A Bayesian network, Bayes network, belief network, Bayes(ian) model or probabilistic directed acyclic graphical model is a probabilistic graphical model (a type of statistical model) that represents a set of random variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic relationships between diseases and symptoms. Given symptoms, the network can be used to compute the probabilities of the presence of various diseases.
Formally, Bayesian networks are directed acyclic graphs whose nodes represent random variables in the Bayesian sense: they may be observable quantities, latent variables, unknown parameters or hypotheses. Edges represent conditional dependencies; nodes which are not connected represent variables which are conditionally independent of each other. Each node is associated with a probability function that takes as input a particular set of values for the node's parent variables and gives the probability of the variable represented by the node. For example, if the parents are 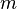 Boolean variables then the probability function could be represented by a table of
Boolean variables then the probability function could be represented by a table of 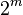 entries, one entry for each of the
entries, one entry for each of the 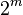 possible combinations of its parents being true or false. Similar ideas may be applied to undirected, and possibly cyclic, graphs; such are called Markov networks.
possible combinations of its parents being true or false. Similar ideas may be applied to undirected, and possibly cyclic, graphs; such are called Markov networks.
Efficient algorithms exist that perform inference and learning in Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks that model sequences of variables (e.g. speech signals or protein sequences) are called dynamic Bayesian networks. Generalizations of Bayesian networks that can represent and solve decision problems under uncertainty are called influence diagrams.

 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...





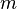 Boolean variables then the probability function could be represented by a table of
Boolean variables then the probability function could be represented by a table of 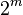 entries, one entry for each of the
entries, one entry for each of the 




