Education may be the passport to the future, but for all the good teaching out there, it would seem that schools are failing to impart some of the most important life skills, according to one educational expert.
Dr. Tony Wagner, co-director of Harvard's Change Leadership Group, argues that today’s school children are facing a “global achievement gap”, which is the gap between what even the best schools are teaching and the skills young people need to learn.
This has been exacerbated by two colliding trends: firstly, the global shift from an industrial economy to a knowledge economy, and secondly, the way in which today’s school children – brought up with the internet – are motivated to learn.
In his book The Global Achievement Gap, Wagner identifies seven core competencies every child needs in order to survive in the coming world of work.
1. Critical thinking and problem-solving
2. Collaboration across networks and leading by influence
3. Agility and adaptability
4. Initiative and entrepreneurialism
5. Effective oral and written communication
6. Accessing and analysing information
7. Curiosity and imagination
Learn more / En savoir plus / Mehr erfahren:
https://gustmees.wordpress.com
Via Gust MEES



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...









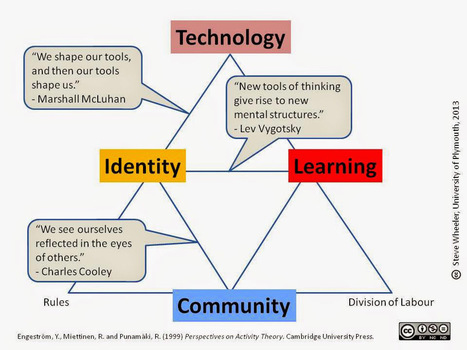






Education may be the passport to the future, but for all the good teaching out there, it would seem that schools are failing to impart some of the most important life skills, according to one educational expert.
Dr. Tony Wagner, co-director of Harvard's Change Leadership Group, argues that today’s school children are facing a “global achievement gap”, which is the gap between what even the best schools are teaching and the skills young people need to learn.
This has been exacerbated by two colliding trends: firstly, the global shift from an industrial economy to a knowledge economy, and secondly, the way in which today’s school children – brought up with the internet – are motivated to learn.
In his book The Global Achievement Gap, Wagner identifies seven core competencies every child needs in order to survive in the coming world of work.
1. Critical thinking and problem-solving
2. Collaboration across networks and leading by influence
3. Agility and adaptability
4. Initiative and entrepreneurialism
5. Effective oral and written communication
6. Accessing and analysing information
7. Curiosity and imagination
Learn more / En savoir plus / Mehr erfahren:
https://gustmees.wordpress.com