 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
The body needs to be flexible to maintain a full range of motion. Stretching keeps the muscles supple, strong, and healthy; without it, the muscles shorten and become stiff and tight. Then, when the muscles are needed, they are weak and unable to extend fully. This increases the risk of joint pain, strains, injuries, and muscle damage. For example, sitting in a chair for a long time results in tight glute muscles and hamstrings, which leads to back discomfort symptoms and inhibits walking. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic can help individuals develop a personalized stretching program to maintain smooth mobility, flexibility, and function. Stretching Objective Benefits The body needs to be flexible to maintain mobility, balance, and independence. The benefits of regularly stretching include: - Muscles function at optimal levels.
- Maintains muscle length.
- Maintains muscle strength.
- Increased blood circulation.
- Endorphin release.
- Parasympathetic activation.
- Relieves stress.
- Natural toxin removal.
- Relieves body aches and soreness.
- Improves ability and performance in physical activities.
- Reduces the risk of injuries.
- Improves posture.
Important Areas The areas critical for mobility include: - Lower back/waistline
- Hip flexors
- Hamstrings
- Quadriceps in the front of the thigh.
- Calves
- Neck
- Shoulders
Stretch Reflex When the muscles are stretched, so are the muscle spindles. The spindle records the change in length and speed and transmits the signals through the spinal cord, which conveys the information. This triggers the stretch reflex, which tries to resist the change by causing the stretched muscle to contract. Muscle spindle function helps maintain muscle tone and protects the body from injury. One of the reasons for holding a stretch for a specific amount of time is because, as the muscle stays in a stretched position, the spindle acclimates to the new condition and reduces its resistance signaling, gradually training the stretch receptors to allow greater lengthening of the muscles. Chiropractic Stretch Training However, stretching once won't generate maximum flexibility. Tight muscles may have taken months or years to develop; therefore, it will take time to achieve flexibility and must be continually worked on to maintain it. Chiropractors and physical therapists are body movement experts and can assess individual muscle strength and develop a customized stretching program. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Bhattacharyya, Kalyan B. "The stretch reflex and the contributions of C David Marsden." Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology vol. 20,1 (2017): 1-4. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.199906 Behm, David G et al. "Acute effects of muscle stretching on physical performance, range of motion, and injury incidence in healthy active individuals: a systematic review." Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism = Physiologie applique, nutrition et metabolism vol. 41,1 (2016): 1-11. doi:10.1139/apnm-2015-0235 Berg, K. Stretching fundamentals. In: Prescriptive Stretching. 2nd ed. Kindle edition. Human Kinetics; 2020. da Costa, Bruno R, and Edgar Ramos Vieira. "Stretching to reduce work-related musculoskeletal disorders: a systematic review." Journal of rehabilitation medicine vol. 40,5 (2008): 321-8. doi:10.2340/16501977-0204 Page, Phil. "Current concepts in muscle stretching for exercise and rehabilitation." International journal of sports physical therapy vol. 7,1 (2012): 109-19. Witvrouw, Erik, et al. "Stretching and injury prevention: an obscure relationship." Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) vol. 34,7 (2004): 443-9. doi:10.2165/00007256-200434070-00003
Introduction When exercising, it is very important to warm each muscle group to prevent injuries from occurring when working out. Stretching the arms, legs, and back can loosen up stiff muscles and increase blood flow to allow each muscle fiber to warm up and allow maximum power when each set is performed. One of the best ways to reduce muscle fatigue or stiffness before working out is to foam roll each muscle group for at least 1-2 minutes max to provide optimal functionality. Foam rolling allows the muscles to warm up before an extensive workout session. Still, it can also offer many benefits when combined with other therapies to reduce pain-like symptoms like trigger point pain from causing further injuries from reoccurring in the body. Today’s article focuses on the benefits of foam rolling, how it reduces trigger point pain, and how it is combined with chiropractic care to achieve optimal health and wellness. We refer patients to certified providers incorporating techniques and therapies for individuals dealing with trigger point pain affecting different body areas. By locating where the trigger points are coming from, many pain specialists utilize a treatment plan to reduce the effects that trigger points are causing on the body while suggesting different tools, like using a foam roller to reduce pain in the other muscle groups. We encourage and appreciate each patient by referring them to associated medical providers based on their diagnosis when it is appropriate. We understand that education is a terrific way when asking our providers intricated questions at the patient’s request and understanding. Dr. Jimenez, D.C., only utilizes this information as an educational service. Disclaimer The Benefits Of Foam Rolling Have you been dealing with pain-like symptoms in different parts of your body? Do you feel stiffness in your muscles? Or have you been feeling exhausted throughout the entire day? Many people often feel stressed, overworked, and exhausted after a long day and need to find different ways to relieve stress. Whether going to the gym to work out or yoga class, many people should warm up for about 5-10 minutes to work out each muscle group to reduce muscle fatigue and stiffness. One of the tools that people should utilize is using a foam roller. Studies reveal that foam rolling before working out can improve muscle performance and flexibility and, at the same time, alleviate muscle fatigue and soreness. Incorporating foam rolling as part of your warm-up can prevent issues like trigger point pain from causing more problems in the affected muscle group and causing more harm. Foam rolling has been known as a self-myofascial release (SMR) tool for many athletic people to relieve delay-onset muscle soreness (DOMS) and can help the recovery process for muscular performance. Studies show that when athletes have DOMS, their muscles are tender and stiff that which causes restricted movement. By foam rolling, each sore muscle group can get rolled out on a dense foam roll from the person’s body weight to apply pressure on the soft tissue. When performed correctly, the body’s range of motion will increase, and soft tissue restriction is prevented. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
Back discomfort sensations and symptoms could indicate pulled-back muscles. Unless you’ve experienced the condition before, determining the cause can be difficult. A pulled-back muscle can start as a sudden, sharp sting when bending, reaching, or twisting. Or it can present gradually, worsening over a few days. It is a common injury, but if left untreated could take several weeks, and in severe cases, a few months, to heal correctly. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic can help diagnose the problem and develop a customized treatment plan to restore optimal function and health. Pulled Back Muscles A pulled muscle describes a strained muscle. - A strain is a muscle or tendon injury that happens when the tissue overstretches or tears.
- When a ligament stretches or tears, it’s called a sprain.
- Most cases can be managed and treated at home.
- But if the symptoms are not improving or make it difficult to move, see a doctor or chiropractor.
Symptoms Common signs and symptoms of a pulled-back muscle include: - Swelling
- Tenderness
- Soreness - Sore muscles that feel tight and achy usually indicate a condition that is likely to improve in a few days. More severe soreness could indicate a more significant injury.
- Spasms - A sudden convulsive spasm in the muscle can also indicate a pull. This can feel like a sudden tightening that does not release. The muscle can continue to spasm and lead to other symptoms.
- Cramping - A muscle can cramp can lead to increased tightness whenever trying to use the muscle.
- Pain - Can be characterized as a constant dullness and/or soreness in most situations or, in severe cases, sharp and shooting.
- Discomfort when moving around. If pain flares up when trying to move or use the back muscles is usually an indication that something is wrong.
- Relief during inactivity and rest. When lying down to rest or taking a temporary break, and the symptoms disappear could also be an indication of a pulled-back muscle or another injury.
Causes The most common causes are: A Strained Muscle - This causes some damage to a region of muscle tissue, usually the result of being over-used or torn from another injury.
Sprained Ligaments - Involves damage to the ligaments in a joint, usually those in the spinal vertebrae.
A Herniated Disc - This involves damage to the discs that can leak out, irritating the surrounding tissues and nerves and can cause shifting and misalignment of the spine.
These conditions are distinct, but the symptoms can be similar. Therapies It is important to consult a medical professional before treating an injury because symptoms of other injuries, such as disc problems or a broken bone, can resemble strains and sprains. Most treatments will utilize: Ice and Heat - Ice helps reduce inflammation.
- The faster ice can be applied to a pulled-back muscle, the quicker pain and swelling are reduced, and the healing process can begin.
- Apply a cold pack for 15-20 minutes as soon as the injury occurs.
- Take a 20-minute break between each cold application.
- After the first days, alternate cold therapy with heat to increase circulation.
- Try a 20-20-20 rule: 20 minutes of an ice pack followed by a 20-minute break, then 20 minutes of heat.
- Repeat as necessary, allowing 20 minutes between heat or ice therapy.
Limited Rest - Right after a muscle strain, limiting physical activity levels and avoiding movements are recommended for a short period.
- After the initial pain subsides, partial activity levels are recommended to help prevent the muscles from weakening.
Compression Stretching - Returning to activities, gentle stretching exercises can improve tissue healing by increasing blood circulation to the injured area.
- Applying heat to the area before stretching can also help.
Strength Training - Ask a doctor or chiropractor about the right strength exercises for your condition.
- Strength training will develop the muscles to prevent future injuries.
Pain Medication - Pain levels are an important indicator during the recovery process.
- Pain medications relieve symptoms but do not assist with healing and should only be used short-term to provide relief.
- If you need pain medication, consult your physician to determine the appropriate type and dosage for your situation.
Massage - Blood circulation to the injured tissues is increased with massage therapy.
Chiropractic - A chiropractor can diagnose back pain from a muscle or disc injury and develop an individualized treatment plan.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References https://www.aans.org/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Low-Back-Strain-and-Sprain Allen, Laura. “Case Study: The Use of Massage Therapy to Relieve Chronic Low-Back Pain.” International journal of therapeutic massage & bodywork vol. 9,3 27-30. 9 Sep. 2016, doi:10.3822/ijtmb.v9i3.267 Kumar, Saravana et al. “The effectiveness of massage therapy for the treatment of nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review of systematic reviews.” International journal of general medicine vol. 6 733-41. 4 Sep. 2013, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S50243 https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/injuries-poisoning/sprains-and-other-soft-tissue-injuries/overview-of-sprains-and-other-soft-tissue-injuries https://www.spine-health.com/conditions/lower-back-pain/exercises-lower-back-muscle-strain
Back pain is one of the most common reasons individuals go to a doctor, massage therapist, physiotherapist, osteopath, and chiropractor. Various health conditions, some spine-related, others not, list back pain as a symptom. Many of these conditions begin in the stomach or abdominal cavity, which leads to stomach and back pain. Stomach and back pain happening simultaneously, independently, or in combination could be caused by gut problems, back issues, or something completely different. Understanding what causes these two types of pain simultaneously can help figure out a treatment plan. Stomach Back Pain Causes Problems in the abdominal cavity and stomach issues can cause back pain and vice versa. Symptoms can also include referred pain when the pain is felt in one part of the body but is caused by pain or injury in another area. Stomach back pain causes depend on the type of condition/s that can include: Appendicitis - Inflammation in the appendix can cause sudden sharp pain in the abdomen.
- It presents mostly in the lower right area of the abdomen but can appear in or spread to other sites, especially the back.
Dysmenorrhea - The medical term for painful menstrual periods.
- Dysmenorrhea can cause pain in the abdomen and back at the same time.
- This type of pain can be:
- Primary - A condition experienced throughout life.
- Secondary - Starts later in life due to another condition.
Endometriosis - Endometriosis causes tissue to grow outside of the uterus.
- Similar to dysmenorrhea, symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain
- Referred low back pain
Fibromyalgia - This condition generates pain across the muscles and joints of the body.
- It shows up with irritable bowel syndrome -IBS.
- Fibromyalgia can simultaneously present a wide range of stomach problems and back pain.
Gallstones - Gallbladder stones or gallstones can cause blockages, inflammation, and painful swelling.
- A major symptom of gallstones is pain in the upper right of the abdomen, which can spread to the back.
Kidney Dysfunction - Kidney stones, infections, and chronic kidney disease can cause pain that's felt in the abdomen/flank and the mid and/or upper back.
Irritable bowel syndrome - IBS Inflammatory Bowel Disease - IBD - Inflammatory Bowel Disease is a family of immune-mediated, similar to autoimmune conditions with back pain as a symptom that includes:
- Crohn's disease
- Ulcerative colitis
Pancreatitis - An inflamed pancreas can cause symptoms like:
- Stomach issues.
- Pain across the abdomen and back.
Pancreatic Cancer - A common symptom of pancreatic cancer is a dull pain in the upper abdomen/belly and/or middle and/or upper back that is on and off.
- This can be because of a tumor that has formed on the tail of the pancreas or an area where it presses on the spine.
Stomach Bloating and Low Back Pain - Bloating is caused by pressure in the abdomen increasing to the point that it causes discomfort and pain.
- It can cause simultaneous stomach and back pain as the bloating adds pressure on the muscles, organs, and spine.
- One of the most common causes of bloating is trapped gas in the GI tract.
- This happens when the body cannot properly move the gas through the system.
- Bloating can also be caused by extra sensitivity to regular pressure increases.
- In these cases, the amount and movement of gas in the system are normal, but the body reacts as though something is wrong.
- Several GI tract disorders can cause similar bloating issues that include:
- Dyspepsia
- Gastritis
- Celiac diseaseDiverticular disease
- Food allergies
A chiropractic functional medicine team can work with an individual's primary physician or specialist to develop a personalized treatment plan to alleviate back pain symptoms, re-balance the body, strengthen the musculoskeletal system and restore function. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Clauw DJ. Chapter 258, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, and Myofascial Pain. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. Goldman L (ed.). 26th ed. Elsevier; 2020. 1774-1778. https://www.clinicalkey.com/#!/content/book/3-s2.0-B9780323532662002587 Ford AC, Talley NJ. Chapter 122, Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Feldman M (ed.). Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Elsevier: 2021. 2008-2020. https://www.clinicalkey.com/#!/content/book/3-s2.0-B9780323609623001223?scrollTo=%23hl0001104 Inadomi JM, Bhattacharya R, Hwang JH, Ko C. Chapter 7, The Patient with Gas and Bloating. Yamada’s Handbook of Gastroenterology. 4th ed. John Wiley & Sons; 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119515777.ch7 Kliegman RM, St Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al. Chapter 378, Pancreatitis. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Elsevier; 2020. 2074-2080. https://www.clinicalkey.com/#!/content/book/3-s2.0-B9780323529501003783 Krames E, Mousad DG. Spinal Cord Stimulation Reverses Pain and Diarrheal Episodes of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Case Report. Neuromodulation. 2004 Mar 22;7(2):82-88. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1094-7159.2004.04011.x Sifri CD, Madoff LC. Chapter 78, Appendicitis. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Bennett JA (ed.). Elsevier; 2020. 1059-1063. https://www.clinicalkey.com/#!/content/book/3-s2.0-B9780323482554000783 Stephen Norman Sullivan, "Functional Abdominal Bloating with Distention," International Scholarly Research Notices, vol. 2012, Article ID 721820, 5 pages, 2012. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/721820 Wang DQH, Afdhal NH. Chapter 65, Gallstone Disease. Feldman M (ed.). Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Elsevier: 2021. 1016-1046. https://www.clinicalkey.com/#!/content/book/3-s2.0-B9780323609623000655?scrollTo=%23hl0001772 Weisman, Michael H et al. "Axial Pain and Arthritis in Diagnosed Inflammatory Bowel Disease: US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data." Mayo Clinic proceedings. Innovations, quality & outcomes vol. 6,5 443-449. 16 Sep. 2022, doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2022.04.007 Whorwell PJ. Chapter 13, Abdominal Bloating. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Diagnosis and Clinical Management. Emmanuel A, Quigley EMM (eds.). John Wiley & Sons; 2013. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118444689.ch13 Yarze JC, Friedman LS. Chapter 12, Chronic Abdominal Pain. Feldman M (ed.). Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Elsevier; 2021. 158-167. https://www.clinicalkey.com/#!/content/book/3-s2.0-B9780323609623000126?scrollTo=%23hl0000408
Uneven hips can throw the back out of natural alignment and cause back stiffness, tightness, discomfort, and pain. Hips that are off-balance unhealthily affect standing, sitting, sleeping posture, walking gait, and overall movements. Biomechanics issues cause the core and spine stabilizing muscles to become weakened and fatigued from overcompensating to keep the body up and moving. Over time this can lead to chronic pain in the back, hips, knees, and feet. Chiropractic care can restore proper hip and spinal alignment and wellness. Uneven Hips Misaligned hips can be caused by work or sports injury, exercise, vehicle collision, and/or general wear and tear. When hips are out of alignment, they have shifted from their centered position. They could be rotated forward or backward, forcing the spine and the lower limbs to compensate, resulting in the spine tilting that can make the legs appear uneven. Discomfort may be one-sided low back pain near the sacroiliac joint, causing a stiff/tight back, limited motion, and/or pain symptoms. Because the spine and lower limbs have to compensate for the unevenness, the shoulders and upper back, connected to the pelvis through the spine, are also affected and result in: - Back pain.
- Hip and gluteal muscle pain.
- Uneven leg length.
- Knee, ankle, and foot issues and pain.
- Uneven shoulders.
- The shoulder blades can stick out on the side of the lower hip.
- Rib discomfort and pain.
- The rib cage could protrude out on one side. However, this could be due to advanced scoliosis.
Therapy Staying active is recommended and includes stretching and core strengthening. General stretches recommended to optimize hip equity include: Hamstring stretch - For this stretch, lie on a flat surface with your legs extended straight out.
- Bend the right leg at the knee, placing the right foot on the ground.
- Use a towel, belt, or band to grab and wrap around the left foot.
- Keep the hip/buttock on the left side planted on the floor.
- Slowly raise the left leg upward as far as possible until you feel the stretch.
- Once you feel a stretch or restriction in the hamstring, hold the position for 30 seconds.
- Repeat on the other side.
- Perform 2 to3 times.
Hip flexor stretch - Kneel on the affected leg and bend the healthy leg out in front with the foot flat on the floor.
- Back straight.
- Slowly push the hips forward until you feel the stretch in the upper thigh and hip.
- Hold the stretch for around 15 to 30 seconds.
Chiropractic Care Chiropractic treatment is a highly recommended non-surgical option for uneven hips and pelvic tilt. Depending on the severity of the misalignment, underlying issues, and body scanning images, hip alignment treatment could include: - Soft tissue therapeutic massage
- Chiropractic muscle release for tight hip flexors, quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes.
- Decompression
- Traction
- Custom orthotics
- Bracing
- Posture training
- Activity modification
- Health Coaching
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Kiapour, Ali et al. “Biomechanics of the Sacroiliac Joint: Anatomy, Function, Biomechanics, Sexual Dimorphism, and Causes of Pain.” International journal of spine surgery vol. 14, Suppl 1 3-13. 10 Feb. 2020, doi:10.14444/6077 Lee, Jeong-Hoon, et al. “The effect of Graston technique on the pain and range of motion in patients with chronic low back pain.” Journal of physical therapy science vol. 28,6 (2016): 1852-5. doi:10.1589/jpts.28.1852 Patel, Rikin V et al. “Pelvic Tilt and Range of Motion in Hips With Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome.” The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons vol. 28,10 (2020): e427-e432. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-19-00155 Rivière, C et al. “Spine-hip relations add understandings to the pathophysiology of femoro-acetabular impingement: A systematic review.” Orthopaedics & traumatology, surgery & research : OTSR vol. 103,4 (2017): 549-557. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2017.03.010 Suits, William H. “Clinical Measures of Pelvic Tilt in Physical Therapy.” International journal of sports physical therapy vol. 16,5 1366-1375. 1 Oct. 2021, doi:10.26603/001c.27978
Introduction When it comes to the body, many factors can cause low back pain without a person knowing they encounter it. Simple actions like sitting, standing, and walking can be difficult or helpful, depending on the person’s actions. Since low back pain tends to vary from person to person and the possible factors that can cause low back pain make diagnosing a bit difficult. Fortunately, there are available treatments that can help manage low back pain symptoms and can help alleviate its associated symptoms in the body. Today’s article examines the causes and symptoms of low back pain, aqua therapy for low back pain, and how chiropractic care goes hand in hand with aqua therapy. We refer patients to certified providers specializing in musculoskeletal treatments and hydrotherapy to help many individuals with low back pain. We also guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is the solution to asking our providers insightful questions. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer The Causes Of Low Back Pain Have you been feeling aches along the sides of your back? Do you feel stiff when hunched over for an extended period? Or does sitting down make the pain go away or worsen? Many of these factors are associated with signs that you could be suffering from low back pain. Low back pain is considered the leading disability causes worldwide, as studies reveal, which can be influenced by many factors that a person is going through. Anyone can risk developing low back pain as it can derive from different sources that overlap many potential issues. Some of the causes associated with low back pain vary depending on how severely the factors affect the individual, which includes: - Muscle and ligament sprain (Overused muscles and ligaments from injuries, poor posture, or lifting heavy objects)
- Herniated discs/ degenerative disc disease (Spinal nerve root compression)
- Joint dysfunction (Cartilage begins to wear down)
- Spinal stenosis
- Trauma
- Deformity
- Osteoarthritis
- Fractures
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
Introduction When many individuals look for ways to relax after a stressful event in their daily lives, many people have an exercise regime that allows them to take their minds off of their hectic lives. When finding the proper exercise, it is best to consider that everybody is different and has different fitness levels. Many individuals could be dealing with chronic issues that affect them drastically and with so much pain in their bodies. When these chronic issues overlap with muscle and joint pain, it can make the body dysfunctional while potentially being involved in environmental factors. Yoga is a low-impact exercise that helps tone muscles, relax tension in the body, and focus on deep breathing. Today’s article looks at the benefits of yoga for the body, how chiropractic care works together with yoga, and different yoga poses can help manage various chronic issues. We refer patients to certified providers specializing in musculoskeletal treatments to help many individuals with musculoskeletal problems affecting their bodies. We also guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is the solution to asking our providers insightful questions. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer The Benefits of Yoga For The Body Have you been dealing with chronic stress affecting your quality of life? Have you been dealing with bladder or gut issues constantly? What about feeling muscle stiffness in your back, neck, shoulders, or pelvic regions? Some of these symptoms are signs that you could risk developing musculoskeletal problems associated with pain. Dealing with musculoskeletal issues related to pain can make a person feel miserable and have stress affecting their bodies. Yoga is a low-impact exercise that doesn’t put pressure on the joints and will provide a full-body workout through strengthening and stretching weak muscles. Yoga has many benefits for many individuals that are dealing with the following: - Muscle weakness
- Back pain
- Neck pain
- Pelvic Pain
- Arthritic symptoms
- Cardiovascular issues
- Chronic stress
Studies reveal that environmental factors are involved in non-specified chronic pain in the spine, overlapping musculoskeletal disorders causing many individuals to try to find relief. Many individuals incorporate yoga because it is a safe and effective way to alleviate various forms of back, neck, or pelvic pain causing issues to the body. Yoga utilizes gentle stretching and strengthening of weak, injured muscles while increasing blood circulation to promote healing in the body. Chiropractic Care & Yoga When people are dealing with health conditions or injuries that have affected their bodies, it can make them feel frustrated and think their injuries are taking forever to heal. Many individuals don’t realize that incorporating yoga practices provides impressive health benefits while mirroring the similar foundations of chiropractic care. Both chiropractic care and yoga provide many beneficial results to an aching body that needs a good stretch and ready the body to heal itself naturally. Chiropractic care includes spinal manipulation to the spinal joints while reducing inflammation and strengthening weak muscles. Yoga allows the body to increase its flexibility and stamina, reduces stress and blood pressure, and provides a better sense of breathing and balance. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
Introduction When the weather becomes hot, and everyone begins to plan fun activities to enjoy, one of the many activities that come to mind is hanging out in the pool. Swimming is an excellent way to combat the summer heat, but it can provide much more for the body. For athletes, it provides another form of cardio exercise to improve their quality performance when they are competing. While for individuals looking for an affordable exercise regime or just some fun activity to do, swimming can become a form of therapy and be beneficial for them if they were previously injured. Today’s article looks at how swimming causes an impact on the musculoskeletal system, its beneficial properties to the heart, and how aqua therapy combined with chiropractic care helps optimize full-body health. We refer patients to certified providers specializing in musculoskeletal treatments and hydrotherapy to help those with musculoskeletal disorders. We also guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is the solution to asking our providers insightful questions. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer Swimming & Its Impact On The Musculoskeletal System Water exercises or swimming can benefit those looking for different cardio exercises to build muscle endurance or have a clear sense of mind. Swimming is fantastic for all body sizes, and when it is done correctly, it can be highly recognized as a form of rehabilitation and injury recovery known as aquatic therapy. Research studies reveal that aquatic treatments and exercises can significantly reduce pain in individuals that suffer from low back pain while increasing physical function. Some of the impacts that swimming/aquatic therapy provides on the musculoskeletal system include: - Builds muscle strength
- Improves endurance
- Stabilizes joints
- Improves poor posture
Swimming/ hydrotherapy is an excellent low-impact exercise that is easy on the back and spine, especially for individuals suffering from low back pain or spinal misalignments. Studies reveal that the efficacy of aquatic activities helps strengthen the abdominals and legs and stretch the back while managing musculoskeletal issues. When individuals suffer from back pain associated with chronic issues can become concerning for the vital organs that have a causal relationship with the muscle as they are affected as well. When spinal joints and muscles begin to suffer from abnormal weight increases, the muscles and ligaments become misaligned. Misalignment or subluxation is defined as spinal vertebrates that are out of place and cause pressure on the surrounding nerves exiting the spinal cord. These spinal issues then become a risk of developing musculoskeletal disorders in the body. Unlike many aerobic exercises like running or cycling that may be hard on the spine, swimming has little to no impact on the spinal structures. So when individuals begin to take up swimming, they realize that the water buoyancy helps support their body weight while relieving stress on all joints and decompressing the spine. This gives the individual a greater range of motion, while the water gives off a sense of purification as it helps the body relax. Hence, hydrotherapy helps relax people who suffer from obesity or muscle injuries associated with muscle and joint pain as the water provides gentle resistance while relaxing the muscles to promote longer exercise sessions. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
Claudication is muscle pain that presents when the body is active and stops when the body is at rest, also known as intermittent claudication. Individuals typically report dull aching, cramping, tingling, and/or numbness. Vascular claudication is caused by circulatory problems like poor blood circulation and peripheral artery disease. Still, spinal conditions can also cause neurogenic claudication caused by problems with the spine and nervous system. Neurogenic Claudication Sciatica is the usual suspect when thigh, hip, buttock, calf, or total leg pain or other sensations are present; however, it could be spinal stenosis with neurogenic claudication. Spinal stenosis is sometimes called pseudo claudication, a narrowing of the space around the low back, which can put pressure on the spinal cord directly and compress the blood vessels around the spine, cutting off oxygen-carrying blood. Pain can start in the lower back and circulate down the legs and cause weakness, tingling, or numbness in the legs and feet. The most common areas of spinal compression include: The narrowing can occur in any of these areas, with the most common cause being lumbar spinal stenosis brought on by lumbar degenerative disease. Symptoms The most common symptoms of neurogenic claudication include: - Pain in the lower extremities, including the buttocks, thighs, and calf, only manifests with activities like walking or standing around.
- Pain that shows up equally on both sides.
- There is no pain when sitting or not walking around.
- Radiculopathy or nerve pain that radiates down an affected limb. Sciatica is a typical example.
However, the symptoms of claudication and radiculopathy are different. - Claudication will be felt all along the length of the nerve.
- Radiculopathy pain is more localized to the buttock, thighs, and calves and can get worse with activity and is generally present even when at rest.
Treatment Non-surgical treatment of neurogenic claudication includes medication to help control pain, chiropractic manual therapy, non-surgical spinal decompression, physical rehabilitation therapy, and steroid shots to reduce inflammation. A doctor will recommend stretching, strengthening exercises, and types of activities to help improve the body’s ability to support itself. This could include swimming, walking, and stationary cycling. However, conservative treatment might not be an option for individuals with more severe cases. If conservative treatment options don’t work, surgery could be recommended. A healthcare provider can help explain treatment options. Successful outcomes have been seen in cases that are diagnosed and treated early. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Colak, Ahmet, et al. “A less invasive surgical approach in the lumbar lateral recess stenosis: a direct approach to the medial wall of the pedicle.” The European spine journal: official publication of the European Spine Society, the European Spinal Deformity Society, and the European Section of the Cervical Spine Research Society vol. 17,12 (2008): 1745-51. doi:10.1007/s00586-008-0801-z Munakomi S, Foris LA, Varacallo M. Spinal Stenosis And Neurogenic Claudication. [Updated 2022 Feb 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430872/ Cleveland Clinic. (2021) “Claudication.” https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21972-claudication
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts work hard to stay in shape, but they are also at an increased risk for a lumbar hyperextension injury. Lumbar hyperextension injuries happen when the low back is bent backward repeatedly or overarches repeatedly. The repetitive stress can lead to severe complications and damage the nerves, vertebrae, and backbones. Motorized decompression therapy could be a treatment option. Lumbar Hyperextension Injury Injuries can be caused by overuse, improper mechanics and technique, lack of proper conditioning, insufficient stretching, or trauma. When looking for symptoms of lumbar hyperextension injuries, the first is low back pain that is severe and lasts at least a few days while becoming more intense with time. The lower back pain that worsens when extending, or arching the back, in addition to stiffness, muscle spasms, radiating buttock and thigh pain, tight hamstrings, and difficulty standing or walking, can be indicators of a lumbar hyperextension injury. However, this could be difficult to distinguish from other injuries like muscle strain, disc herniation, and stenosis; this is why a proper examination by a medical professional is recommended. Treatment - Initial treatment consists of resting, sitting out from the sport, and other activities that could aggravate the back.
- A doctor may recommend over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications.
- Heat and ice can also be used to increase circulation and relieve pain.
If hyperextension of the back continues even after rest, it could signify a stress fracture in the vertebrae. This condition is referred to as spondylolysis. Spondylolysis is an overuse injury. It occurs in individuals who participate in sports like gymnastics, diving, volleyball, football, and weight lifting. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis are common in adolescent athletes experiencing lower back pain. - A doctor may assign a back brace to prevent movement, allowing the bone to heal back together.
- A doctor could also recommend physical therapy for 6-12 weeks after the diagnosis and once the bones have had time to heal.
- Rehabilitation exercises focus on improving back flexibility and strength.
- Athletes can be cleared to return to their sport within 3-6 months.
- Surgery is rarely necessary and only looked into if the individual continues to have persistent pain after 6-12 months of treatment.
Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression - Spinal decompression works by gently stretching the spine.
- This changes the spine's position, takes the pressure off the nerves and discs, and restores the cushioning.
- As the machine pulls the body, a vacuum effect fills the discs with oxygen and nutrients to stimulate healing.
- Computer technology controls treatment duration, angle, intensity, and relaxation.
Prevention Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are recommended to seek professional help to retrain how they perform repetitive and excessive high-impact activities. Specifically, those involving hyperextension movements like kicking, jumping, running, and back bending help minimize the risk of developing a back injury. They are also recommended to maintain body conditioning, back and hamstring flexibility, core muscle strength and endurance, cardiovascular fitness, and properly warming up and stretching before and after the physical activities. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Ball, J.R., Harris, C.B., Lee, J. et al. Lumbar Spine Injuries in Sports: Review of the Literature and Current Treatment Recommendations. Sports Med - Open 5, 26 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40798-019-0199-7 Carter, D R, and V H Frankel. “Biomechanics of hyperextension injuries to the cervical spine in football.” The American journal of sports medicine vol. 8,5 (1980): 302-9. doi:10.1177/036354658000800502 Goetzinger, Sara, et al. “Spondylolysis in Young Athletes: An Overview Emphasizing Nonoperative Management.” Journal of sports medicine (Hindawi Publishing Corporation) vol. 2020 9235958. 21 Jan. 2020, doi:10.1155/2020/9235958 Lawrence, Kevin J et al. “Lumbar spondylolysis in the adolescent athlete.” Physical therapy in sport: official journal of the Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Sports Medicine vol. 20 (2016): 56-60. doi:10.1016/j.ptsp.2016.04.003 Low Back Pain: Could it be a Spondy? Nationwide Children’s Hospital. (n.d.). https://www.nationwidechildrens.org/specialties/sports-medicine/sports-medicine-articles/low-back-pain-could-it-be-a-spondy.
Stretching Fundamentals: Stretching benefits the body by keeping the muscles flexible, strong, healthy, and able to maintain optimal physical performance. As with any other discipline stretching correctly requires using the proper form, correct technique, and practicing regularly. The angles need to be accurate; the body has to move at the right speed and maintain correct posture. The focus should be moving the joint as little as possible as the muscle/s stretch and elongate. Stretching Fundamentals Stretching should become a daily activity that turns into a healthy habit. The muscles need frequent maintenance from daily/nightly bending, twisting, reaching, carrying, and lifting work. This is especially true for individuals dealing with constant soreness, aches, pains, and problems with tight, tense, and stressed-out muscles. When the body is stressed, heart rate increases, and individuals tend to tighten up. Stretching benefits include: - Stress relief.
- Increased muscle blood flow.
- Increased body flexibility.
- Helps joints move through their full range of motion.
- Improves performance in physical activities.
- Decreases soreness, aches, and pains.
- Injury prevention.
- Improves posture.
- Improves sleep.
- Preps the body for exercise and activities.
- Improves mental health.
Human nature is to take the path of least resistance, which makes the body feel flexible and comfortable. This is a common reason individuals consider stretching unnecessary or too painful to engage in. However, stretching fundamentals need to be maintained as stretching carelessly or poorly can negatively affect other muscles and joints and worsen injuries/conditions. Guidelines To stretch safely, it is recommended to do a proper warm-up, stretch slowly, working the right muscles and joints. The guidelines make stretching safer, more effective, and increase body awareness. Warm-Up - Warming the muscles increases blood flow.
- Warming up muscles before physical activity/workout is crucial for preventing injuries and maximizing effectiveness.
- Stretching cold muscles activates a reflex that prevents overstretching, resulting in shortening and tightening of the muscles.
- A healthy warm-up should consist of light cardio and dynamic stretches for the major muscle groups.
- Dynamic stretching involves moving into and out of positions through a full range of motion rather than holding a stretch for a prolonged period.
- Dynamic stretches are recommended to be held for 2-3 seconds for 4-6 repetitions.
Take It Slow - Stretching out too fast can make the body think that the muscle is about to get torn or injured.
- To protect the muscle, it contracts, preventing it from reaching the full stretch.
- This is why the correct technique needs to be observed.
- A couple of degrees in the wrong direction can mean the difference between a healthy stretch and pulling a joint capsule causing injury.
Muscle Recovery When engaged in physical activity, exercise, or working, microscopic tears are happening to muscle cells. Because of the body's stress and fatigue, hormone and enzyme levels fluctuate, and inflammation increases. This helps in fat loss, increases metabolism, increases strength and muscle growth. However, these benefits only happen with proper recovery. Different types of recovery include: Immediate Recovery - These are the quick moments' in-between physical movements.
- For example, the time between each stride when jogging.
Short-Term Recovery - This is the time between activities or sets of exercises.
- For example, the rest periods between doing a heavy job or sprint intervals.
Training Recovery - This is the time between when one workout or job ends, and the next begins.
There is no one size fits all, as everyone's body is different; it is recommended to consult with a trainer or fitness expert and experiment with what feels right. - For some individuals, 24 hours is enough.
- For others, it can take 48 or 72 hours to feel fully recovered.
- Other factors that affect recovery are:
- Age
- Fitness level
- Work/exercise intensity
- Diet
- Sleep
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Behm, David G, and Anis Chaouachi. "A review of the acute effects of static and dynamic stretching on performance." European Journal of applied physiology vol. 111,11 (2011): 2633-51. doi:10.1007/s00421-011-1879-2 Freitas, S R et al. “Stretching Effects: High-intensity & Moderate-duration vs. Low-intensity & Long-duration.” International journal of sports medicine vol. 37,3 (2016): 239-44. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1548946 Hotta, Kazuki et al. "Daily muscle stretching enhances blood flow, endothelial function, capillarity, vascular volume and connectivity in aged skeletal muscle." The Journal of physiology vol. 596,10 (2018): 1903-1917. doi:10.1113/JP275459 Kataura, Satoshi et al. "Acute Effects of the Different Intensity of Static Stretching on Flexibility and Isometric Muscle Force." Journal of strength and conditioning research vol. 31,12 (2017): 3403-3410. doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000001752
When individuals think about wellness and health, they usually think about a checkup with their doctor. However, wellness treatment with chiropractic is much more proactive. Chiropractic focuses on keeping the body functioning properly and allowing its natural healing properties to activate and do its job. Chiropractic checks to ensure the spine is correctly aligned and correct any subluxation/misalignment before pain occurs. Pain is one of the body's warnings that something is wrong. Chiropractic wellness care aims to catch and correct any issues before it becomes a problem, keeping the central nervous system in top form, increasing the immune system's strength, making the body healthier. Chiropractic Increases Wellness and Health Levels The body's baseline level of health can be improved. Individuals can feel that they are fulfilling their responsibilities and maintaining health by engaging in physical exercise and eating a healthy diet. It is believed that lifestyle is largely the extent of an individual's ability to maintain their health, without realizing that optimal wellness and health can be increased through chiropractic, the ideal supplement to a healthy life. Chiropractic improves body process functions by: - Increasing circulation.
- Facilitating detoxification.
- Balancing the distribution of hormones and nutrients.
- Regulating the heart’s rhythm.
- Soothing the nervous system.
- Increased mobility.
- Decreased pain.
- Better flexibility.
Chiropractic serves as supportive treatment to other types of therapeutic care like physical therapy and massage therapy. Improves Physical Performance A chiropractor will recommend adjustments, manual muscle manipulation, tissue manipulation, and massage customized for the body’s needs, focusing specifically on long-term realignment. A variety of treatments help to improve the body’s structure, alignment, and energy flow. Chiropractic makes a significant difference in: - Endurance
- Explosiveness
- Flexibility
- Speed
- Mobility
- Adaptability
Chiropractic also: - Realigns joints and bones.
- Decompresses nerves.
- Releases muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
- Detoxifies stagnant areas of the body.
Chiropractic is the perfect supplement to increasing performance, wellness, and health by increasing the health and alignment of the physical body and energy flow. Improves Mental Health Chiropractic also benefits mental health. The mind is controlled by the central nervous system or CNS and is directly affected by chiropractic treatment. With hands-on manipulation, adjustments, or traction, bones and joints move back toward optimal alignment, causing the nervous system's structure to move toward optimal capacity and efficiency. Nerve channels and bundles can become decompressed, bruised, and pinched. The flow of electrical impulses is regulated within the body through the nervous system. Cognitive performance becomes enhanced from the improvement in communication across the central and peripheral nervous systems. Mental performance is also supported through the rush of cerebrospinal fluid/CSF. Cerebrospinal fluid removes waste and toxins from the brain and supplies the brain with oxygen and nutrients. CSF floods the brain after a chiropractic adjustment. Improves Immune System Function Chiropractic improves immune system function by increasing energy circulation, blood circulation, and lymphatic fluid flow. Treatment combats stagnation allowing the body to purge toxins and waste accumulated in joints, tissues, and near organs. Chiropractic loosens up areas of the body that have been compressed, crushed, strained, and divided because of misalignment, lack of physical activity/exercise, or stiffness and injury. This allows the flow of lymphatic fluid and white blood cells to regulate areas that may have previously been difficult to access. This helps to increase the immune system’s ability to fight off infection. Get More Sleep Sleep is a strong regulator of immune system functions and operates to enhance the adaptive immune system. When the body is deprived of adequate sleep, it becomes more susceptible to various infectious agents. Sleep deprivation weakens the body making it harder to recover from bacteria or virus infections. When the body sleeps, it utilizes the time to strengthen the immune system and move T cells to the lymph nodes. These are the vessels of the immune system responsible for filtering harmful substances. T cells produce cytokines activated when there is inflammation in the body or under stress. Inadequate sleep causes cytokine production to decrease, causing damage to the immune system. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Besedovsky, Luciana et al. “Sleep and immune function.” Pflugers Archiv: European journal of physiology vol. 463,1 (2012): 121-37. doi:10.1007/s00424-011-1044-0 Goncalves, Guillaume et al. “Effect of chiropractic treatment on primary or early secondary prevention: a systematic review with a pedagogic approach.” Chiropractic & manual therapies vol. 26 10. 5 Apr. 2018, doi:10.1186/s12998-018-0179-x Iben, Axén, et al. “Chiropractic maintenance care - what's new? A systematic review of the literature.” Chiropractic & manual therapies vol. 27 63. 21 Nov. 2019, doi:10.1186/s12998-019-0283-6 Vining, Robert et al. “Effects of Chiropractic Care on Strength, Balance, and Endurance in Active-Duty U.S. Military Personnel with Low Back Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” Journal of alternative and complementary medicine (New York, N.Y.) vol. 26,7 (2020): 592-601. doi:10.1089/acm.2020.0107
Regularly doing planks can support/strengthen the spine and prevent back pain no matter the fitness level. It's estimated that 70% of adults will experience back problems and pain. One of the best ways to keep the spine healthy is by strengthening the core muscles. The more these muscles are built up, the healthier the body will become. The plank position activates the entire core taking the pressure off of the spine. Core Anatomy The core is the center of the body. It contains all the muscles surrounding the torso. These muscles work together to: - Stabilize the body during movement.
- Prevent injury when engaged in physical activity/exercise.
- Provide spinal support.
The core is split into two groups of muscles: The inner core and the outer core. Inner Core The inner core consists of: Multifidus Muscles Quadratus Lumborum - The deep abdominal muscle in the lower back sits on either side of the lumbar region of the spine.
Transversus Abdominis - Located between the lower ribs and the top of the pelvis.
Pelvic Floor - This base group of muscles stretches from the tailbone to the pubic bone.
Diaphragm - A dome-shaped muscle that rests below the lungs.
Outer Core Rectus Abdominis - These are more commonly known as the abs.
External Obliques - These muscles are located on either side of the rectus abdominis.
Internal Obliques - These muscles are located below the external obliques, inside the hip bones.
Erector Spinae - These muscles surround the spine and extend up both sides of the vertebral column.
Planks and Back Pain Prevention When the core is not strong enough, the spine and back muscles overcompensate to keep the body standing correctly. Studies have shown how planks effectively activate the muscles responsible for spinal stabilization. The exercise targets the entirety of the core and strengthens the shoulders and glutes. Strengthening these muscles improves posture, helping to alleviate back problems and pain. However, it's recommended to talk to a doctor before beginning a plank regimen if back pain is present. If done incorrectly, they could aggravate the back muscles. Proper Form Choose an area clear of furniture where the whole body can stretch out. Follow these steps: - Begin with hands and knees on the floor.
- Extend the legs back while keeping the elbows directly below the shoulders and the wrists below the elbows.
- Keep the head down, looking at the space just above the hands.
- Engage the abs and keep the body rigid.
- Imagine a perfectly straight line from the neck to the toes.
- Hold the position for 10 to 60 seconds, depending on fitness level.
- Lower the body gently to the floor.
- Make sure not to curve the back as curving means that the abdominal muscles are being engaged, and tilting the head up can strain the neck.
- Both can lead to injury, which is why maintaining proper form is essential.
Plank Variations There are variations of this exercise for different levels of physical fitness. Once the modified and full plank has been mastered, various planks can target other areas of the body. These include: Side Plank - These involve shifting the weight to one forearm while extending the other arm into the air.
One-arm Plank - These involve lifting one hand off the ground, then alternating.
Single-leg Plank Walking Plank Reverse Plank Anybody can work up to a plank at any age at any fitness level; it just takes time. Once achieved, it is a great way to keep the body's core strong, healthy and helps prevent back problems. Band Lateral Raise The lateral band raise is an excellent workout for the shoulders. It works out the lateral deltoid, anterior deltoid, and serratus anterior. - Grasp one band in one hand.
- Step on the free end with the opposite foot.
- Right hand and left foot and vice versa.
- Slowly extend and raise the arm until they are parallel to the floor.
- Lower the arms in the same manner.
- If the shoulders are healthy and strong enough, try adding dumbbells or kettlebells to increase the resistance.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Calatayud, Joaquín et al. "Tolerability and Muscle Activity of Core Muscle Exercises in Chronic Low-back Pain." International journal of environmental research and public health vol. 16,19 3509. 20 Sep. 2019, doi:10.3390/ijerph16193509 World Health Organization. (2013) "Low back pain." https://www.who.int/medicines/areas/priority_medicines/Ch6_24LBP.pdf Youdas, James W et al. "Magnitudes of muscle activation of spine stabilizers in healthy adults during prone on elbow planking exercises with and without a fitness ball." Physiotherapy Theory and practice vol. 34,3 (2018): 212-222. doi:10.1080/09593985.2017.1377792
|
Introduction The various muscles and ligaments that encompass the back help protect the spine’s thoracic region. The spine has three sections: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar, which assist the body with bending, turning, and twisting. For the thoracic spine, various muscles like the rhomboid, trapezoid, and other superficial muscles provide functionality to the scapula or shoulder blades to stabilize the ribcage. When the body succumbs to injuries or traumatic forces, it can develop myofascial pain syndrome associated with upper back pain. Upper back pain can lead to unwanted symptoms affecting their quality of life. Fortunately, various exercises target the upper portion of the back and can strengthen multiple muscles from injuries. Today’s article looks at the effects of upper back pain in the body and shows a few stretches and exercises that can support the various muscle groups in the upper back region. We refer our patients to certified providers that incorporate techniques and multiple therapies for many individuals suffering from upper back pain and its correlating symptoms that can affect the musculoskeletal system in the neck, shoulders, and thoracic region of the spine. We encourage and appreciate each patient by referring them to associated medical providers based on their diagnosis when it is appropriate. We understand that education is a fantastic way when asking our providers intricated questions at the patient’s request and understanding. Dr. Jimenez, D.C., only utilizes this information as an educational service. Disclaimer The Effects Of Upper Back Pain In The Body Have you been experiencing stiffness around or near your shoulder blades? Do you feel muscle strain when you are rotating your shoulders? Or does it hurt when you stretch your upper back in the morning? Many of these issues are signs and symptoms of upper back pain. Studies reveal that back pain is one of the most common complaints many individuals would go for emergency care. Back pain can affect the different regions in the back and cause unwanted symptoms in various areas in the upper back. Additional studies mentioned that persistent pain in the thoracic region could cause hyper-sensitization of the intercoastal nerves that mimic other conditions affecting the back. Some of the causes and effects that can lead to the development of upper back pain include: - Poor posture
- Improper lifting
- Traumatic events or injuries
- Chronic diseases (Osteoporosis, Scoliosis, Kyphosis)
When this happens, it can lead to overlapping conditions that mimic other issues and, if not treated right away, leave individuals with chronic disabling symptoms that correlate with upper back pain. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
Agility is the ability to accelerate, decelerate, stabilize, and quickly change directions with proper form and posture. Everyone, athletes and non-athletes, use agility every day. This can be maneuvering around objects during a jog, shifting movements or positions when walking through a crowd, reaching toward the highest shelf, or carrying things upstairs. These controlled reactions require a balance of coordination, speed, stamina, and strength. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic can provide agility enhancement through adjustments, massage, and decompression to relax the body, strengthen the muscles, and improve circulation and nerve function. Agility Enhancement Individuals need skill and control to react to a stimulus or movement. Agility requires muscular coordination, efficiency, and cohesiveness between the upper and lower body. Agility and reaction time are two components of neuromusculoskeletal health that work together. Agility enhancement can improve cognitive ability, power production, and physical performance. Agility enhancement improves overall physical skills, including: - Balance
- Stability
- Coordination
- Body Control
- Cognition
- Recovery time
Chiropractic Care Chiropractic improves agility neurologically through improved circulation and energy flow in the nervous system. Injury Treatment and Prevention Agility enhancement can help with injury prevention, as agility training increases control, balance, and flexibility. It teaches the correct body placement while moving to protect the knees, shoulders, and lower back. It also helps to strengthen the muscles and improve the resiliency of the connective tissue allowing them to shorten and lengthen rapidly. This helps prevent injuries and relieves pain and stiffness associated with muscle overuse. - Stiffness often occurs from the overuse of muscles.
- Stiffness reduces flexibility, increasing the risk of injury and affecting movement and physical capabilities.
- Stiffness can even occur from changes in everyday routines.
- Chiropractic prevents the muscles from tensing up, reducing stiffness and increasing your range of motion.
- Chiropractic helps strengthen the musculoskeletal system, which makes it easier to maintain normal balance.
- Chiropractic can strengthen the muscles by making the muscle fibers more excitable, contributing to quicker reaction time.
We create rehabilitation and strength and conditioning treatment plans that are individualized for each individual. This program entails the following: - Chiropractic assessment.
- Therapeutic massage.
- Rehabilitation exercises.
- Strengthening of the whole body.
- Posture, mobility, and performance education for improved movement.
- Health and nutritional recommendations.
Our treatment programs are designed to improve each individual's whole body health and decrease the risk of injury. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, don't hesitate to get in touch with Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Ali, Kamran, et al. "Comparison of Complex Versus Contrast Training on Steroid Hormones and Sports Performance in Male Soccer Players." Journal of chiropractic medicine vol. 18,2 (2019): 131-138. doi:10.1016/j.jcm.2018.12.001 Järvinen, Tero A H, et al. "Muscle injuries: optimizing recovery." Best practice & research. Clinical rheumatology vol. 21,2 (2007): 317-31. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2006.12.004 Lennemann, Lynette M et al. "The influence of agility training on physiological and cognitive performance." Journal of strength and conditioning research vol. 27,12 (2013): 3300-9. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e31828ddf06 Miners, Andrew L. "Chiropractic treatment and the enhancement of sports performance: a narrative literature review." The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association vol. 54,4 (2010): 210-21.
Preparing for the holidays is exciting but can generate intense stress and anxiety. This can cause individuals to feel tired constantly, which can lead to other issues like sleep problems, brain fog, digestive issues, and musculoskeletal disorders. Chiropractic care can return the body to optimal function, increasing circulation, restoring spinal alignment, re-energizing the mind and body, and preventing future fatigue and exhaustion. Exhaustion and Fatigue Primary causes of fatigue and exhaustion are stress, overworking, school work, lack of sound sleep, excessive caffeine or other energy boosters, and the holidays. Stress Reduction Stress is a leading contributor to fatigue and exhaustion. - Stress causes the muscles to contract, restricting blood circulation.
- Chronic stress causes the musculoskeletal system to be in a state of continued constriction.
- Constant muscle tension can cause injury and chronic conditions that can lead to secondary disorders like tension headaches and migraines.
Quality Sleep High-quality rest means falling asleep naturally, staying asleep through the night comfortably, and waking rested and refreshed. - Lack of enough sleep strains the nervous system.
- Not enough sleep or disruptions to the sleep-wake cycle (that can happen with shift work or traveling work) can cause physiological fatigue.
- This causes reduced motor skills, similar to having a blood alcohol content of 0.1.
Nutrition Proper nutrition is key to overall health and stress management. An unhealthy diet can be the main cause of fatigue. Just like putting the wrong gas into your car can cause major issues stalling or stopping entirely. The same is true with the body. The body is a complicated engine that requires healthy fuel to work properly. - Macronutrients (fat, carbohydrates, and protein) and Micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) are essential.
Chiropractic Care and Functional Medicine Chiropractic care can be a long-term solution for fatigue and exhaustion. Spine Realignment Spinal realignment resets the body through better posture and brain function through the improved circulation flowing through the spinal cord. - Optimal spinal realignment:
- Relieves headaches
- Alleviates discomfort symptoms
- Increases energy
- Restores range of motion
Relieve Pressure On The Nerves Chiropractic releases pressure on the nerves. - The central nervous system's response to pain, energy levels, comfort, and mobility is impacted by the health of the nerves.
- Just a minimal amount of pressure can reduce the strength of a nerve by 90%.
- Nerves that are not working correctly have difficulty transmitting messages, often causing pain.
Loosen Tense Muscles Chiropractic care and massage therapy can help relieve the tension in overworked muscles. - Fatigue and exhaustion can cause the muscles to work harder/overcompensate to try to maintain balance.
- Over time, the muscles can't keep it up and become frozen and tense.
Nervous System Regulation Chiropractic care can restore nervous system function. - When the spine is not correctly aligned, the electrical impulses are not transmitted properly.
- Common side effects include headaches, neck and back problems, and digestive issues.
Chiropractic care can restore the body to a refreshed and rejuvenated state. It can improve circulation, rebalance the body, increase oxygen levels and strengthen the immune system. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Azzolino, Domenico, et al. “Nutritional Status as a Mediator of Fatigue and Its Underlying Mechanisms in Older People.” Nutrients vol. 12,2 444. 10 Feb. 2020, doi:10.3390/nu12020444 Chaudhuri, Abhijit, and Peter O Behan. “Fatigue in neurological disorders.” Lancet (London, England) vol. 363,9413 (2004): 978-88. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15794-2 Evans, William J, and Charles P Lambert. “Physiological basis of fatigue.” American journal of physical medicine & rehabilitation vol. 86,1 Suppl (2007): S29-46. doi:10.1097/phm.0b013e31802ba53c Finsterer, Josef, and Sinda Zarrouk Mahjoub. “Fatigue in healthy and diseased individuals.” The American journal of hospice & palliative care vol. 31,5 (2014): 562-75. doi:10.1177/1049909113494748 Rosenthal, Thomas C et al. “Fatigue: an overview.” American family physician vol. 78,10 (2008): 1173-9.
Diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis usually involves multiple tests. When doctors order blood tests to diagnose ankylosing spondylitis, an individual is experiencing worsening symptoms in their back and joints. Often, a blood test diagnosis means the doctor is looking for evidence of anything else that could be causing the symptoms. However, blood tests by themselves cannot definitively diagnose ankylosing spondylitis, but when combined with imaging and assessment, they can provide important clues that point to the answers. Ankylosing Spondylitis Blood Test Diagnosis Ankylosing spondylitis is arthritis that primarily affects the spine and hips. It can be difficult to diagnose as no single test can provide thorough information for a definitive diagnosis. A combination of diagnostic tests are utilized, including a physical exam, imaging, and blood tests. Doctors are not only looking for results that will point to ankylosing spondylitis, but they are looking for any results that might point away from the spondylitis results that might provide a different explanation for symptoms. Physical Exam The diagnostic process will begin with the individual's medical history, family history, and physical exam. During the exam, the doctor will ask questions to help rule out other conditions: - How long have symptoms been presenting?
- Do symptoms get better with rest or exercise?
- Are the symptoms getting worse or staying the same?
- Are the symptoms worse at a particular time of day?
The doctor will check for limitations in mobility and palpate tender areas. Many conditions can cause similar symptoms, so the doctor will check to see if the pain or lack of mobility is consistent with ankylosing spondylitis. The feature sign of ankylosing spondylitis is pain and stiffness in the sacroiliac joints. The sacroiliac joints are located in the lower back, where the base of the spine and pelvis meet. The doctor will look at other spinal conditions and symptoms: - Back pain symptoms caused by - injuries, posture patterns, and/or sleeping positions.
- Lumbar spinal stenosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis
Family History - Family history plays a part in diagnosis because of the genetic element of ankylosing spondylitis.
- The HLA-B27 gene corresponds with ankylosing spondylitis; if an individual has it, one of their parents has it.
Imaging - X-rays often serve as the first step to a diagnosis.
- As the disease progresses, new small bones form between the vertebrae, eventually fusing them.
- X-rays work best at mapping the disease progression than the initial diagnosis.
- An MRI provides clearer images in the early stages as smaller details are visible.
Blood Tests Blood tests can help rule out other conditions and check for signs of inflammation, providing supportive evidence along with the results of imaging tests. It typically only takes about a day or two to get the results. The doctor may order one of the following blood tests: HLA-B27 HLA-B27 test. - The HLA-B27 gene reveals a red flag that ankylosing spondylitis could be present.
- Individuals with this gene have a much higher risk of developing the condition.
- Combined with symptoms, other labs, and tests, it can help confirm a diagnosis.
ESR Erythrocyte sedimentation rate or ESR test. - An ESR test measures inflammation in the body by calculating the rate or how fast red blood cells settle to the bottom of a blood sample.
- If they settle faster than normal, the result is elevated ESR.
- That means the body is experiencing inflammation.
- ESR results may come back high, but these alone do not diagnose AS.
CRP C-reactive protein - CRP test. - A CRP test checks CRP levels, a protein associated with inflammation in the body.
- Elevated CRP levels signal inflammation or infection in the body.
- It is a useful tool for measuring disease progression after diagnosis.
- It often corresponds with changes in the spine shown on X-ray or MRI.
- Only 40-50% of individuals with ankylosing spondylitis experience an increased CRP.
ANA ANA test - Antinuclear antibodies, or ANA, go after the proteins in the cell's nucleus, telling the body its cells are the enemy.
- This activates an immune response that the body fights to eliminate.
- A study determined that ANA is found in 19% of individuals suffering from ankylosing spondylitis and is higher in women than men.
- Combined with other tests, the presence of ANA provides another clue to a diagnosis.
Gut Health - The gut microbiome plays an important role in triggering the development of ankylosing spondylitis and its treatment.
- Tests to determine the gut's health can give a doctor a complete picture of what is happening inside the body.
- Blood test diagnoses for ankylosing spondylitis and other inflammatory conditions rely heavily on piecing together different tests alongside clinical exams and imaging.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Cardoneanu, Anca, et al. "Characteristics of the intestinal microbiome in ankylosing spondylitis." Experimental and therapeutic medicine vol. 22,1 (2021): 676. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10108 Prohaska, E et al. "Antinukleäre Antikörper bei Spondylitis ankylosans (Morbus Bechterew)" [Antinuclear antibodies in ankylosing spondylitis (author's transl)]. Wiener klinische Wochenschrift vol. 92,24 (1980): 876-9. Sheehan, Nicholas J. "The ramifications of HLA-B27." Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine vol. 97,1 (2004): 10-4. doi:10.1177/014107680409700102 Wenker KJ, Quint JM. Ankylosing Spondylitis. [Updated 2022 Apr 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470173/ Xu, Yong-Yue, et al. "Role of the gut microbiome in ankylosing spondylitis: an analysis of studies in the literature." Discovery medicine vol. 22,123 (2016): 361-370.
Sports exercise headaches are exertion headaches that involve pain during or immediately after sports, exercise, or some physical activity. They come on quickly but can last a few minutes, hours, or days. Activities associated with exercise headaches include running, weightlifting, tennis, swimming, and rowing. Chiropractic, massage, decompression, and traction therapies can realign the body and relax the muscles allowing for optimal circulation and certain strategies to help prevent future episodes. Usually, there is no underlying disease or disorder, but it is recommended to talk to a healthcare provider to make sure. Sports Exercise Headaches When individuals exert their bodies intensely, they need added blood and oxygen, particularly with activities that involve tightening/tensing the abdominal muscles or increasing chest pressure. Doctors and scientists believe an exertional headache occurs when intense physical activity causes the veins and arteries to expand to circulate more blood. The expansion and increased blood circulation generate pressure in the skull that can cause pain. Alternate Triggers Exercising is not the only cause; other physical activities that can trigger an exertion headache include: - Sneezing
- Coughing
- Straining to use the bathroom
- Sexual intercourse
- Lifting or moving a heavy object
Symptoms Symptoms of a sports exercise headache include: - Neck stiffness or pain
- Pain on one or both sides of the head
- Pulsating pain discomfort
- Throbbing pain discomfort
- Shoulder tightness, discomfort, and/or pain
Sometimes individuals report the headache can feel like a migraine that could include: - Vision problems like blind spots
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Light sensitivity
Most exercise headaches last five to 48 hours and can continue for three to six months. Diagnosis An underlying disease or disorder does not cause most exertional headaches. However, individuals experiencing severe or frequent headaches should consult their doctor or a healthcare provider. Tests will be ordered to rule out possible causes that include: If there is no underlying cause found, the medical provider can diagnose exertion headaches if there have been at least two headaches that: - Were caused by exercise or physical activity.
- Started during or after the physical activity.
- Lasted less than 48 hours.
Chiropractic Treatment According to the American Chiropractic Association, spinal adjustments are an effective headache treatment option. This includes migraines, tension headaches, or sports exercise headaches. Using the targeted approaches, chiropractic restores the body's natural alignment to improve function and alleviate stress on the nervous system. This allows the body to operate at optimal levels reducing muscle stress and muscle tension. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References American Migraine Foundation. Secondary Headaches. (https://americanmigrainefoundation.org/resource-library/secondary-headaches/) Accessed 11/17/2021. Evans, Randolph W. "Sports and Headaches." Headache vol. 58,3 (2018): 426-437. doi:10.1111/head.13263 International Headache Society. HIS Classification ICHD-3. (https://ichd-3.org/other-primary-headache-disorders/4-2-primary-exercise-headache/) Accessed 11/17/2021. McCrory, P. "Headaches and exercise." Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) vol. 30,3 (2000): 221-9. doi:10.2165/00007256-200030030-00006 National Headache Foundation. Exertional Headaches. (https://headaches.org/2007/10/25/exertional-headaches/) Accessed 11/17/2021. Ramadan, Nabih M. "Sports-related headache." Current pain and headache reports vol. 8,4 (2004): 301-5. doi:10.1007/s11916-004-0012-1 Trotta K, Hyde J. Exercise-induced headaches: prevention, management, and treatment. (https://www.uspharmacist.com/article/exerciseinduced-headaches-prevention-management-and-treatment) U.S. Pharm. 2017;42(1):33-36. Accessed 11/17/2021.
Introduction Many people worldwide know that exercising has impressive benefits that help improve the body’s overall wellness. The body has different muscle groups that have a casual relationship with the vital organs inside the body. Organs like the heart, lungs, gut, and bladder correlate with the different muscles through the nerve roots that connect them. When the body suffers from various factors that affect it, it causes referred pain to the body where one pain is at one location but radiates from the other side. Exercising can help the body recover through physical rehabilitation by reducing inflammation and scarring on the muscle tissues. One of the many exercises that helps strengthen the muscles, increase flexibility, and even improve posture is Pilates. Today’s article looks at Pilates, its benefits, and how it can help alleviate back pain. We refer patients to certified providers specializing in musculoskeletal treatments to help many individuals with low back pain issues affecting their bodies. We also guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is the solution to asking our providers insightful questions. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer What Is Pilates? Have you been feeling sluggish or having low energy throughout the entire day? What about experiencing pain in your lower back? Have you experienced muscle stiffness in certain areas around your body? Many of these symptoms are associated with musculoskeletal issues that correlate with different factors that affect the body; why not try an exercise regime like Pilates? Pilates is a system of exercises that uses a particular machine or body to improve a person’s physical strength and posture while increasing the body’s flexibility and enhancing mental awareness. Joseph Pilates developed Pilates in the early 20th century as an exercise program to help World War I soldiers improve their physical fitness levels. Pilates was used as rehabilitation therapy for injured individuals by incorporating resistance, stretching, and target muscle strengthening. Pilates is now utilized for all individuals with different bodies and fitness levels and can provide tremendous benefits. What Are The Benefits? Pilates, like any other form of exercise, has many beneficial properties that help improve a person’s health and wellness. Studies reveal that Pilates helps many individuals, including older adults, by improving their posture by decreasing thoracic flexion while increasing lumbar extension for pain relief. Some of the beneficial properties that Pilates offer to the body include: - Increasing core strength: The deep muscles in the abdomen, back, and pelvic regions become stronger and help stabilize the body more.
- Strengthen muscle groups: Pilates helps make the muscles not only strong but also helps stretch them so that they can look long and lean. This makes the individual look toned.
- It’s a whole body workout: As many exercises work on specific body parts, Pilates focuses on each muscle part of the body and helps muscle development.
- Posture Improvement: Pilates help keep the spine aligned while strengthening the body and core. Over time a person’s posture will improve naturally, making them stand taller, stronger, and even more graceful.
- Increases energy: Like all exercises, Pilates will give a person the energy boost they need. This is due to the focused breathing and increased blood circulation that stimulates the muscles and the spine.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
Introduction Everyone is trying to find what exercise works for them as they start looking for ways to improve their health and wellness. Many individuals who begin to work out would go with finding a personal trainer or a gym that helps incorporate muscle strength training and cardio training to improve their heart and lung capacity to make the body feel good while strengthening their muscles. One of the unique forms of exercise that involve both the heart and muscles is dancing. Dancing is a great way to not only improve musculoskeletal and cardiovascular health but can help reduce overlapping conditions that a person is dealing with in their bodies. Today’s article looks at how dancing helps with musculoskeletal health, affects the heart and brain, and how chiropractic care goes hand in hand with dancing. We refer patients to certified providers specializing in musculoskeletal and cardiovascular therapies to help those with heart and muscle issues. We also guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is the solution to asking our providers insightful questions. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer Dancing For Musculoskeletal Health Have you ever noticed people take a cardio class with music playing in the background and see them happy afterward? How do athletes incorporate cardio into their exercise regime to improve their mobility and flexibility? Or how do particular video games make you get up and move around? All these scenarios imply that cardio exercises like dancing may help improve musculoskeletal function. Dancing is one of the many aerobic exercises that can help improve a person’s social skills and is something that can be taken up early while providing many beneficial qualities like: - Increase strength
- Improve gait and balance
- Reduce functional loss
- Reducing the risk of falls
- Rehabilitating musculoskeletal injuries
- Stabilize core muscles
For the musculoskeletal system, dance would be considered an isometric exercise involving different muscle groups like the hips, shoulders, back, and abdominals without using the joints. When a person is dancing, each of the various movements is related to strengthening the core muscles by working thoroughly with the abdominals. Dance can even help improve posture by maintaining strength and enhancing stability in the body. Studies reveal that dance’s impact on individuals with chronic issues like Parkinson’s disease associated with motor and non-motor symptoms can increase their quality of life. So what does that mean? It means that dancing, even for just one song, can help with movement and foster balance, flexibility, and muscle endurance through repeated tasks while associating with accessible, social, and attractive aspects of a person’s physical abilities. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
Gardening is healthy for the body and does count as exercise, which works the major muscle groups that include the neck, shoulders, arms, abdomen, back, glutes, and legs. However, gardening can cause stress to the body with unhealthy posture/positioning, not using proper lifting techniques, using the wrong tools, and not taking breaks to stretch out the body, move around, and rehydrate. This can lead to body soreness, pain, and injuries. Here are some recommended gardening tips and stretches for pain prevention. Gardening Tips and Stretches A sore back and body can stem from staying in a single posture for too long and repetitive motions/movements. Here are a few tips to help maintain musculoskeletal health while gardening: Tools - Choosing the right garden tools can spare a lot of pain and money.
- Focus on the fundamental tools and purchase the best quality tools that the budget will allow.
- Size weight, task level, material, grips, handle length, and attachments are things to consider
- Maintaining quality tools will go a long way.
Digging - Digging requires the right tools to get the job done safely and efficiently.
- Make sure the shovel is sharp enough to reduce using extra force to break up the dirt.
- The shovel handle should be long enough to avoid excessive bending.
- Utilize proper digging posture while using a shovel.
- If using too much pressure, soak the soil to loosen it up.
- Try not to twist when shoveling the dirt/soil; instead, move the whole body to where the dirt needs to be.
Lifting - Prolonged lifting of bags, plants, pots, and equipment can take a toll on the spine and spinal muscles.
- Bend the knees and use the hips to lift, as the hip muscles are stronger than the low back muscles.
- Do not bend the waist to come back; use the hips.
- Investing in an elevated garden or gardening seat/stool is recommended to avoid bending.
Weeding - Weeding can require prolonged sitting or bending, depending on the number of weeds.
- To avoid excessive sitting and bending, a gardening seat/stool can help, as well as a standing weeding tool will reduce the pressure on the back.
- This is also helpful for knee and/or hip pain.
Mowing Take Breaks - Do not push through; take a break even if the body feels great.
- Every half hour, the body needs to rest.
- Try to work in 30-minute increments then break to move around, stretch, relax, and rehydrate.
- Squatting, bending, digging, lifting bags, and pushing wheelbarrows is a form of strength training that helps achieve stronger muscles, healthier bones, and joints.
- But if there are no breaks, the chances for pain and injuries increase.
Stretches Simple stretches can reduce the strain and pain of gardening. Stretching before, during, and after the gardening session is recommended. Cat Stretch - This is a simple yoga pose that helps with back soreness.
- On your hands and knees, keep the hands at shoulder distance and the knees at hip distance.
- Pull the navel up to the spine and arch/round the back.
- Slowly straighten the back.
Cow Stretch - The cow stretch is the opposite of the cat pose.
- Start in the same position.
- Drop the stomach to the floor and lift the head up and back.
- The spine will arch and gently stretch the back.
Head Rolls - Head rolls will help with shoulder and neck pain.
- Drop the chin down toward the chest.
- Gently roll the head to one side going around back to the center.
- Repeat in the opposite direction.
Supine Twists - Supine twists can help the lower back.
- Lay down with the legs at a 45-degree angle and the arms out to the sides.
- Twist the legs to one side and look in the opposite direction.
- Hold the pose until the stretch is felt, and then move back to the starting point.
- Repeat on the opposite side.
Chiropractic Chiropractic medicine can help alleviate aches and pains and rehabilitate, realign, and strengthen the body to optimal health. Individuals are educated on the musculoskeletal system, injury prevention, nutrition, and exercise to maintain wellness and a pain-free lifestyle. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Howarth, Michelle et al. "What is the evidence for the impact of gardens and gardening on health and well-being: a scoping review and evidence-based logic model to guide healthcare strategy decision making on the use of gardening approaches as a social prescription." BMJ open vol. 10,7 e036923. 19 Jul. 2020, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-036923 Masashi Soga A et al. "Gardening is beneficial for health: A meta-analysis" https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5153451/pdf/main.pdf. Scott, Theresa L et al."Positive aging benefits of home and community gardening activities: Older adults report enhanced self-esteem, productive endeavors, social engagement, and exercise" SAGE open medicine vol. 8 2050312120901732. 22 Jan. 2020, doi:10.1177/2050312120901732
Injury Medical Chiropractic Decompression Clinic focuses on the whole body, realigns the bones and joints, and helps strengthen the muscles. This helps prevent pain and injury and maintains spinal stability. Strong back muscles can help promote correct posture and keep the spine free from restriction. A stable spine is achieved when the back muscles can support and balance the everyday forces and stress of rigorous physical activity. Strengthening the back muscles can be done through yoga, weightlifting, and other recommended chiropractic exercises. Sports Strength, Balance, Core Decompression Clinic The primary muscles in the back include: - Latissimus dorsi/lats) are in the area below the armpits and down the sides of the back
- Rhomboids are in the mid-upper back
- Trapezius/traps run from the neck to the mid-back
- Erector spinae run along the spine
Major Core Muscles - The transverse abdominis
- Multifidus
- Internal and external obliques
- Erector spinae
- Diaphragm
- Pelvic floor muscles
- The rectus abdominis/abs
Minor Core Muscles Exercises should target a combination of these muscles. Core Importance The core is a crucial area of the body. The body utilizes the core for all movements and as a stabilization unit. Lack of strength places unwanted tension and pressure on the spine. Chiropractic ensures all the joints function correctly and enhances the core to brace more effectively and efficiently. Chiropractic Balance Adjustments and decompression realign the muscles into the proper position and help lubricate the muscles to help ease the stabilizer muscles that could be tight or tense. Treatments used can include: - Spinal manual and motorized decompression
- Extremity adjustments
- Myofascial release
- Active Release Technique
- Trigger point therapy
Benefits - Natural pain relief
- Injury prevention
- Enhanced muscle performance
- Expedited recovery
- Increased endurance
- Mobility enhancement
- Increased strength
Core strength and stability play a huge factor in everyday life and functions. Maintaining health results requires attention to detail. Injury Medical Decompression Clinic will create a personalized optimal health treatment plan that focuses on whole-body realignment, simple lifestyle adjustments, health coaching/nutrition, and strength training to improve balance, strength, and core stability. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, or licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Globe G, Morris C, Whalen W, et al., "Chiropractic Management of Low Back Disorders: Report from a Consensus Process," Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics November/December 2008: 651-658. Keller, MD, et al., "Trunk Muscle Strength, Cross-sectional Area, and Density in Patients With CLBP Randomized to Lumbar Fusion or Cognitive Intervention and Exercises," Spine, 2004 29(1): 3-8 (3) Mayer J, DC, Ph.D. Mooney V, MD, Dagenais S, DC Ph.D., "Evidence-informed management of CLBP with lumbar extensor strengthening exercises," T Spine J, 2008;8:96-113. (3) McKenzie, RA, "The Lumbar Spine: Mechanical Diagnosis and Therapy," Spinal Publications/Printed by Wright & Carman, LTD, Upper Hutt, New Zealand, 1989 reprinted. Sculco AD, Paup DC, Fernhall B, Sculco MJ, "Effects of aerobic exercise on low back pain patients in treatment," Spine J, 1(2):95-101 (2001).
Anybody can become dehydrated if they don’t take care of themselves and drink plenty of water. Being dehydrated happens when there is insufficient water in the body or increased water loss through sweating, vomiting, and/or diarrhea, along with certain medications, can increase urination and dehydration. Older adults have an increased risk of dehydrating because their body’s fluid reserves decrease, and their body’s ability to signal that they are thirsty does not work as effectively, especially those with memory problems. Dehydrated Symptoms Signs of dehydration include: - Muscle cramps.
- Dry mouth
- Dry cough.
- Tiredness/fatigue.
- Flushed red skin.
- Swollen feet.
- High heart rate but low blood pressure.
- Dizziness, weakness, light-headedness.
- Headache, delirium, confusion.
- Loss of appetite with a sugar craving.
- Heat intolerance or chills.
- Constipation.
- Dark-colored urine. Urine should be a pale clear color.
Dehydration Levels Dehydration is categorized as: Mild - The body needs more fluids to be taken in.
- Drink water
- Drinks containing electrolytes are recommended if experiencing significant sweating or fluid losses from vomiting and diarrhea.
- The body should feel better after five or ten minutes.
Moderate - Moderate dehydration requires intravenous hydration.
- This is done in urgent care, emergency room, or a hospital.
Severe - If symptoms of dehydration are severe, call 911 or go to an emergency clinic.
Brain Health - Severe hydration shrinks the blood vessels in the brain.
- When fluid levels in the brain are low, this affects memory and coordination.
Diagnosis Laboratory tests can diagnose dehydration and include: The amount of water needed daily is different for all individuals; therefore, it is recommended to check in with a healthcare provider to determine how much is required to maintain health. Enjoy Drinking Water - Carry a water bottle, keep it filled, and get used to taking sips throughout the day to start a healthy habit.
- Add flavor like a wedge of lemon/lime, lime or lemon juice, or a healthy water additive.
- Choose water or healthy hot or iced tea instead of sugary drinks, including at meals.
- Eat foods high in water content, like fruits and vegetables.
General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Bhave, Gautam, and Eric G Neilson. “Volume depletion versus dehydration: how understanding the difference can guide therapy.” American journal of kidney diseases: the official journal of the National Kidney Foundation vol. 58,2 (2011): 302-9. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.02.395 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Drinking-Water. (https://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/drinking/nutrition/index.html) HealthFirst. What Happens to Your Body When You’re Dehydrated? (https://healthyliving.healthfirst.org/happens-body-youre-dehydrated/) Kenefick, Robert W, and Michael N Sawka. “Hydration at the worksite.” Journal of the American College of Nutrition vol. 26,5 Suppl (2007): 597S-603S. doi:10.1080/07315724.2007.10719665 Thomas, David R et al. “Understanding clinical dehydration and its treatment.” Journal of the American Medical Directors Association vol. 9,5 (2008): 292-301. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2008.03.006
Sports chiropractic athletes: A sports chiropractor is a specialist that works with athletes to improve their performance. These doctors specialize in assessing and treating sports injuries. Treatment also prevents future damage/injury by providing a customized rehabilitation, strengthening, flexibility, and mobility program, that includes: - Exercise prescription
- Ergonomic recommendations
- Health coaching/counseling
- Therapeutic sports massage
Sports chiropractic deals with preventing, diagnosing, and treating sports-athletic-based injuries to muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints. Sports chiropractors have extensive training in evaluating muscular-skeletal problems related to sports participation overuse. Diagnosis is acquired through: Sports Chiropractic Athletes Chiropractors are masters of the human body and trained to use advanced diagnostics tools. A sports chiropractor evaluates individuals from all levels of sports and fitness, including: - Athletes - professional or recreational
- Weekend warriors
- Military personnel
The objective is to identify musculoskeletal problems related to sporting activity or overuse, alleviate pain, rehabilitate, and strengthen to prevent future injury. They can diagnose and treat sports-related injuries from common overuse injuries like: - Hip pain from frequently running on pavement.
- Shoulder pain from damage caused by continued overhead throwing or hitting.
- Low back and leg issues from twisting, bending, jumping, and reaching.
Balance Athletes need a healthy balance of endurance, strength, and structure. Through biomechanics training, sports chiropractic restores the body's natural balance and proper function. The goal is to get the athlete re-engaged and protected against further injury and play without any problems or limitations. Sports chiropractic athletes can return in a short amount of time from injuries that include: - Torn ACLs
- MCL Sprain
- Ankle Sprain
- Achilles Tendonitis
- Rotator cuff tears
- Quadriceps Strains
- Hamstrings Strains
- Shin Splints
- Sports Hernia
- Neck Pain
- Back Pain
- Spondylolisthesis
Prevention Regimen They can recommend prevention programs to prevent potential problems before an athlete gets hurt. A chiropractor will detect developing muscle imbalances before they turn into a chronic condition that can lead to damage to the rest of the body. Additional therapies include: - Massage
- Hot/cold treatments
- Ultrasound therapy
- Low-level laser therapy
Adjustments, stretching, core training, therapeutic sports massage, health coaching, and nutritional counseling will strengthen the body, allowing for performing physical activities and sports at optimum levels. Sports Performance Working with sports chiropractic athletes means achieving a balance of lean mass to maintain sports performance and reduce the risk of injury. Athletes, doctors, and trainers monitor gains over time to maximize performance and watch for signs of potential injury. A method of monitoring for potential injury is the ECW/TBW Analysis. When training and engaging in sports, the body is under physical stress. The proper amount of rest and recovery are needed to allow muscles to recover and regrow. Inflammation is reflected in the ECW/TBW by monitoring changes over time. A steady increase can indicate a sign of overtraining or improper recovery. Monitoring this progression can alert doctors and trainers that an athlete needs a less intense workout or longer recovery to reduce the potential for overtraining injury. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References Corcoran, Kelsey L et al. "Association Between Chiropractic Use and Opioid Receipt Among Patients with Spinal Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis." Pain medicine (Malden, Mass.) vol. 21,2 (2020): e139-e145. doi:10.1093/pm/pnz219 Naqvi U, Sherman Al. Muscle Strength Grading. [Updated 2021 Sep 2]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (F.L.): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK436008/ Nelson, Luke et al. "A descriptive study of sports chiropractors with an International Chiropractic Sports Science Practitioner qualification: a cross-sectional survey." Chiropractic & manual therapies vol. 29,1 51. 13 Dec. 2021, doi:10.1186/s12998-021-00405-1 Williams, Sean et al. "Kinesio taping in treatment and prevention of sports injuries: a meta-analysis of the evidence for its effectiveness." Sports medicine (Auckland, N.Z.) vol. 42,2 (2012): 153-64. doi:10.2165/11594960-000000000-00000
Recovery and rehabilitation after spinal fusion surgery take time. Gentle yoga poses can help expedite recovery from spinal fusion surgery and are recommended in a rehabilitation program. The spine is the body's central support structure that allows the body to stand upright, bend, and stay balanced. However, an individual may need to have vertebrae fused to repair painful back problems. Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure that permanently connects/fuses two or more vertebrae into a single bone. The procedure is done to help: - Correct a deformity
- Improve stability
- Reduce pain
At the beginning of the recovery process, the doctor may recommend light physical activity like walking. As the spine continues to heal, moderate exercise is essential for optimal recovery. Doctors are recommending gentle yoga to increase mobility, flexibility and regain strength. Gentle Yoga and Spine Surgery Recovery Yoga has become a way to stretch the body, exercise, promote physical and mental well-being. There are different styles of yoga, ranging from gentle stretching to advanced poses. Yoga focuses on stretching, coordination, and balance. When stretching the body, the range of motion is improved. Yoga also helps improve balance and increases strength to reduce the risk of falls and injuries. Gentle yoga after spinal fusion benefits include: - Pain relief
- Stress reduction
- Improved mental health
- Increased flexibility and strength
- Improved balance
- Increase in energy levels
Gentle yoga after surgery focuses on an improved range of motion/coordination of the arms and legs with the torso. This allows the spine to safely flex, not become stiff, and avoid strain, leading to fuller activity. When To Begin Yoga After Spinal Fusion? A reduced range of motion and loss of muscle mass is expected in the weeks and months following surgery. The healthcare/rehabilitation team will address this through exercise and physical therapy once the doctor clears the individual to begin rehabilitation training. The doctor will use some form of diagnostic imaging to determine if the vertebrae have fully fused before giving the ok for exercise. Most individuals can begin light physical activity four to six weeks after the procedure. If the fusion surgery was fused in only one place, individuals could start gentle yoga poses within two to three months. For a multi-level fusion surgery, individuals may need to wait four to six months after the procedure before they can safely begin. Yoga Recovery Program It's essential to take it slow and steady when first beginning yoga after spinal fusion. As the body continues to heal, gradually add more challenging poses and stretches to the routine. This is a graduated recovery program separated into stages to help the individual build back strength and flexibility. In the first stages of recovery, gentle poses that have minimal effects on the spine are recommended. These include: A few weeks to a month later, with the doctor's clearance, the individual can advance to poses that stretch/flex the spine a little more, including: Eventually, individuals can slowly increase the challenge further, with poses like: Garudasana - Eagle pose
Gomukhasana - Cow Face pose
Vasisthasana - Side plank pose It's crucial to listen to the body as a guide when moving through the poses, no matter what stage of recovery. The fusion needs time to heal and stabilize, so any poses that involve twisting movements and flexing should be avoided. Seek advice if there is confusion about how or whether or not to proceed. It is recommended to work with an experienced yoga teacher after spinal fusion. A knowledgeable instructor can guide with the poses, inform which poses to avoid and make modifications to get the most out of the gentle poses. How Heat Affects Basal Metabolic Rate Gender, height, and age influence Basal Metabolic Rate. These are factors individuals cannot control or change. However, individuals can increase the calories the body burns by regulating body temperature. Both the internal and external temperatures influence metabolic rate. The chemical reactions that contribute to metabolism happen more quickly if the temperature is higher, as the body works harder to restore normal temperature balance. For example, when a fever is present, the Basal Metabolic Rate will jump up to a much higher rate than usual to increase the speed of cellular metabolic reactions to combat the fever and get the body back to a healthy state. When it comes to external temperature, it's only prolonged exposure to heat that raises the Basal Metabolic Rate. General Disclaimer * The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health care professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request. We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN* email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico* References American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons. (June 2018). "Spinal Fusion." https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/spinal-fusion/ Gillooly, James F, and Andrew P Allen. "Changes in body temperature influence the scaling of VO2max and aerobic scope in mammals." Biology letters vol. 3,1 (2007): 99-102. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2006.0576 National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. (February 2020) "Yoga for Health: What the Science Says." https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/providers/digest/yoga-for-health-science National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. (April 2021) "Yoga: What You Need to Know." https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/yoga-what-you-need-to-know
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...






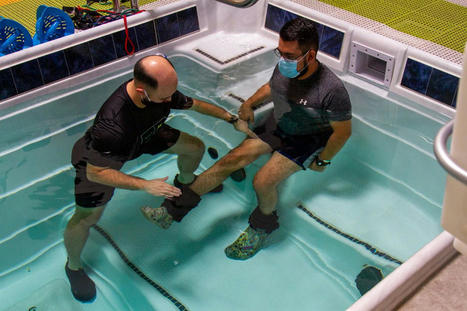

























Stretching Objective: Injury Medical Chiropractic can help individuals develop a personalized program to maintain flexibility and function. For answers to any questions you may have, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900 or 915-412-6677