Pro-inflammatory cytokines are directly implicated in the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Variable clinical response to cytokine targeted therapies as TNFalpha and IL-6, strongly highlights the heterogeneity of inflammatory process in RA.
Results
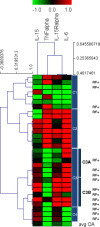
We found higher and significant levels of TNFalpha, IL-6 and IL-15Ralpha but not of IL-15 in RA compared with the OA group. Additionally, a high inter-individual variability in the levels of these 4 cytokines was observed in RA, although we identified 4 patients’ subgroups by cluster analysis of cytokines concentration in SF. We also found a positive correlation between IL-15Ralpha-IL-6 and IL-15Ralpha-IL-15, but not for other pairs of cytokines in RA. In addition we found correlation between the value of IL-15Ralpha in SF and disease activity score, DAS28.
Conclusions
In our current work we found a high inter-individual variability in the levels of TNFalpha, IL-6, IL-15 and IL-15Ralpha in SF of RA patients and were identified four principal clusters of cytokines concentration in SF, suggesting the importance of identifying disease subset of patients for personalized treatment. Finally, we found a correlation between IL-15Ralpha-IL-6, IL-15Ralpha-IL-15, but we did not find any correlation between other pairs of studied cytokines in SF.
Via Krishan Maggon

 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...









Research article
Differential expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-15Ralpha, IL-15, IL-6 and TNFalpha in synovial fluid from Rheumatoid arthritis patientsAlicia Santos Savio1*, Ana Cecilia Machado Diaz1, Araceli Chico Capote2, Jamilet Miranda Navarro3, Yunier Rodríguez Alvarez1, Ricardo Bringas Pérez3, Miguel Estévez del Toro2and Gerardo E Guillen Nieto1
*Corresponding author: Alicia Santos Savio alicia.santos@cigb.edu.cu
Author Affiliations
1Pharmaceutical Division, Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Havana CP 10600, Cuba
2Rheumatology Department, H. Ameijeiras Hospital, San Lazaro 701, Havana, Cuba
3Bioinformatics Department, Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Havana CP 10600, Cuba
For all author emails, please log on.
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2015, 16:51 doi:10.1186/s12891-015-0516-3
The electronic version of this article is the complete one and can be found online at:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2474/16/51