During his talk at HOPE/X Jonathan Zdziarski detailed several undocumented services (with names like 'lockdownd,' 'pcapd,' 'mobile.file_relay,' and 'house_arrest') that run in the background on over 600 million iOS devices.
Zdziarski's questions for Apple include:
- Why is there a packet sniffer running on 600 million personal iOS devices instead of moved to the developer mount?
- Why are there undocumented services that bypass user backup encryption that dump mass amounts of personal data from the phone?
- Why is most of my user data still not encrypted with the PIN or passphrase, enabling the invasion of my personal privacy by YOU?
- Why is there still no mechanism to review the devices my iPhone is paired with, so I can delete ones that don’t belong?
... and his last slide (page 57 of the PDF) sums it up nicely:
- Apple is dishing out a lot of data behind our backs
- It’s a violation of the customer’s trust and privacy to bypass backup encryption
- There is no valid excuse to leak personal data or allow packet sniffing without the user’s knowledge and permission.
- Much of this data simply should never come off the phone, even during a backup.
- Apple has added many conveniences for enterprises that make tasty attack points for .gov and criminals
- Overall, the otherwise great security of iOS has been compromised… by Apple… by design.
Learn more:
Via
Gust MEES



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...

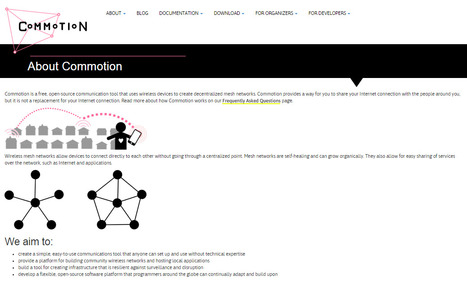









Commotion is a free, open-source communication tool that uses wireless devices to create decentralized mesh networks. Commotion provides a way for you to share your Internet connection with the people around you, but it is not a replacement for your Internet connection. Read more about how Commotion works on our Frequently Asked Questions page.