getting caught in or compressed/crushed by the vehicle or objects.
Injuries The most common injuries that result from lift accidents include: - Contusions
- Sprains
- Muscle tears
- Back pain disorders
- Crush injuries
- Fractures
Chiropractic Therapy and Rehabilitation Chiropractic therapy can help heal and rehabilitate musculoskeletal injuries. A chiropractic team will relieve pain symptoms and restore the body’s alignment and function. Treatment includes: Adjustments - To gently realign joints.
- Decrease pain.
- Increase range of motion.
- Improves posture.
Soft-tissue massage - To relax tight muscles.
- Relieve spasms.
- Release tension in the connective tissue surrounding the muscles.
- Reduces pain.
- Improves the range of motion of the spine and joints.
Exercises and stretches - To restore and maintain flexibility, joint stability, and mobility.
Joint bracing and taping - To support sprained joints or muscles during healing.
Health Coaching - Guides diet and nutrition to reduce inflammation and promote healthy eating to manage weight.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Bage, T et al. “Forklift-related lower limb injuries: a retrospective case series study with patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs).” Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England vol. 103,10 (2021): 730-733. doi:10.1308/rcsann.2020.7124 Born, C T et al. “Patterns of injury and disability caused by forklift trucks.” The Journal of trauma vol. 40,4 (1996): 636-9. doi:10.1097/00005373-199604000-00020 Hong, Choon Chiet, et al. “Forklift-Related Crush Injuries of the Foot and Ankle.” Foot & ankle international vol. 36,7 (2015): 806-11. doi:10.1177/1071100715576486 Ull, Christopher et al. “Injuries after Forklift Trucks Accidents - Injury Patterns, Therapy and Outcome in the Context of the Statutory Accident Insurance.” “Gabelstaplerunfälle – Verletzungsmuster, Therapie und Outcome im berufsgenossenschaftlichen Kontext.” Zeitschrift fur Orthopadie und Unfallchirurgie, 10.1055/a-1402-1649. 19 Apr. 2021, doi:10.1055/a-1402-1649 Waters, Thomas et al. “Lower back disorders among forklift operators: an emerging occupational health problem?.” American journal of industrial medicine vol. 47,4 (2005): 333-40. doi:10.1002/ajim.20146
Dislocations impact the joint and are injuries that force/knock the bones out of position. Dislocations can be caused by a motor vehicle collision, falls, sports trauma, or weakened muscles and tendons. However, less impact/force is needed to dislocate smaller joints. Dislocations commonly occur at the shoulders, ankles, knees, hips, elbows, fingers and toes, and the jaw. The experience causes swelling, inability to move, and pain. A joint dislocation chiropractor can manipulate, reset, rehabilitate and strengthen the affected area and rebalance the body. Joint Dislocation The region where two or more bones come together is a joint. Each has a primary function, but their functions overlap. The joints allow the bones to move/articulate the skeletal system. Maintaining the body's balance requires mobility and stability. - Mobility is the ability to move the body without restriction.
- Stability is maintaining equilibrium, healthy posture, and support during movement.
- The stable joints do not dislocate easily because their structures are not as flexible.
- Mobile joints are at an increased risk, as they can move in almost any direction.
The stability joints include the following: - Cervical spine
- Elbow
- Lumbar spine
- Knee
- Foot
The mobility joints include: - Shoulder
- Wrist
- Thoracic spine
- Hip
- Ankle
The kinetic chain is a sequence of joints forming an alternating pattern of stability and mobility that create a solid platform for dynamic movement. However, any joint can become dislocated, causing the affected area to become unsteady or immobile, strain or tear the surrounding muscles, nerves, and tendons which are the tissues that connect the bones to a joint. - A joint can be partially dislocated/subluxation or fully dislocated.
- Joints dislocated previously have an increased risk of re-dislocating because the surrounding tissues that hold the joint have been torn or overly stretched.
Symptoms Symptoms vary depending on the severity and location of the injury. Common symptoms include: - Instability
- Loss of ability to move
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Pain
- Visible deformation
Increased Risk Various factors can lead to joint dislocation, including: - Weakness of the supporting ligaments and muscles from natural wear and tear/age or lack of physical conditioning.
- Older individuals with poor balance are more vulnerable to falls that can knock joints out of place.
- Young children developing have more elastic supporting ligaments and are prone to falls, collisions, and other injuries.
- Previous dislocations with overstretched or torn supporting tissues.
- Repeated dislocations are likely to follow the shoulder, knee, and hip.
- Inherited conditions can cause the elastic tissues to overstretch. Examples include Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and Marfan syndrome.
- Physical activities like extreme sports, contact sports, or sports that involve quick body shifts, twists, and turns on the feet.
- Physically demanding job.
- Operating heavy machinery/equipment.
- Joint hypermobility is common in children and around 5% of adults. It can be caused by weak or loose ligaments, weak or loose muscles, and/or shallow joint sockets.
Joint Dislocation Chiropractic Treatment will vary based on the severity of the injury and the dislocated joint. Depending on the location and severity, a chiropractor will perform different movements/manipulations to realign the joint and strengthen the area. - Significant force could be necessary to pull the bones apart to realign them back into their proper position.
- The joint may need to be pulled out and rotated slightly before being put back.
- The focus is on increasing ligament strength.
- Once the joint is back in place, it may need to remain immobile, possibly using a sling or splint to help fully heal the injury.
- Physical therapy exercises will be recommended to strengthen the muscles and ligaments around the joint to support it optimally.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Dizdarevic, Ismar, et al. "Epidemiology of Elbow Dislocations in High School Athletes." The American journal of sports medicine vol. 44,1 (2016): 202-8. doi:10.1177/0363546515610527 Hodge, Duncan K, and Marc R Safran. "Sideline management of common dislocations." Current sports medicine reports vol. 1,3 (2002): 149-55. doi:10.1249/00149619-200206000-00005 Prechel, Ulla et al. “The Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation.” Deutsches Arzteblatt international vol. 115,5 (2018): 59-64. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2018.0059 Skelley, Nathan W et al. "In-game Management of Common Joint Dislocations." Sports health vol. 6,3 (2014): 246-55. doi:10.1177/1941738113499721
Motor vehicle crashes and accidents cause significant trauma in a few seconds changing an individual's life completely. Severe injuries include traumatic brain injury, spinal cord damage, fractures, and amputations. Many individuals experience post-traumatic stress disorder - PTSD after a vehicle collision; even a minor accident can cause emotional trauma symptoms. PTSD commonly presents with other symptoms that range from depression to heart disease, and the most frequent symptom is physical pain. Chiropractic decompression, physical therapy, and therapeutic massage can help alleviate physical pain. PTSD Physical Pain Physical trauma can cause immediate physical effects and injury, as well as physical symptoms that present later on. Symptoms - Flashbacks or reliving the collision incident.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Nightmares about the wreck.
- Fatigue.
- Memory and concentration problems.
- Hyperarousal.
- Fear.
- Anxiety.
- Irritability or anger.
- Avoiding driving or riding in a vehicle.
- Trying not to talk or think about the crash or accident with friends, family, places, or anything associated with the trauma.
- Avoiding activities.
- Emotional numbness.
- Detachment.
All can generate physical muscle tension and chronic stress, leading to headaches, migraines, back pain, stomach pain, and body aches. Long-term physical pain symptoms can turn chronic pain and medication dependency into a vicious cycle. Chiropractic Therapy Chiropractic care diagnoses and treats disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Chiropractic treatment is recommended to help alleviate the physical symptoms of PTSD. Trauma causes individuals to store intense emotions in their bodies. Chiropractic manipulation and decompression release the tension in the muscles caused by the trauma and the emotional stress. Adjustments restore the body's alignment and open the nervous system circulation, allowing signals to flow freely, leading to a healthier mind-body connection. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Beck, J Gayle, and Scott F Coffey. "Assessment and treatment of PTSD after a motor vehicle collision: Empirical findings and clinical observations." Professional psychology, research, and practice vol. 38,6 (2007): 629-639. doi:10.1037/0735-7028.38.6.629 Elder, Charles et al. "Comparative Effectiveness of Usual Care With or Without Chiropractic Care in Patients with Recurrent Musculoskeletal Back and Neck Pain." Journal of general internal medicine vol. 33,9 (2018): 1469-1477. doi:10.1007/s11606-018-4539-y https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd Hu, JunMei, et al. "Chronic widespread pain after motor vehicle collision typically occurs through immediate development and nonrecovery: results of an emergency department-based cohort study." Pain vol. 157,2 (2016): 438-444. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000388
Forearm pain refers to soreness, aches, or discomfort between the wrist and the elbow. An injury or inflammation can affect any tissues, including muscles, bones, blood vessels, tendons, and the skin. The causes usually include overuse injuries, pinched nerves, accidents causing trauma, lifting or heaving heavy objects, sports injuries, and fractures. If left untreated, issues like chronic muscle pain and decreased and disrupted blood/nerve circulation can develop, leading to numbness and weakness. Chiropractic treatment can release tension, massage, reset, and stretch the muscles to expedite healing. Anatomy The forearm comprises the radius and ulna, which extend the forearm's length and cross at the wrist. The Radius - This bone starts at the elbow and connects to the wrist on the thumb side.
Ulna - This bone begins at the elbow and connects to the wrist on the side of the little finger.
Muscles - Several muscles operate to rotate the forearm up/supination and down/pronation and flex and extend the fingers.
Causes Forearm pain can happen to anyone and is usually related to traumatic or repetitive use injury. In other cases, pain may be associated with a benign growth, like a cyst or possibly a malignant tumor. Common causes include: - Pulled and/or strained muscles
- Muscle ruptures or small tears
- A direct blow, fall, or any extreme twisting, bending or jamming action.
- Tendonitis from tennis or golfers elbow.
- Tennis elbow is caused by inflammation or tiny tears in the forearm muscles and tendons outside the elbow.
- Golfers' elbow is on the inside of the elbow.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a repetitive stress disorder that affects the nerves and tendons of the wrist and forearm.
Musculoskeletal Causes The musculoskeletal causes involve issues in how the forearm components operate together. - Repetitive actions like lifting, gripping, and typing can compress nerves and blood vessels throughout the forearm.
- Repetitive positional injury can lead to swelling.
- Forearm problems like dislocations or sprains can also lead to chronic inflammation and pain.
Traumatic Causes Traumatic causes include those that result in injury to components of the forearm. - Anything that causes a direct injury to the forearm, including an automobile crash or accident, fall, or a direct hit, can fracture bones in the forearm.
- A sprain can twist or stretch a ligament or tendon.
- Activities that cause bending, twisting, quick sudden movement or direct impact can result in sprained multiple ligaments in the forearm.
Chiropractic Treatment Healing forearm pain depends on the type of injury, location, and cause of the pain. Chiropractic addresses arm pain, tingling, and numbness in ways often overlooked by general physicians. - A chiropractor will perform a physical examination to determine if there are any underlying causes.
- They may apply an ice pack to help control inflammation before the massage.
- The chiropractor will perform gentle adjustments to the wrist, arm, and shoulder.
- They may recommend a forearm brace to help retrain positioning and movement.
- They will recommend exercises and stretches to strengthen and maintain the adjustments.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Ellenbecker, Todd S et al. "Current concepts in examination and treatment of elbow tendon injury." Sports health vol. 5,2 (2013): 186-94. doi:10.1177/1941738112464761 Shamsoddini, Alireza, and Mohammad Taghi Hollisaz. "Effects of taping on pain, grip strength and wrist extension force in patients with tennis elbow." Trauma monthly vol. 18,2 (2013): 71-4. doi:10.5812/traumamon.12450 Suito, Motomu, et al. "Intertendinous epidermoid cyst of the forearm." Case reports in plastic surgery & hand surgery vol. 6,1 25-28. 28 Jan. 2019, doi:10.1080/23320885.2018.1564314
When the body goes through intense trauma like a car, truck, crash, or accident, the trauma can slip, bulge, herniate, or rupture the spinal fluid-filled discs that can extrude from the disc space, causing the nucleus pulposus to tear through the annulus fibrosus and compress the nerve roots causing pain. Depending on the severity and force of the crash or accident, a herniated disc can cause the vertebrae to push into the spinal canal, where it can compress, irritate, and/or injure the spinal cord, which can lead to other health issues. Nerve impingement from a herniated disc can also cause numbness and tingling in the hands, arms, legs, and feet. A chiropractic spine disc herniation decompression treatment plan can heal the herniation, realign the spine, stretch the muscles and joints, and rehabilitate the body back to top form. Spine Disc Herniation Symptoms of Herniation Signs and symptoms depend on the spinal area and whether the disc is rubbing or compressing a nerve. Pain is often described as a sharp or burning sensation. A herniated disc usually affects one side of the body. Pain Presents When Sitting Down - sitting causes a significant strain on the lower spinal discs. When sitting, the pain experienced can worsen. Arm or leg pain - Depending on the herniated disc, pain can spread to other surrounding areas. - For a lower herniation, this could be the buttock, thigh, calf, and foot.
- For a herniated disc in the neck region, pain can be felt in the shoulder and arm.
Pain can present in the arm or leg when coughing, sneezing, or moving into certain positions. Numbness or tingling - presents from the compressed nerves and spreads as the average blood/energy flow is disrupted. Muscle Weakness - the affected nerves that support the spinal muscles can lose normal strength causing awkward postures and fatigue. A herniated disc can be present without symptoms - individuals won't know unless spinal imaging is ordered. Sciatica Sensations - the damaged nerve roots affect the ability to function correctly and can cause burning pain, numbness, weakness, and tingling along the front and/or back of the thigh, leg, and/or foot. This can result from direct compression or chemical irritation from a leaked out herniated disc that causes inflammation around the nerve root area. Chiropractic Injury Care When a disc herniates, it inhibits the body from communicating and healing itself. To activate proper communication from the brain to the rest of the body, chiropractors perform spine disc herniation decompression which clears the neural system and opens the lines of communication. Spine Disc Herniation Decompression Nonsurgical spinal decompression gently stretches the spine to relieve pressure and heal the herniated disc. It is a safe procedure considered a natural alternative compared to surgery or pharmaceutical approaches. Spinal decompression therapy: - It is safe for all ages
- It is non-invasive
- Sessions take between 30 to 45 minutes, depending on the individual and the injury that could require multiple sessions.
- Offers a quicker recovery time
- It is performed on a computer-controlled table customized to the individual's specific needs and injuries.
A treatment plan can expedite the recovery process, rehabilitate and strengthen the whole body, and help avoid minimally invasive spine surgery. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Atlas, Steven J et al. "The impact of disability compensation on long-term treatment outcomes of patients with sciatica due to a lumbar disc herniation." Spine vol. 31,26 (2006): 3061-9. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000250325.87083.8d Dydyk AM, Ngnitewe Massa R, Mesfin FB. Disc Herniation. [Updated 2022 Jan 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/ Gane, Elise M et al. "The Impact of Musculoskeletal Injuries Sustained in Road Traffic Crashes on Work-Related Outcomes: A Systematic Review." International journal of environmental research and public health vol. 18,21 11504. 1 Nov. 2021, doi:10.3390/ijerph182111504 Scuderi, Gaetano J et al. "Symptomatic cervical disc herniation following a motor vehicle collision: return to work comparative study of workers' compensation versus personal injury insurance status." The spine journal: official journal of the North American Spine Society vol. 5,6 (2005): 639-44; discussion 644. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2005.04.007
Injury Medical Spinal Decompression: Spinal decompression therapy/treatment can be surgical or non-surgical, with differences in the procedure, recovery time, and results. Individuals who experience compression-related problems can have severe and prolonged spinal conditions that can lead to various health issues. Individuals experiencing persistent or chronic neck, back, or leg pain should know the differences between surgical and non-surgical spinal decompression. Spinal decompression aims to relieve pressure on the discs and reduce stress on the nerves to eliminate the pain associated with compression on the spine, restoring optimal circulation and improving spinal function. Surgical Procedure - It is invasive, must be performed by a surgeon, and can have a recovery time of up to 6 weeks.
- Surgery is usually suggested as a last resort after alternative therapies have not succeeded or when the compression is so severe that surgery is the only option.
- Surgical spinal decompression is directed towards removal to reduce pressure instead of adjusting or stretching the discs.
- In cases of severe nerve compression, surgery can be an effective option.
- Risks include infection, damage to the spinal cord, and blood clots.
Types of Spinal Decompression Surgery Types of surgeries; spinal fusion could be necessary to stabilize the spine. Common types of back surgery: Discectomy - This procedure removes a portion of the disc to relieve pressure on nerves.
Laminotomy - The procedure removes a small portion of the bone or a section of the bony arch to increase the size of the spinal canal and relieve pressure.
Laminectomy - The procedure removes the entire bony arch or lamina to increase the size of the spinal canal and relieve pressure.
Foraminotomy - This procedure removes bone and other tissue to widen the openings for the nerve roots to pass through.
Osteophyte Removal - The procedure involves removing bony growths.
Corpectomy - The procedure removes a vertebral body along with discs.
Injury Medical Spinal Decompression Surgery for a damaged/injured spine is not always necessary. Treatment regimes vary depending on each individual’s medical condition. Non-surgical motorized spinal decompression is a non-invasive back treatment that uses a mechanized decompression table to slowly and gently stretch the spine. The therapy gradually relieves the pressure on the compressed nerve root/s resulting in reduced or complete alleviation of pain. Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression Treats - Neck pain
- Back pain
- Sciatica
- Injured, damaged, or diseased nerve roots
- Damaged discs
- Deteriorated discs
- Bulging or Herniated discs
- Osteoarthritis
- Facet Joint Syndrome
Benefits - Painless
- Non-invasive
- Sessions only take 30-45 minutes
- Feel immediate results
Decompression Program An Injury Medical Spinal Decompression program incorporates: Injury Medical Spinal Decompression Sessions - Decompression treatment sessions last about 30-45 minutes for 4-6 weeks.
- The sessions are conducted in the chiropractor's office.
Post Decompression Treatment - This is necessary to ensure that the injured areas are fully relaxed and conditioned for chiropractic manual adjustments.
- Massage therapy
- Percussive massage
- Cold laser
- Heat and/or ice
- These treatments facilitate blood and nerve circulation.
Chiropractic Adjustments - Chiropractic adjustments enhance decompression by fine-tuning mechanical and structural misalignments.
Health Coaching Supplements and essential vitamins: - Support, repair, and restore the discs
- Decrease inflammation
- Increase healing
Core Strengthening/Postural Rehabilitation - Core exercises are recommended to strengthen the muscles and soft tissues.
- Posture exercises
Oxygen, water, and nutrients circulate abundantly, promoting healing as the discs re-hydrate, and are re-nourished, improving and enhancing spine function. Individuals can enjoy increased levels of mobility, strength in the spine and muscles, and more flexibility. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References American Spinal Decompression Association: "Spinal Decompression Therapy." Daniel, D.M. Chiropractic and Osteopathy, 2007. Macario, Alex, and Joseph V Pergolizzi. “Systematic literature review of spinal decompression via motorized traction for chronic discogenic low back pain.” Pain practice: the official journal of World Institute of Pain vol. 6,3 (2006): 171-8. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2006.00082.x O'Hara K, editor. Decompression: a treatment for back pain. Vol. 11. National Association of Healthcare Professionals; 2004. pp. 1-2.http://www.naohp.com/menu/publications/mccu/bibliography.htm#10 [Google Scholar]
Stress health recognizes how stress affects the body, thoughts, feelings, and behavior. Stress that's left untreated can contribute to various health problems. These include: - Anxiety
- Decreased energy levels
- Digestive dysfunction
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Abnormal heart rate
- Heart disease
- Mental problems
Chiropractic serves as a powerful intervention for anxiety-related symptoms. Stress Health Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Balance Chiropractic benefits cardiovascular health as it directly affects the nervous and other body systems that include the spinal system, the bones, joints, and muscular system, affecting the function of the cardiovascular system. Chiropractic regulates these system's functions allowing for a moderate heart rate and blood pressure. Balanced blood pressure and heart rate can help minimize stress and anxiety, making it much easier to stay relaxed and focused. Individuals report experiencing decreased blood pressure and lower heart rate with long-term chiropractic treatment. Mental Clarity Cerebrospinal fluid/CSF is necessary for detoxifying the brain and helping to protect the brain. CSF transports oxygen and nutrients to the brain, helping to increase brain function efficiency. Chiropractic has been shown to increase the amount of cerebrospinal fluid delivered to the brain. This is because the spine is aligned correctly, allowing for a smooth flow of blood and nerve energy from the brain through the spine to the rest of the body. This provides: - Sustained mental alertness
- Awareness
- Mental Clarity
This helps to combat mental fog or anxiety hyperactivity. Improve Energy Levels Chiropractic can help increase energy levels in different ways for different individuals. - For some, this works by eliminating headaches, migraines, and other nerve dysfunction/s.
- For others, this happens by decreasing or eliminating pain symptoms.
These conditions can contribute to lowered energy levels. Constant stress can change the body's chemistry, leading to increased stress hormones like cortisol. Over time, these hormone releases can decrease energy, causing interference with the body/brain's natural rejuvenating processes that reduce stress. With chiropractic, the therapeutic effects help correct body chemistry and improve energy levels. Increase Immune Function Lymphatic fluid has a vital role in stress health and the function of the immune system. Lymphatic fluid helps separate and release: - Toxins
- Viruses
- Fungus
- Bacteria from the body.
When lymphatic fluid flows smoothly and is not impeded or trapped in tissues, joints, or muscles, the immune system operates at a high level. Chiropractic helps drive lymphatic fluid out of the tissues, joints, and muscles of the body, facilitating optimal immune function. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Dragoş, Dorin, and Maria Daniela Tănăsescu. "The effect of stress on the defense systems." Journal of medicine and life vol. 3,1 (2010): 10-8. Meier, Jacqueline Katharina et al. "Stress Alters the Neural Context for Building New Memories." Journal of cognitive neuroscience vol. 32,12 (2020): 2226-2240. doi:10.1162/jocn_a_01613 Pickar, Joel G. "Neurophysiological effects of spinal manipulation." The spine journal: official journal of the North American Spine Society vol. 2,5 (2002): 357-71. doi:10.1016/s1529-9430(02)00400-x
A science teacher contacted me with concerns about a story he saw on his local TV news. It featured a chiropractor in his area who is treating athletes with concussions.He claims that with dynamic...
Functional and holistic medicine both have their merits, so it is important to understand the differences between them.
|
The NHTSA records show that rear-end collisions are the most common and make up 30% of all traffic accidents, crashes, and collisions. Rear-end collisions can come out of nowhere. One moment a driver is waiting at a stop or light, and suddenly they are catapulted forward by the intense force of another vehicle/s resulting in serious and sustaining injuries that can impact an individual's physical capabilities. Rear-end collision injuries most commonly affect the neck and back. This is because of the excessive force and intense shifting and whipping the body goes through. Chiropractic care, massage, and decompression therapy can realign the body, relax the muscles, release compressed nerves, expedite recovery, and restore mobility and function. Rear-End Collision Injuries Rear-end collision injuries can range from mild to serious, and what seems like a minor pull can result in a severe injury. The most common injuries include: - Contusions
- Neck and spinal injuries
- Whiplash
- Concussion
- Traumatic brain and other head injuries.
- Facial injuries
- Dental injuries
- Lacerations
- Broken bones
- Crushed or fractured ribs
- Punctured lungs
- Internal bleeding
- Paralysis
- Pre-existing conditions such as degenerative disc disease can worsen.
Collision Types A rear-end collision can occur in several ways. The most common types include: Tailgating - When drivers in the rear follow another motorist too closely, and the lead motorist slows down or has to stop quickly, the rear driver hits the vehicle because there was not enough adequate time and distance to stop.
Slow Speed Collisions - Slow-speed/low-impact collisions or fender benders can result in spinal injuries and concussions.
- They can also lead to facial and head injuries from sudden airbag deployment.
Vehicle Pile-Ups - A single rear-end collision on a busy street or interstate highway can cause a chain reaction of multiple-vehicle collisions.
- These accidents can cause devastating injuries.
Causes Causes that can take attention away from the road include: - Speeding
- Distracted driving - Talking or texting.
- Tailgating
- Looking at something like an accident while driving by.
- Unsafe lane changes
- Drowsy or fatigued driving
- Construction site hazards
- Poor weather conditions
- Parking lot accidents
Chiropractic Care Symptoms of rear-end collision injuries may not immediately present following an accident. It can take 24 to 48 hours for discomfort symptoms to come on and sometimes longer. The adrenaline rush allows the individual not to experience the physical symptoms, which is why individuals think they're fine when they are not. Ignoring signs increases the risk of permanent injury. A herniated disc, for example, left untreated, can lead to permanent nerve damage. Chiropractic treatment for rear-end collisions is one of the most effective options available. A chiropractor manipulates the spine to realign the spinal cord, allowing the body to decrease inflammatory cytokine production, which reduces the inflammatory response. Specific techniques and various tools can realign individual vertebrae, restore joint flexibility, and break up the scar tissue so the areas can heal faster. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Chen, Feng, et al. "Investigation on the Injury Severity of Drivers in Rear-End Collisions Between Cars Using a Random Parameters Bivariate Ordered Probit Model." International journal of environmental research and public health vol. 16,14 2632. 23 Jul. 2019, doi:10.3390/ijerph16142632 Davis, C G. "Rear-end impacts: vehicle and occupant response." Journal of manipulative and physiological therapeutics vol. 21,9 (1998): 629-39. Dies, Stephen, and J Walter Strapp. "Chiropractic treatment of patients in motor vehicle accidents: a statistical analysis." The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association vol. 36,3 (1992): 139–145. Garmoe, W. "Rear-end collisions." Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation vol. 79,8 (1998): 1024-5. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(98)90106-x
There is a multitude of reasons why back muscles tighten and stiffen up. Muscles pull the bones and joints. Overuse and/or injuries can pull the bones, joints, and tendons out of place, thus causing the muscles to stay in a flexed or stretched position, the inability for the muscles to relax and return to their normal position, resulting in symptoms of discomfort, stiffness, and pain. Individuals can have reoccurring bouts of tight muscles, eventually becoming chronic. Chronic muscle tension can pull the spine out of alignment even if there is no specific injury. The Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Wellness Team can relieve tight back muscle tension and restore positioning, mobility, and function. Muscles are the Key Muscles make the body move and greatly impact the skeletal and nervous systems. When a muscle is overstretched or pulled, there is not just injury to the muscles but the potential for injury to the bones and tendons in the area. This, in turn, can pinch nerves and cause problems with the nervous system, especially in pain signal transmissions. Symptoms Symptoms will depend on the cause and severity. The most common include: - Constant or chronic muscle achiness, soreness, stiffness, and tightness.
- Even after stretching or flexing, there is a dull aching or pain.
More serious symptoms may include: - Electrical or burning sensations
- Sharp or stabbing pain.
- Weakness in the legs or arms
- Tingling or numbness in the legs, arms, or chest.
- Chest discomfort symptoms.
Causes Aging The older a person is, the more likely they will experience back discomfort symptoms. Back issues most likely occur in 30- to 50-year-olds. - The aging process naturally wears the body.
- Thinning bones
- Muscle mass reduction
- Fluid loss between joints in the spine.
- All these can cause back issues and problems.
Unhealthy posture Constant pressure on the spine can lead to general back discomfort symptoms. Practicing unhealthy posture can generate this pressure. The muscles and ligaments must work harder to keep the body balanced because the muscles are out of position, and the other muscles can't perform their job properly. Overworking and overuse lead to tight back muscles, aches, and pain. Muscle sprain or strain Sprains are the tearing or stretching of ligaments. Strains are the tearing or stretching of muscles and tendons. Lifting heavy objects without proper form can easily cause a back sprain or strain. Sprains and strains can also occur after an awkward, sudden, or jerking movement. Herniated disc A herniated, slipped, or ruptured disc puts pressure on a nerve/s. This can stress the surrounding muscles causing tension to build up. Fall or other injuries Tight back muscles can result from the following: - A fall
- Vehicle accident
- Force Trauma
- Sports accident
Weight gain Added weight stresses and pulls the body down. This causes unhealthy posture and muscle tension. Chiropractic Functional Wellness Usually, tight muscles can be relieved with a hot bath or cold therapy. Reoccurring bouts of, or chronically tense back muscles, are signals that something is wrong and should not be ignored. Chiropractic care can release and relax tight back muscles and get them back into a natural state by re-aligning the spine through tissue manipulation, decompression, massage, and adjustments. The various treatment methods will relieve the discomfort, pain, tension, and realign the spinal column, and strengthen the body. When spinal components are put back into their proper place, the surrounding muscles no longer need to provide a counter-balance to the misalignment and begin to relax. Chiropractors can also recommend ways to improve posture and strengthen muscles to incur less wear and tear. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Furlan, Andrea D et al. "Complementary and alternative therapies for back pain II." Evidence report/technology assessment,194 (2010): 1-764. Geneen, Louise J et al. "Physical activity and exercise for chronic pain in adults: an overview of Cochrane Reviews." The Cochrane database of systematic reviews vol. 4,4 CD011279. 24 Apr. 2017, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011279.pub3 Mayo Clinic Staff. (2017). Back pain: Symptoms. mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/back-pain/basics/symptoms/con-20020797 Miake-Lye, Isomi M et al. "Massage for Pain: An Evidence Map." Journal of alternative and complementary medicine (New York, N.Y.) vol. 25,5 (2019): 475-502. doi:10.1089/acm.2018.0282 Nahian, Ahmed, et al. "Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment: Facial Muscle Energy, Direct MFR, and BLT Procedure – for TMJ Dysfunction." StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing, 12 September 2022. Rahman Shiri, Jaro Karppinen, Päivi Leino-Arjas, Svetlana Solovieva, Eira Viikari-Juntura, The Association Between Obesity and Low Back Pain: A Meta-Analysis, American Journal of Epidemiology, Volume 171, Issue 2, 15 January 2010, Pages 135–154, https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwp356
Whiplash-associated disorders, or WAD, describe injuries sustained from sudden acceleration/deceleration movements. It is a common outcome after a motor vehicle collision but can also be caused by sports injuries, falls, or assaults. Whiplash refers to the mechanism of the injury, while WAD refers to the presence of symptoms like pain, stiffness, muscle spasm, and headaches. A WAD prognosis is unpredictable, with some cases remaining acute with a full recovery, while others progress to chronic conditions with long-term symptoms and disability. Early intervention recommendations include rest, chiropractic care and physical rehabilitation, massaging and stretching exercises, and an anti-inflammatory diet. Whiplash Associated Disorders Cervical hyperextension injuries happen to drivers and passengers of moving, slow-moving (less than 14 miles per hour), and stationary vehicles when struck from behind. - The individual's body is thrown forward, but the head does not follow the body and instead whips forward, resulting in hyperflexion or extreme forward movement of the neck.
- The chin limits forward flexion, but the momentum can be sufficient to cause cervical distraction and neurological injuries.
- When the head and neck have reached maximum flexion, the neck snaps back, resulting in hyperextension or extreme backward movement of the neck.
Pathology Most WADs are considered soft tissue-based injuries with no fractures. Stages The injury goes through stages: Stage 1 - The upper and lower spine experiences flexion in stage one.
Stage 2 - The spine takes on an S-shape while extending and eventually straightens, causing lordosis.
Stage 3 - The entire spine is hyperextending with an intense force that causes the facet joint capsules to compress.
Symptoms Whiplash-associated disorders can be classified through grades by the severity of symptoms, including neck pain, stiffness, occipital headache, cervical, thoracic, and lumbar back pain, upper-limb pain, and paraesthesia. Grade 0 - No complaints or physical symptoms.
Grade 1 - Neck complaints but no physical symptoms.
Grade 2 - Neck complaints and musculoskeletal symptoms.
Grade 3 - Neck complaints and neurological symptoms.
Grade 4 - Neck complaints and fracture and/or dislocation.
- Most cervical fractures occur predominantly at C2 or C6, or C7.
- Most fatal cervical spine injuries occur at the craniocervical junction C1 or C2.
Affected Spinal Structures Some symptoms are thought to be caused by injury to the following structures: Causes of pain can be from any of these tissues, with the strain of the injury causing secondary edema, hemorrhage, and inflammation. Joints - Zygapophyseal joints
- Atlanto-axial joint
- Atlanto-occipital joint
- Intervertebral discs
- Cartilaginous endplates
Adjacent Joints Ligaments - Alar ligament
- Anterior atlanto-axial ligament
- Anterior atlanto-occipital ligament
- Apical ligament
- Anterior longitudinal ligament
- Transverse ligament of the atlas
Bones - Atlas
- Axis
- Vertebrae C3-C7
Nervous Systems Structures - Nerve roots
- Spinal cord
- Brain
- Sympathetic nervous system
Vascular System Structures - Internal carotid artery
- Vertebral artery
Chiropractic Care A chiropractor will identify areas of restricted joint motion, muscle tension, muscle spasm, intervertebral disc injury, and ligament injury. - They will analyze posture, and spinal alignment, check for tenderness, tightness, and how well the spinal joints move.
- This will allow the chiropractic physical therapy team to understand the injured body mechanics and how the spine is operating to make a thorough diagnosis.
- The doctor will order imaging tests like an x-ray or an MRI to evaluate any degenerative changes that may have existed before the whiplash injury.
- Once the injury has been accurately diagnosed, the chiropractor will design a personalized treatment plan.
Spinal Adjustments - Spinal manipulation is applied to areas of the spine that are out of alignment to realign the spine and activate the healing process.
- Flexion-distraction technique is a gentle technique that uses slower, less intense pushing motions on the discs used to treat disc herniations that often occur after a whiplash injury.
- Instrument-assisted manipulation utilizes special instruments to apply various forces or massage settings to the area.
- Targeted spinal manipulation targets specific areas to rework, release, and rebuild the structures.
- Massage Therapy stimulates the affected muscles to relax them from their tense state.
- A treatment plan may utilize:
- Instrument-assisted therapy
- Trigger point therapy
- Resistance-based stretches to rehabilitate soft tissue damage.
Our chiropractic team is ready to help you feel your best so you can return to normal activities and get on with your life. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Pastakia, Khushnum, and Saravana Kumar. "Acute whiplash associated disorders (WAD)." Open access emergency medicine: OAEM vol. 3 29-32. 27 Apr. 2011, doi:10.2147/OAEM.S17853 Ritchie, C., Ehrlich, C. & Sterling, M. Living with ongoing whiplash-associated disorders: a qualitative study of individual perceptions and experiences. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 18, 531 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-017-1882-9 https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/whiplash-associated-disorder Sterling, Michele. "Whiplash-associated disorder: musculoskeletal pain and related clinical findings." The Journal of manual & manipulative therapy vol. 19,4 (2011): 194-200. doi:10.1179/106698111X13129729551949 Wong, Jessica J et al. "Are manual therapies, passive physical modalities, or acupuncture effective for the management of patients with whiplash-associated disorders or neck pain and associated disorders? An update of the Bone and Joint Decade Task Force on Neck Pain and Its Associated Disorders by the OPTIMa collaboration." The spine journal: official Journal of the North American Spine Society vol. 16,12 (2016): 1598-1630. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2015.08.024 Woodward, M N et al. "Chiropractic treatment of chronic 'whiplash' injuries." Injury vol. 27,9 (1996): 643-5. doi:10.1016/s0020-1383(96)00096-4
Back injuries from vehicle collisions vary from person to person. Common injuries may include strains, sprains, herniated discs, and fractures, and individuals dealing with certain spinal conditions like spinal stenosis may cause the medical condition to accelerate. Still, the force and physical impact the body absorbs during a crash, no matter how minor the accident or how safe the car is, will cause bodily aches and pains with the potential for other spinal conditions. Chiropractic care, massage, decompression, and traction therapy can relieve symptoms and restore mobility and function. Back Injuries From Vehicle Collisions Depending on how the impact affects the spine, problems can present in various areas of the back. The violent motion can sprain, strain, and fracture spinal components. Even minor incidents can impact mobility. Symptoms can stem from inflammation, compressed nerves, or fractures. Any damage can have long-lasting effects on the vertebrae, nerve roots, and back muscles. A vehicle collision can affect the following: - Lumbar vertebrae - lower back
- Thoracic vertebrae - middle/upper back
- Cervical vertebrae - neck
Each area consists of bones, tissues, muscles, nerves, tendons, and ligaments extending from the neck to the pelvis. - The most common back injuries are to the neck and lower back, where the most movement and shifting occurs, often causing nerve damage.
- The central placement and rigid structure make middle back injuries less common.
- Upper back injuries that connect the rib and chest region can affect breathing.
- Soft tissue injuries might not show up immediately.
Symptoms After a vehicle collision, it's common to feel sore all over. The symptoms can range from manageable discomfort to complete immobility. Individuals may experience the following: Muscle spasms - The muscle may repeatedly twitch, feel like hard knots, and feel tender to the touch.
- Muscle spasms can vary in pain levels from mild to debilitating.
Stiffness - Individuals may not feel as flexible because of the muscle tension that activated during the crash to protect the body.
- Stiffness can go away after light stretching or continue throughout the day.
Burning or Shooting Pain - A burning or shooting pain may travel down the back and buttocks through the back of one or both legs.
- It can be mild, dull aches and pains that go away quickly or last for days.
- Changing positions, such as sitting up after waking up or standing up after sitting, can cause sharp acute pain.
- Facet disease may cause neck or shoulder pain.
Discomfort When Walking or Standing - Certain physical activities can cause a throbbing sensation or mild pain when attempting to perform various tasks.
Tingling and/or Numbness - Tense muscles can pinch nerves leading to sensations of tingling or numbness in the legs, feet, arms, or hands.
Head Issues - Headaches, dizziness, or disorientation can present.
Spinal Disorders Back injuries from vehicle collisions can result in a degenerative disc disorder months or years later. It can also speed up health issues individuals didn't know they had before the crash. As the body ages, previous damage combined with degeneration can result in: - Pinched nerves
- Sciatica
- Bulging discs
- Herniated discs
- Spinal stenosis
- Degenerative disc disease
- Foraminal stenosis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Spinal osteoarthritis
- Bone spurs
- Degenerative scoliosis
Discogenic pain - Damage to spinal discs causes discogenic pain, often sharp impulses or shooting sensations.
- Individuals can experience symptoms in different ways:
- Some individuals feel better when standing, sitting, or lying down, while the positions or motions worsen the symptoms for others.
Chiropractic Care and Therapies Chiropractic treatment can rule out critical issues and expedite recovery time. Benefits include: Pain Symptom Relief - Chiropractic relieves pain in the affected areas and throughout the body.
- Massaging and decompression release endorphins.
Inflammation Alleviation - Micro-tears within the muscles and ligaments are common and cannot be found through a standard x-ray.
- Spinal adjustments can bring the spine back into alignment, producing natural anti-inflammatory properties to assist with discomfort and heal the tears.
Scar Tissue Breakdown - Muscles can get scarred, causing stiffness and soreness.
- Chiropractic massage targets these areas and breaks down the build-up quicker than if it was left to heal on its own.
- Less scar tissue means faster recovery.
Range of Motion and Mobility Restored - Back injuries can result in restricted mobility.
- It may be difficult to turn or move when the muscles are inflamed.
- Mobilizing the spine through adjustments restores the proper range of motion.
Decreased Medication Use - Prescription pain medications can turn into dependency.
- Chiropractic adjustments can ensure that the injury is healed and the pain is not just masked.
Long-Term Benefits - Receiving chiropractic care can help prevent minor injuries from worsening into serious and chronic conditions.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Erbulut, Deniz U. "Biomechanics of neck injuries resulting from rear-end vehicle collisions." Turkish neurosurgery vol. 24,4 (2014): 466-70. doi:10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.9218-13.1 National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center. (2020) "Spinal Cord Injury: Facts and Figures at a Glance." https://www.nspine injurysc.uab.edu/Public/Facts%20and%20Figures%202020.pdf Rao, Raj D et al. "Occupant and Crash Characteristics of Elderly Subjects With Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Injuries After Motor Vehicle Collisions." Spine vol. 41,1 (2016): 32-8. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000001079 Rao, Raj D et al. "Occupant and crash characteristics in thoracic and lumbar spine injuries resulting from motor vehicle collisions." The spine journal: official journal of the North American Spine Society vol. 14,10 (2014): 2355-65. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2014.01.038
Spinal disc deterioration from aging is normal, but health issues or injuries can advance the degenerative process. Disc protrusions are related to herniated discs but are the mildest form of the condition and are a common form of spinal disc deterioration that can cause neck and back issues. However, individuals may have a small protruding disc that can go undetected unless it irritates or compresses the surrounding nerves. Chiropractic care, decompression, and massage therapy can realign the disc back into position, relieving discomfort and pain. Disc Protrusion A disc is like a sturdy soft rubber shock absorber/cushion with added gel inside. The gel acts as a shock absorber. When the gel begins to protrude out slightly, this is a disc protrusion. Once a protruding disc begins to develop, it usually remains in that position. The disc can sometimes reabsorb on its own and realign back into position, but there is no way of knowing that will happen or how long it will take. With age and/or injuries, the body's parts change. The spine's discs dehydrate and lose elasticity weakening the discs and making them more vulnerable to herniation stages: First Stage - Following natural weakening can be classified as a disc protrusion when the disc's core begins pushing into the spinal column.
- Disc protrusions can be tiny or push out an entire side of the disc.
Second Stage - Disc deterioration often consists of a bulging disc when the core pushes out farther around the circumference beyond the disc's outer layer, called the annulus fibrosus, creating the telltale bulge.
- A bulging disc involves more than 180 degrees of the disc's circumference.
Third Stage - The third stage is a herniated disc, meaning the disc's outer wall has torn, allowing the inner gel to leak out, usually irritating the surrounding nerves.
Fourth Stage - The fourth stage is sequestration, a herniated disc in which a piece of the nucleus breaks free of the vertebral disc fragments and falls into the spinal canal.
Types A disc protrusion is one type of disc herniation that pushes out but remains connected. Different types compress and irritate the discs differently and produce various symptoms, including: Paracentral - This is the most common, where the disc protrusion jams the space between the central canal and the foramen.
Central - This is where the disc protrusion impinges into the spinal canal, with or without spinal cord compression.
Foraminal - The disc intrudes into the foramen, the space through which nerve roots branch off the spinal cord and exit the vertebrae.
Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Chiropractic Care Individuals with a disc protrusion can have symptoms similar to sciatica, which includes back, buttock, and leg discomfort, numbness, and pain sensations. - Treatment for disc protrusion will be based on the individual's symptoms.
- A chiropractor will take a detailed medical history and perform a physical examination.
- A spinal MRI test could be ordered depending on the injury or condition.
- A customized treatment plan will be developed to fit the individual's medical needs.
Most disc protrusions improve after a few weeks of rest, avoiding strenuous activities, activity modification, an anti-inflammatory diet, and gentle exercises that the chiropractic team will provide. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Fardon, David F et al. "Lumbar disc nomenclature: version 2.0: Recommendations of the combined task forces of the North American Spine Society, the American Society of Spine Radiology and the American Society of Neuroradiology." The spine journal: official journal of the North American Spine Society vol. 14,11 (2014): 2525-45. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2014.04.022 Mysliwiec, Lawrence Walter, et al. "MSU classification for herniated lumbar discs on MRI: toward developing objective criteria for surgical selection." The European spine journal: official publication of the European Spine Society, the European Spinal Deformity Society, and the European Section of the Cervical Spine Research Society vol. 19,7 (2010): 1087-93. doi:10.1007/s00586-009-1274-4 https://www.ninds.nih.gov/low-back-pain-fact-sheet#3102_7 Urban, Jill P G, and Sally Roberts. "Degeneration of the intervertebral disc." Arthritis research & therapy vol. 5,3 (2003): 120-30. doi:10.1186/ar629
T-bone accidents/collisions, also known as side-impact or broadside collisions where the front end of one car slams into the side of another, can result in severe injuries and tend to have a more devastating effect on the body. Side impact collisions account for 24% of driver or passenger deaths; even at 30 mph, side-impacts regularly cause injuries to the occupants of the struck car. Modern vehicles have many safety features, including safety belt features, airbags, and collision avoidance systems that protect drivers and passengers from front and rear collisions; however, when it comes to side-impact, occupants tend to remain unprotected. T-Bone Side Collision Causes T-bone accidents usually happen at intersections. Usual Causes of T-bone accidents involve someone failing to yield the right of way. The most common causes include: - A driver makes a risky left turn at an intersection, believing the other car/s will stop.
- A driver decides to run a red light crashing into a vehicle making a left turn.
- A driver runs through a stop sign, slams into a vehicle, or gets slammed.
- Distracted driving.
- Defective automotive equipment like faulty brakes.
Injuries T-bone collision-related injuries include the head, neck, arms, shoulders, chest, ribs, abdominals, pelvis, legs, and feet: - Abrasions
- Bruising
- Cuts
- Gashes
- Soft tissue strains
- Whiplash
- Nerve damage
- Dislocations
- Fractures
- Internal damage to the organs
- Concussions
- Brain trauma
- Partial or complete paralysis
Back injuries can damage the spinal cord causing herniated discs, sciatica, and chronic pain that can radiate to the rest of the body. Treatment and Recovery Individuals have different recovery times and depend on the severity of the injury and on any pre-existing conditions. Brain injuries and spinal issues can take months to recover fully. Fractures placed in a hard or soft cast to heal for weeks or months can lead to muscle atrophy. Chiropractic therapeutic massage and decompression strengthens muscle weakness, resets and realigns the spinal column, improves range of motion/movement, strengthens grip, and relieves pain. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Gierczycka, Donata, and Duane Cronin. “Importance of impact boundary conditions and pre-crash arm position for the prediction of thoracic response to pendulum, side sled, and near side vehicle impacts.” Computer methods in biomechanics and biomedical engineering vol. 24,14 (2021): 1531-1544. doi:10.1080/10255842.2021.1900132 Hu, JunMei, et al. “Chronic widespread pain after motor vehicle collision typically occurs through immediate development and nonrecovery: results of an emergency department-based cohort study.” Pain vol. 157,2 (2016): 438-444. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000388 Lidbe, Abhay, et al. “Do NHTSA vehicle safety ratings affect side impact crash outcomes?.” Journal of safety research vol. 73 (2020): 1-7. doi:10.1016/j.jsr.2020.02.001 Mikhail, J N. “Side impact motor vehicular crashes: patterns of injury.” International journal of trauma nursing vol. 1,3 (1995): 64-9. doi:10.1016/s1075-4210(05)80041-0 Shaw, Greg et al. “Side impact PMHS thoracic response with a large-volume airbag.” Traffic injury prevention vol. 15,1 (2014): 40-7. doi:10.1080/15389588.2013.792109
Introduction Everybody is always moving in their vehicles as they go from one place to another in less time. Sometimes accidents happen as vehicles collide with each other and cause excruciating pain to the body as it lunges forward, causing back and neck pain to the individual. These are physical effects on the body, but the emotional impact also takes a toll on the individual. It can cause a person to become miserable and affect their quality of life. Today’s article discusses the effects of an auto accident are cause the back and body, as well as how non-surgical decompression therapy can help alleviate the pain in the back from an auto accident. Patients are referred to qualified, skilled providers specializing in spinal decompression and non-surgical treatments. We go hand in hand with our patients by referring them to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is valuable for asking critical questions to our providers. Dr. Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer Can my insurance cover it? Yes, it may. If you are uncertain, here is the link to all the insurance providers we cover. If you have any questions or concerns, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900. The Effects Of Auto Accidents On The Back Have you suffered from back pain after a vehicle collision? What about experiencing whiplash or neck pain? Or has your lower back been feeling stiff and aches more? Many of these symptoms are signs that the spine, back, and neck all have suffered from the effects of an auto accident. Research has shown that the impact of a person in an auto accident causes the body to rapidly lunge forward and back after a complete stop, causing damage to the body, especially on the spine. After the auto accident has occurred, many individuals don’t feel the effects of the injuries that are caused by auto accidents sometimes until the day after the accident. This is due to the adrenaline in the body, which is both a neurotransmitter and a hormone and is fully turned on to the max. Additional information has stated that many individuals suffer from low back pain after a motor vehicle collision. Even if the accident was non-lethal, the impact can cause strain on the lower back muscles and compress the spinal nerves, making them irritated. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
Introduction The body is a well-tuned machine that is on the move constantly. The different systems like the musculoskeletal system, the immune system, and the joint system, to name a few, can help the body’s motor function to get the body from point A to point B. When injuries or auto accidents affect the body, it can cause various issues to affect the body over time. Many people who suffer from an auto accident injury will experience pain in the cervical and lumbar portions of their spine. It can be nerve-wracking as they are trying to comprehend what is happening. Today’s article will focus on herniation due to auto accidents, how it affects the spine, and how decompression treatments can help many suffering individuals with auto accident herniation. Referring patients to qualified and skilled providers who specialize in spinal decompression therapy. We guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is essential for asking insightful questions to our providers. Dr. Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer Can my insurance cover it? Yes, it may. If you are uncertain, here is the link to all the insurance providers we cover. If you have any questions or concerns, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900. How Do Auto Accidents Cause Herniation? Have you experienced pain in your neck or low back? Did you experience whiplash in your neck? Has the pain progressively gotten worse after the accident? Many of the symptoms are primarily the after-effects of an auto accident involving a person. After a person has been involved in an auto accident, the injuries and symptoms usually occur within a few minutes until the next day. Research studies have shown that auto accident injury symptoms like herniation occur when the cervical and lumbar portions are injured, causing symptoms like soft tissue strain and disc derangement to be accompanied by radicular pain symptoms. Auto accident herniation also starts to compress the surrounding nerves around the spine. It induces inflammatory markers in the affected areas situated in the neck and lower back. Additional studies have found that auto accident herniation also affects the thoracic portion of the back. Many individuals that suffer from herniation will experience posterior shoulder pain and upper/lower back pain from being involved in an auto accident. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
Introduction The neck holds the head in place in the body like the lower back has the upper body. The neck’s primary function is to support the head and allow it to turn left to right, rotate both counters and clockwise, and stretch to some extent. The neck is part of the cervical area of the spine and is composed of soft tissue muscles, ligaments, and nerve roots that connect to the central nervous system and the musculoskeletal system. However, like the lower back, the neck is sustainable to injuries that can affect a person. This could be numerous scenarios like an auto accident, neck strains, poor posture, or stiff neck muscles that cause the neck to ache and tense up. Fortunately, non-surgical treatments can help alleviate neck stiffness and bring back mobility to the neck muscles. Today’s article focuses on how whiplash injuries occur, their symptoms, and how cervical decompression can help alleviate whiplash on a person’s neck. By referring patients to qualified and skilled providers specializing in spinal decompression therapy. To that end, and when appropriate, we advise our patients to refer to our associated medical providers based on their examination. We find that education is the key to asking valuable questions to our providers. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer Can my insurance cover it? Yes, it may. If you are uncertain, here is the link to all the insurance providers we cover. If you have any questions, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900. How Does Whiplash Injuries Occur? Whiplash is a common injury in many auto accidents and can range from mild to severe depending on which neck muscle is affected or injured. Since the neck is composed of soft tissue muscle, ligaments, and nerves that help protect the cervical area of the spine, injuries can occur to the neck, causing unwanted symptoms like whiplash to cause many issues to the neck. Research studies have found that whiplashes happen when a person has a traumatic experience that causes their neck to be forcefully moved back and forth rapidly like a whip. Other research studies have mentioned that since auto accidents like rear-end collisions are the leading causes of whiplash, other causes like trauma due to sports injuries like football or contact sports can also cause whiplash to occur in the individual. The Symptoms When a person gets rear-ended from an auto collision or suffers from a brutal fall due to a sports injury, it can impact the body and the neck, causing unwanted symptoms to occur. Research studies have shown that a whiplash injury causes hyperextension to the neck muscles causing the individual to jerk forward and whip back rapidly, causing pain and injuring the ligaments to the neck. This causes various issues in the aftermath after a person suffers from whiplash and has neck-related symptoms pop up. Other research studies have stated that some of the signs that occur after whiplash has affected a person include: When this happens to many individuals suffering from whiplash, treatments can help with whiplash symptoms and ease the neck back to functioning normally. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
Individuals drive to jobs, to school, run errands, take road trips, spending a lot of time on the road. Accidents and crashes happen more frequently with all kinds of injuries. The National Highway Traffic Safety Commission has found that 37% of car accidents and crashes involve leg injuries and damage. Chiropractic physical rehabilitation and functional medicine can help heal injuries getting the individual back to everyday life. Leg Injuries Common leg injuries include: Bruising and Cuts Bruising and cuts are typical from the impact and the body getting slammed around. Lacerations can be noticed right away, but bruising comes from blood pooling underneath the skin and can take time to present, possibly 24 to 48 hours. Most bruises and cuts heal independently from home first aid care. A standard recovery used to take care of bruising is R.I.C.E or rest, ice, compression, and elevation. This helps the healing process; however, if the injury/s are more severe, chiropractic can help with therapeutic massage to relieve pain and strengthen the injured muscles, tendons, and ligaments. ACL Injuries The femur or thigh bone has several bands of tissue connecting it to the patella or kneecap and tibia or shin bone. One of the bands is the anterior cruciate ligament or ACL. Injuries to this band of tissue are common in sports. Car accidents and crashes are another common cause, specifically tearing the ligament. Individuals experiencing a tear may notice some or all of the following symptoms: - A cracking or popping sound when the accident or crash took place.
- Swelling in and around the knee.
- Severe pain in and around the knee.
- Unstable and unsteady when walking or standing.
- Reduced range of motion that makes walking or moving difficult.
A chiropractor can help treat the injury and help correct any muscular imbalances. Meniscus Tears Tears to the meniscus are also common in car accidents and crashes. The meniscus is a part of the knee. Two wedge-shaped pieces of cartilage provide a cushion where the femur and tibia meet to absorb shock. The wedges are called menisci. - When the meniscus tears, individuals might feel or hear a pop and could feel the leg suddenly give out.
- Swelling in the knee.
- Some pain but still be able to walk.
- The knee will be stiff for the next few days.
- More difficulty bearing weight or walking.
The RICE method is a recommended method of self-care. Many meniscus tears do not require surgery to improve knee function. Mild to moderate meniscus tears can be successfully treated with chiropractic techniques like soft tissue work, corrective stretches, and exercises. Surgery could eventually be necessary for severe cases to repair the meniscus to prevent long-term complications. Broken Crushed Bones From the hips to the toes, the bottom half of the body bones are vulnerable to fractures. Physical trauma from prolonged pressure on the body can cause bones to get shattered from a crush injury. Crush injuries affect the bones, soft tissues, and other leg areas. Different forms of fractures range in severity. There are partial fractures that do not cause the bone to separate and complete fractures that break apart and open fractures that pierce the skin. Some fractures are hard to detect for up to several days. Chiropractic care can help the body heal and recover from a bone fracture. A patient’s bone density is evaluated and tested with an individualized treatment plan to help regain and maintain optimal bone strength. The treatments strengthen the muscles, reduce stiffness, improve nutrition, and relieve pain. Manipulation adjustments, rehabilitation, relaxation techniques, and dietary health coaching help individuals heal faster and strengthen their bones. The objective is to help regain increased mobility and range of motion. Sciatica Car accidents and crashes are one instance where the spine can be damaged enough to bring on sciatic pain where no back problems were present before. The impact from a car accident can cause the discs to be knocked out of place, damaged, and/or rupture around the surrounding tissue. Any of these results can pinch the sciatic nerve, leading to pain and other sciatica symptoms. Chiropractic can realign the spine and relieve pressure from the nerve/s. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Atkinson, T, and P Atkinson. “Knee injuries in motor vehicle collisions: a study of the National Accident Sampling System database for the years 1979-1995.” Accident; analysis and prevention vol. 32,6 (2000): 779-86. doi:10.1016/s0001-4575(99)00131-1 Foulk, David M, and Brian H Mullis. “Hip dislocation: evaluation and management.” The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons vol. 18,4 (2010): 199-209. doi:10.5435/00124635-201004000-00003 Reynolds, April. “The fractured femur.” Radiologic technology vol. 84,3 (2013): 273-91; quiz p.292-4. Wilson, L S Jr et al. “Foot and ankle injuries in motor vehicle accidents.” Foot & ankle international vol. 22,8 (2001): 649-52. doi:10.1177/107110070102200806
Automobile accidents and crashes can cause all kinds of damage to the body even when the accident/crash is not severe. Physical symptoms might not present at all for several days, even weeks. This is known as having delayed injury symptoms. These can include: - Swelling.
- Stiffness.
- Aching.
- Pain that radiates all over the body.
- Sleep problems.
- Headaches.
- Brain fog.
- Disorientation.
- Memory problems.
Chiropractic and physical therapy rehabilitation can restore the body's alignment, stop inflammation, loosen, stretch and strengthen the musculoskeletal system restoring optimal health. Adrenaline When the body is involved in a dangerous physical situation, it protects itself by releasing a surge of adrenaline. This hormone protects the body, causing the fight or flight response when in danger. Adrenaline causes several preservation responses that include: - Intense increase in energy.
- Little or no pain.
- Enlarged blood vessels and airways increase oxygen flow.
- Increased strength from increased blood flow to the muscles.
- Changes in vision and hearing that focus on sights and sounds all around.
- Endorphins are released that make the body feel calm and in control.
- Endorphins affect the way the body responds to pain and stress.
Individuals don't start feeling aches and pains until the adrenaline and endorphins wear off. However, because everybody is different and the emergency response has turned off, the body still might not feel the injury symptoms. These are delayed injury symptoms. Rate of Speed When riding in a vehicle, the body moves at the same speed as the vehicle. During an impact, the vehicle stops, but the body continues moving until it stops, typically with a lot of force from the seatbelt, airbag, or other barriers. The intense momentum change can cause soft tissue damage and ligament or muscle strains from the stretching, pulling, contracting, and tearing. Also, the intervertebral discs can tear, bulge, or herniate over time, creating pressure on nerves and the surrounding tissues. Delayed Injury Symptoms Headaches - Headaches that develop days after an accident/crash are common.
- They can signal a possible injury to the neck or head, a blood clot on the brain, or a concussion.
Numbness - Loss of feeling in arms and hands could indicate a whiplash-associated disorder.
- The loss of feeling/sensation results from damage to the neck or spinal column.
- Around 20 percent of individuals impacted by a rear-end crash develop some whiplash symptoms.
Neck or Shoulder Pain and/or Stiffness - Whiplash is a classic delayed symptom injury associated with accidents.
- Most delayed whiplash injuries are caused by rear-end vehicle collisions at speeds of less than 14 miles an hour.
- Whiplash injuries usually require x-rays, CT scans, or MRIs for proper diagnosis.
Abdominal Pain or Swelling - This could indicate internal bleeding.
- Internal bleeding can remain undiscovered for hours or days.
- This can be a life-threatening condition that needs to be diagnosed and treated by emergency medical personnel.
- Other symptoms include:
- Large areas of deep bruising.
- Dizziness.
- Fainting.
Back Aches and Pains - Back pain can be caused by injury to the muscles, ligaments, nerves, or damage to the vertebrae.
- Low back pain occurs in more than half of rear-impact collisions and almost three-quarters of side-impact crashes.
Chiropractic Rehabilitation After an accident, soft tissues can sustain minimal damage; however, the minimal damage left untreated can start to worsen and turn into a painful condition. Emergency room visits are to rule out major injuries like brain/nerve injuries, bleeding, punctures, lacerated organs, fractures that require emergency stabilization. Chiropractors look for other symptoms and mechanisms that indicate damage to the body's soft tissues and nerves to see if they have been stretched or torn and dysfunction in the nervous system. Calorie Counting Counting calories can be a stepping stone to change behavior towards food. Tracking what foods are being taken into the body promotes mindfulness of dietary habits. Studies on the subject reveal a significant association between self-monitoring and weight loss. Takeaways include: General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Burke, Lora E et al. "Self-monitoring in weight loss: a systematic review of the literature." Journal of the American Dietetic Association vol. 111,1 (2011): 92-102. doi:10.1016/j.jada.2010.10.008 D'Elia, Michael A et al. "Motor vehicle collision with seatbelt sign and traumatic abdominal wall hernia should raise suspicion for hollow viscus injury." Trauma case reports vol. 22 100206. 25 May. 2019, doi:10.1016/j.tcr.2019.100206 Kacprzynski, Gregory, and Joshua Bucher. "Delayed vertebral artery dissection after mild trauma in a motor vehicle collision." The American Journal of emergency medicine vol. 45 (2021): 678.e1-678.e2. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.11.028 Olinger, Catherine, and Richard Bransford. "Upper Cervical Trauma." The Orthopedic clinics of North America vol. 52,4 (2021): 451-479. doi:10.1016/j.ocl.2021.05.013 Sterling, Michele. "Whiplash-associated disorder: musculoskeletal pain and related clinical findings." The Journal of manual & manipulative therapy vol. 19,4 (2011): 194-200. doi:10.1179/106698111X13129729551949
Dr. Mark Hyman is leading a health revolution—one revolved around using food as medicine to support longevity, energy, mental clarity ...
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...









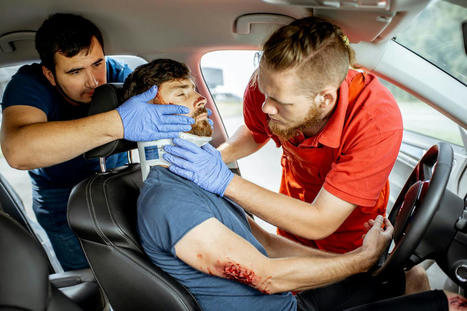
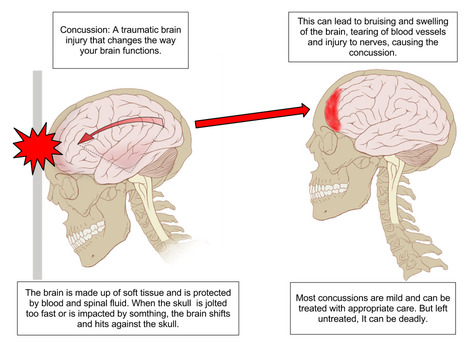








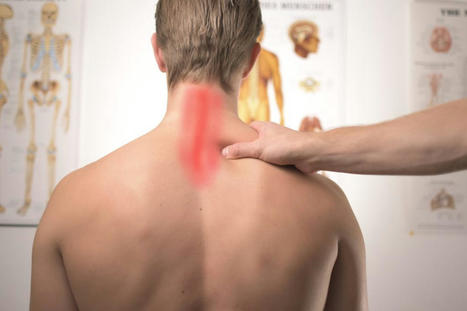










Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic can develop a personalized treatment plan for slipping and falling injuries. For answers to any questions you may have, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900 or 915-412-6677