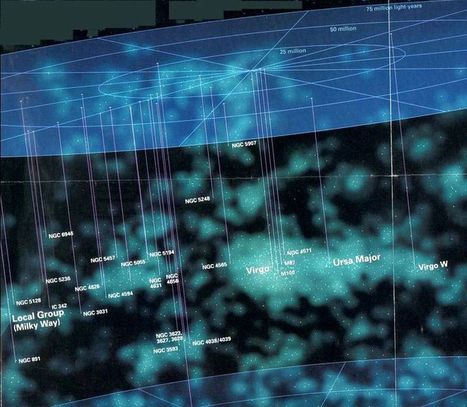
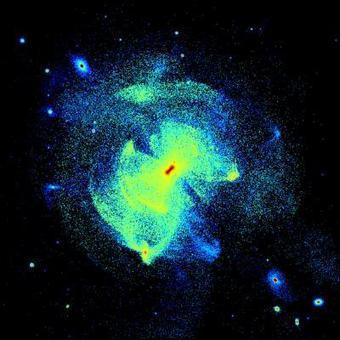
The Milky Way's supermassive black hole is generally a picky eater, but NASA's NuSTAR spacecraft recently caught it in the act of having a snack!
Follow, research and publish the best content
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
Already have an account: Login

 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
|
|