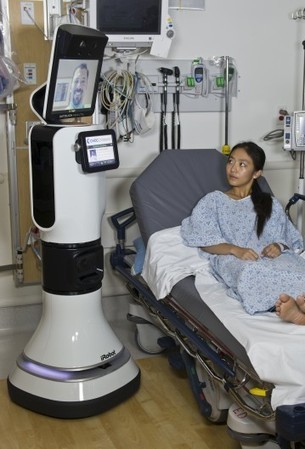
Right now about 10 percent of ICU beds in the US are monitored in part from an off-hospital site. And the number of sites using remote monitoring are on the rise, increasing exponentially over the past 5 to 7 years.
Tele-ICU monitoring involves satellite-linked video and communications links to electronic records so that the distant intensivists – doctors that specialize in intensive care – can watch over the patient in real-time, 24 hours a day. A video camera operates on-demand to observe the patient and communicate with them via a microphone and speakers. Through this two-way communication tele-intensivists can aid local intensivists by helping to enforce the patient’s daily goals, review their performance with them and respond to alarms if the local doctor has been called away.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...