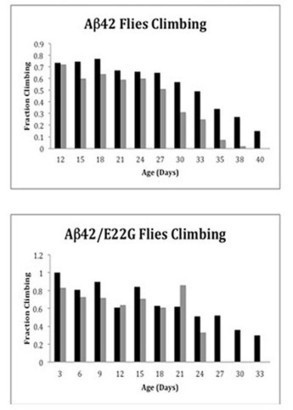
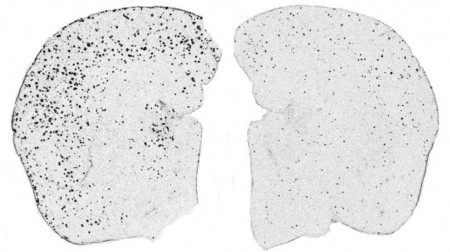
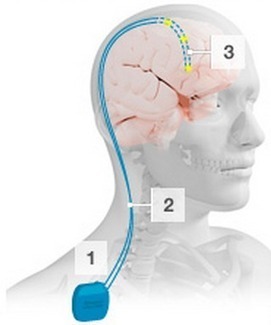
There is a large body of evidence to suggest that omega-3s are beneficial for brain health and heart health. A new study evaluated omega-3 supplements and their effect on cognitive performance. The findings supported established health benefits of these supplements.
The researchers concluded that supplementation with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) could postpone the onset of metabolic disorders and associated declines in cognitive functioning.



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...