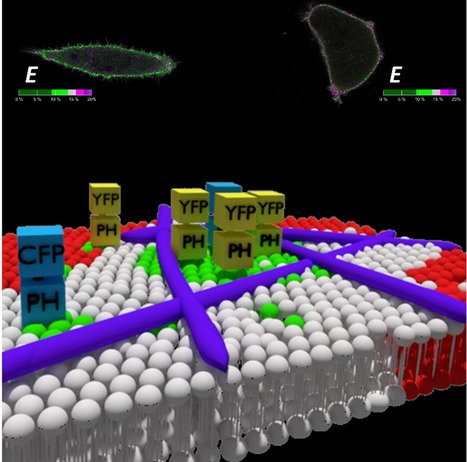
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) is crucial to many cellular processes in eukaryotes, including membrane trafficking, signal transduction, ion channel function and cytoskeleton dynamics. This function multiplicity is partially achieved through a dynamic spatiotemporal organization of PI(4,5)P2 within the membrane. In a recent paper published in IJMS, an IBB team (Maria J. Sarmento, Luís Borges-Araújo, Sandra N.Pinto, Nuno Bernardes, Joana Ricardo, Ana Coutinho, Manuel Prieto and Fábio Fernandes) was able to quantify PI(4,5)P2 confinement in living cells making use of FRET imaging measurements. PI(4,5)P2 was found to be significantly compartmentalized at the plasma membrane of HeLa cells. These PI(4,5)P2 enriched domains were shown to not depend on cholesterol content, ruling out an association with lipid rafts. On the other hand, upon inhibition of actin polymerization, compartmentalization of PI(4,5)P2 was almost entirely eliminated, confirming that the cytoskeleton network is the critical component responsible for the formation of nanoscale PI(4,5)P2 domains.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...